Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sci 5
Sci 5
Uploaded by
Thameiyenthi Letchumanan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesThe document discusses the process of gaseous exchange in plants through their leaves, stems, and roots, which provide a large surface area. It describes how carbon dioxide diffuses into leaf cells through stomata, driven by concentration gradients between the air spaces and cells. Stomata are made of guard cells that regulate opening and closing via osmosis - photosynthesis in guard cells causes water influx and their expansion during the day, while water efflux causes their contraction at night. Air pollution like haze, dust, and acidic gases can damage stomata and cells, acidify soils, and reduce photosynthesis, threatening plant survival. Preventive measures include limiting open burning, vehicles, and encouraging alternative energy.
Original Description:
Original Title
sci 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the process of gaseous exchange in plants through their leaves, stems, and roots, which provide a large surface area. It describes how carbon dioxide diffuses into leaf cells through stomata, driven by concentration gradients between the air spaces and cells. Stomata are made of guard cells that regulate opening and closing via osmosis - photosynthesis in guard cells causes water influx and their expansion during the day, while water efflux causes their contraction at night. Air pollution like haze, dust, and acidic gases can damage stomata and cells, acidify soils, and reduce photosynthesis, threatening plant survival. Preventive measures include limiting open burning, vehicles, and encouraging alternative energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesSci 5
Sci 5
Uploaded by
Thameiyenthi LetchumananThe document discusses the process of gaseous exchange in plants through their leaves, stems, and roots, which provide a large surface area. It describes how carbon dioxide diffuses into leaf cells through stomata, driven by concentration gradients between the air spaces and cells. Stomata are made of guard cells that regulate opening and closing via osmosis - photosynthesis in guard cells causes water influx and their expansion during the day, while water efflux causes their contraction at night. Air pollution like haze, dust, and acidic gases can damage stomata and cells, acidify soils, and reduce photosynthesis, threatening plant survival. Preventive measures include limiting open burning, vehicles, and encouraging alternative energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
▪
Most plants carry out the process of gaseous exchange with their
surroundings through their leaves, stems and roots.
▪
These three parts provide a large surface area for gaseous
exchange.
Diffusion of Carbon Dioxide
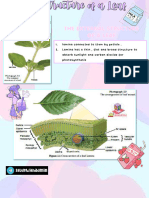
The structure in leaves that shows the pathway of gaseous exchange is as
shown in diagram below. The diffusion of carbon dioxide occurs through the
stoma according to the difference in concentration of carbon dioxide in the
cells and in the air spaces between the cells during photosynthesis.
▪
When carbon dioxide is used in photosynthesis, the concentration
of carbon dioxide in the cells becomes lower compared to the
concentration of carbon dioxide in the air space between the cells.
▪
This difference in concentrations allows the dissolved carbon
dioxide in the moist surface of cells to diffuse from the air space
between the cells into the cells.
▪
This causes the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air space
between the cells to become lower compared to the concentration of
carbon dioxide in the air outside the stoma.
▪
This difference in concentrations causes the diffusion of carbon
dioxide from the atmosphere into the air space between the cells
through the stoma which is open.
Stomatal Pore and Guard Cells
▪
Stoma is made up of a stomatal pore bounded by a pair of guard
cells. Guard cells contain chloroplasts to carry out photosynthesis.
▪
Stomata of plants open during photosynthesis when there is light
and close when it gets dark or when the plant loses a lot of water on
a hot day
Process of Osmosis Affects the Stoma
Concept of Osmosis
▪
Osmosis is the process of movement of water molecules from a
region of high concentration of water molecules (solution with a low
concentration of solutes) to a region of low concentration of water
molecules (solution with a high concentration of solutes) through a
semipermeable membrane.
▪
This membrane is permeable to water but not permeable to some
solutes such as sucrose molecules.
Process of Osmosis in Guard Cells
▪
When there is light, guard cells carry out photosynthesis to
produce glucose.
▪
The concentration of glucose in guard cells increases and causes
water from surrounding cells to diffuse into the guard cells through
osmosis. Hence, the guard cells become turgid and curved.
▪
Conversely, at night or on a hot day, water diffuses out of the
guard cells also through osmosis and causes the guard cells to
become flaccid and straight.
