Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Example Health Risk Assessment
Example Health Risk Assessment
Uploaded by
Ali Al BarwaniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Road Marking WorksDocument5 pagesRoad Marking Workstariq1987100% (2)
- Jsa ExcavatorDocument1 pageJsa Excavatorbladeliger2250% (2)
- JHA HousekeepingDocument3 pagesJHA HousekeepingFatin ZawawiNo ratings yet
- The Florence Academy of Art Student HandbookDocument40 pagesThe Florence Academy of Art Student HandbookUlises OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Excavation Job Safety AnalysisDocument1 pageExcavation Job Safety AnalysisVishal Upadhyay100% (3)
- Fall Protection Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesFall Protection Risk Assessmentsimone0% (1)
- JHA Manual HandlingDocument5 pagesJHA Manual HandlingFatin Zulkifli100% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis Sheet: Operation Concrete Batching PlantDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis Sheet: Operation Concrete Batching Plantzabiulla100% (7)
- Risk Assessment For Confined Space Activities (Thrust Boring)Document4 pagesRisk Assessment For Confined Space Activities (Thrust Boring)Melwin Paul100% (1)
- Rig Up Rig DownDocument4 pagesRig Up Rig DownIng IngNo ratings yet
- 5.19 JSP Electrical Power InstallationDocument4 pages5.19 JSP Electrical Power InstallationDarius Dsouza100% (1)
- JSA-049 Valves & Support Installation and DismantlingDocument4 pagesJSA-049 Valves & Support Installation and DismantlingMoaatazz Nouisri75% (4)
- Job HazardDocument2 pagesJob HazardBre WirabumiNo ratings yet
- Selenium Interview Questions - CognizantDocument20 pagesSelenium Interview Questions - CognizantJessie SokhiNo ratings yet
- f1 in School Project MGMTDocument13 pagesf1 in School Project MGMTFaizal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- JHA MaintenanceDocument9 pagesJHA Maintenancejherson gravidesNo ratings yet
- JHSA For Temporary Plastic Septic TankDocument4 pagesJHSA For Temporary Plastic Septic TankAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- Fall Protection Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesFall Protection Risk AssessmentsimoneNo ratings yet
- 17-Using Portable Power ToolsDocument2 pages17-Using Portable Power Toolshsse.maltaNo ratings yet
- Cleaning: Risk Assessment For: Establishment: Assessment By: DateDocument4 pagesCleaning: Risk Assessment For: Establishment: Assessment By: DateEzzati AzizNo ratings yet
- 1 - R.A. - 004 - ShutteringDocument4 pages1 - R.A. - 004 - ShutteringmahmoudabidaliNo ratings yet
- 1 - R.A. - 005 - De-ShutteringDocument4 pages1 - R.A. - 005 - De-ShutteringmahmoudabidaliNo ratings yet
- 5.19 JSP ScaffoldDocument4 pages5.19 JSP Scaffoldpoorm879No ratings yet
- Cleaning Site (Hirac)Document4 pagesCleaning Site (Hirac)jovyNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Jsa Cable TerminationDocument4 pagesDokumen - Tips - Jsa Cable Terminationshaibaz chafekarNo ratings yet
- Iso 45001 Corrective Action ProgramDocument3 pagesIso 45001 Corrective Action Programsaif KhanNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis: (Risk Assessment)Document9 pagesJob Safety Analysis: (Risk Assessment)MarhendraNo ratings yet
- JHA (85T Crawler Crane & Drill Rig Machine Assembling and Inspection)Document2 pagesJHA (85T Crawler Crane & Drill Rig Machine Assembling and Inspection)Armando AballeNo ratings yet
- Fall PreventionsDocument16 pagesFall PreventionsRajesh gp100% (1)
- 3.gypsum CeilingDocument5 pages3.gypsum Ceilingmohammed sohailNo ratings yet
- JHA Welding Pipe BenderDocument2 pagesJHA Welding Pipe Bendermohammad arshadNo ratings yet
- JHA RA FormatDocument5 pagesJHA RA Formatmadellekylenetabinas01No ratings yet
- HIRARC Effluent Plant CleaningDocument3 pagesHIRARC Effluent Plant CleaningFAHIMNo ratings yet
- RA Personal Fall Arrest Fall Restraint Equipment 0007 July 2017Document3 pagesRA Personal Fall Arrest Fall Restraint Equipment 0007 July 2017um erNo ratings yet
