Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views Metallic Bonding
Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
ClopzThe document discusses metallic bonding and properties of metals. It explains that metals have a giant metallic lattice structure formed from layers of metal cations surrounded by delocalized electrons. These delocalized electrons allow metals to conduct electricity and heat well. The strong metallic bonds throughout the lattice give metals high melting and boiling points and properties like malleability from the layers being able to slide over one another. Alloys and allotropes are also discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 3 Metallic Bonding InfoDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Metallic Bonding InfoShehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocument16 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- Giant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond NotesDocument8 pagesGiant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond Notesnihan.8558No ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding - 1 - Free Electron ModelDocument21 pagesMetallic Bonding - 1 - Free Electron Modelsherin joyNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument2 pagesMetallic BondLiton DasNo ratings yet
- Describe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesDescribe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent Compoundsmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding - Electron Sea ModelDocument13 pagesMetallic Bonding - Electron Sea ModelMirza MohammadNo ratings yet
- L05 (Bonding+Crystalline) 01Document14 pagesL05 (Bonding+Crystalline) 01amy.like.cooking.77No ratings yet
- Summary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 2.2 Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesSummary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 2.2 Metallic BondingRachel JeffresonNo ratings yet
- Bonding Revision GuidesDocument1 pageBonding Revision Guidesapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument10 pagesMetallic BondAbhishek NayakNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Document11 pagesCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Interactive ReaderDocument3 pagesMetallic Bonding Interactive Readerclarisse.ionicNo ratings yet
- 3.2.5. Metallic Bonding PDFDocument2 pages3.2.5. Metallic Bonding PDFClinton ChikengezhaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Board NotesDocument19 pagesChemical Bonding Board NotesEmaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Interactive ReaderDocument3 pagesMetallic Bonding Interactive Readerfortnitekiller871No ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic BondingboyaneshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 2Document32 pagesChemical Bond 2Yak Raj PandeyNo ratings yet
- تقرير محمدDocument8 pagesتقرير محمدm6czcv4mycNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Metallic Bonding-1Document4 pagesPresentation On Metallic Bonding-1emmyloverboy2020No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes STD Vii Chapter: Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesChemistry Notes STD Vii Chapter: Metallic BondingRafit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument16 pagesMetallic Bondingmathvin thummalaNo ratings yet
- My FileDocument12 pagesMy FileKeeben BadoyNo ratings yet
- Notes For Metallic BondingDocument12 pagesNotes For Metallic Bondingいい子No ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry PDFFahimDayhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding NotesAyesha Awan100% (1)
- Metallic BondingDocument26 pagesMetallic BondingAlaa HafizNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2Document15 pagesAssignment - 2padhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- 4 4 Metallic BondingDocument2 pages4 4 Metallic BondingNguyenHoangMinhDucNo ratings yet
- Chpter 2 - Metal Materials 1Document18 pagesChpter 2 - Metal Materials 1Hiếu TrầnNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument12 pagesMetallic BondingilyasNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument5 pagesMetallic BondDinak ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Elmira 422.22eDocument15 pagesElmira 422.22eIk.ElmiraNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingCristina Lopez AndesNo ratings yet
- Notes W4Document5 pagesNotes W4sy.valNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-METALLIC BONDING-SbH-L5Document21 pagesCHAPTER 3-METALLIC BONDING-SbH-L5ezanaNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument1 pageMetallic BondingSoraya DeenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocument14 pagesLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNo ratings yet
- Metalic BondingDocument1 pageMetalic Bondingmuhammad abdullahNo ratings yet
- BondsDocument24 pagesBondsPavithran Kamaleswari Year 10No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project in Which My Group Didnt Help??Document9 pagesChemistry Project in Which My Group Didnt Help??muhammadumarlol10yrsNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument28 pagesMetallic BondingLysha Kana-an CarampatanaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument8 pagesNotes On Covalent and Metallic Bondingselma samadNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument1 pageMetallic BondingJennnytotsNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument5 pagesMetallic BondingsamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document83 pagesUnit 5mtayyab zahidNo ratings yet
- Che 90308 TypesofsolidsDocument4 pagesChe 90308 Typesofsolidsapi-218511741No ratings yet
- BONDING IN METALS BY K.N.S.SWAMI..pptx477Document33 pagesBONDING IN METALS BY K.N.S.SWAMI..pptx477Suman KusumNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesChemistry - Chemical BondingMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes: Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesChemistry Notes: Atomic StructureHTPavillionNo ratings yet
- Metallic Properties Report in Science 02Document6 pagesMetallic Properties Report in Science 02Jimwell SiegoNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and AtomsDocument12 pagesElements, Compounds and Atomsananya.arumugarajanNo ratings yet
- Teks 7d Metallic Bonding Lesson NotesDocument4 pagesTeks 7d Metallic Bonding Lesson Notesapi-236826747No ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument7 pagesMetallic BondingkaileymawsonNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals and AlloysDocument19 pagesProperties of Metals and AlloysIlhamsidiqNo ratings yet
- Why Do Metals Conduct ElectricityDocument14 pagesWhy Do Metals Conduct ElectricityHennie VeldmanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 SyllabusDocument23 pagesGrade 8 SyllabusClopzNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 SyllabusDocument23 pagesGrade 9 SyllabusClopzNo ratings yet
- Dear HeadmasterDocument1 pageDear HeadmasterClopzNo ratings yet
- Food Items and PricesDocument4 pagesFood Items and PricesClopzNo ratings yet
- Habit TrackerDocument1 pageHabit TrackerClopzNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondingDocument1 pageCovalent BondingClopzNo ratings yet
Metallic Bonding
Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
Clopz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesThe document discusses metallic bonding and properties of metals. It explains that metals have a giant metallic lattice structure formed from layers of metal cations surrounded by delocalized electrons. These delocalized electrons allow metals to conduct electricity and heat well. The strong metallic bonds throughout the lattice give metals high melting and boiling points and properties like malleability from the layers being able to slide over one another. Alloys and allotropes are also discussed.
