Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Set 5
Set 5
Uploaded by
Gil Diane AlcontinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Set 5
Set 5
Uploaded by
Gil Diane AlcontinCopyright:
Available Formats
PRACTICE SET 5
GEOMETRIC DESIGNS
SCORE
Name : Date :
College/Program : Time / Schedule :
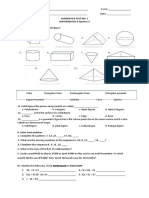
Geometric Shapes
A polygon is a two-dimensional shape with straight sides. It can be classified according to
number of its sides.
A solid or form is the geometry of three-dimensional space, the kind of space we live in. It is
called three-dimensional or 3D because there are three dimensions: width, depth and height.
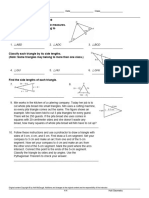
A. Name each of the following polygons and identify the type of each accordingly.
Sum of Type
Shape Name internal Simple/ Convex/ Regular/
angles Complex Concave Irregular
1.
square 360º simple convex regular
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Mathematics in the Modern World Page 43
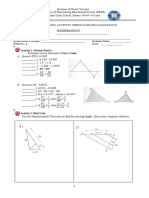
Practice Set 5 – Geometric Designs Mathematics as a Tool (Part 2)
B. Name the solid and classify each as polyhedron or non-polyhedron
1. Sample 2. 3.
Sphere (non-polyhedron) __________________ __________________
4. 5. 6.
__________________ __________________ __________________
7. 8. 9.
__________________ __________________ __________________
10. 11. 12.
__________________ __________________ __________________
13. 14. 15.
__________________ __________________ __________________
Mathematics in the Modern World Page 44
Practice Set 5 – Geometric Designs Mathematics as a Tool (Part 2)
Transformation
Geometric transformation of shapes is a change of its size, orientation or position following
certain techniques in mathematics. The original shape is called the object and the new shape is called
its image. Some types of transformations include:
• Translation – the object is slide in any direction.
• Reflection – the object is flipped over a line.
• Rotation – the object is rotated a certain degree about a point.
• Glide Reflection – a composition of translation and reflection in a line parallel to the direction of
translation.
• Dilation – the object is enlarged or reduced.
C. Identify the following transformations (shaded shape is the object).
1. 2.
________________________________ ________________________________
3. 4.
________________________________ ________________________________
5. 6.
________________________________ ________________________________
7. 8.
________________________________ ________________________________
Mathematics in the Modern World Page 45
Practice Set 5 – Geometric Designs Mathematics as a Tool (Part 2)
Patterns and Diagrams
Reflection symmetry - if a figure can be reflected over a line in such a way that the resulting
image coincides with the original. Reflection symmetry is also called bilateral symmetry. The
reflection line is called the line of symmetry.
Rotational symmetry - if a figure can be rotated about a point in such a way that its rotated
image coincides with the original figure.
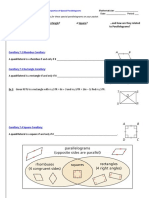
D. Determine the symmetry group in the following figures. For cyclic group (Cn), determine the order of
rotation; and for dihedral groups (Dn), determine the number of reflection lines.
1. 2. 3.
__________________ __________________ __________________
4. 5. 6.
__________________ __________________ __________________
7. 8. 9.
__________________ __________________ __________________
10. 11. 12.
__________________ __________________ __________________
13. 14. 15.
__________________ __________________ __________________
Mathematics in the Modern World Page 46
Practice Set 5 – Geometric Designs Mathematics as a Tool (Part 2)
Patterns and Diagrams
An infinite strip with a repeating pattern is called a frieze pattern, or sometimes a border
pattern or an infinite strip pattern. The term "frieze" is from architecture, where a frieze refers to a
decorative carving or pattern that runs horizontally just below a roofline or ceiling.
E. Using the International Union of Crystallography (IUC) notation, identify the names of
symmetry groups in the following frieze patterns.
1.
______________________________
2.
______________________________
3.
______________________________
4.
______________________________
5.
______________________________
Mathematics in the Modern World Page 47
Practice Set 5 – Geometric Designs Mathematics as a Tool (Part 2)
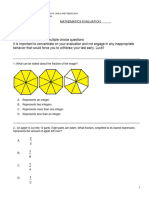
Patterns and Diagrams
A tessellation is defined as a pattern of shapes that covers a plane without any gaps or
overlaps. Tessellations can be found on pavements, patios and wallpapers. Tiled surface of flooring
and walls is an example of tessellation where there are no tiles which overlap and there are no gaps
between shapes.