- JSA 03 Gate Entrance Traffic ProposalDocument10 pagesJSA 03 Gate Entrance Traffic Proposalrahul tkNo ratings yet
- Apds-Ra-011 Filtration Operation of Apds Filtration System Rev BDocument4 pagesApds-Ra-011 Filtration Operation of Apds Filtration System Rev BHua Tien DungNo ratings yet
- Behavior-Based Safety Observation Checklist - SafetyCultureDocument5 pagesBehavior-Based Safety Observation Checklist - SafetyCultureconstantinop.gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Jsa Installing BracketDocument3 pagesJsa Installing BracketHow Chin Engineering Sdn Bhd100% (1)
- RA of Grass Cutting by Strimmer Brushcutter & Removing Weeds MannualyDocument1 pageRA of Grass Cutting by Strimmer Brushcutter & Removing Weeds MannualySaifulNo ratings yet
- Travelling of CraneDocument3 pagesTravelling of CraneDelta akathehuskyNo ratings yet
- JSA-054 Crossing WorksDocument6 pagesJSA-054 Crossing WorksMajdiSahnounNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For HallDocument8 pagesRisk Assessment For Hallapi-346994220No ratings yet
- AHA Painting WorkDocument3 pagesAHA Painting Workanilkumaranoop74No ratings yet
- Fall Protection and Ladder SafetyDocument17 pagesFall Protection and Ladder SafetyCharlamagne MirandaNo ratings yet
- JSA Mobile CranesDocument2 pagesJSA Mobile CranesAmanya DickallansNo ratings yet
- Hot Work Gift Gift / Near Gis SEPCOO III Early Comb: Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) WorksheetDocument4 pagesHot Work Gift Gift / Near Gis SEPCOO III Early Comb: Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) Worksheet王志伟No ratings yet
- JSA 173 - CRT RIG UP - Updated 21.10.2019Document11 pagesJSA 173 - CRT RIG UP - Updated 21.10.2019tafhim rashidNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Concreate and CivilworksDocument7 pagesJsa For Concreate and CivilworksAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Risk Assessment - Finishing WorksDocument10 pages5 - Risk Assessment - Finishing Worksmahmoud nadaNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument7 pagesRisk AssessmentMajaga MabhenaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For HallDocument8 pagesRisk Assessment For Hallapi-344537129No ratings yet
- Slasher Tractor MountedDocument4 pagesSlasher Tractor Mountedanon-246285No ratings yet
- JHSA Water Supply and Sewer InstallationDocument4 pagesJHSA Water Supply and Sewer InstallationAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- JSA TubularDocument4 pagesJSA TubularRahul M.RNo ratings yet
- Plant Hazard ReportDocument4 pagesPlant Hazard ReportNader DallejNo ratings yet
- BeltsanderriskmgtformDocument11 pagesBeltsanderriskmgtform185428No ratings yet
- Jsa Civil Work (00000002)Document6 pagesJsa Civil Work (00000002)Ali AlahmaNo ratings yet
- TTEC Fencing RADocument7 pagesTTEC Fencing RAGeml TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) Worksheet: Jerp # 3, Aromatics Unit CompanyDocument9 pagesJob Hazard Analysis (JHA) Worksheet: Jerp # 3, Aromatics Unit CompanyTeodoro Esquillo100% (1)
- Jsa Cable TerminationDocument4 pagesJsa Cable Terminationshaibaz chafekarNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For .Testing and Commissioning of Fire DamperDocument9 pagesRisk Assessment For .Testing and Commissioning of Fire Damperarun kurlanNo ratings yet
- S07 Tank Project - JSA - Erection of Scaffolding 2nd LevelDocument6 pagesS07 Tank Project - JSA - Erection of Scaffolding 2nd LevelKrishVy KumærNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - PTWDocument1 pageCourse Outline - PTWAli Al BarwaniNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health RisksDocument31 pagesOccupational Health RisksAli Al BarwaniNo ratings yet
- SP 1157Document88 pagesSP 1157Allocation ResourceNo ratings yet
- HSE Apprenticeship FrameworkDocument4 pagesHSE Apprenticeship FrameworkAli Al BarwaniNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Mission Theology, History, Perspectives Müller, KarlDocument552 pagesDictionary of Mission Theology, History, Perspectives Müller, KarlRev. Johana VangchhiaNo ratings yet