Original Description:
Metallic Bonding Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses metallic bonding and properties of metals. It explains that metals have a giant metallic lattice structure formed from layers of metal cations surrounded by delocalized electrons. These delocalized electrons allow metals to conduct electricity and heat well. The strong metallic bonds throughout the lattice give metals high melting and boiling points and properties like malleability from the layers being able to slide over one another. Alloys and allotropes are also discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pages Metallic Bonding
Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
ClopzThe document discusses metallic bonding and properties of metals. It explains that metals have a giant metallic lattice structure formed from layers of metal cations surrounded by delocalized electrons. These delocalized electrons allow metals to conduct electricity and heat well. The strong metallic bonds throughout the lattice give metals high melting and boiling points and properties like malleability from the layers being able to slide over one another. Alloys and allotropes are also discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Metallic Bonding
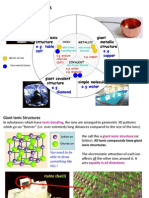
Q:- Describe the structure or bonding in a metal.
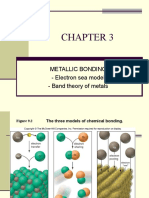
Ans: Metals have a giant metallic lattice structure held together by
electrostatic forces of attraction between the layers of metal cations
and the sea of freely moving delocalized electrons.
Q:- Why do metals have high melting and boiling points?
Ans: There are many strong metallic bonds in giant metallic structures
so large amounts of heat energy are needed to overcome these forces
and break these bonds.
Q:- Why metals are good conductors of electricity and heat?
Ans: Metals are good conductors because of the free electrons that are
available to move and carry a charge.
Q:- Why are metals malleable and ductile?
Ans: Metals have a layered structure of metal cations surrounded by
delocalized electrons. Therefore, when force is applied, these layers
slide over each other while the delocalized electrons move along the
layers keeping the metallic bonding intact.
Q:- What are alloys?
Ans: Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals.
Q:- Why alloys are harder than pure metals?
Ans: Because alloys contain cations of different sizes. The larger metal
cations block the layers of smaller metal cations and hence the layers of
smaller cations can’t slide over each other.
Metallic Bonding
Q:- What are allotropes?
Ans: The different physical forms of the same element are called
allotropes.
Q:- Why do Fullerenes have a very low melting point as compared to
graphite or diamond?
Ans: Fullerene exists as a simple molecular structure making it have
weak intermolecular forces. Therefore, less energy is required to break
these weak intermolecular forces.
On the other hand, Diamond or Graphite exists as a giant covalent
structure making them have strong covalent bonds. Therefore, a lot of
energy is required to break these strong covalent bonds.
Q:- Why graphite is a soft material?
Ans: Graphite has weak intermolecular forces between the layers.
Therefore, when force is applied, these layers slide over each other.
Q:- Why graphite is an electrical conductor?
Ans: Because graphite has delocalized electrons.
Q- Why SiO2 and Diamond are not electrical conductors?
Ans: SiO2 and Diamond don’t have delocalized electrons because all the
outermost electrons are used in making covalent bonds.