F. Name the following tessellations.
1. 2.
__________________ __________________
3. 4.
__________________ __________________
5. 6.
__________________ __________________
7. 8.
__________________ __________________
9. 10.
__________________ __________________
Mathematics in the Modern World Page 48
Practice Set 5 – Geometric Designs Mathematics as a Tool (Part 2)
Mindanao Designs, Arts and Culture
G. Create a fabric design inspired by the Mindanaoan indigenous culture and arts with an application of
mathematical concepts. Make a short description of your design.
Mathematics in the Modern World Page 49
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Study GuideDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Study Guidesarahleeabc100% (2)
- Mg623 - Project Management PlanDocument79 pagesMg623 - Project Management PlanIBRAHIM NYIRENDANo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - HV 11kV Cable, Joint & TerminationDocument90 pagesRisk Assessment - HV 11kV Cable, Joint & TerminationJobish PK0% (2)
- Self-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)Document33 pagesSelf-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)BNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - Math in The Modern WorldDocument4 pagesMidterm Exam - Math in The Modern Worldjncardano90% (10)
- Earth-And-Life-Science-G11-Whlp-Week-1-2 - Quarter 2 HeDocument2 pagesEarth-And-Life-Science-G11-Whlp-Week-1-2 - Quarter 2 Hecristina maquinto100% (5)
- Learning Activity Sheet Grade - 4 MathematicsDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Grade - 4 MathematicsChris AlbinoNo ratings yet
- What I Know What's in (Act. 1) What's MoreDocument4 pagesWhat I Know What's in (Act. 1) What's MoreGerald PangonNo ratings yet
- Geoboard ActivityDocument6 pagesGeoboard ActivitysandeepNo ratings yet
- mth516 Mod3 App Cylinder Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesmth516 Mod3 App Cylinder Lesson Planapi-349546233No ratings yet
- Practice B: Classifying TrianglesDocument2 pagesPractice B: Classifying TrianglesAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Tle Ict 10 Long QuizDocument2 pagesTle Ict 10 Long Quizcid ladjamatliNo ratings yet
- Template Activity Sheet English7 10Document4 pagesTemplate Activity Sheet English7 10Ruben Padilla Dolor LagueNo ratings yet
- 2ndQ LAB 1 - Fault ModelDocument1 page2ndQ LAB 1 - Fault ModelgeekerytimeNo ratings yet
- Writeshops in ResearchDocument10 pagesWriteshops in ResearchEloisa Antonette LoteyroNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Learning Contract-GeometryDocument13 pages6th Grade Learning Contract-Geometryapi-252331860No ratings yet
- Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles: Practice and Problem Solving: A/BDocument2 pagesIsosceles and Equilateral Triangles: Practice and Problem Solving: A/BJosé PerezNo ratings yet
- 2018 Y10 5.3 Yearly FinalDocument14 pages2018 Y10 5.3 Yearly FinalSujay ModyNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 USLeM Grade 4 Week 7 MandanaoDocument12 pagesGrade 4 USLeM Grade 4 Week 7 MandanaoChris AlbinoNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week7g56Document4 pagesQ2 Week7g56Judy Anne NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- 2ND QUARTER MATHEMATICS 8 ANSWER SHEET Edited 1Document2 pages2ND QUARTER MATHEMATICS 8 ANSWER SHEET Edited 1Timothy Jay AbaoNo ratings yet
- Graphing Using Vertex FormDocument5 pagesGraphing Using Vertex FormdevikaNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Numbers in Nature and The World: WorksheetDocument3 pagesPatterns and Numbers in Nature and The World: WorksheetAngeline ReasNo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument4 pagesTrianglecyantlnureNo ratings yet
- Mod 3Document3 pagesMod 3Kevin ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Investigation 2023Document6 pagesGrade 7 Investigation 2023zwonizwonakaNo ratings yet
- Pre APhysics Required PracticalsDocument22 pagesPre APhysics Required PracticalsShaguNo ratings yet
- ANSWER SHEET PHILO DeathDocument7 pagesANSWER SHEET PHILO DeathJoiemmy GayudanNo ratings yet