- Coast Artillery Journal - Oct 1946Document84 pagesCoast Artillery Journal - Oct 1946CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy-Large FontDocument35 pagesPharmacognosy-Large FontArantxa HilarioNo ratings yet
- Marked Fake Deck Tricks3Document7 pagesMarked Fake Deck Tricks3Tito Banerjee100% (1)
- The Bishop ScoreDocument3 pagesThe Bishop ScoreJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- The Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai, India: in Service For SightDocument4 pagesThe Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai, India: in Service For Sighttirth viraNo ratings yet
- Utpaladeva's Lost Vivrti On The Ishwara Pratyabhijna Karika - Raffaele TorellaDocument12 pagesUtpaladeva's Lost Vivrti On The Ishwara Pratyabhijna Karika - Raffaele Torellaraffaeletorella100% (1)
- 02TP PrelimExam MITDocument2 pages02TP PrelimExam MITSnapShop by AJNo ratings yet
- Av 10 Universal Remote Control ManualDocument13 pagesAv 10 Universal Remote Control Manualovidiu200970% (10)
- 3987 SDS (GHS) - I-ChemDocument4 pages3987 SDS (GHS) - I-ChemAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- The Migration Industry and Future Directions For Migration PolicyDocument4 pagesThe Migration Industry and Future Directions For Migration PolicyGabriella VillaçaNo ratings yet
- PDF Sermon Notes - The Temptation of Christ (Luke 4.1-13)Document5 pagesPDF Sermon Notes - The Temptation of Christ (Luke 4.1-13)fergie45315No ratings yet
- Pipe Pressure Drope ASEREHDocument3 pagesPipe Pressure Drope ASEREHSenghou MeasNo ratings yet
- XC9572 PDFDocument9 pagesXC9572 PDFAvs ElectronNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 24 Practice QuestionsArlene F. Montalbo100% (1)
- NIDAR, Franced Haggai G. The Brain Is The Vehicle of The MindDocument1 pageNIDAR, Franced Haggai G. The Brain Is The Vehicle of The MindHaggai NidarNo ratings yet
- A 201Document1 pageA 201AnuranjanNo ratings yet
- 2intro To LLMDDocument2 pages2intro To LLMDKristal ManriqueNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Course Test (Word)Document4 pagesEnd-Of-Course Test (Word)los ikandasNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Ucv SedapalDocument2 pagesCurriculum Ucv SedapalSheyler Alvarado SanchezNo ratings yet
- UN - HIV and Prison - Policy BriefDocument12 pagesUN - HIV and Prison - Policy BriefParomita2013No ratings yet
- NO Memo No. 21 S. 2018 Adherence To Training Policy PDFDocument10 pagesNO Memo No. 21 S. 2018 Adherence To Training Policy PDFKemberly Semaña PentonNo ratings yet
- Recruitment & Selection Reliance Jio Full Report - 100 Page MANU SHARMA MBA 3rd SEMDocument102 pagesRecruitment & Selection Reliance Jio Full Report - 100 Page MANU SHARMA MBA 3rd SEMImpression Graphics100% (4)
- Price Bubble Indicators by LindtDocument17 pagesPrice Bubble Indicators by LindtOlmedo FarfanNo ratings yet
- Mock Trial Task CardsDocument8 pagesMock Trial Task CardsVitaliy Fedchenko0% (1)
- Swathi Final Project AnilDocument100 pagesSwathi Final Project AnilHussainNo ratings yet
- Clear Codes List-NokiaDocument8 pagesClear Codes List-NokiaocuavasNo ratings yet
Example Health Risk Assessment
Example Health Risk Assessment
Uploaded by
Ali Al BarwaniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Example Health Risk Assessment
Example Health Risk Assessment
Uploaded by
Ali Al BarwaniCopyright:
Available Formats
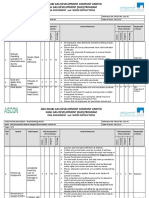
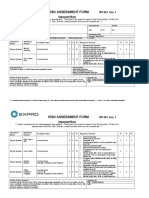
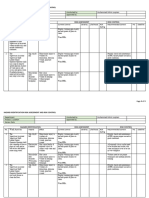
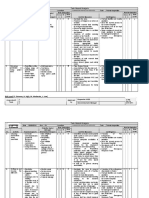
Example of an Occupational Health Risk Assessment
ASSESSMENT EQUIPMENT/ ASSESSED
SITE: Sorting Floor – Manual Sorting
DATE: AREA/TASK: BY:
RISK
WHEN
DONE
WHO
TASK/ PERSONS RATING
HAZARD EXISITING CONTROL MEASURES FURTHER ACTION REQUIRED
EQUIPMENT AT RISK S L R
R
See Page 2 for explanation of risk assessment, activity / area of assessment, hazard, risk, control measures, severity, likelihood, and rating.
