Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anxiety, Trauma
Anxiety, Trauma
Uploaded by
nauw zCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Filipino Psychology ReviewerDocument13 pagesFilipino Psychology Reviewernauw z100% (2)
- Micro Case Study IDocument7 pagesMicro Case Study Iiris040% (1)
- Arts and Design - Q1 - Mod2 - ArtistryRelatedInjuries - Version1 by Romel SabidorDocument26 pagesArts and Design - Q1 - Mod2 - ArtistryRelatedInjuries - Version1 by Romel SabidorJayson Paul Dalisay Datinguinoo100% (2)
- Abpsych RationalizationDocument443 pagesAbpsych RationalizationLalaine_Sarno_2100% (1)
- Anxiety DisordersDocument21 pagesAnxiety DisorderskarthikkandaNo ratings yet
- Appendix Chapter, Sabiston Textbook of SurgeryDocument43 pagesAppendix Chapter, Sabiston Textbook of SurgeryShuo Huang100% (2)
- CHAPTER 5 - AbpsychDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 5 - AbpsychehhlluhhNo ratings yet
- HO AnxietyDocument5 pagesHO Anxiety20210023707No ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorder ReviewerDocument3 pagesAnxiety Disorder ReviewerRhea Mae TabayagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Anxiety, Trauma and Stressor - Related, Obsessive Compulsive Related DisordersDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Anxiety, Trauma and Stressor - Related, Obsessive Compulsive Related DisordersAnnie SumacotNo ratings yet
- Neuroses: Anxiety DisordersDocument12 pagesNeuroses: Anxiety DisordersHaggai lundaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Anxiety DisordersDocument6 pagesNature of Anxiety Disorderssanyamana935No ratings yet
- Midterms Abno1Document22 pagesMidterms Abno1Allana Ruth P. AbudaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Midterm NotesDocument22 pagesAbnormal Psychology Midterm NotesAllana Ruth P. AbudaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology (Chapter 4)Document9 pagesAbnormal Psychology (Chapter 4)Mavy QueenNo ratings yet
- Anxietydisorders 220401155226Document38 pagesAnxietydisorders 220401155226Neharika KumariNo ratings yet
- Psychological Contributions: Comorbidity of Anxiety DisordersDocument2 pagesPsychological Contributions: Comorbidity of Anxiety DisordersJM ANo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders (Ch. 18, 19, 20) : Panic AttacksDocument3 pagesAnxiety Disorders (Ch. 18, 19, 20) : Panic AttacksHaley Vest MustaficNo ratings yet
- Anxiety, Panic Disorder and StressDocument11 pagesAnxiety, Panic Disorder and StressLoren Sangalang100% (1)
- Abnormal Psychology ReviewerDocument23 pagesAbnormal Psychology ReviewerAllissa RossNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorder-1Document14 pagesAnxiety Disorder-1Naeem Khan AfridiNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument11 pagesAnxiety DisordersMahmoud emadNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument16 pagesAnxiety DisorderPetracharles AkashiNo ratings yet
- Advanced PSYDocument201 pagesAdvanced PSYPetracharles AkashiNo ratings yet
- Anxiety ReportDocument72 pagesAnxiety Reportcatherine faith gallemitNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders: Powerpoint Lecture Notes PresentationDocument43 pagesAnxiety Disorders: Powerpoint Lecture Notes PresentationErsido SamuelNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders - HTMLDocument28 pagesAnxiety Disorders - HTMLLealiza B. BruceNo ratings yet
- Presentation 16Document8 pagesPresentation 16Naman MansotraNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders: Moges Ayehu, MD, Psychiatrist Assistant Professor, HUCMHDocument38 pagesAnxiety Disorders: Moges Ayehu, MD, Psychiatrist Assistant Professor, HUCMHsoran muzeyinNo ratings yet
- Panic Disorder & Generalized Anxiety DisorderDocument13 pagesPanic Disorder & Generalized Anxiety Disordersanyamana935No ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorde RS: Abnormal PsychologyDocument39 pagesAnxiety Disorde RS: Abnormal PsychologyMariella LimNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument20 pagesAnxiety DisordersHndrNo ratings yet