- Square and Cube Root Values and Order of Operations Notes SheetDocument3 pagesSquare and Cube Root Values and Order of Operations Notes SheetKenneth NewsomeNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets - STAT m1-m2Document4 pagesActivity Sheets - STAT m1-m2Rey GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 1ST Summative in Mathematics 4Document3 pages1ST Summative in Mathematics 4Geian Dave BarriosNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Module 1-1Document22 pagesNumerical Methods Module 1-1johnmichaelpilota51No ratings yet
- 1st Monthly Examination in Mathematics 9Document2 pages1st Monthly Examination in Mathematics 9Erjohn OcaNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Summative Test 1-q3Document7 pagesMath 6 Summative Test 1-q3Hylord GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Algebra Name - Section 9.8 Period - Is It Linear, Quadratic, or Exponential?Document4 pagesAlgebra Name - Section 9.8 Period - Is It Linear, Quadratic, or Exponential?Nathan KabNo ratings yet
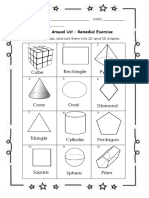
- Shapes - Remedial ExerciseDocument2 pagesShapes - Remedial ExerciseCChloeNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheets For MATH 8 LAS 1 2 and 3Document4 pagesAnswer Sheets For MATH 8 LAS 1 2 and 3roseerose.1002No ratings yet
- CBR Group Activity 2Document11 pagesCBR Group Activity 2Monica ZarembaNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1 Quiz #1Document1 pageQuiz #1 Quiz #1Amy LiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 - Answer SheetDocument15 pagesMathematics 9 - Answer Sheetgladys jane arabejoNo ratings yet
- GR 10 ReviewDocument12 pagesGR 10 ReviewHoda RagabNo ratings yet
- Worktext 1 Final TermDocument8 pagesWorktext 1 Final Termrhosegurion25No ratings yet
- Worksheet 4Document1 pageWorksheet 4AllanEvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Everyday Math Grade 3 Unit 5 Study Guide PAPERDocument18 pagesEveryday Math Grade 3 Unit 5 Study Guide PAPERChandni Samar KagalwallaNo ratings yet
- Ntctaoc Toonmi Stceboj Rceof NeriitaDocument16 pagesNtctaoc Toonmi Stceboj Rceof NeriitaMary Luz Dolente EderNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Math Full Revision 2018-2019 Abdulrazak Paper 2Document13 pagesGrade 8 Math Full Revision 2018-2019 Abdulrazak Paper 2Abdulrazak JamaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Sample Exam PaperDocument14 pagesYear 10 Sample Exam Papererikyo3No ratings yet
- Arithmetic Sequences and SeriesDocument6 pagesArithmetic Sequences and SeriesManisah Mohd ShahNo ratings yet
- Geo Unit 1Document25 pagesGeo Unit 1Grace QiuNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Grade & SectionDocument3 pagesName: - Date: - Grade & SectionLeonard PialoNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines: Lopez, Quezon BranchDocument3 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines: Lopez, Quezon Branchacurvz2005No ratings yet
- Dbes Learning Activity Sheet/Gawaing PagkatutoDocument9 pagesDbes Learning Activity Sheet/Gawaing PagkatutoMarwin NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 - Subject Science - Topic Measurement and Motion-Worksheet No 4Document2 pagesGrade 6 - Subject Science - Topic Measurement and Motion-Worksheet No 4bhatepoonamNo ratings yet
- Mousetrap Cars - Student Worksheets: Mathematics, Science and Technology PartnershipDocument11 pagesMousetrap Cars - Student Worksheets: Mathematics, Science and Technology PartnershipLauren PerryNo ratings yet
- Free Exams Mathematics 6Document10 pagesFree Exams Mathematics 6ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- GR 7 - Revision Ws 2Document6 pagesGR 7 - Revision Ws 21190570No ratings yet
- ANINO-Math100 PREFINAL M4 L4Document11 pagesANINO-Math100 PREFINAL M4 L4EvilGenius OfficialNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Notes GeomAdv 20-21Document3 pages7.4 Notes GeomAdv 20-21Barry HintonNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 READING AND WRITING SKILLS Answer SheetDocument2 pagesGRADE 11 READING AND WRITING SKILLS Answer SheetUel Cabz LaquihonNo ratings yet