Sorting floor – Cuts/lacerations to Sorting Trained operatives 1 3 3
manual sorting hand – sharp operatives Health & safety induction for all
objects/tins/needles operatives
/glass present in Appropriate equipment in place for
material to be removing sharps including receptacle
sorted for safe storage
Appropriate protective gloves for all
sorters
Pause facility on sorting belt to stop belt
whilst removing sharps
First aiders on site
Emergency stop facility at all picking
stations
Material quality inspection and sampling
procedures in place
Sharps procedure in place
Cuts/lacerations to Sorting Trained operatives 1 3 3
forearms – sharp operatives Health & safety induction for all
objects/tins/needles operatives
/glass present in Appropriate equipment in place for
material to be removing sharps including receptacle
sorted for safe storage
Appropriate protective gloves for all
sorters
Protective arm gauntlets in pre-sort
cabin
Pause facility on sorting belt to stop belt
whilst removing sharps
First aiders on site
Emergency stop facility at all picking
stations
Material quality inspection and sampling
Example Risk Assessment Form Page 1 of 5
Example of an Occupational Health Risk Assessment
procedures in place
Sharps procedure in place
Upper limb Sorting Trained operatives in manual handling 1 3 3
disorders – leaning operatives risks and techniques
forward over Health & safety induction for all
conveyor belt, operatives
outstretched reach, Platforms where required for shorter
highly repetitious operators
No excessive shift lengths and regular
breaks for all sorters.
Operators forced to change position on
belt at regular intervals so not twisting in
the same direction for long periods
Lower limb Sorting Trained operatives in manual handling 1 2 2
disorders – operatives risks and techniques
standing in the Health & safety induction for all
same place for long operatives
periods of time No excessive shift lengths and regular
breaks for all sorters.
Operators forced to change position on
belt at regular intervals so not twisting in
the same direction for long periods
Noise Sorting Trained operatives 1 2 2
operatives Health & safety induction for all
operatives
Enclosed cabins
Ear defenders available and
compulsory to wear in noise protection
areas.
