Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day2 Pabalinas
G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day2 Pabalinas
Uploaded by
Thanie Abrasaldo NadalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day2 Pabalinas
G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day2 Pabalinas
Uploaded by
Thanie Abrasaldo NadalCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade: 10 Subject: SCIENCE
Quarter/Semester: FIRST Week No: 1 Day 2
I. OBJECTIVES
Content Standard The learners demonstrate an understanding of the
relationship among the locations of volcanoes,
earthquake epicenters, and mountain ranges.
Performance Standard The learners shall be able to demonstrate ways to
ensure disaster preparedness during earthquakes,
tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.
Learning Competency The learners should be able to describe the distribution
of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and major
mountain belts.
S10ES –Iaj-36.1
Knowledge Identify the layers of lithospheric plates and determine
the kind of crust
Skills Compare and contrast the two kinds of crust
Attitude Establish camaraderie among groups by locating
countries where major plates are present using the world
map
II. CONTENT WHAT IS PLATE TECTONICS?
III. LEARNING
RESOURCES
References Grade 10 Science Learner’s Material pp. 4-5
Grade 10 Science Teacher’s Guide pp. 4-5
Other Learning Resources https://earthhow.com/7-major-tectonic-plates/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=et0DcFhX8Ig&t=18s
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Preparatory Activities Ask learner’s output or responses based on the
assignment given the previous day.
1. What is Plate Tectonics?
(Ans. The plates move very slowly but constantly,
and this movement is called tectonics; thus the theory
of moving lithospheric plates is called plate tectonics.)
2. What is lithosphere?
(Ans. The rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of
the crust and upper mantle.)
3. What are the two layers of the lithosphere?
(Ans. Crust and Upper Mantle)
4. Define the two kinds of crust.
(Ans. There are two kinds of crust: the thicker but
less dense continental crust and the oceanic crust
which is relatively thinner but denser than continental
crust)
Prepared by: LESTER C.
PABALINAS
Teacher III – Masulog HS
Canlaon II
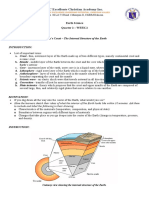
B. Motivation https://geologyportfoliokxz.weebly.com/layers-of-earth.html
LM Figure 1, p 6
Present to the class the picture of
the two kinds of crust. Let the
students describe what can they
say about the picture.
Present to the class the picture of
Map of Plate Boundaries. Let the
students describe how the plates
are divided into such manner?
(Ans. Plate boundaries are divided into such manner in
terms of their boundaries.)
C. Activity Let the students watch the video found on this link:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=et0DcFhX8Ig&t=18s
D. Analysis What do you call the rigid outer part of the earth? What
are its layers?
(Ans. Lithosphere, Upper Mantle)
Do you believe that these plates are moving?
(Ans. Yes)
Based on the video presented, what is tectonic?
(Ans. Tectonic refers to the movement of plates)
How will you compare continental crust and oceanic
crust?
(Possible Answers will be based on the learners
perception but the teacher should emphasize that the
correct answers are found in the abstraction part.)
E. Abstraction Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth's outer shell is
divided into large slabs of solid rock, called “plates,” that
glide over Earth's mantle, the rocky inner layer above
Earth’s core. Earth’s solid outer layer, which includes the
crust and the uppermost mantle, is called the
lithosphere.
The lithosphere is said to be in constant but slow motion.
This movement of the lithosphere is called tectonics.
Earth’s lithosphere consists of layers, the crust and the
Prepared by: LESTER C.
PABALINAS
Teacher III – Masulog HS
Canlaon II
upper part of the mantle. The discussion will focus on
the outermost layer which is the crust.
The crust is made of a variety of solid rocks like
sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. It has an
average density of 2.8 g/cm3 and its thickness ranges
from 5 to 50 km. The crust is thickest in a part where a
relatively young mountain is present and thinnest along
the ocean floor.
Oceanic crust
Outer layer of lithosphere that is found under oceans. It
is about 6 km thick composed solidly of different layers.
The outer most layer is about 500 m thick made out of
lavas and basalt rocks. under is a layer of basalt
sheeted dikes that is about 1 km thick and acts as a
plumbing system for molten rocks and magmas to travel
to the sea-floor.
