Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cricket 3
Cricket 3
Uploaded by
Aniket AgarwalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cricket 3
Cricket 3
Uploaded by
Aniket AgarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
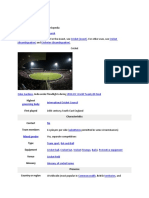
A field with a wicket at either end made of two bails balanced on three stumps is used for the bat-
and-ball game of cricket, which is played between two teams of eleven players. The pitch is 22 yards
(or 20 metres) long. By preventing the ball from leaving the field and reaching either wicket, the
bowling and fielding side attempts to stop this from happening and dismisses each batter. Running
between the wickets after striking a ball that has been thrown at one of the wickets with a bat is
how the batting side scores runs (so they are "out"). Dismissal can occur in a variety of ways, such as
being bowled, having the ball strike the stumps and remove the bails, having the ball caught by the
fielding side after it has been struck by the bat but before it hits the ground, or having the ball strike
a wicket before the batter can cross the crease in front of the wicket. When 10 batters have been
retired, an inning comes to an end, and the teams trade positions. In international games, in addition
to the two umpires who call the shots, there is also a match referee and a third umpire. Two off-field
scorers who monitor the game's statistics information interact with them.
There are many different ways to play cricket, from Twenty20, when each team bats for a single
innings of 20 overs (each "over" is a set of six fair opportunities for the batting team to score), to
Test matches, which are played over five days. In contrast to the traditional all-white uniform,
players in limited overs cricket wear club or team colours. Players should wear protective gear in
addition to their regular equipment since the ball, which is a solid, hard spheroid made of
compressed leather with a slightly elevated stitched seam enclosing a cork core wrapped with tightly
coiled string, can hurt them.
At the middle of the 16th century, South East England was where cricket was first mentioned. It
spread around the globe with the expansion of the British Empire when the first international games
were played in the second half of the 19th century. The body in charge of regulating the sport is the
International Cricket Council (ICC), which has more than 100 members and 12 full members who
take part in Test matches. The Rules of Cricket, which regulate the game, are upheld by the
Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) in London. The countries with the highest popularity for the sport
are South Asia, Australasia, the United Kingdom, Southern Africa, and the West Indies. [1]
The game of women's cricket, which is organised and played autonomously, has also advanced to a
high level on the global scene. Australia is the most successful international cricket team, having won
more Test series triumphs than any other country and more One Day International trophies,
including five World Cups.
You might also like
- Physical Education Project On CricketDocument36 pagesPhysical Education Project On CricketSonal Sachin Gupte67% (236)
- Team Sports P.E Finals QUIZES AND EXAMDocument14 pagesTeam Sports P.E Finals QUIZES AND EXAMJayson Lucena100% (2)
- Presentation On CricketDocument6 pagesPresentation On CricketMohammad Sazid Hossain86% (7)
- BWTS 2014 Performance Turbo Catalog PDFDocument68 pagesBWTS 2014 Performance Turbo Catalog PDFАндрей СтрилецNo ratings yet
- Swinton Park Viability ReportDocument32 pagesSwinton Park Viability ReportMathew ShoreNo ratings yet
- Cricket 5Document1 pageCricket 5Aniket AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Cricket 4Document1 pageCricket 4Aniket AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Cricket 2Document1 pageCricket 2Aniket AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument1 pageCricketAniket AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument1 pageCricketJitendra PandeyNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument1 pageCricketalphyvavaNo ratings yet