Ear defenders available but optional in
other work areas
Periodic noise monitoring
Microbiological Sorting Trained operatives 2 1 2
hazards – dust, operatives Health & safety induction for all
weils disease, operatives
inhaling Appropriate equipment in place for
bioaerosols, handling contamination including
contamination in removing from belt, receptacle for safe
material presented storage and cleaning up liquid spills
Appropriate protective gloves for all
sorters
Example Risk Assessment Form Page 2 of 5
Example of an Occupational Health Risk Assessment
Dust masks and eye protection
compulsory for all sorters
Enclosed cabins
Air conditioned
Personal hygiene facilities provided and
good personal hygiene encouraged
Material quality inspection and sampling
procedures in place
First aiders on site
Automatic bag breaker
Handling of offensive and hygiene
waste procedure
Chemical hazards Sorting Trained operatives 2 1 2
– chemical operatives Health & safety induction for all
contamination in operatives
material presented Appropriate equipment in place for
handling contamination including
removing from belt, receptacle for safe
storage and cleaning up liquid spills
Appropriate protective gloves for all
sorters
Dust masks and eye protection
compulsory for all sorters
Personal hygiene facilities provided and
good personal hygiene encouraged
Material quality inspection and sampling
procedures in place
First aiders on site
Automatic bag breaker
Handling of offensive and hygiene
waste procedure
Pinching/ Sorting Trained operatives 2 1 2
entrapment in operatives Health & safety induction for all
conveyor operatives
Conveyor designed to ensure risk is
very low
Preventative maintenance on all belts
and regular inspections for damage and
wear
Example Risk Assessment Form Page 3 of 5
Example of an Occupational Health Risk Assessment
Insects and vermin Sorting Trained operatives 1 2 2
bites operatives Health & safety induction for all
operatives
Personal hygiene facilities provided and
good personal hygiene encouraged
Material quality inspection and sampling
procedures in place
First aiders on site
Slips, trips & falls Sorting Trained operatives 1 2 2
operatives Health & safety induction for all
operatives
Equipment in place to clean up
spillages
Suitable non-slip flooring
Safety boots worn by all operatives
All work areas and floor surfaces
maintained and inspected regularly for
damage or wear
Housekeeping programme developed
Stress and violence Sorting Trained operatives 2 1 2
operatives Health & safety induction for all
operatives
Communication encouraged
Workloads monitored
No excessive shift lengths and regular
breaks for all sorters.
Certain equipment Sorting No employees allowed to work in MRF 3 1 3
including industrial operatives when fitted with a pacemaker
magnets and eddy
current separators
fitted to sorting
equipment can emit
a powerful
magnetic field
when energised.
This can have an
effect on
pacemakers.
Example Risk Assessment Form Page 4 of 5
Example of an Occupational Health Risk Assessment
A risk assessment is simply a careful examination of what, in your work, could cause harm to people, so that you can weigh up whether you have taken enough
precautions or should do more to prevent harm. Workers and others have a right to be protected from harm caused by a failure to take reasonable control measures.
A register of Risk Assessments will be maintained and planned reviews undertaken as and when required.
Definitions
• Task/Equipment - is the type of work being carried out in the workplace. e.g. using a power saw.
• Hazard - is the potential to cause harm. e.g. an electric shock from using electrical equipment.
• Persons At Risk – the people who are involved in the task or who could be affected by the task.
• Existing Control Measures - are the actions taken to prevent harm (e.g. an electric shock) as a result of using electrical equipment - such as regular visual
inspections to ensure there is no damage to the cable or the plug, making sure the cable is gripped correctly, making sure the right fuse is fitted, making sure
sockets are not overloaded, arranging for an annual check by a ‘competent’ person (i.e. a qualified electrician) etc. Control Measures include such areas as
training, supervision, instruction, information, safe systems of work, proper maintenance procedures, as well as physical measures such as guard rails (to
prevent falls), barriers (to prevent access to hazardous areas), guarding of machinery and PPE.
• Risk - is the likelihood that harm will occur, after the control measures have been carried out.
• Severity - rated as follows: - MINOR Cuts/grazes/bumps – any incident that does not result in an LTA = RATING 1
- SERIOUS Any incident that would result in an LTA = RATING 2
- MAJOR Death, loss of limbs or sight. Fractures excluding fingers and toes = RATING 3
• Likelihood - rated as follows: - LOW Unlikely under normal working conditions = RATING 1
- MEDIUM Possible under specific circumstances = RATING 2
- HIGH Possible under normal working conditions = RATING 3
• Risk Rating - is a means of measuring the risk by multiplying the severity rating by the likelihood rating e.g. a severity rating ‘ SERIOUS’ with a likelihood rating
‘MEDIUM’ would give a risk rating of 2 x 2 which gives a score of 4.
• Further Action Required - Risk rated from 1- 3 may be considered acceptable (still give consideration to other risk reduction measures)
from 4 - 5 requires action as soon as possible.
from 6- 9 unacceptable risk and immediate action required.
For risks rated 4 to 9 further control measures need to be implemented and action plans arranged.