Continental crust
Layer consisting solidly of granitic rocks and thicker
(25km-70km) than the oceanic crust. Its existence
allowed life to form on land. Different parts collide and
separate to change the Earth's geographic form and that
is a part of the super-continent cycle.
F. Application Using the world map, the class will be divided into five
groups. Provide a copy of the template to each group
found on attachment A. Also, provide a copy of world
map to each group for guidance.
G. Practical Applications The teacher will be asked to perform activity which can
of Concepts and be seen on the link:
Skills in Daily Living
Prepared by: LESTER C.
PABALINAS
Teacher III – Masulog HS
Canlaon II
https://www.amnh.org/explore/ology/earth/plates-on-the-
move2/game
Point the cursor in the orange circle and you will be
prompted with practical questions relative to plate
tectonics.
For teachers with no interconnection, the teacher should
explore in advance the link and grab a picture or screen
shot of every question.
H. Generalization What are the different major plates of our planet?
(Ans.: Pacific Plate, North American Plate, Eurasian
Plate, African Plate, Antarctic Plate, Antarctic Plate,
Indo-Australia Plate)
What do you call that rigid outer layer of the earth where
the crust and mantle is located?
(Ans.: Lithosphere)
When two crust will collide or hit one another, which do
you think will most likely to submerge or subduct?
(Possible Ans.: Continental Plate)
I. Evaluation See Attachment B
J. Additional activities Research on the following questions:
for application or What do you call the waves released during
remediation earthquake?
(assignment) (Ans.: Seismic Waves)
What are its types?
(Ans.: P-Waves, S-Waves, Surface Waves)
How will you compare the movement of the waves that
travels in the interior layer of the earth?
Prepared by: LESTER C.
PABALINAS
Teacher III – Masulog HS
Canlaon II
(Possible Ans.: They differ in terms of velocity upon
reaching the seismic stations)
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation
No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation
Did the remedial lesson
work? No. of learners
who caught up the lesson
No. of learners who
require remediation
Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did these work?
What difficulties did I
encounter which principal
and supervisor can help
or solve?
What innovation or
localized did I
use/discover which I wish
to share?
Prepared by: LESTER C.
PABALINAS
Teacher III – Masulog HS
Canlaon II
ATTACHMENT A
Name of Student: _________________________ Grade & Section: __________ Score: ______
Instruction/s: Complete the table below. Using the world map and the map of plate boundaries,
in Column 2, identify the continents and oceans where the major plate is present and in Column
3, enumerate at least five countries belonging to each plate.
Using the World Map,
Enumerate at least five
Major Plate Name Oceans
countries under each
plate
No country covered by this
Pacific Plate Ans.: Pacific Ocean
plate
1. United States
2. Canada
North American Plate Ans.:Atlantic Ocean 3. Greenland
4. Cuba
5. Bahamas
1. England
2. Russia
Eurasian Plate Ans.: Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Ocean 3. Sweden
4. Germany
5. Philippines
1. Africa
2. Ethiopia
African Plate Ans.: Atlantic Ocean 3. Ghana
4. Kenya
5. Tanzania
Antarctic Plate Ans.: Antarctic Ocean 1. Antarctica
1. Australia
2. India
Indo-Australia Plate Ans.: Oceania, Indian Ocean 3. New Zealand
4. Pakistan
5. Papua New Guinea
1. Brazil
2. Argentina
South American Plate Ans.: Atlantic Ocean 3. Bolivia
4. Paraguay
5. Peru
(The answers in the template are sample answers only, the teacher should conduct the activity
in advance)
Prepared by: LESTER C.
PABALINAS
Teacher III – Masulog HS
Canlaon II
ATTACHMENT B
Name of Student: _________________________ Grade & Section: __________ Score: ______
A. Instruction/s: Label the picture below and write a short description about it.
(Ans.: Oceanic crust
(Ans.: Continental crust
Outer layer of lithosphere that is
Layer consisting solidly
found under oceans. It is about
of granitic rocks and
6 km thick composed solidly of
thicker (25km-70km)
different layers. The outer most
than the oceanic crust.
layer is about 500 m thick made
Its existence allowed life
out of lavas and basalt rocks.
to form on land. Different
under is a layer of basalt
parts collide and
sheeted dikes that is about 1
separate to change the
km thick and acts as a plumbing
Earth's geographic form
system for molten rocks and
and that is a part of the
magmas to travel to the sea-
super-continent cycle.)
floor.)