- CrickDocument1 pageCrickSuryansh RajputNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument1 pageCricketKumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pe FileDocument6 pagesPe FileGauransh Sharma100% (1)
- CricketDocument4 pagesCricketAmaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Laws of CricketDocument2 pagesLaws of CricketLeinaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAbhijitNo ratings yet
- Cricket BasicDocument1 pageCricket BasicPankNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument6 pagesCricketMarissa SamsundarNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument23 pagesCricketVaibhav SattirajuNo ratings yet
- IPL SquardDocument2 pagesIPL SquardShishir AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Cricket (Insect) Cricket (Disambiguation) Cricketer (Disambiguation)Document1 pageCricket (Insect) Cricket (Disambiguation) Cricketer (Disambiguation)praneethNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument10 pagesCricketAakash GroverNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument6 pagesCricketdhruvarora434No ratings yet
- Cricket Rules: Object of The GameDocument6 pagesCricket Rules: Object of The GameRyanNo ratings yet
- PSL SquardDocument3 pagesPSL SquardShishir AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document14 pagesPresentation 1Amaan KhanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL EDUCATION TakeemDocument22 pagesPHYSICAL EDUCATION Takeemselina fraser0% (1)
- CRICKETDocument10 pagesCRICKETRishi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Project On Cricket: Cricket - "A Magic Word in The Sphere of Sports."Document31 pagesPhysical Education Project On Cricket: Cricket - "A Magic Word in The Sphere of Sports."JsmBhanotNo ratings yet
- Queenie SbaDocument15 pagesQueenie SbaDumissa MelvilleNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Project On Cricket: Cricket - "A Magic Word in The Sphere of Sports."Document38 pagesPhysical Education Project On Cricket: Cricket - "A Magic Word in The Sphere of Sports."JsmBhanot0% (1)
- Labelled Diagram of 400m TrackDocument3 pagesLabelled Diagram of 400m TrackRitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument87 pagesCrickettavish koulNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument1 pageCricketrahulNo ratings yet
- CrickettDocument2 pagesCrickettARUN PRASATHNo ratings yet
- Cricket Is Played With A Bat and Ball and Involves Two Competing SidesDocument10 pagesCricket Is Played With A Bat and Ball and Involves Two Competing SidesAshutosh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cricket PE PaperDocument2 pagesCricket PE PaperInday MiraNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument24 pagesPhysical EducationNeel WankhadeNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument5 pagesCricketAmit Jung SubediNo ratings yet
- Nik UuuuDocument1 pageNik UuuuAmrit TejaniNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Project On Cricket: Ishwar DassDocument52 pagesPhysical Education Project On Cricket: Ishwar Dassheerein jetley100% (1)
- Growth of Amateur and Professional Cricket in EnglandDocument1 pageGrowth of Amateur and Professional Cricket in EnglandJitendra PandeyNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument2 pagesCricketTushar BansalNo ratings yet
- Cricket: Ana HorvatDocument12 pagesCricket: Ana HorvatIvana ŽgelaNo ratings yet
- Chemistryinvestigatoryprojec1 150313025225 Conversion Gate01Document13 pagesChemistryinvestigatoryprojec1 150313025225 Conversion Gate01Kvs kartikNo ratings yet
- CricketDocument20 pagesCricketAnand DoijodeNo ratings yet
- Cricket AssignmentDocument13 pagesCricket AssignmentMuhammad Tariq100% (1)
- 619086Document1 page619086Bibun ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Physical Education ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysical Education ProjectYash MahajanNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: CricketDocument15 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: CricketC.N. KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Cricket - WikipediaDocument44 pagesCricket - Wikipediaaditya thoratNo ratings yet
- Field HockeyDocument1 pageField HockeyRamesh LaishettyNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Project On Cricket: Cricket - "A Magic Word in The Sphere of Sports."Document33 pagesPhysical Education Project On Cricket: Cricket - "A Magic Word in The Sphere of Sports."JsmBhanot100% (1)
