Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edgcse Aap sb3d Trans Trans
Edgcse Aap sb3d Trans Trans
Uploaded by
Marcus Wright0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views1 pageOriginal Title
edgcse_aap_sb3d_trans_trans
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views1 pageEdgcse Aap sb3d Trans Trans
Edgcse Aap sb3d Trans Trans
Uploaded by
Marcus WrightCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
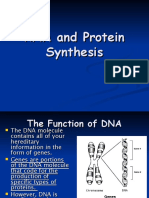
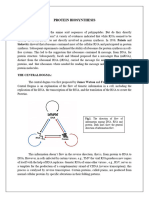
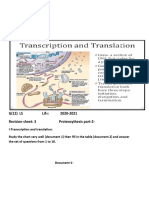
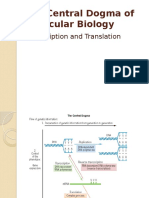
SB3d.
2 Transcription and translation
1 Cut out the cards below.
2 Sort the descriptions into the order in which they occur.
3 Stick the cards onto a piece of paper and add labels to show which parts of the process are transcription
and which are translation.
RNA polymerase links the RNA nucleotides together to form a
strand of mRNA.
A tRNA molecule pairs up with each codon.
In the cytoplasm, a ribosome attaches to the mRNA strand.
Inside the nucleus, RNA polymerase attaches to a non-coding
section of DNA.
RNA polymerase adds complementary RNA nucleotides to the
template strand.
The enzyme separates the two strands of DNA.
The ribosome joins together the amino acids carried by the tRNA
molecules.
The strand of mRNA travels out of the nucleus through a
nuclear pore.
The types and order of amino acids in the chain cause it to fold into
a specific shape.
RNA polymerase continues to move along the DNA to reach the
coding region of a gene.
This results in the formation of a polypeptide.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2016. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 3
You might also like
- Transcription & TranslationDocument8 pagesTranscription & TranslationDr DapperNo ratings yet
- Polypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionDocument3 pagesPolypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionliklyNo ratings yet
- Rna & Protein SynthesisDocument41 pagesRna & Protein SynthesisJoeric CarinanNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis, Brief NoteDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis, Brief NoteosunfisanayomideNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisDocument46 pagesGenetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisdeepakNo ratings yet
- Sandra Loranger Stacie Daer Mike ReillyDocument9 pagesSandra Loranger Stacie Daer Mike ReillyBabasChongNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument44 pagesGene Expressionaymnhssn2020No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis FoldableDocument5 pagesProtein Synthesis FoldableBryanNo ratings yet
- L18 Polypeptide SynthesisDocument18 pagesL18 Polypeptide Synthesisareejhussaini26No ratings yet
- Transcription & TranslationDocument5 pagesTranscription & TranslationJerico NaveraNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??Document33 pagesProtein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??Poy AlisNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Final DNA RNA TrancriptionDocument4 pagesFinal DNA RNA Trancriptiondave del campoNo ratings yet
- RNA Protein SynthesisDocument14 pagesRNA Protein SynthesisLAL BUKHSHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldAndrew BurtsfieldNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument10 pagesProteinsنور خليل صالح سنافيNo ratings yet
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocument26 pages05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet
- Bio AssessmentDocument5 pagesBio Assessmentxx nataliaNo ratings yet
- Harper S Illustrated Biochemistry by Vic-385-403Document19 pagesHarper S Illustrated Biochemistry by Vic-385-403DavidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationDocument14 pagesChapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationAdonias NiyurukundoNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument35 pagesTranscription and TranslationJaneNo ratings yet
- 4.9 Cell Division & Protein SynthesisDocument21 pages4.9 Cell Division & Protein Synthesis2023875802No ratings yet
- Protein Biosynthesis - 070214Document7 pagesProtein Biosynthesis - 070214LakshmipriyaNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument15 pagesTranscriptioncamila hartmannNo ratings yet
- Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument37 pagesTranscription and RNA ProcessingEarl ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument42 pagesDna StructureCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- DNADocument64 pagesDNAsapphireriego01No ratings yet
- Learner's Activity Sheet: Science (Quarter III - Week 4)Document10 pagesLearner's Activity Sheet: Science (Quarter III - Week 4)MARITESS COLLADONo ratings yet
- Topic 15-18 Content ADocument28 pagesTopic 15-18 Content ALeanne Krystel CastroNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: ADA School Biology DepartmentDocument27 pagesProtein Synthesis: ADA School Biology DepartmentAydan BadalliNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication PDFDocument6 pagesDna Replication PDFCarpioNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet 3 GDocument4 pagesRevision Sheet 3 GJoelle AssafNo ratings yet
- 4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - TranscriptionDocument19 pages4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - Transcriptionlilpidas54No ratings yet
- A TRNA Is Made From A Single Strand of RNADocument2 pagesA TRNA Is Made From A Single Strand of RNAbiñan lagunaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis423003157No ratings yet
- 3.10 Protein-SynthesisDocument20 pages3.10 Protein-SynthesisPratika MNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument17 pagesProtein Synthesis Notesapi-655732711100% (1)