You might also like
- Chapter 3 Metallic Bonding InfoDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Metallic Bonding InfoShehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocument16 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- Giant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond NotesDocument8 pagesGiant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond Notesnihan.8558No ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding - 1 - Free Electron ModelDocument21 pagesMetallic Bonding - 1 - Free Electron Modelsherin joyNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument2 pagesMetallic BondLiton DasNo ratings yet
- Describe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesDescribe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent Compoundsmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding - Electron Sea ModelDocument13 pagesMetallic Bonding - Electron Sea ModelMirza MohammadNo ratings yet
- L05 (Bonding+Crystalline) 01Document14 pagesL05 (Bonding+Crystalline) 01amy.like.cooking.77No ratings yet
- Summary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 2.2 Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesSummary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 2.2 Metallic BondingRachel JeffresonNo ratings yet
- Bonding Revision GuidesDocument1 pageBonding Revision Guidesapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument10 pagesMetallic BondAbhishek NayakNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Document11 pagesCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Interactive ReaderDocument3 pagesMetallic Bonding Interactive Readerclarisse.ionicNo ratings yet
- 3.2.5. Metallic Bonding PDFDocument2 pages3.2.5. Metallic Bonding PDFClinton ChikengezhaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Board NotesDocument19 pagesChemical Bonding Board NotesEmaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Interactive ReaderDocument3 pagesMetallic Bonding Interactive Readerfortnitekiller871No ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic BondingboyaneshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 2Document32 pagesChemical Bond 2Yak Raj PandeyNo ratings yet
- تقرير محمدDocument8 pagesتقرير محمدm6czcv4mycNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Metallic Bonding-1Document4 pagesPresentation On Metallic Bonding-1emmyloverboy2020No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes STD Vii Chapter: Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesChemistry Notes STD Vii Chapter: Metallic BondingRafit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument16 pagesMetallic Bondingmathvin thummalaNo ratings yet
- My FileDocument12 pagesMy FileKeeben BadoyNo ratings yet
- Notes For Metallic BondingDocument12 pagesNotes For Metallic Bondingいい子No ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry PDFFahimDayhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding NotesAyesha Awan100% (1)
- Metallic BondingDocument26 pagesMetallic BondingAlaa HafizNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2Document15 pagesAssignment - 2padhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- 4 4 Metallic BondingDocument2 pages4 4 Metallic BondingNguyenHoangMinhDucNo ratings yet
- Chpter 2 - Metal Materials 1Document18 pagesChpter 2 - Metal Materials 1Hiếu TrầnNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument12 pagesMetallic BondingilyasNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument5 pagesMetallic BondDinak ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Elmira 422.22eDocument15 pagesElmira 422.22eIk.ElmiraNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingCristina Lopez AndesNo ratings yet
- Notes W4Document5 pagesNotes W4sy.valNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-METALLIC BONDING-SbH-L5Document21 pagesCHAPTER 3-METALLIC BONDING-SbH-L5ezanaNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument1 pageMetallic BondingSoraya DeenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocument14 pagesLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNo ratings yet
- Metalic BondingDocument1 pageMetalic Bondingmuhammad abdullahNo ratings yet
- BondsDocument24 pagesBondsPavithran Kamaleswari Year 10No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project in Which My Group Didnt Help??Document9 pagesChemistry Project in Which My Group Didnt Help??muhammadumarlol10yrsNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument28 pagesMetallic BondingLysha Kana-an CarampatanaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument8 pagesNotes On Covalent and Metallic Bondingselma samadNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument1 pageMetallic BondingJennnytotsNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument5 pagesMetallic BondingsamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document83 pagesUnit 5mtayyab zahidNo ratings yet
- Che 90308 TypesofsolidsDocument4 pagesChe 90308 Typesofsolidsapi-218511741No ratings yet
- BONDING IN METALS BY K.N.S.SWAMI..pptx477Document33 pagesBONDING IN METALS BY K.N.S.SWAMI..pptx477Suman KusumNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesChemistry - Chemical BondingMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes: Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesChemistry Notes: Atomic StructureHTPavillionNo ratings yet
- Metallic Properties Report in Science 02Document6 pagesMetallic Properties Report in Science 02Jimwell SiegoNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and AtomsDocument12 pagesElements, Compounds and Atomsananya.arumugarajanNo ratings yet
- Teks 7d Metallic Bonding Lesson NotesDocument4 pagesTeks 7d Metallic Bonding Lesson Notesapi-236826747No ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument7 pagesMetallic BondingkaileymawsonNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals and AlloysDocument19 pagesProperties of Metals and AlloysIlhamsidiqNo ratings yet
- Why Do Metals Conduct ElectricityDocument14 pagesWhy Do Metals Conduct ElectricityHennie VeldmanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 SyllabusDocument23 pagesGrade 8 SyllabusClopzNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 SyllabusDocument23 pagesGrade 9 SyllabusClopzNo ratings yet
- Dear HeadmasterDocument1 pageDear HeadmasterClopzNo ratings yet
- Food Items and PricesDocument4 pagesFood Items and PricesClopzNo ratings yet
- Habit TrackerDocument1 pageHabit TrackerClopzNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondingDocument1 pageCovalent BondingClopzNo ratings yet