- Physical Education ProjectDocument31 pagesPhysical Education ProjectRamesh Chand100% (1)
- Football: HistoryDocument9 pagesFootball: HistoryAshwin Singh50% (2)
- CricketgpDocument11 pagesCricketgpAmalNo ratings yet
- Nail SBA On Cricket (AutoRecovered)Document1 pageNail SBA On Cricket (AutoRecovered)Anthony JõrdáñNo ratings yet
- Cricket: Learn The Basics, The History, The Rules and How To Play in 30 MinutesFrom EverandCricket: Learn The Basics, The History, The Rules and How To Play in 30 MinutesNo ratings yet
- Cricket: The Ultimate Guide to Cricket Skills, Strategies, and PerformanceFrom EverandCricket: The Ultimate Guide to Cricket Skills, Strategies, and PerformanceNo ratings yet
- An Tra Niks Bodyweight Routine Printer Friendly VersionDocument2 pagesAn Tra Niks Bodyweight Routine Printer Friendly VersionDerrek KangNo ratings yet
- Bike Leaflet HighDocument2 pagesBike Leaflet HighFebri YantaNo ratings yet
- Mazda Carburetor Manual 1979-1985Document133 pagesMazda Carburetor Manual 1979-1985PIlkadutNo ratings yet
- Alur Outbound Arah MatahariDocument2 pagesAlur Outbound Arah MatahariWAHYU AGUNG CNo ratings yet
- How To Use This Training TemplateDocument12 pagesHow To Use This Training TemplateLouis TrầnNo ratings yet
- BSC2021 Ruleset enDocument45 pagesBSC2021 Ruleset enMaxim GreadcencoNo ratings yet
- Scholastic Scope Magazine May 2017 - Nick VenturaDocument5 pagesScholastic Scope Magazine May 2017 - Nick VenturaPatty Rice100% (2)
- Friday Basketball-1 Ape Unit Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFriday Basketball-1 Ape Unit Lesson Planapi-329237531No ratings yet
- SFS Calisthenics Workout Program-2Document60 pagesSFS Calisthenics Workout Program-2Rod PNo ratings yet
- Rangers Football Club Matchday Programme 18.03.2021Document68 pagesRangers Football Club Matchday Programme 18.03.2021Fred BlackadderNo ratings yet
- Used To Homework PDFDocument1 pageUsed To Homework PDFRedes ItcNo ratings yet
- Cristiano Ronaldo and Lionel Messi Are Two of The Greatest Footballers of All Time and Have Achieved A Great Number of Successes and Awards Throughout Their CareersDocument3 pagesCristiano Ronaldo and Lionel Messi Are Two of The Greatest Footballers of All Time and Have Achieved A Great Number of Successes and Awards Throughout Their CareersJss TrraNo ratings yet
- Result of The Draw: Round of 32 and Round of 16 - 20 December 2012Document2 pagesResult of The Draw: Round of 32 and Round of 16 - 20 December 2012AguesBudi S TalawangNo ratings yet
- Itachi Uchiha Workout Routine PDFDocument9 pagesItachi Uchiha Workout Routine PDFAdna VitóriaNo ratings yet
- Football Fortunes Player Cards 2Document14 pagesFootball Fortunes Player Cards 2colinbunNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Project Final Presentation: Ice Hockey StickDocument25 pagesTerm Paper Project Final Presentation: Ice Hockey Stickhzstorm11No ratings yet
- The Last StrategyDocument3 pagesThe Last StrategyCardoso TochaNo ratings yet
- Shimano Cycling Catalogue PDF - Soup - IoDocument2 pagesShimano Cycling Catalogue PDF - Soup - Iommmmm1900No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document13 pagesChapter 5lui navidadNo ratings yet
- Yachts Yachting November 2015Document100 pagesYachts Yachting November 2015Anantoly KoretskyNo ratings yet
- Chacha Chaudhary Aur Cricket Match PDFDocument36 pagesChacha Chaudhary Aur Cricket Match PDFsarvesh.3587461No ratings yet
- Sample Spring Games Opening Ceremony ScriptDocument5 pagesSample Spring Games Opening Ceremony ScriptJo-an CastañedaNo ratings yet
- PE Examination 8 GradeDocument9 pagesPE Examination 8 GradeScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- GRUP MAHASISWA SEM GENAP 22 Feb 2022Document51 pagesGRUP MAHASISWA SEM GENAP 22 Feb 2022Nurul NajibNo ratings yet
- Raph Planned Workout Routine by SixtusDocument4 pagesRaph Planned Workout Routine by Sixtuscliffordtor16No ratings yet
- Practical 3 - Pay Roll PDFDocument2 pagesPractical 3 - Pay Roll PDFmasood khanNo ratings yet
- Playbook v2b〡Hawkin Dynamics 2024Document12 pagesPlaybook v2b〡Hawkin Dynamics 2024Carles PeiroNo ratings yet