Importance of Unpolluted Environment for the Survival
of Plants
Effects of Haze and Dust on the Survival of Plants
▪
The reducing sunlight from reaching the plants and reducing the
rate of photosynthesis, haze and dust that settle on stomata prevent
gaseous exchange between plants and their surroundings.
Effects of Acidic Gases in the Air on the Survival of Plants
▪
Air pollutant gases which are acidic such as sulphur dioxide and
nitrogen dioxide dissolve in rainwater to produce acid rain.
▪
Acid rain kills plant cells and causes soil to be acidic and less
fertile.
▪
Most plants cannot live in highly acidic soil. This will reduce
agricultural produce and cause food shortage.
The preventive measures against the effects of pollution on plants
▪
Ban open burning in Indonesia and Malaysia
▪
Limit the number of motor vehicles on the road in Beijing, China
▪
Encourage the use of alternative energy such as solar energy
You might also like
- AITAS 8th Doctor SourcebookDocument192 pagesAITAS 8th Doctor SourcebookClaudio Caceres100% (14)
- Evolution of Investment Banking in IndiaDocument3 pagesEvolution of Investment Banking in IndiaChsudarshanDhaveji100% (2)
- Tdm850 '99 Wiring Diagram: Color CodeDocument1 pageTdm850 '99 Wiring Diagram: Color CodeХаджи Христо БуюклиевNo ratings yet
- Slide Sains NagoDocument9 pagesSlide Sains NagoMUHAMMAD ARASH BIN ABD RAHIMNo ratings yet
- Sains CHP 2.5 VR4 Auto's TeamDocument11 pagesSains CHP 2.5 VR4 Auto's Teamjessiejoanna59No ratings yet
- Lec. 06Document15 pagesLec. 06Wilson BhutiaNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument12 pagesBiology NotesDarrell Ibrahim NaryamaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (F1)Document18 pagesPhotosynthesis (F1)Andy GibbsNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition & TransportDocument21 pagesPlant Nutrition & TransportKim-Elaine Pohatu100% (1)
- Transport in PlantsDocument9 pagesTransport in PlantsTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument5 pagesPlant Nutritionpetersirgwa5No ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesDocument50 pagesAlwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Transpiration 2080Document25 pagesTranspiration 2080Subham KalwarNo ratings yet
- GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS - Form 2 Biology NotesDocument17 pagesGASEOUS EXCHANGE IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS - Form 2 Biology Notesakristo47No ratings yet
- Life Processes - Nutrition in Plants - AutosavedDocument20 pagesLife Processes - Nutrition in Plants - AutosavedraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in PlantsDocument6 pagesGas Exchange in PlantsMaria Theresa HerreroNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 16 - Gas Exchange - NotesDocument4 pagesLecture - 16 - Gas Exchange - NotesSarah GoNo ratings yet
- 3 - Plant Processes - Respiration in PlantsDocument20 pages3 - Plant Processes - Respiration in Plantsalicia.ayubi01No ratings yet
- Give Two Ways of Determining The Genotypes (Height) of The Pawpaw Plant ShownDocument246 pagesGive Two Ways of Determining The Genotypes (Height) of The Pawpaw Plant ShownAbigail ChepkuruiNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in PlantsDocument18 pagesGas Exchange in Plantsmannatm458No ratings yet
- Bio CH2 F5 StudywithadminDocument12 pagesBio CH2 F5 StudywithadminariananitafahNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument4 pagesPlant Cellemdadul2009No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in PlantsDocument2 pagesGas Exchange in PlantsWhat do you mean mhNo ratings yet
- Plant Water Relation: Grade 12Document16 pagesPlant Water Relation: Grade 12jovellamNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision: Plants, Water and MineralsDocument3 pagesBiology Revision: Plants, Water and MineralsMegan Taylor100% (1)
- TranspirationDocument68 pagesTranspirationOGAANSHO TUBENo ratings yet
- Transpiration 11.03.2024Document18 pagesTranspiration 11.03.2024Paramveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Transpiration in PlantsDocument29 pagesTranspiration in PlantsDhanush PSNo ratings yet
- 8 - Ses-607Document19 pages8 - Ses-607Nor579No ratings yet