B. Identify the term/s describe by the following statements below:
1. Made of a variety of solid rocks like sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous.
Ans. Crust
2. The theory that Earth's outer shell is divided into large slabs of solid rock, called
“plates,” that glide over Earth's mantle, the rocky inner layer above Earth’s core.
Ans. Plate Tectonic Theory
3. Earth’s solid outer layer, which includes the crust and the uppermost mantle, is ______.
Ans. Lithosphere
4. The thicker but less dense crust and its existence allowed life to form on land. Different
parts collide and separate to change the Earth's geographic form and that is a part of
the super-continent cycle.
Ans. Continental Crust
5. Relatively thinner but denser than the other crust and outer layer of lithosphere that is
found under oceans. It is about 6 km thick composed solidly of different layers.
Ans. Oceanic Crust
Prepared by: LESTER C.
PABALINAS
Teacher III – Masulog HS
Canlaon II
You might also like
- The Big History of Modern Science Hannu Rajaniemi TEDxDanubiaDocument17 pagesThe Big History of Modern Science Hannu Rajaniemi TEDxDanubiaCathleen Abiera100% (4)
- Science 10 Unit PlanDocument50 pagesScience 10 Unit PlanEisle Keith Rivera TapiaNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument39 pagesFinal ReportSamhith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Format For Course FileDocument40 pagesFormat For Course FilePrateek PandeyNo ratings yet
- DLL G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day2Document7 pagesDLL G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day2Thomas JillNo ratings yet
- Science For Grade 10 (1ST Quarter Module)Document85 pagesScience For Grade 10 (1ST Quarter Module)Norigen ItangNo ratings yet
- DLP 1 Yas Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesDLP 1 Yas Plate Tectonicsfabillardevinegrace94No ratings yet
- Science Modules: Quarter 1 - Weeks 1 - 4Document41 pagesScience Modules: Quarter 1 - Weeks 1 - 4Emily RamosNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Module: Unit 1. Earth and SpaceDocument35 pagesScience 10 Module: Unit 1. Earth and SpaceJudith DurensNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE M1 Week1Document8 pagesSCIENCE M1 Week1Vyrox MPNo ratings yet
- Oct 2-6Document11 pagesOct 2-6Joana Marie NuqueNo ratings yet
- 2NDSEM - DLL Q1 WEEK 8 - Earth ScienceDocument5 pages2NDSEM - DLL Q1 WEEK 8 - Earth ScienceMarianne Joy Flormata AlulodNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13-Teacher's GuideDocument14 pagesLesson 13-Teacher's GuideAllyssa LimosNo ratings yet
- 8 DLL Sept 21Document2 pages8 DLL Sept 21Vincent Paul ReyesNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Qtr1 Lesson 3Document2 pagesGrade 10 Qtr1 Lesson 3Niña Catubig - TangcalaganNo ratings yet
- 3 Plate TectonicsDocument19 pages3 Plate TectonicsJenneth Cabinto DalisanNo ratings yet
- First Quarter: ScienceDocument9 pagesFirst Quarter: Science11-AB10 Marquez, Rence Joseph L.No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SeafloorDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Seaflooramie lazaga100% (1)
- Science 10 w1L1Document11 pagesScience 10 w1L1Melerose Dela SernaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Week 1Document10 pagesScience 10 Week 1Princess EstropeNo ratings yet
- Q1 Melc3 RibayaDocument9 pagesQ1 Melc3 RibayaElaine MagpatagNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M04 - L02 - Q2 - W2Document2 pagesEarth Science - M04 - L02 - Q2 - W2Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanLowel AndrewNo ratings yet
- a-semi-detailed-Lesson-Plan-in-science 10Document4 pagesa-semi-detailed-Lesson-Plan-in-science 10ESTEPHANIE TUMAGANNo ratings yet
- Science10 q1 slk1 Plate-Tectonics v1Document14 pagesScience10 q1 slk1 Plate-Tectonics v1Ervis BahintingNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-Science 10 (PLATE TECTONICS) - FinalDocument45 pagesGrade 10-Science 10 (PLATE TECTONICS) - FinalNorberto J. Manjares Jr.100% (2)
- Science10 Q1 W1Document38 pagesScience10 Q1 W1Rainier G. de Jesus100% (2)
