Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsModule Four Lesson Six Guided Notes
Module Four Lesson Six Guided Notes
Uploaded by
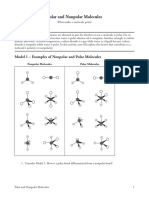
Soraya SThe document discusses polarity and intermolecular forces. It defines the electronegativity differences that result in ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds. Symmetrical molecules are nonpolar while asymmetrical molecules are polar. The phrase "like dissolves like" means that polar substances dissolve polar substances and nonpolar dissolve nonpolar, but polar and nonpolar do not mix. There are three main intermolecular forces: dispersion forces between nonpolar molecules, dipole forces between polar molecules, and hydrogen bonding between molecules with hydrogen-fluorine, hydrogen-oxygen, or hydrogen-nitrogen bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilDocument6 pagesPolar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilLily Stanton67% (3)
- Lab Report On Bonding and StructureDocument9 pagesLab Report On Bonding and StructureOdongo Tonny100% (1)
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE Q3 Week 2 - v2Document31 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE Q3 Week 2 - v2Evangelyn Patatag-CatacutanNo ratings yet
- 6-1 Concept ReviewDocument2 pages6-1 Concept ReviewEmilyNo ratings yet
- PS Q3 Module2 WK2Document20 pagesPS Q3 Module2 WK2Jason PojasNo ratings yet
- Polar and Non Polar Molecules Physical ScienceDocument19 pagesPolar and Non Polar Molecules Physical ScienceAthaliah Eunice DenamarcaNo ratings yet
- Grade11 Physical Science - Module 3Document5 pagesGrade11 Physical Science - Module 3Erickson SongcalNo ratings yet
- Properties of Covalent BondingDocument9 pagesProperties of Covalent BondingMBOTAKE LawsonNo ratings yet
- Grade: Physical ScienceDocument7 pagesGrade: Physical Sciencemaxene jadeNo ratings yet
- The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its StructureDocument8 pagesThe Polarity of Molecule Based On Its StructureAlexa RamosNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 2Document7 pagesPhysical Science Week 2Rona Grace MartinezNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument26 pagesLesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsLyndy PantaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its StructureDocument48 pagesLesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its Structuretheresa balaticoNo ratings yet
- 8 - MODULE 3 - Molecular Polarity Rev 2022Document20 pages8 - MODULE 3 - Molecular Polarity Rev 2022ROGELIO RIVERA100% (1)
- Chemical Compounds LabDocument6 pagesChemical Compounds LabGbmNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds in Biology - SolutionsDocument6 pagesChemical Bonds in Biology - SolutionspokemongalaxyNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity of An AtomDocument4 pagesElectronegativity of An AtomLindsay AgabasNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument43 pagesMolecular Polaritychubbskie00No ratings yet
- Notes Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesNotes Intermolecular Forceslaliberte68100% (3)
- Intermolecular Forces WorksheetDocument3 pagesIntermolecular Forces WorksheetMark John DumaslanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesDocument15 pagesPhysical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesJodi RempilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Test Study GuideDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Test Study GuideDeepti SailappanNo ratings yet
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Intermolecular Forces)Document10 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Intermolecular Forces)Jane182004No ratings yet
- q1l3 - 2nd Sem Physical ScienceDocument12 pagesq1l3 - 2nd Sem Physical ScienceBilly Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Properties of Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesDocument23 pages2.1 Properties of Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesmckhiandivinoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Modules Week 2Document6 pagesPhysical Science Modules Week 2RODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL-BOND IdkDocument15 pagesCHEMICAL-BOND Idk14A - BANTANG, Mark Joshua R.No ratings yet
- Lesson 7: Polarity of MoleculesDocument9 pagesLesson 7: Polarity of MoleculesRAENA MARIE PENDRASNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Properties of Molecules and Its PolarityDocument6 pagesGROUP 3 Properties of Molecules and Its PolarityJay Em Kristel MengulloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04 - Physical ScienceDocument24 pagesLesson 04 - Physical ScienceAngelo Freidrich O AmbalongNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Physical ScienceDocument13 pagesReviewer For Physical ScienceTimothy James Tolentino BruceNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsDocument47 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solidsapi-683027695No ratings yet
- Intramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDocument12 pagesIntramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDuyen Nguyen100% (1)
- Exploring Polarity of Molecules and Its Properties: Physical Science Quarter 3 Module 2Document18 pagesExploring Polarity of Molecules and Its Properties: Physical Science Quarter 3 Module 2Maricar DimasNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document2 pagesModule 4Christopher Agustin Tambogon LptNo ratings yet
- Polarity Of: MoleculesDocument22 pagesPolarity Of: MoleculesChing ChongNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Document40 pagesPolarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Yson GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 8 Summary By: Hassan Al-Alawi 11red: Covalent BondDocument5 pagesChemistry Chapter 8 Summary By: Hassan Al-Alawi 11red: Covalent BondXIBG21SANIANo ratings yet
- U18.1 Covalent Compounds and The Formation of Covalent BondsDocument18 pagesU18.1 Covalent Compounds and The Formation of Covalent BondsMaria Luisa BernalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Review: Vocabulary Section 7.3Document4 pagesChapter 7 Review: Vocabulary Section 7.3Christopher HurtNo ratings yet
- Polar and Non PolarDocument22 pagesPolar and Non PolarRowena FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Review: VocabularyDocument4 pagesChapter 8 Review: VocabularyChristopher HurtNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 The Polarity of A MoleculeDocument21 pagesLesson 4 The Polarity of A MoleculeMichelle GuevarraNo ratings yet
- WEEK 10 - Intermolecular Forces of Attraction - 0Document16 pagesWEEK 10 - Intermolecular Forces of Attraction - 0Micz Ryan OcheaNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Polarity C11!4!5Document8 pagesSolubility and Polarity C11!4!5doctorguy770% (1)
- Polarity NotesDocument5 pagesPolarity NotesShailesh GhediyaNo ratings yet
- 3qt Physical Science Week 5 Day 1Document33 pages3qt Physical Science Week 5 Day 1katelardizabal228No ratings yet
- Polymers JOMDocument12 pagesPolymers JOMDario KataniNo ratings yet
- Physical SCience Lesson 4 The Structure and Properties of MatterDocument9 pagesPhysical SCience Lesson 4 The Structure and Properties of MatterJustin BirdNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Physical Science Molecular PolarityDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Physical Science Molecular Polarityartjill printingNo ratings yet
- Types of Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument9 pagesTypes of Intermolecular Forces of AttractionTrisha Mae FrialaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bond: Molecules and Molecular CompoundsDocument24 pagesCovalent Bond: Molecules and Molecular CompoundsIlina DameskaNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Intermolecular ForcesDocument5 pages4.7 Intermolecular ForcesrachpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chemical Context of LifeDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Chemical Context of LifeJADEN MANNNo ratings yet
- 6 - Notes - Bond PolarityDocument2 pages6 - Notes - Bond PolaritySomeone PersonNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 5Document3 pagesPhysical Science Week 5Aira EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Spanish 112 Module 2Document2 pagesSpanish 112 Module 2Soraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Five Lesson Two AssignmentDocument1 pageModule Five Lesson Two AssignmentSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Three Lesson One Guided NotesDocument5 pagesModule Three Lesson One Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module One Lesson Four AssignmentDocument2 pagesModule One Lesson Four AssignmentSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Six Lesson One Guided NotesDocument4 pagesModule Six Lesson One Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Five Science Journal DownloadDocument9 pagesModule Five Science Journal DownloadSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Six Lesson One Guided NotesDocument4 pagesModule Six Lesson One Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Week Seven Warm UpDocument1 pageWeek Seven Warm UpSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Four Lesson Five AssignmentDocument3 pagesModule Four Lesson Five AssignmentSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Four Lesson Five Guided NotesDocument2 pagesModule Four Lesson Five Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Two Science JournalDocument5 pagesModule Two Science JournalSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document3 pagesModule 10Soraya SNo ratings yet