- Smackslidecom Exchanging Mate 5fca76fcdc9b2Document23 pagesSmackslidecom Exchanging Mate 5fca76fcdc9b2Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lesson 2 Transpiration and TranslocationDocument20 pagesChapter 8 Lesson 2 Transpiration and TranslocationAli waleed AbdalmoatyNo ratings yet
- Stoma - WikipediaDocument56 pagesStoma - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutition - 230204 - 212736 PDFDocument10 pagesPlant Nutition - 230204 - 212736 PDFashraf alaqilyNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsDocument17 pages7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsTheresa IzaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants Y9Document20 pagesTransport in Plants Y9htgvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - Transport in PlantsLeann LeeNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Lab SlidesDocument22 pagesTranspiration Lab SlidesSTUTI MATHURNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport and Nutrition-1Document18 pagesPlant Transport and Nutrition-1Bryan DellomosNo ratings yet
- Water Regulation in Plant and Stomatal Conductance: Table of ContentDocument5 pagesWater Regulation in Plant and Stomatal Conductance: Table of ContentAmna NasirNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 5 - Transpiration Revision NotesDocument5 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 5 - Transpiration Revision NoteshkkcreativityNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange Through Stomatal Chamber - : Stomatal Opening and ClosingDocument6 pagesGaseous Exchange Through Stomatal Chamber - : Stomatal Opening and Closingعمیرہ ملکNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Academic Script200318111103034343Document13 pagesModule 3 Academic Script200318111103034343Shailendra Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument20 pagesTransport in PlantsForthtNo ratings yet
- Transpiration LabDocument17 pagesTranspiration Labvinayakjeet03No ratings yet
- GANIA, Cheane Y. - DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS EXPERIMENTDocument3 pagesGANIA, Cheane Y. - DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS EXPERIMENTCheane GaniaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Bio Notes 2Document14 pagesCSEC Bio Notes 2MiaNo ratings yet
- 4-Basic Needs of PlantsDocument34 pages4-Basic Needs of PlantsFadhil FbiNo ratings yet
- Transport in Vascular PlantsDocument23 pagesTransport in Vascular PlantsAnonymous u7cQyr3QYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6,8 BiologyDocument4 pagesChapter 6,8 BiologyParshvaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Plants. G1Document11 pagesGas Exchange in Plants. G1Teofilo Matthew AriñoNo ratings yet
- Plant Biology - IB Biology SL Grade 11Document6 pagesPlant Biology - IB Biology SL Grade 11atharNo ratings yet
- B4: Plant NutritionDocument8 pagesB4: Plant NutritionJoelle SwaisNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 2.2Document14 pagesBiology Chapter 2.2m-9152866No ratings yet
- Hydroponics Home BuildDocument54 pagesHydroponics Home BuildAlexe MihaiyNo ratings yet
- Exchanging Materials in PlantsDocument17 pagesExchanging Materials in PlantsJadesola AwosikaNo ratings yet
- Transpiration E - BookDocument18 pagesTranspiration E - BookAkku Tyagi50% (2)
- 9.1 Transport in Xylem of PlantsDocument15 pages9.1 Transport in Xylem of PlantsJason CharlesNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument44 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISsuggaballNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Plants (Transpiration)Document24 pagesTransportation in Plants (Transpiration)shongwekhulile958No ratings yet
- Ivory Brown Vintage Old Daily NotesDocument3 pagesIvory Brown Vintage Old Daily NotesPrajvi PatelNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Transport System in Plants: TranspirationDocument27 pages2.3 Transport System in Plants: TranspirationSandera Abdul ManafNo ratings yet