- What Are AnxietyDocument8 pagesWhat Are AnxietyMalik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit-VI Anxiety DisordersDocument198 pagesUnit-VI Anxiety DisordersDemis TekleNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument60 pagesAnxiety Disorderssaturninecore100% (1)
- Anxiety DisorderDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisordergwenstacyNo ratings yet
- Abpsych RationalizationDocument442 pagesAbpsych Rationalizationyvon's dumpNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportErna Lorn DelaCerna EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument56 pagesAnxiety DisorderDr TNTNo ratings yet
- ANXIETY DISORDERS-psychespaceDocument20 pagesANXIETY DISORDERS-psychespaceM. BalachandranNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2020-01-13 at 2.35.04 PMDocument50 pagesScreenshot 2020-01-13 at 2.35.04 PMSharifah NabaahaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders FR ClassDocument11 pagesAnxiety Disorders FR ClassPranali M.No ratings yet
- P110 - Module 7Document9 pagesP110 - Module 7Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument18 pagesAnxietyRizwana MBTNo ratings yet
- What Is AnxietyDocument4 pagesWhat Is AnxietyUTTARA NAIRNo ratings yet
- Clinical PsychologyDocument26 pagesClinical PsychologyGURNOOR KAURNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument44 pagesAnxiety DisorderKemal AmanoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology (Mild To Moderate Psychological Problems)Document59 pagesAbnormal Psychology (Mild To Moderate Psychological Problems)Mahwish Bilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument11 pagesAnxiety DisorderBiswas AruNo ratings yet
- Pressures of The Outside World and The Person's EgoDocument7 pagesPressures of The Outside World and The Person's EgoPatricia Denise OrquiaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument7 pagesAnxiety Disorderssuresh patilNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and StressDocument6 pagesAnxiety and StressRubilyn SumayloNo ratings yet
- STAI F vrsaUPD PracticalDocument17 pagesSTAI F vrsaUPD Practicalkhushi chopra 0050No ratings yet
- ANXIETY-a Fear or Fate.: By: Shubham Kumar REG NO.: 19105109034 Roll No.: 19CS19 Nalanda College of EngineeringDocument22 pagesANXIETY-a Fear or Fate.: By: Shubham Kumar REG NO.: 19105109034 Roll No.: 19CS19 Nalanda College of EngineeringShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Fear&AnxietyDocument56 pagesChapter 6 - Fear&AnxietyAngela Abigail AbingNo ratings yet
- Understanding Psychological Disorders-I PracticalDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Psychological Disorders-I Practicalkhushi chopra 0050No ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesAnxiety Disorders Lecture NotesHerme BorladoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psychology Material Day 2Document3 pagesClinical Psychology Material Day 2Swarali JoshiNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument66 pagesAnxietyMoses LaiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Exam 1 ReviewDocument49 pagesAbnormal Psychology Exam 1 ReviewJimmy Nguyen100% (7)
- Calm and Centered: Overcoming Anxiety and Panic Attacks NaturallyFrom EverandCalm and Centered: Overcoming Anxiety and Panic Attacks NaturallyNo ratings yet
- Stop the Fear: Learn to Stop Anxiety Panic Attacks and Take Control of Your LifeFrom EverandStop the Fear: Learn to Stop Anxiety Panic Attacks and Take Control of Your LifeNo ratings yet
- PAP Code of Ethics (2022)Document27 pagesPAP Code of Ethics (2022)nauw zNo ratings yet
- IO Psych in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesIO Psych in The Philippinesnauw zNo ratings yet
- AdoldevstagesDocument1 pageAdoldevstagesnauw zNo ratings yet
- I-O Printables 1Document4 pagesI-O Printables 1nauw zNo ratings yet
- List of Psychological TestsDocument15 pagesList of Psychological Testsnauw zNo ratings yet