• Who / When / Done – A responsible person must be assigned responsibility for arranging the actions with a target completion date and the actual completion
date noted in the DONE column.
Example Risk Assessment Form Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- Road Marking WorksDocument5 pagesRoad Marking Workstariq1987100% (2)
- Jsa ExcavatorDocument1 pageJsa Excavatorbladeliger2250% (2)
- JHA HousekeepingDocument3 pagesJHA HousekeepingFatin ZawawiNo ratings yet
- The Florence Academy of Art Student HandbookDocument40 pagesThe Florence Academy of Art Student HandbookUlises OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Excavation Job Safety AnalysisDocument1 pageExcavation Job Safety AnalysisVishal Upadhyay100% (3)
- Fall Protection Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesFall Protection Risk Assessmentsimone0% (1)
- JHA Manual HandlingDocument5 pagesJHA Manual HandlingFatin Zulkifli100% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis Sheet: Operation Concrete Batching PlantDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis Sheet: Operation Concrete Batching Plantzabiulla100% (7)
- Risk Assessment For Confined Space Activities (Thrust Boring)Document4 pagesRisk Assessment For Confined Space Activities (Thrust Boring)Melwin Paul100% (1)
- Rig Up Rig DownDocument4 pagesRig Up Rig DownIng IngNo ratings yet
- 5.19 JSP Electrical Power InstallationDocument4 pages5.19 JSP Electrical Power InstallationDarius Dsouza100% (1)
- JSA-049 Valves & Support Installation and DismantlingDocument4 pagesJSA-049 Valves & Support Installation and DismantlingMoaatazz Nouisri75% (4)
- Job HazardDocument2 pagesJob HazardBre WirabumiNo ratings yet
- Selenium Interview Questions - CognizantDocument20 pagesSelenium Interview Questions - CognizantJessie SokhiNo ratings yet
- f1 in School Project MGMTDocument13 pagesf1 in School Project MGMTFaizal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- JHA MaintenanceDocument9 pagesJHA Maintenancejherson gravidesNo ratings yet
- JHSA For Temporary Plastic Septic TankDocument4 pagesJHSA For Temporary Plastic Septic TankAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- Fall Protection Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesFall Protection Risk AssessmentsimoneNo ratings yet
- 17-Using Portable Power ToolsDocument2 pages17-Using Portable Power Toolshsse.maltaNo ratings yet
- Cleaning: Risk Assessment For: Establishment: Assessment By: DateDocument4 pagesCleaning: Risk Assessment For: Establishment: Assessment By: DateEzzati AzizNo ratings yet
- 1 - R.A. - 004 - ShutteringDocument4 pages1 - R.A. - 004 - ShutteringmahmoudabidaliNo ratings yet
- 1 - R.A. - 005 - De-ShutteringDocument4 pages1 - R.A. - 005 - De-ShutteringmahmoudabidaliNo ratings yet
- 5.19 JSP ScaffoldDocument4 pages5.19 JSP Scaffoldpoorm879No ratings yet
- Cleaning Site (Hirac)Document4 pagesCleaning Site (Hirac)jovyNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Jsa Cable TerminationDocument4 pagesDokumen - Tips - Jsa Cable Terminationshaibaz chafekarNo ratings yet
- Iso 45001 Corrective Action ProgramDocument3 pagesIso 45001 Corrective Action Programsaif KhanNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis: (Risk Assessment)Document9 pagesJob Safety Analysis: (Risk Assessment)MarhendraNo ratings yet
- JHA (85T Crawler Crane & Drill Rig Machine Assembling and Inspection)Document2 pagesJHA (85T Crawler Crane & Drill Rig Machine Assembling and Inspection)Armando AballeNo ratings yet
- Fall PreventionsDocument16 pagesFall PreventionsRajesh gp100% (1)
- 3.gypsum CeilingDocument5 pages3.gypsum Ceilingmohammed sohailNo ratings yet
- JHA Welding Pipe BenderDocument2 pagesJHA Welding Pipe Bendermohammad arshadNo ratings yet