- T L E-Final-CarpentryDocument15 pagesT L E-Final-CarpentryRoxanne AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Mod 3Document3 pagesMod 3Kevin ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Booklet Quarter 4 Week 1Document10 pagesAnswer Sheet Booklet Quarter 4 Week 1Jeric Rodriguez LiquiganNo ratings yet
- Specimen Set1 2h Physics Sep Qs With Ms 1Document24 pagesSpecimen Set1 2h Physics Sep Qs With Ms 1newynaw75No ratings yet
- AA 4-Assignment 5 Page 77Document1 pageAA 4-Assignment 5 Page 77Gil Diane AlcontinNo ratings yet
- AA 3-Exercise 2 Page 57Document1 pageAA 3-Exercise 2 Page 57Gil Diane AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Set 7Document11 pagesSet 7Gil Diane AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Case 002 MC DonaldsDocument2 pagesCase 002 MC DonaldsGil Diane AlcontinNo ratings yet
- Embankment Construction MethodologyDocument16 pagesEmbankment Construction MethodologyTinwin HtutNo ratings yet
- EXAM in Statistics and ProbabilityDocument7 pagesEXAM in Statistics and Probabilityjennilyn bulaonNo ratings yet
- University of Illinois The Grainger College of EngineeringDocument5 pagesUniversity of Illinois The Grainger College of EngineeringVinamr SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2 MethodDocument4 pagesAssignment # 2 MethodEmy heartNo ratings yet
- Agri CollegesDocument4 pagesAgri Collegesjaimaruthi internetnamakkalNo ratings yet
- Perspectives2 Worbook U2Document12 pagesPerspectives2 Worbook U2Eric Gabriel De La Puente PeloquinNo ratings yet
- Table of MesonsDocument2 pagesTable of MesonsGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- CHCCCS017 STDNT Assess BK V1 29.05.19 2Document71 pagesCHCCCS017 STDNT Assess BK V1 29.05.19 2Silvia BuiNo ratings yet
- From Haiku To Shinrin-Yoku: A Brief History of Forest BathingDocument3 pagesFrom Haiku To Shinrin-Yoku: A Brief History of Forest BathingEfra LlebaríaNo ratings yet
- 1 Sem. Finals Performance Tasks in Earth & Life Science: Mr. Ingiebert E. Sulapas Mcss FacultyDocument18 pages1 Sem. Finals Performance Tasks in Earth & Life Science: Mr. Ingiebert E. Sulapas Mcss FacultyMary Ann PateñoNo ratings yet
- Lorus Watch Manual PDFDocument2 pagesLorus Watch Manual PDFDave Long100% (1)
- MC74VHC00 D-2315589Document9 pagesMC74VHC00 D-2315589rajabur688No ratings yet
- Management 3-4-1Document9 pagesManagement 3-4-1Jewel Galvez OctavianoNo ratings yet
- For English CriticDocument2 pagesFor English CriticSari Sari Store VideoNo ratings yet
- Emf Values of Organic CompoundsDocument34 pagesEmf Values of Organic CompoundsPrabir SahaNo ratings yet
- Yg-1 V7plusa Endmill America YuDocument25 pagesYg-1 V7plusa Endmill America YuLuis CoolNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 IENG584Document3 pagesHomework 2 IENG584Frida YoungNo ratings yet
- Programme - DIES Alumni Forum - Preliminary 2022 - 10.10Document6 pagesProgramme - DIES Alumni Forum - Preliminary 2022 - 10.10D SusiloNo ratings yet
- Motivation: Archit GuptaDocument19 pagesMotivation: Archit GuptaArchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Random Variate Generation: 3.1 Inverse Transform MethodDocument14 pagesRandom Variate Generation: 3.1 Inverse Transform MethodLuka TodorNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Dust and Heat On Photovoltaic Modules: Impacts and SolutionsDocument318 pagesThe Effects of Dust and Heat On Photovoltaic Modules: Impacts and SolutionsEUGENNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 International Marketing ResearchDocument13 pagesChapter 3 International Marketing ResearchNhat Quang HuynhNo ratings yet
- Public Administration (OB)Document4 pagesPublic Administration (OB)kiran100% (1)
- System Identification ThesisDocument5 pagesSystem Identification Thesisjpcbobkef100% (2)
- Saribuhay (News) - FINALDocument1 pageSaribuhay (News) - FINALJEREMAEH DELOSANo ratings yet
- RA - Trays InstallationDocument11 pagesRA - Trays InstallationIbrahim EsmatNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water System (Training)Document34 pagesCooling Water System (Training)M. ade Dwi MaesandiNo ratings yet