- TCPR June2017 IDESPAIRR-A Mnomic For Diagnosing BPDDocument1 pageTCPR June2017 IDESPAIRR-A Mnomic For Diagnosing BPDnauw zNo ratings yet
- AnhedoniaDocument4 pagesAnhedonianauw zNo ratings yet
- Dr. Vodde Changes in Specific Diagnoses From DSM IV To 5Document183 pagesDr. Vodde Changes in Specific Diagnoses From DSM IV To 5nauw zNo ratings yet
- Narcissistic Personality DisorderDocument6 pagesNarcissistic Personality Disordernauw zNo ratings yet
- DSM V MNEMONICSDocument2 pagesDSM V MNEMONICSnauw zNo ratings yet
- Health Beliefs and Living With Chronic DiseasesDocument25 pagesHealth Beliefs and Living With Chronic DiseasesAllan SantanaNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Pharmaceutical Dosage FormsDocument169 pagesDictionary of Pharmaceutical Dosage FormsNguyễn Trần LinhNo ratings yet
- NCLEK IngDocument7 pagesNCLEK IngMona IndahNo ratings yet
- Medicine JC-SC WCS Summary (Neurology)Document6 pagesMedicine JC-SC WCS Summary (Neurology)Peter LeeNo ratings yet
- Ebook Clinical Immunology Principles and Practice PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Clinical Immunology Principles and Practice PDF Full Chapter PDFrobert.wheat692100% (30)
- Massive HemorrhageDocument17 pagesMassive HemorrhageShannen Madrid Tindugan100% (1)
- Valo Health - Pitchdeck - March 2021Document21 pagesValo Health - Pitchdeck - March 2021Rattanan WanikornNo ratings yet
- Radiofrequency AblationDocument7 pagesRadiofrequency AblationRohit singhNo ratings yet
- Brcu17 25Document10 pagesBrcu17 25Moaz TajammalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans k6Document13 pagesLesson Plans k6Regine Delfin AclaracionNo ratings yet
- Hemoragiile DigestiveDocument36 pagesHemoragiile DigestiveMihaela BirligeaNo ratings yet
- Total Hip and Knee ReplacementsDocument57 pagesTotal Hip and Knee ReplacementsBryndenNo ratings yet
- Hesi Mental Health RN v1 v3 2020 Test BankDocument44 pagesHesi Mental Health RN v1 v3 2020 Test Bankgithijidennis99No ratings yet
- Infective EndocarditisDocument58 pagesInfective EndocarditisTok KeawkaewNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Basic InformationDocument8 pagesHypertension: Basic InformationHector OrtegaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionsigit_riyantono100% (1)
- Ice Chips GiDocument2 pagesIce Chips GiJANELLE GIFT SENARLONo ratings yet
- Week 4 # 2 Dehydration-1Document22 pagesWeek 4 # 2 Dehydration-1charissaNo ratings yet
- Medicare Inpatient 2017Document8,939 pagesMedicare Inpatient 2017Shashi Shirke100% (1)
- Philippine Clinical Practice Guidelines On The Diagnosis andDocument83 pagesPhilippine Clinical Practice Guidelines On The Diagnosis andREnren ConsolNo ratings yet
- Transitioning To New Normal-ANGELO WALID V. IDOLORDocument10 pagesTransitioning To New Normal-ANGELO WALID V. IDOLORShino HireshtakNo ratings yet
- BCG Vaccine EDocument17 pagesBCG Vaccine Edr.kendrickNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Low Back Pain: Elizabeth Huntoon, MD, and Marc Huntoon, MDDocument7 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Low Back Pain: Elizabeth Huntoon, MD, and Marc Huntoon, MDGangsar DamaiNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Assisting Sitz Bath: Camarines Sur Polytechnic CollegesDocument2 pagesProcedure Checklist Assisting Sitz Bath: Camarines Sur Polytechnic CollegesElaine Frances IlloNo ratings yet
- Edema in ChildDocument16 pagesEdema in ChildKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Kent Smith 2 010812 WebDocument4 pagesKent Smith 2 010812 WebmonicaNo ratings yet
- Keperawatan Menjelang Ajal Dan PaliatifDocument15 pagesKeperawatan Menjelang Ajal Dan PaliatifLaiLa CiracesiliakencanaNo ratings yet
Anxiety, Trauma
Anxiety, Trauma
Uploaded by
nauw zOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anxiety, Trauma
Anxiety, Trauma
Uploaded by
nauw zCopyright:
Available Formats
Anxiety, trauma- and stressor-related, and obsessive-compulsive and related disorders
Anxiety – is a negative mood state characterized by bodily symptoms of physical tension and by
apprehension about the future.