- JHA RA FormatDocument5 pagesJHA RA Formatmadellekylenetabinas01No ratings yet
- HIRARC Effluent Plant CleaningDocument3 pagesHIRARC Effluent Plant CleaningFAHIMNo ratings yet
- RA Personal Fall Arrest Fall Restraint Equipment 0007 July 2017Document3 pagesRA Personal Fall Arrest Fall Restraint Equipment 0007 July 2017um erNo ratings yet
- JSA 03 Gate Entrance Traffic ProposalDocument10 pagesJSA 03 Gate Entrance Traffic Proposalrahul tkNo ratings yet
- Apds-Ra-011 Filtration Operation of Apds Filtration System Rev BDocument4 pagesApds-Ra-011 Filtration Operation of Apds Filtration System Rev BHua Tien DungNo ratings yet
- Behavior-Based Safety Observation Checklist - SafetyCultureDocument5 pagesBehavior-Based Safety Observation Checklist - SafetyCultureconstantinop.gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Jsa Installing BracketDocument3 pagesJsa Installing BracketHow Chin Engineering Sdn Bhd100% (1)
- RA of Grass Cutting by Strimmer Brushcutter & Removing Weeds MannualyDocument1 pageRA of Grass Cutting by Strimmer Brushcutter & Removing Weeds MannualySaifulNo ratings yet
- Travelling of CraneDocument3 pagesTravelling of CraneDelta akathehuskyNo ratings yet
- JSA-054 Crossing WorksDocument6 pagesJSA-054 Crossing WorksMajdiSahnounNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For HallDocument8 pagesRisk Assessment For Hallapi-346994220No ratings yet
- AHA Painting WorkDocument3 pagesAHA Painting Workanilkumaranoop74No ratings yet
- Fall Protection and Ladder SafetyDocument17 pagesFall Protection and Ladder SafetyCharlamagne MirandaNo ratings yet
- JSA Mobile CranesDocument2 pagesJSA Mobile CranesAmanya DickallansNo ratings yet
- Hot Work Gift Gift / Near Gis SEPCOO III Early Comb: Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) WorksheetDocument4 pagesHot Work Gift Gift / Near Gis SEPCOO III Early Comb: Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) Worksheet王志伟No ratings yet
- JSA 173 - CRT RIG UP - Updated 21.10.2019Document11 pagesJSA 173 - CRT RIG UP - Updated 21.10.2019tafhim rashidNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Concreate and CivilworksDocument7 pagesJsa For Concreate and CivilworksAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Risk Assessment - Finishing WorksDocument10 pages5 - Risk Assessment - Finishing Worksmahmoud nadaNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument7 pagesRisk AssessmentMajaga MabhenaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For HallDocument8 pagesRisk Assessment For Hallapi-344537129No ratings yet
- Slasher Tractor MountedDocument4 pagesSlasher Tractor Mountedanon-246285No ratings yet
- JHSA Water Supply and Sewer InstallationDocument4 pagesJHSA Water Supply and Sewer InstallationAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- JSA TubularDocument4 pagesJSA TubularRahul M.RNo ratings yet
- Plant Hazard ReportDocument4 pagesPlant Hazard ReportNader DallejNo ratings yet
- BeltsanderriskmgtformDocument11 pagesBeltsanderriskmgtform185428No ratings yet
- Jsa Civil Work (00000002)Document6 pagesJsa Civil Work (00000002)Ali AlahmaNo ratings yet
- TTEC Fencing RADocument7 pagesTTEC Fencing RAGeml TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) Worksheet: Jerp # 3, Aromatics Unit CompanyDocument9 pagesJob Hazard Analysis (JHA) Worksheet: Jerp # 3, Aromatics Unit CompanyTeodoro Esquillo100% (1)
- Jsa Cable TerminationDocument4 pagesJsa Cable Terminationshaibaz chafekarNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For .Testing and Commissioning of Fire DamperDocument9 pagesRisk Assessment For .Testing and Commissioning of Fire Damperarun kurlanNo ratings yet