- Lesson Plan - ElementaryDocument12 pagesLesson Plan - Elementaryannf38562No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 9 Grade 10-Demeter, Nike, Dionysus, Hestia, Poseidon July 29, 2019 I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 9 Grade 10-Demeter, Nike, Dionysus, Hestia, Poseidon July 29, 2019 I. ObjectivesIRISNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Plate": Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 5Document6 pagesTectonic Plate": Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 5Niel SantosNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document9 pagesWeek 4Chenee TanNo ratings yet
- G10 Lasno1q1Document8 pagesG10 Lasno1q1Jysn EspejoNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide SampleDocument11 pagesLearning Guide Samplelj BoniolNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 Ho Q1 - 1Document2 pagesSci 10 Ho Q1 - 1Karl BadolesNo ratings yet
- Science 10: Department of EducationDocument10 pagesScience 10: Department of EducationClint Harvey C. BicoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q1 Week 1Document11 pagesScience 10 Q1 Week 1Mark Shalli G. BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q1 Week 1Document11 pagesScience 10 Q1 Week 1Mark Shalli G. BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Science Q1week 1Document11 pagesScience Q1week 1Catheriner100% (1)
- Science 10 (W1)Document21 pagesScience 10 (W1)Gregorio Rizaldy100% (1)
- Module 5 Layers of The EarthDocument3 pagesModule 5 Layers of The EarthGabby GallardoNo ratings yet
- Science10 q1 slk1 Plate-Tectonics V1-Converted-1 PDFDocument14 pagesScience10 q1 slk1 Plate-Tectonics V1-Converted-1 PDFRoMe LynNo ratings yet
- Samuel - Module 3 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument14 pagesSamuel - Module 3 - Earth and Life ScienceMa Angelica BanariaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 QUARTER 1, Week 1: Figure 1: Mayon VolcanoDocument6 pagesScience 10 QUARTER 1, Week 1: Figure 1: Mayon Volcanodaisy sorianoNo ratings yet
- Elemsci Volume 3Document131 pagesElemsci Volume 3Marc Laurenze CelisNo ratings yet
- Sabinay Science 10 1st Quart Compressed 2Document16 pagesSabinay Science 10 1st Quart Compressed 2Yanyan AlfanteNo ratings yet
- DLP For Final DemoDocument5 pagesDLP For Final Demoreiner castilloNo ratings yet
- WEEK5Document5 pagesWEEK5Marianne Joy Flormata AlulodNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Lesson Plan For Interior Structure of The EarthDocument15 pagesGroup 4 Lesson Plan For Interior Structure of The EarthmarieNo ratings yet
- Science Gr.10 Module 1Document4 pagesScience Gr.10 Module 1Shmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- SCI10 - Q1 - M1 - Plate Tectonics and Geologic ActivitiesDocument34 pagesSCI10 - Q1 - M1 - Plate Tectonics and Geologic ActivitiesLiam PitchanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 9 Grade 10-Demeter, Nike, Dionysus, Hestia, Poseidon July 29, 2019 I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 9 Grade 10-Demeter, Nike, Dionysus, Hestia, Poseidon July 29, 2019 I. ObjectivesIRISNo ratings yet
- LP Lesson 4 Plate BoundariesDocument10 pagesLP Lesson 4 Plate BoundariesNash VargasNo ratings yet
- Science10 q1 slk7 Possible-Causes-Of-Plate-Movements v1Document12 pagesScience10 q1 slk7 Possible-Causes-Of-Plate-Movements v1Ervis BahintingNo ratings yet
- Mikula Tect Boundary 2 LDocument6 pagesMikula Tect Boundary 2 Lapi-710735237No ratings yet
- Grade 12 - Week 1 (1ST QTR)Document24 pagesGrade 12 - Week 1 (1ST QTR)JochelleNo ratings yet
- EASE Module 12 Inside The Solid EarthDocument42 pagesEASE Module 12 Inside The Solid EarthArianne Alano100% (1)
- Science 10 ModuleDocument21 pagesScience 10 ModuleGregorio Rizaldy100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Maam LadesmaDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Maam LadesmaSalvaña Ruel JamesNo ratings yet
- For Sped - Science ActivityDocument16 pagesFor Sped - Science ActivityMarineilNo ratings yet
- LAS Science-8-MELC 3 Q1 Week 3Document7 pagesLAS Science-8-MELC 3 Q1 Week 3ian barcenaNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Geology; Adapted to the Use of Schools and CollegesFrom EverandThe Elements of Geology; Adapted to the Use of Schools and CollegesNo ratings yet