— In humans it can be a subjective sense of unease, a set of behaviors (looking worried and
anxious or fidgeting), or a physiological response originating in the brain and reflected in
elevated heart rate and muscle tension.
Anxiety: anticipation of future threat- a vague feeling bakit mo nararamdamn, future oriented
Fear- emotional response to real or perceived imminent threat. Ex: gagamba, aso sa harap mo
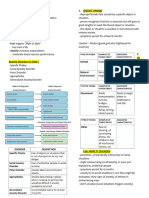
ANXIETY DISORDERS
- Include disorders that share features of excessive fear and anxiety and related behaviors.
GENERALIZED ANXIETY DISORDER – pangmatagalan; you’re always anxious(free floating anxiety)
- Excessive anxiety and worry (apprehensive expectation), occurring more days than not for at 6
least months, about a number of events or activities (such as work or school performance)
NOTE: only one item is required in children
1. Restlessness or feeling keyed up on edge
2. Being easily fatigued
3. Difficulty concentrating or mind going blank
4. Irritability
5. Muscle tension
6. Sleep disturbance (difficulty falling or staying asleep, or restless, unsatisfying sleep).
Risk and Prognostic Factors
Temperamental
- Behavioral inhibition, negative affectivity (neuroticism), harm avoidance, reward dependence,
and attentional bias to threat have been associated with generalized anxiety disorder
Environmental
- Childhood advertise and parenting practices (eg. Overprotection, over control, reinforcement of
avoidance) have been associated with gad
Genetic and Psychosocial
- One third of the risk of experiencing gad is genetic, and these genetic factors overlap with the
risk of negative affectivity (neuroticism) and are shared with other anxiety and mood disorders,
particularly major depressive disorder.
Panic Attack – biglaan pero maikli; episodic
- Represents the alarm response of the real fear, but there is no actual danger.
- Are periodic, short bouts of panic that occur suddenly, reach a peak within 10 minutes, and
gradually pass.
Panic attack maybe:
Unexpected (without warning)
Situationally bound (always occurring in a specific situation)
Situationally predisposed (likely but unpredictable in a specific situation)
The attacks feature at least 4 of the following symptoms of panic:
Palpitations of the heart
Tingling in the hands or feet
Shortness of breath
Sweating, hot and cold flashes
Chest pains
Choking sensations
Faintness
Dizziness
Trembling
Feeling of unreality
Panic Disorder – panic attacks that occur repeatedly and unexpectedly and without apparent reason
Experience dysfunctional changes in their thinking or behavior as a result of the attacks
Risk and Prognostic Factors:
- Temperamental
Negative affectivity (neuroticism) (i.e., proneness to experiencing negative emotions),
anxiety sensitivity (i.e., the disposition to believe that symptoms of anxiety are harmful),
behavioral inhibition, and harm avoidance are risk factors for the onset of panic attacks and
panic disorder.
History of “fearful spells” (i.e., limited-symptom attacks that particularly when the first panic
experience is appraised as negative.
Although separation anxiety in childhood, especially when severe, may precede the later
development of panic disorder, it is not a consistent risk factor.
Phobia
Phobic Disorder
1. Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia)
A fear of being around others, particularly in situations that call for some kind of
“performance” in front of other people in which embarrassment may occur.
The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is persistent, typically lasting for 6 months or more.
Taijin Kyofusho- a Japanesse culture-specific syndrome le characterized by an individual’s
intense fear that his or her body is embarrassing to others
2. Agoraphobia
Fear or venturing into public places, especially when one is alone.
3. Specific Phobia
Is a persistent fear of a specific object or situation
When sufferers are exposed
Categories of Phobia
1. Natural environment phobias: fear of storms, water, heights or natiral phenomena
2. Blood-injection phobia
3. Situational phobias
4. Animal phobia
5. Other types of specific phobias – irrational
Trauma and Stressor- Related Disorders
In which exposure to a traumatic or stressful event is listed explicitly as a diagnostic criterion.