- Bohr Model ExampleDocument1 pageBohr Model ExampleSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module One Science JournalDocument5 pagesModule One Science JournalSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Two Lesson Two Guided NotesDocument2 pagesModule Two Lesson Two Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
Module Four Lesson Six Guided Notes
Module Four Lesson Six Guided Notes
Uploaded by
Soraya S0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesThe document discusses polarity and intermolecular forces. It defines the electronegativity differences that result in ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds. Symmetrical molecules are nonpolar while asymmetrical molecules are polar. The phrase "like dissolves like" means that polar substances dissolve polar substances and nonpolar dissolve nonpolar, but polar and nonpolar do not mix. There are three main intermolecular forces: dispersion forces between nonpolar molecules, dipole forces between polar molecules, and hydrogen bonding between molecules with hydrogen-fluorine, hydrogen-oxygen, or hydrogen-nitrogen bonds.
Original Description:
Original Title
Copy of Module Four Lesson Six Guided notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses polarity and intermolecular forces. It defines the electronegativity differences that result in ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds. Symmetrical molecules are nonpolar while asymmetrical molecules are polar. The phrase "like dissolves like" means that polar substances dissolve polar substances and nonpolar dissolve nonpolar, but polar and nonpolar do not mix. There are three main intermolecular forces: dispersion forces between nonpolar molecules, dipole forces between polar molecules, and hydrogen bonding between molecules with hydrogen-fluorine, hydrogen-oxygen, or hydrogen-nitrogen bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesModule Four Lesson Six Guided Notes
Module Four Lesson Six Guided Notes
Uploaded by
Soraya SThe document discusses polarity and intermolecular forces. It defines the electronegativity differences that result in ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds. Symmetrical molecules are nonpolar while asymmetrical molecules are polar. The phrase "like dissolves like" means that polar substances dissolve polar substances and nonpolar dissolve nonpolar, but polar and nonpolar do not mix. There are three main intermolecular forces: dispersion forces between nonpolar molecules, dipole forces between polar molecules, and hydrogen bonding between molecules with hydrogen-fluorine, hydrogen-oxygen, or hydrogen-nitrogen bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Module 4 Lesson 6 Guided Notes (Polarity and Intermolecular Forces)
Essential Standards Addressed: 1.2.3 , 1.2.5
Slide 2-5
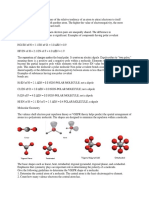
1. What is the electronegativity difference for ionic compounds? when the
electronegativity difference between atoms is greater than 1.7.
2. What is the electronegativity difference for polar covalent compounds? In
general the electronegativity difference must be 0.5 or more before the bond is
labeled as a polar covalent bond instead of nonpolar covalent bond.
3. What is the electronegativity difference for nonpolar covalent
compounds? Nonpolar bonds have an electronegativity difference of less than
0.4, and have an equal sharing of the electron pair.
4. Most compounds are __either ____ completely ionic or covalent.
5. What is example of a volatile liquid? alcohol
6. Most nonpolar compounds are ___gases_________.
Slides 6-8
7. Symmetrical molecules will be _nonpolar_____________.
8. Asymmetrical molecules will be ____polar__________.
9. Draw an example of a symmetrical molecule.
10. Draw an example of an asymmetrical molecule
Slides 9-15
11.Explain what the phrase “Like dissolves Like” means? What this means is that
polar compounds dissolve polar compounds, nonpolar compounds dissolve
nonpolar compounds, but polar and nonpolar do not dissolve in each other
12. Distinguish between the three intermolecular forces?
dispersion forces occure between non polar molecules
dipole forces occure between polar moecules
hydrogen bonding occurs between molecules with H-F, H-O, or H-N bonds.