- Sci 8Document4 pagesSci 8Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Sci 2Document7 pagesSci 2Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Sci 12Document6 pagesSci 12Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Sci 11Document4 pagesSci 11Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Sci 10Document2 pagesSci 10Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Sci 3Document5 pagesSci 3Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 AkDocument20 pagesLecture3 AkThameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Human Geography Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesHuman Geography Lecture NotesThameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Number System: Mohd. Yamani Idris/ Noorzaily Mohamed NoorDocument29 pagesNumber System: Mohd. Yamani Idris/ Noorzaily Mohamed NoorThameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Integrated English SimplifiedDocument232 pagesIntegrated English SimplifiedThameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- BST Notes 2 F1-F4Document345 pagesBST Notes 2 F1-F4Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Form 3Document148 pagesForm 3Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Geography-1Document175 pagesForm 3 Geography-1Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Extractor de Probetas DEMTECHDocument2 pagesExtractor de Probetas DEMTECHPaul Alex Quiroz BarrionuevoNo ratings yet
- Dh3 Generation Lototo Plan Phase 1 RGC 08sep2023Document8 pagesDh3 Generation Lototo Plan Phase 1 RGC 08sep2023Borislav VulicNo ratings yet
- Investment ProgrammingDocument14 pagesInvestment ProgrammingDILG NagaNo ratings yet
- M.najib CV 2023 Foto ScaffDocument12 pagesM.najib CV 2023 Foto Scaffamad copyitamNo ratings yet
- DBX PA Cut SheetA2Document2 pagesDBX PA Cut SheetA2Willy WakkerNo ratings yet
- Nihms 1713249Document13 pagesNihms 1713249Achilles Fkundana18No ratings yet
- English 8 Third Quarter Curriculum MapDocument5 pagesEnglish 8 Third Quarter Curriculum MapAgnes Gebone TaneoNo ratings yet
- GMSH RefManualDocument396 pagesGMSH RefManualJosé Antonio MoríñigoNo ratings yet
- The Implementation of FOC For PMSM Drive Based On TMS320F28035 DSP ControllerDocument5 pagesThe Implementation of FOC For PMSM Drive Based On TMS320F28035 DSP ControllerJashan BelagurNo ratings yet
- District Profile ThattaDocument52 pagesDistrict Profile ThattaUrooj Fatima100% (1)
- Lexical and Syntax Analysis: TopicsDocument5 pagesLexical and Syntax Analysis: TopicsReshma PiseNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property RightsDocument7 pagesIntellectual Property RightsVidhu JainNo ratings yet
- Blue-Eyes White Dragon DeckDocument1 pageBlue-Eyes White Dragon DeckJad hack'sNo ratings yet
- Competitive Strategy Notes at MBADocument26 pagesCompetitive Strategy Notes at MBABabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- Gibbs Reflective Cycle EssaysDocument7 pagesGibbs Reflective Cycle Essaysertzyzbaf100% (2)
- Part 1: Back in The . Century, Kenya Was A More . Society Compared To Today. MenDocument3 pagesPart 1: Back in The . Century, Kenya Was A More . Society Compared To Today. MenthaonguyenwindNo ratings yet
- CrsDocument660 pagesCrsaamirmehmoodkhanNo ratings yet
- Piping SystemsDocument137 pagesPiping SystemsSwapnil KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Branding Across BordersDocument26 pagesBranding Across BordersLokendra BainsNo ratings yet
- Rift Valley University: Department: - Weekend Computer ScienceDocument13 pagesRift Valley University: Department: - Weekend Computer ScienceAyele MitkuNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test in Mathematics 7: Violeta Integrated SchoolDocument4 pagesThird Periodical Test in Mathematics 7: Violeta Integrated SchoolWerty Gigz DurendezNo ratings yet
- Future Trends in European Public Administration and Management: An Outside-In PerspectiveDocument45 pagesFuture Trends in European Public Administration and Management: An Outside-In PerspectivevickyNo ratings yet
- TV BroadcastingDocument6 pagesTV Broadcastingpinoy foreverNo ratings yet
- BTBS Tính T + TR NG TDocument12 pagesBTBS Tính T + TR NG Thoangdieulinh0305No ratings yet
- G006 Sinexcel BESS Micro Grid Solution - MalawiDocument2 pagesG006 Sinexcel BESS Micro Grid Solution - MalawiSyed Furqan RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Academic Year 2019-2020: St. John College of Humanities & SciencesDocument78 pagesAcademic Year 2019-2020: St. John College of Humanities & SciencesRinkesh SoniNo ratings yet
- An5265 LT5265Document4 pagesAn5265 LT5265maldomattNo ratings yet