These include reactive attachment disorder
You might also like
- Filipino Psychology ReviewerDocument13 pagesFilipino Psychology Reviewernauw z100% (2)
- Micro Case Study IDocument7 pagesMicro Case Study Iiris040% (1)
- Arts and Design - Q1 - Mod2 - ArtistryRelatedInjuries - Version1 by Romel SabidorDocument26 pagesArts and Design - Q1 - Mod2 - ArtistryRelatedInjuries - Version1 by Romel SabidorJayson Paul Dalisay Datinguinoo100% (2)
- Abpsych RationalizationDocument443 pagesAbpsych RationalizationLalaine_Sarno_2100% (1)
- Anxiety DisordersDocument21 pagesAnxiety DisorderskarthikkandaNo ratings yet
- Appendix Chapter, Sabiston Textbook of SurgeryDocument43 pagesAppendix Chapter, Sabiston Textbook of SurgeryShuo Huang100% (2)
- CHAPTER 5 - AbpsychDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 5 - AbpsychehhlluhhNo ratings yet
- HO AnxietyDocument5 pagesHO Anxiety20210023707No ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorder ReviewerDocument3 pagesAnxiety Disorder ReviewerRhea Mae TabayagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Anxiety, Trauma and Stressor - Related, Obsessive Compulsive Related DisordersDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Anxiety, Trauma and Stressor - Related, Obsessive Compulsive Related DisordersAnnie SumacotNo ratings yet
- Neuroses: Anxiety DisordersDocument12 pagesNeuroses: Anxiety DisordersHaggai lundaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Anxiety DisordersDocument6 pagesNature of Anxiety Disorderssanyamana935No ratings yet
- Midterms Abno1Document22 pagesMidterms Abno1Allana Ruth P. AbudaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Midterm NotesDocument22 pagesAbnormal Psychology Midterm NotesAllana Ruth P. AbudaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology (Chapter 4)Document9 pagesAbnormal Psychology (Chapter 4)Mavy QueenNo ratings yet
- Anxietydisorders 220401155226Document38 pagesAnxietydisorders 220401155226Neharika KumariNo ratings yet
- Psychological Contributions: Comorbidity of Anxiety DisordersDocument2 pagesPsychological Contributions: Comorbidity of Anxiety DisordersJM ANo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders (Ch. 18, 19, 20) : Panic AttacksDocument3 pagesAnxiety Disorders (Ch. 18, 19, 20) : Panic AttacksHaley Vest MustaficNo ratings yet
- Anxiety, Panic Disorder and StressDocument11 pagesAnxiety, Panic Disorder and StressLoren Sangalang100% (1)
- Abnormal Psychology ReviewerDocument23 pagesAbnormal Psychology ReviewerAllissa RossNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorder-1Document14 pagesAnxiety Disorder-1Naeem Khan AfridiNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument11 pagesAnxiety DisordersMahmoud emadNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument16 pagesAnxiety DisorderPetracharles AkashiNo ratings yet
- Advanced PSYDocument201 pagesAdvanced PSYPetracharles AkashiNo ratings yet
- Anxiety ReportDocument72 pagesAnxiety Reportcatherine faith gallemitNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders: Powerpoint Lecture Notes PresentationDocument43 pagesAnxiety Disorders: Powerpoint Lecture Notes PresentationErsido SamuelNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders - HTMLDocument28 pagesAnxiety Disorders - HTMLLealiza B. BruceNo ratings yet
- Presentation 16Document8 pagesPresentation 16Naman MansotraNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders: Moges Ayehu, MD, Psychiatrist Assistant Professor, HUCMHDocument38 pagesAnxiety Disorders: Moges Ayehu, MD, Psychiatrist Assistant Professor, HUCMHsoran muzeyinNo ratings yet
- Panic Disorder & Generalized Anxiety DisorderDocument13 pagesPanic Disorder & Generalized Anxiety Disordersanyamana935No ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorde RS: Abnormal PsychologyDocument39 pagesAnxiety Disorde RS: Abnormal PsychologyMariella LimNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument20 pagesAnxiety DisordersHndrNo ratings yet