You might also like
- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilDocument6 pagesPolar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilLily Stanton67% (3)
- Lab Report On Bonding and StructureDocument9 pagesLab Report On Bonding and StructureOdongo Tonny100% (1)
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE Q3 Week 2 - v2Document31 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE Q3 Week 2 - v2Evangelyn Patatag-CatacutanNo ratings yet
- 6-1 Concept ReviewDocument2 pages6-1 Concept ReviewEmilyNo ratings yet
- PS Q3 Module2 WK2Document20 pagesPS Q3 Module2 WK2Jason PojasNo ratings yet
- Polar and Non Polar Molecules Physical ScienceDocument19 pagesPolar and Non Polar Molecules Physical ScienceAthaliah Eunice DenamarcaNo ratings yet
- Grade11 Physical Science - Module 3Document5 pagesGrade11 Physical Science - Module 3Erickson SongcalNo ratings yet
- Properties of Covalent BondingDocument9 pagesProperties of Covalent BondingMBOTAKE LawsonNo ratings yet
- Grade: Physical ScienceDocument7 pagesGrade: Physical Sciencemaxene jadeNo ratings yet
- The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its StructureDocument8 pagesThe Polarity of Molecule Based On Its StructureAlexa RamosNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 2Document7 pagesPhysical Science Week 2Rona Grace MartinezNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument26 pagesLesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsLyndy PantaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its StructureDocument48 pagesLesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its Structuretheresa balaticoNo ratings yet
- 8 - MODULE 3 - Molecular Polarity Rev 2022Document20 pages8 - MODULE 3 - Molecular Polarity Rev 2022ROGELIO RIVERA100% (1)
- Chemical Compounds LabDocument6 pagesChemical Compounds LabGbmNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds in Biology - SolutionsDocument6 pagesChemical Bonds in Biology - SolutionspokemongalaxyNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity of An AtomDocument4 pagesElectronegativity of An AtomLindsay AgabasNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument43 pagesMolecular Polaritychubbskie00No ratings yet
- Notes Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesNotes Intermolecular Forceslaliberte68100% (3)
- Intermolecular Forces WorksheetDocument3 pagesIntermolecular Forces WorksheetMark John DumaslanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesDocument15 pagesPhysical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesJodi RempilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Test Study GuideDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Test Study GuideDeepti SailappanNo ratings yet
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Intermolecular Forces)Document10 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Intermolecular Forces)Jane182004No ratings yet
- q1l3 - 2nd Sem Physical ScienceDocument12 pagesq1l3 - 2nd Sem Physical ScienceBilly Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Properties of Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesDocument23 pages2.1 Properties of Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesmckhiandivinoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Modules Week 2Document6 pagesPhysical Science Modules Week 2RODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL-BOND IdkDocument15 pagesCHEMICAL-BOND Idk14A - BANTANG, Mark Joshua R.No ratings yet
- Lesson 7: Polarity of MoleculesDocument9 pagesLesson 7: Polarity of MoleculesRAENA MARIE PENDRASNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Properties of Molecules and Its PolarityDocument6 pagesGROUP 3 Properties of Molecules and Its PolarityJay Em Kristel MengulloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04 - Physical ScienceDocument24 pagesLesson 04 - Physical ScienceAngelo Freidrich O AmbalongNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Physical ScienceDocument13 pagesReviewer For Physical ScienceTimothy James Tolentino BruceNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsDocument47 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solidsapi-683027695No ratings yet
- Intramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDocument12 pagesIntramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDuyen Nguyen100% (1)
- Exploring Polarity of Molecules and Its Properties: Physical Science Quarter 3 Module 2Document18 pagesExploring Polarity of Molecules and Its Properties: Physical Science Quarter 3 Module 2Maricar DimasNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document2 pagesModule 4Christopher Agustin Tambogon LptNo ratings yet
