Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BAND Theory
BAND Theory
Uploaded by
Tangent Chauhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views10 pagesThe document discusses the band theory of solids. It explains that in metals, the atomic orbitals of neighboring atoms overlap to form energy bands separated by forbidden gaps. Metals have a partially filled or overlapping conduction band, resulting in metallic bonding and high electrical conductivity. Semiconductors have a small band gap between the valence and conduction bands, while insulators have a large band gap. The band theory classifies solids as conductors, semiconductors, or insulators based on their band structure and whether electrons can easily move between bands.
Original Description:
Original Title
BAND theory ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the band theory of solids. It explains that in metals, the atomic orbitals of neighboring atoms overlap to form energy bands separated by forbidden gaps. Metals have a partially filled or overlapping conduction band, resulting in metallic bonding and high electrical conductivity. Semiconductors have a small band gap between the valence and conduction bands, while insulators have a large band gap. The band theory classifies solids as conductors, semiconductors, or insulators based on their band structure and whether electrons can easily move between bands.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views10 pagesBAND Theory
BAND Theory
Uploaded by
Tangent ChauhanThe document discusses the band theory of solids. It explains that in metals, the atomic orbitals of neighboring atoms overlap to form energy bands separated by forbidden gaps. Metals have a partially filled or overlapping conduction band, resulting in metallic bonding and high electrical conductivity. Semiconductors have a small band gap between the valence and conduction bands, while insulators have a large band gap. The band theory classifies solids as conductors, semiconductors, or insulators based on their band structure and whether electrons can easily move between bands.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Contents
Introduction Of Metallic bond
Concept of band formation
Types of band
Classification of solids on the
basis of band concept
BAND THEORY OF SOLIDS
This theory explains about metallic bond.
Metallic bond can be defined as the electromagnetic interaction
between delocalized electrons, called conduction electrons and the
metallic nuclei within metals.
Metallic bonding is responsible for many physical properties of metals,
such as strength, malleability, thermal and electrical conductivity,
opacity, and luster.
In solids ,atoms are arranged in a regular closed packed pattern. All the
spherical atoms are influenced by neighbouring atoms and their closeness
results into intermixing of neighbouring electrons
In an isolated atom ,as energy levels are discrete. So when N number of
energy levels of atoms interact with each other, N number of molecular
orbitals are formed with very small energy difference.
It can be understood with the help of taking the example
BAND THEORY OF SOLIDS
When a huge number of atoms are combined to form a solid however,
where discrete energy levels can be considered as discrete ranges of
energy, or energy bands, formation of energy band takes place.
It can be understood as when two atoms are brought close to each
other, it leads to intermixing of electrons in the valence shell.
As a result, the number of permissible energy levels is formed, which
is called an energy band.
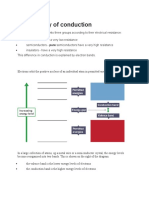
BAND THEORY OF SOLIDS
The highest occupied band (HOMO)is called valence band in which
valence electrons are filled. The valence band is the band made up of
the occupied molecular orbitals and is lower in energy than the so-
called conduction band and are generally fully or partially filled .
The next higher unoccupied band (LUMO) is called conduction band
which is vacant or partially filled. The conduction band is the band of
orbitals that are high in energy and are generally empty.
BAND THEORY OF SOLIDS
The gap between valence and conduction band is called band gap/
forbidden gap/ forbidden zone where no electron can exist .
BAND THEORY OF SOLIDS
On the basis of this band concept, solids can be differentiated into
conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
A solid is a conductor if it has highest occupied band partially filled or
a completely filled overlapping with a completely filled band. There is
no forbidden gap between valence and conduction band in conductors.
e.g. Na, Mg, Be, K etc.
A solid is a semiconductors if there is a very small energy difference
between valence and conduction bands and electrons and can easily jump
by acquiring a small amount of energy. Semiconductors have very small
forbidden gap between valence and conduction bands. e.g Si, Ge etc.
A solid is an insulator if it has filled valence band,empty conduction band
and possessing a large energy gap between valence and conduction band .
All energy bands are completely filled and there exist a large forbidden
zone .e.g. Diamond ,glass etc.