- What Are AnxietyDocument8 pagesWhat Are AnxietyMalik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit-VI Anxiety DisordersDocument198 pagesUnit-VI Anxiety DisordersDemis TekleNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument60 pagesAnxiety Disorderssaturninecore100% (1)
- Anxiety DisorderDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisordergwenstacyNo ratings yet
- Abpsych RationalizationDocument442 pagesAbpsych Rationalizationyvon's dumpNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportErna Lorn DelaCerna EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument56 pagesAnxiety DisorderDr TNTNo ratings yet
- ANXIETY DISORDERS-psychespaceDocument20 pagesANXIETY DISORDERS-psychespaceM. BalachandranNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2020-01-13 at 2.35.04 PMDocument50 pagesScreenshot 2020-01-13 at 2.35.04 PMSharifah NabaahaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders FR ClassDocument11 pagesAnxiety Disorders FR ClassPranali M.No ratings yet
- P110 - Module 7Document9 pagesP110 - Module 7Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument18 pagesAnxietyRizwana MBTNo ratings yet
- What Is AnxietyDocument4 pagesWhat Is AnxietyUTTARA NAIRNo ratings yet
- Clinical PsychologyDocument26 pagesClinical PsychologyGURNOOR KAURNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument44 pagesAnxiety DisorderKemal AmanoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology (Mild To Moderate Psychological Problems)Document59 pagesAbnormal Psychology (Mild To Moderate Psychological Problems)Mahwish Bilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument11 pagesAnxiety DisorderBiswas AruNo ratings yet
- Pressures of The Outside World and The Person's EgoDocument7 pagesPressures of The Outside World and The Person's EgoPatricia Denise OrquiaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument7 pagesAnxiety Disorderssuresh patilNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and StressDocument6 pagesAnxiety and StressRubilyn SumayloNo ratings yet
- STAI F vrsaUPD PracticalDocument17 pagesSTAI F vrsaUPD Practicalkhushi chopra 0050No ratings yet
- ANXIETY-a Fear or Fate.: By: Shubham Kumar REG NO.: 19105109034 Roll No.: 19CS19 Nalanda College of EngineeringDocument22 pagesANXIETY-a Fear or Fate.: By: Shubham Kumar REG NO.: 19105109034 Roll No.: 19CS19 Nalanda College of EngineeringShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Fear&AnxietyDocument56 pagesChapter 6 - Fear&AnxietyAngela Abigail AbingNo ratings yet
- Understanding Psychological Disorders-I PracticalDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Psychological Disorders-I Practicalkhushi chopra 0050No ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesAnxiety Disorders Lecture NotesHerme BorladoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psychology Material Day 2Document3 pagesClinical Psychology Material Day 2Swarali JoshiNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument66 pagesAnxietyMoses LaiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Exam 1 ReviewDocument49 pagesAbnormal Psychology Exam 1 ReviewJimmy Nguyen100% (7)
- Calm and Centered: Overcoming Anxiety and Panic Attacks NaturallyFrom EverandCalm and Centered: Overcoming Anxiety and Panic Attacks NaturallyNo ratings yet
- Stop the Fear: Learn to Stop Anxiety Panic Attacks and Take Control of Your LifeFrom EverandStop the Fear: Learn to Stop Anxiety Panic Attacks and Take Control of Your LifeNo ratings yet
- PAP Code of Ethics (2022)Document27 pagesPAP Code of Ethics (2022)nauw zNo ratings yet
- IO Psych in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesIO Psych in The Philippinesnauw zNo ratings yet
- AdoldevstagesDocument1 pageAdoldevstagesnauw zNo ratings yet