- Page No: Prokaryotic Messenger RnaDocument17 pagesPage No: Prokaryotic Messenger Rnasplinterof2005No ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protsin 2020Document48 pagesDna Rna Protsin 2020RaragloriaaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisEverly Joy JingcoNo ratings yet
- Types of RNA'sDocument17 pagesTypes of RNA'sRohit100% (2)
- Protein Synthesis Completed Green PacketDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis Completed Green PacketrltradetrashNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3B - RNA Metabolizing Enzymes and Regulation of TranscriptionDocument3 pagesLesson 3B - RNA Metabolizing Enzymes and Regulation of Transcriptionhannah CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Protein SynthesisMarc Laurence LadoresNo ratings yet
- THE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutDocument6 pagesTHE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutLeah AturoNo ratings yet
- Transcription Study GuideDocument5 pagesTranscription Study GuideSubhajit AdakNo ratings yet
- Studying BiologyDocument62 pagesStudying BiologyNicolas AliasNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocument65 pagesQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- C Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Document14 pagesC Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Daisy Soriano Prestoza100% (1)
- The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationDocument37 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationfangirltonNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionmohammedNo ratings yet
- From Genes To ProteinsDocument32 pagesFrom Genes To ProteinsVanessa QuinolNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesProtein SynthesisRussel OtillaNo ratings yet
- 6.2 D Protein Synthesis: ContosoDocument13 pages6.2 D Protein Synthesis: Contosoruva gundaNo ratings yet
- Chap 17 From Gene To Protein FixDocument30 pagesChap 17 From Gene To Protein FixRizaldi Al FauzanNo ratings yet
- Protein-SynthesisDocument57 pagesProtein-SynthesisMA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- Triple Titration Quiz AnswersDocument1 pageTriple Titration Quiz AnswersMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Triple Titration QuizDocument1 pageTriple Titration QuizMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- T8 Titration CalculationsDocument1 pageT8 Titration CalculationsMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- 3stave 1Document3 pages3stave 1Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- June FoundationDocument30 pagesJune FoundationMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- 7af7cf0c 5378 4452 8097 9fc9707eabcc - Lesson 2 - Measuring WavesDocument12 pages7af7cf0c 5378 4452 8097 9fc9707eabcc - Lesson 2 - Measuring WavesMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Titration - Calculation Answers (2) Core PraticalDocument4 pagesTitration - Calculation Answers (2) Core PraticalMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - AtomsDocument15 pagesLesson 1 - AtomsMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- The Film Studies TIme LineDocument3 pagesThe Film Studies TIme LineMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision KS4Document11 pagesChemistry Revision KS4Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- CompetitionDocument1 pageCompetitionMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- 2016 EdExcel Biology Topic 5 Health Disease and MedicinesDocument39 pages2016 EdExcel Biology Topic 5 Health Disease and MedicinesMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- GenreDocument1 pageGenreMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- .... Lesson 3 - Background RadiationDocument12 pages.... Lesson 3 - Background RadiationMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Physics Energy Radiation and More GcseDocument4 pagesPhysics Energy Radiation and More GcseMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- .Lesson 3 - Background RadiationDocument12 pages.Lesson 3 - Background RadiationMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- RL Lesson 1 Millfield Merry MashDocument1 pageRL Lesson 1 Millfield Merry MashMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Recall Lesson 1Document1 pageYear 10 Recall Lesson 1Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- KS3 Revision 6th July 2020Document25 pagesKS3 Revision 6th July 2020Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Exam Q Theme of Christmas 1Document3 pagesExam Q Theme of Christmas 1Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Page 117Document2 pagesPage 117Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Rivers Revision ClockDocument1 pageRivers Revision ClockMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- 2020 11 19 Year10 MissingAnglesGCSEQuestionsDocument1 page2020 11 19 Year10 MissingAnglesGCSEQuestionsMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- 2020 11 19 Year10 MissingAnglesDocument1 page2020 11 19 Year10 MissingAnglesMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- To A Daughter Leaving Home Guided AnnotationDocument2 pagesTo A Daughter Leaving Home Guided AnnotationMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Page 115Document1 pagePage 115Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Page 129Document1 pagePage 129Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- Page 125Document2 pagesPage 125Marcus WrightNo ratings yet
- 2020-11!23!10B1-Solving Linear Equations Both Sides RAGDocument1 page2020-11!23!10B1-Solving Linear Equations Both Sides RAGMarcus WrightNo ratings yet
- 5 What Constitues Life BeginningDocument23 pages5 What Constitues Life BeginningMarcus WrightNo ratings yet