Thank
You
You might also like
- General Chemistry The Essential Concepts 7Th Edition Chang Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesGeneral Chemistry The Essential Concepts 7Th Edition Chang Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDebraPricemkw100% (11)
- ch9 Test-BankDocument85 pagesch9 Test-Bank박훈희No ratings yet
- Energy Band TheoryDocument2 pagesEnergy Band Theoryaownaown68No ratings yet
- Energy Band TheoryDocument2 pagesEnergy Band Theoryaownaown68No ratings yet
- Band Theory in Solid StateDocument4 pagesBand Theory in Solid StatePaulami Bose100% (1)
- Group Four Write UpDocument11 pagesGroup Four Write Upgodspower odiorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Energy Band For EngineersDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Energy Band For EngineersDerbew Gahaw100% (1)
- Lect # 3Document15 pagesLect # 3Rameen WaseemNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of SolidsDocument26 pagesBand Theory of SolidsDizney Lobaton EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Band TheoryDocument19 pagesBand TheoryTwishaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Solids Interms of Forbidden Energy GapDocument29 pagesClassification of Solids Interms of Forbidden Energy GapAnik ManojNo ratings yet
- Energy Band in Solids: Fig 2: Valence Band and Conduction BandDocument5 pagesEnergy Band in Solids: Fig 2: Valence Band and Conduction BandPrashant BhandariNo ratings yet
- Band GapDocument13 pagesBand Gapit rewaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project: Semiconductors and Band TheoryDocument23 pagesPhysics Project: Semiconductors and Band TheoryAkbar HashmiNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of ConductionDocument4 pagesBand Theory of ConductionRushita LingiahNo ratings yet
- Module - Iv Semiconductor PhysicsDocument22 pagesModule - Iv Semiconductor PhysicsAyushNo ratings yet
- EdcDocument33 pagesEdcVikramNo ratings yet
- Introductory ElectronicsDocument25 pagesIntroductory ElectronicsDahamani bukari Al-fayeedNo ratings yet
- Solid State PhysicsDocument17 pagesSolid State PhysicsMariam AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Nano Electronics ROLL NO 15800321052Document12 pagesNano Electronics ROLL NO 15800321052Biswajit LoharNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument198 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsRamyasri100% (2)
- Electronic Engineering 2Document82 pagesElectronic Engineering 2ShafiNo ratings yet
- Electrical PropertiesDocument33 pagesElectrical PropertiesNicole Anne BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of SolidsDocument18 pagesBand Theory of SolidsSachi SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument114 pagesBasic ElectronicsfawNo ratings yet
- Electrical PropertiesDocument50 pagesElectrical PropertiesLouise UmaliNo ratings yet
- Quantum Confinement in NanoparticlesDocument35 pagesQuantum Confinement in NanoparticlesPunit Yadav YadavNo ratings yet
- Electronic Band StructureDocument17 pagesElectronic Band StructurepoomagalNo ratings yet
- r19 Edc Notes - All UnitsDocument165 pagesr19 Edc Notes - All Unitsbaburao_kodavatiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties-II: Energy Band Structures in SolidsDocument6 pagesElectrical Properties-II: Energy Band Structures in SolidsHritik LalNo ratings yet
- EEC 112 TheoryDocument54 pagesEEC 112 Theorysamson ochaglaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple CircuitsDocument33 pagesSemiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple CircuitsJanardan MuniNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple CircuitsDocument58 pagesSemiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple CircuitsKaushik KumarNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of SolidsDocument5 pagesBand Theory of SolidsUsama HafeezNo ratings yet
- Electronic Band StructureDocument11 pagesElectronic Band StructureinfistudeeeeNo ratings yet
- Semi ConductorsDocument14 pagesSemi Conductorsppj25945No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics NotesDocument114 pagesBasic Electronics NotessmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?lianghoo94No ratings yet
- Band Theory of ConductorsDocument29 pagesBand Theory of ConductorsSivakumar PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicDocument12 pagesBasic Electronicglobal kind resortNo ratings yet
- BONDING IN METALS BY K.N.S.SWAMI..pptx477Document33 pagesBONDING IN METALS BY K.N.S.SWAMI..pptx477Suman KusumNo ratings yet
- Protons,: Electrons Distributed in Different Orbits (Shells)Document17 pagesProtons,: Electrons Distributed in Different Orbits (Shells)Mati Sahab BhattiNo ratings yet
- The Bohr Model of The Atom: A Brief DescriptionDocument45 pagesThe Bohr Model of The Atom: A Brief Descriptiondineshk3No ratings yet
- Class Lecture Atomic Model Conductor SemiconductorDocument8 pagesClass Lecture Atomic Model Conductor SemiconductorRajaul Morshad SaikotNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Molecular Structure and Theories of BondingDocument13 pagesUnit - I: Molecular Structure and Theories of BondingAthirath VeldandaNo ratings yet
- ConductorDocument1 pageConductorzafar_iqbal_36No ratings yet
- Introduction and Intrinsic SemiconductorsDocument16 pagesIntroduction and Intrinsic Semiconductorsdarex22ssdNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Solar EnergyDocument18 pagesWeek 3 Solar EnergyAleydaNo ratings yet