- I-O Printables 1Document4 pagesI-O Printables 1nauw zNo ratings yet
- List of Psychological TestsDocument15 pagesList of Psychological Testsnauw zNo ratings yet
- TCPR June2017 IDESPAIRR-A Mnomic For Diagnosing BPDDocument1 pageTCPR June2017 IDESPAIRR-A Mnomic For Diagnosing BPDnauw zNo ratings yet
- AnhedoniaDocument4 pagesAnhedonianauw zNo ratings yet
- Dr. Vodde Changes in Specific Diagnoses From DSM IV To 5Document183 pagesDr. Vodde Changes in Specific Diagnoses From DSM IV To 5nauw zNo ratings yet
- Narcissistic Personality DisorderDocument6 pagesNarcissistic Personality Disordernauw zNo ratings yet
- DSM V MNEMONICSDocument2 pagesDSM V MNEMONICSnauw zNo ratings yet
- Health Beliefs and Living With Chronic DiseasesDocument25 pagesHealth Beliefs and Living With Chronic DiseasesAllan SantanaNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Pharmaceutical Dosage FormsDocument169 pagesDictionary of Pharmaceutical Dosage FormsNguyễn Trần LinhNo ratings yet
- NCLEK IngDocument7 pagesNCLEK IngMona IndahNo ratings yet
- Medicine JC-SC WCS Summary (Neurology)Document6 pagesMedicine JC-SC WCS Summary (Neurology)Peter LeeNo ratings yet
- Ebook Clinical Immunology Principles and Practice PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Clinical Immunology Principles and Practice PDF Full Chapter PDFrobert.wheat692100% (30)
- Massive HemorrhageDocument17 pagesMassive HemorrhageShannen Madrid Tindugan100% (1)
- Valo Health - Pitchdeck - March 2021Document21 pagesValo Health - Pitchdeck - March 2021Rattanan WanikornNo ratings yet
- Radiofrequency AblationDocument7 pagesRadiofrequency AblationRohit singhNo ratings yet
- Brcu17 25Document10 pagesBrcu17 25Moaz TajammalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans k6Document13 pagesLesson Plans k6Regine Delfin AclaracionNo ratings yet
- Hemoragiile DigestiveDocument36 pagesHemoragiile DigestiveMihaela BirligeaNo ratings yet
- Total Hip and Knee ReplacementsDocument57 pagesTotal Hip and Knee ReplacementsBryndenNo ratings yet
- Hesi Mental Health RN v1 v3 2020 Test BankDocument44 pagesHesi Mental Health RN v1 v3 2020 Test Bankgithijidennis99No ratings yet
- Infective EndocarditisDocument58 pagesInfective EndocarditisTok KeawkaewNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Basic InformationDocument8 pagesHypertension: Basic InformationHector OrtegaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionsigit_riyantono100% (1)
- Ice Chips GiDocument2 pagesIce Chips GiJANELLE GIFT SENARLONo ratings yet
- Week 4 # 2 Dehydration-1Document22 pagesWeek 4 # 2 Dehydration-1charissaNo ratings yet
- Medicare Inpatient 2017Document8,939 pagesMedicare Inpatient 2017Shashi Shirke100% (1)
- Philippine Clinical Practice Guidelines On The Diagnosis andDocument83 pagesPhilippine Clinical Practice Guidelines On The Diagnosis andREnren ConsolNo ratings yet
- Transitioning To New Normal-ANGELO WALID V. IDOLORDocument10 pagesTransitioning To New Normal-ANGELO WALID V. IDOLORShino HireshtakNo ratings yet
- BCG Vaccine EDocument17 pagesBCG Vaccine Edr.kendrickNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Low Back Pain: Elizabeth Huntoon, MD, and Marc Huntoon, MDDocument7 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Low Back Pain: Elizabeth Huntoon, MD, and Marc Huntoon, MDGangsar DamaiNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Assisting Sitz Bath: Camarines Sur Polytechnic CollegesDocument2 pagesProcedure Checklist Assisting Sitz Bath: Camarines Sur Polytechnic CollegesElaine Frances IlloNo ratings yet
- Edema in ChildDocument16 pagesEdema in ChildKesava DassNo ratings yet
- Kent Smith 2 010812 WebDocument4 pagesKent Smith 2 010812 WebmonicaNo ratings yet
- Keperawatan Menjelang Ajal Dan PaliatifDocument15 pagesKeperawatan Menjelang Ajal Dan PaliatifLaiLa CiracesiliakencanaNo ratings yet