- S07 Tank Project - JSA - Erection of Scaffolding 2nd LevelDocument6 pagesS07 Tank Project - JSA - Erection of Scaffolding 2nd LevelKrishVy KumærNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - PTWDocument1 pageCourse Outline - PTWAli Al BarwaniNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health RisksDocument31 pagesOccupational Health RisksAli Al BarwaniNo ratings yet
- SP 1157Document88 pagesSP 1157Allocation ResourceNo ratings yet
- HSE Apprenticeship FrameworkDocument4 pagesHSE Apprenticeship FrameworkAli Al BarwaniNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Mission Theology, History, Perspectives Müller, KarlDocument552 pagesDictionary of Mission Theology, History, Perspectives Müller, KarlRev. Johana VangchhiaNo ratings yet
- Coast Artillery Journal - Oct 1946Document84 pagesCoast Artillery Journal - Oct 1946CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy-Large FontDocument35 pagesPharmacognosy-Large FontArantxa HilarioNo ratings yet
- Marked Fake Deck Tricks3Document7 pagesMarked Fake Deck Tricks3Tito Banerjee100% (1)
- The Bishop ScoreDocument3 pagesThe Bishop ScoreJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- The Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai, India: in Service For SightDocument4 pagesThe Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai, India: in Service For Sighttirth viraNo ratings yet
- Utpaladeva's Lost Vivrti On The Ishwara Pratyabhijna Karika - Raffaele TorellaDocument12 pagesUtpaladeva's Lost Vivrti On The Ishwara Pratyabhijna Karika - Raffaele Torellaraffaeletorella100% (1)
- 02TP PrelimExam MITDocument2 pages02TP PrelimExam MITSnapShop by AJNo ratings yet
- Av 10 Universal Remote Control ManualDocument13 pagesAv 10 Universal Remote Control Manualovidiu200970% (10)
- 3987 SDS (GHS) - I-ChemDocument4 pages3987 SDS (GHS) - I-ChemAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- The Migration Industry and Future Directions For Migration PolicyDocument4 pagesThe Migration Industry and Future Directions For Migration PolicyGabriella VillaçaNo ratings yet
- PDF Sermon Notes - The Temptation of Christ (Luke 4.1-13)Document5 pagesPDF Sermon Notes - The Temptation of Christ (Luke 4.1-13)fergie45315No ratings yet
- Pipe Pressure Drope ASEREHDocument3 pagesPipe Pressure Drope ASEREHSenghou MeasNo ratings yet
- XC9572 PDFDocument9 pagesXC9572 PDFAvs ElectronNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 24 Practice QuestionsArlene F. Montalbo100% (1)
- NIDAR, Franced Haggai G. The Brain Is The Vehicle of The MindDocument1 pageNIDAR, Franced Haggai G. The Brain Is The Vehicle of The MindHaggai NidarNo ratings yet
- A 201Document1 pageA 201AnuranjanNo ratings yet
- 2intro To LLMDDocument2 pages2intro To LLMDKristal ManriqueNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Course Test (Word)Document4 pagesEnd-Of-Course Test (Word)los ikandasNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Ucv SedapalDocument2 pagesCurriculum Ucv SedapalSheyler Alvarado SanchezNo ratings yet
- UN - HIV and Prison - Policy BriefDocument12 pagesUN - HIV and Prison - Policy BriefParomita2013No ratings yet
- NO Memo No. 21 S. 2018 Adherence To Training Policy PDFDocument10 pagesNO Memo No. 21 S. 2018 Adherence To Training Policy PDFKemberly Semaña PentonNo ratings yet
- Recruitment & Selection Reliance Jio Full Report - 100 Page MANU SHARMA MBA 3rd SEMDocument102 pagesRecruitment & Selection Reliance Jio Full Report - 100 Page MANU SHARMA MBA 3rd SEMImpression Graphics100% (4)
- Price Bubble Indicators by LindtDocument17 pagesPrice Bubble Indicators by LindtOlmedo FarfanNo ratings yet
- Mock Trial Task CardsDocument8 pagesMock Trial Task CardsVitaliy Fedchenko0% (1)
- Swathi Final Project AnilDocument100 pagesSwathi Final Project AnilHussainNo ratings yet
- Clear Codes List-NokiaDocument8 pagesClear Codes List-NokiaocuavasNo ratings yet