- Polarity Of: MoleculesDocument22 pagesPolarity Of: MoleculesChing ChongNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Document40 pagesPolarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Yson GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 8 Summary By: Hassan Al-Alawi 11red: Covalent BondDocument5 pagesChemistry Chapter 8 Summary By: Hassan Al-Alawi 11red: Covalent BondXIBG21SANIANo ratings yet
- U18.1 Covalent Compounds and The Formation of Covalent BondsDocument18 pagesU18.1 Covalent Compounds and The Formation of Covalent BondsMaria Luisa BernalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Review: Vocabulary Section 7.3Document4 pagesChapter 7 Review: Vocabulary Section 7.3Christopher HurtNo ratings yet
- Polar and Non PolarDocument22 pagesPolar and Non PolarRowena FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Review: VocabularyDocument4 pagesChapter 8 Review: VocabularyChristopher HurtNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 The Polarity of A MoleculeDocument21 pagesLesson 4 The Polarity of A MoleculeMichelle GuevarraNo ratings yet
- WEEK 10 - Intermolecular Forces of Attraction - 0Document16 pagesWEEK 10 - Intermolecular Forces of Attraction - 0Micz Ryan OcheaNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Polarity C11!4!5Document8 pagesSolubility and Polarity C11!4!5doctorguy770% (1)
- Polarity NotesDocument5 pagesPolarity NotesShailesh GhediyaNo ratings yet
- 3qt Physical Science Week 5 Day 1Document33 pages3qt Physical Science Week 5 Day 1katelardizabal228No ratings yet
- Polymers JOMDocument12 pagesPolymers JOMDario KataniNo ratings yet
- Physical SCience Lesson 4 The Structure and Properties of MatterDocument9 pagesPhysical SCience Lesson 4 The Structure and Properties of MatterJustin BirdNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Physical Science Molecular PolarityDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Physical Science Molecular Polarityartjill printingNo ratings yet
- Types of Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument9 pagesTypes of Intermolecular Forces of AttractionTrisha Mae FrialaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bond: Molecules and Molecular CompoundsDocument24 pagesCovalent Bond: Molecules and Molecular CompoundsIlina DameskaNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Intermolecular ForcesDocument5 pages4.7 Intermolecular ForcesrachpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chemical Context of LifeDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Chemical Context of LifeJADEN MANNNo ratings yet
- 6 - Notes - Bond PolarityDocument2 pages6 - Notes - Bond PolaritySomeone PersonNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 5Document3 pagesPhysical Science Week 5Aira EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Spanish 112 Module 2Document2 pagesSpanish 112 Module 2Soraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Five Lesson Two AssignmentDocument1 pageModule Five Lesson Two AssignmentSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Three Lesson One Guided NotesDocument5 pagesModule Three Lesson One Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module One Lesson Four AssignmentDocument2 pagesModule One Lesson Four AssignmentSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Six Lesson One Guided NotesDocument4 pagesModule Six Lesson One Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Five Science Journal DownloadDocument9 pagesModule Five Science Journal DownloadSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Six Lesson One Guided NotesDocument4 pagesModule Six Lesson One Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Week Seven Warm UpDocument1 pageWeek Seven Warm UpSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Four Lesson Five AssignmentDocument3 pagesModule Four Lesson Five AssignmentSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Four Lesson Five Guided NotesDocument2 pagesModule Four Lesson Five Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Two Science JournalDocument5 pagesModule Two Science JournalSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document3 pagesModule 10Soraya SNo ratings yet
- Bohr Model ExampleDocument1 pageBohr Model ExampleSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module One Science JournalDocument5 pagesModule One Science JournalSoraya SNo ratings yet
- Module Two Lesson Two Guided NotesDocument2 pagesModule Two Lesson Two Guided NotesSoraya SNo ratings yet