- Conductors & Insulators-1Document35 pagesConductors & Insulators-1mariam.ahmed03No ratings yet
- Material DifferencesDocument9 pagesMaterial Differencesawanhaseeb1122No ratings yet
- Band Theory GanDocument29 pagesBand Theory GanRussell TempleNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor ElectronicsDocument46 pagesSemiconductor Electronicspraveen2910No ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument7 pagesDirect and IndirectsushmaNo ratings yet
- NCERT SemiconductorNCERT Class 12 Physics Part 2Document91 pagesNCERT SemiconductorNCERT Class 12 Physics Part 2Ranjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Lewis Dot Carbon Hydrogen OxygenDocument17 pagesChemical Bonding: Lewis Dot Carbon Hydrogen OxygenSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory MatterDocument3 pagesAtomic Theory MatterIan MutugiNo ratings yet
- What is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionFrom EverandWhat is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionNo ratings yet
- 05 Phase RuleDocument15 pages05 Phase RuleTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Liquid CrystalDocument16 pagesLiquid CrystalTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 02 ElectrochemistryDocument14 pages02 ElectrochemistryTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ponit DefectsDocument6 pagesPonit DefectsTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 03 - Introduction of Corrosion and Electrochemical TheoryDocument13 pages03 - Introduction of Corrosion and Electrochemical TheoryTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Elecctronics Unit 1Document17 pagesElecctronics Unit 1Tangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Part 1 - Communication EnggDocument18 pagesUnit 5 Part 1 - Communication EnggTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cathode - Ray - Oscilloscop First Year 1Document7 pagesCathode - Ray - Oscilloscop First Year 1Tangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Communication System Unit VDocument8 pagesCommunication System Unit VTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Two Terminal Special Purpose Devices First YearDocument6 pagesTwo Terminal Special Purpose Devices First YearTangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- NMR-1 BasicDocument52 pagesNMR-1 Basicamit086No ratings yet
- Fundamental PrinciplesDocument31 pagesFundamental PrinciplesKassimNo ratings yet
- ESR and NMRDocument20 pagesESR and NMRUmang SoniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ch#6 MCQ Ist YearDocument2 pagesChemistry ch#6 MCQ Ist YearMohammad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Auger Electron Spectroscopy - 97-2003Document5 pagesAuger Electron Spectroscopy - 97-2003Kannan BaskarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PGopherDocument3 pagesIntroduction To PGopherxiaoyuzhouingermanyNo ratings yet
- UV-VIS Spektrum-1Document14 pagesUV-VIS Spektrum-1HendySuwandiNo ratings yet
- Spin Echo v3Document16 pagesSpin Echo v3purplefokNo ratings yet
- Modelo VSEPR PDFDocument11 pagesModelo VSEPR PDFArgenis Serafin ValerioNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Molecules 2019 2nd Yr Michaelmas TermDocument71 pagesBonding in Molecules 2019 2nd Yr Michaelmas Termtresa.george27No ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure-2022-23Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure-2022-23Malolan SriramNo ratings yet
- NMR - History - VarianDocument20 pagesNMR - History - VarianlauracmorrisNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument175 pagesThesisSanam Sri RanjanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal Metal ComplexesDocument9 pagesMagnetic Properties of Transition Metal Metal ComplexestharanginiNo ratings yet
- Electron Micros CoupDocument23 pagesElectron Micros Coupeli4741No ratings yet
- Valence Bond Theory - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument2 pagesValence Bond Theory - Chemistry LibreTextsguddanNo ratings yet
- Omni-Vhs - Used at BallmillDocument5 pagesOmni-Vhs - Used at BallmillRakesh Karan SinghNo ratings yet
- Origins of Atomic SpectraDocument2 pagesOrigins of Atomic SpectraSean CollinsNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Matter Class DiscussionDocument6 pagesMagnetism and Matter Class DiscussionNajilaNo ratings yet
- 382 Ch. 7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: RNQ (A) CosDocument1 page382 Ch. 7 Itinerant Electron Magnetism: RNQ (A) CosKetanNo ratings yet
- Coupled Ferroelectric Polarization and Magnetization in Spinel FeCr2S4Document9 pagesCoupled Ferroelectric Polarization and Magnetization in Spinel FeCr2S4Carlos SouzaNo ratings yet
- C-13 NMR and DEPTDocument41 pagesC-13 NMR and DEPTV G Viju Kumar100% (1)
- Textbook Interaction Induced Electric Properties of Van Der Waals Complexes 1St Edition Victor N Cherepanov Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Interaction Induced Electric Properties of Van Der Waals Complexes 1St Edition Victor N Cherepanov Ebook All Chapter PDFkeith.boggan743100% (11)
- Worksheet13 VSEPR KeyDocument4 pagesWorksheet13 VSEPR KeyBrent DawnNo ratings yet
- CHM3105 Short PaperDocument4 pagesCHM3105 Short PaperTrimal AccraNo ratings yet
- Lec 05 (Atomic Structure V)Document3 pagesLec 05 (Atomic Structure V)Md Abdus SaburNo ratings yet
- Week 2 L1 Electronic StatesDocument16 pagesWeek 2 L1 Electronic StatesFalak NazNo ratings yet
- Paramagnetism and Conduction ElectronsDocument3 pagesParamagnetism and Conduction Electronsjose miranda100% (1)