- G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day5 PabalinasDocument4 pagesG10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day5 PabalinasThanie Abrasaldo NadalNo ratings yet
- G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day4 PabalinasDocument6 pagesG10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day4 PabalinasThanie Abrasaldo NadalNo ratings yet
- G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day3 PabalinasDocument9 pagesG10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day3 PabalinasThanie Abrasaldo NadalNo ratings yet
- G10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day1 PabalinasDocument6 pagesG10 - 1QTR - Week1 - Day1 PabalinasThanie Abrasaldo NadalNo ratings yet
- BASIC II-2nd term-D-DFDocument7 pagesBASIC II-2nd term-D-DFMichael StevenNo ratings yet
- PWS 005311 PDFDocument4 pagesPWS 005311 PDFJoseph TingNo ratings yet
- STHE2Document129 pagesSTHE2Eman Abdel Raouf100% (1)
- (PDF) Chemistry NTSE Stage-1 - CompressDocument7 pages(PDF) Chemistry NTSE Stage-1 - CompressQWERTY111No ratings yet
- Summative Test 1Document3 pagesSummative Test 1Glenda AstodilloNo ratings yet
- Imp MSBRDocument81 pagesImp MSBRGUNNUNo ratings yet
- UP2 - 1.3. Thermal Expansion - pg12-19Document8 pagesUP2 - 1.3. Thermal Expansion - pg12-19Mohammed KamalNo ratings yet
- Shams Dubai Consultants and Contractor ListDocument4 pagesShams Dubai Consultants and Contractor Listknotship.comNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic CellsDocument31 pagesPhotovoltaic Cellssalem BEN MOUSSANo ratings yet
- I. Soil-Water-Plant RelationshipDocument50 pagesI. Soil-Water-Plant RelationshipJose Carlo Dizon0% (1)
- Argumentative EssayDocument6 pagesArgumentative EssayisaenitNo ratings yet
- I S 2099Document38 pagesI S 2099Hariprasad gantyalaNo ratings yet
- Solar Trillions 7 Market and Investment Opportunities in The Emerging Clean-Energy EconomyDocument24 pagesSolar Trillions 7 Market and Investment Opportunities in The Emerging Clean-Energy EconomyRamadan RashadNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS Proving PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS Proving PhotosynthesisMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- MHD Power Generation: Technical Seminar ReportDocument18 pagesMHD Power Generation: Technical Seminar ReportnancusharmaNo ratings yet
- Entrpy and Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesEntrpy and Second Law of ThermodynamicsMarion AlyssaNo ratings yet
- Property Table and ChartsDocument18 pagesProperty Table and ChartsCovyn YongNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document16 pagesCH 3Iratechaos100% (2)
- Heat CapacitiesDocument9 pagesHeat Capacitiesanwar9602020No ratings yet
- 2Nd Prelim Examination Ecology 1 NAME: - MAJOR/SESSION: - SCORE: - No Erasures No Alterations Wrong Spelling Is Wrong Test 1-IdentificationDocument2 pages2Nd Prelim Examination Ecology 1 NAME: - MAJOR/SESSION: - SCORE: - No Erasures No Alterations Wrong Spelling Is Wrong Test 1-Identificationaaron canoyNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharges. Their Mechanism Detection and MeasurementDocument46 pagesPartial Discharges. Their Mechanism Detection and MeasurementHUGO GOMESNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed SystemsDocument300 pagesFluidized Bed SystemshexbiNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Deposition - Thermal and E-Bean EvaporationDocument96 pagesThin Film Deposition - Thermal and E-Bean EvaporationAnurag KumarNo ratings yet
- MEC 4105 Test Marking GuideDocument4 pagesMEC 4105 Test Marking GuideBirimumaso DavidNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation-CYL VERTICAL 1.0mDIA X 1.10m ST HT TankDocument17 pagesDesign Calculation-CYL VERTICAL 1.0mDIA X 1.10m ST HT TankEleazar Mendoza50% (2)
- Quarter 2 Earth Science Module 14 v2Document17 pagesQuarter 2 Earth Science Module 14 v2Jaemee Agnes BoadoNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics of A RocketDocument38 pagesAerodynamics of A RocketMaMLoOoOo7No ratings yet