Professional Documents
Culture Documents
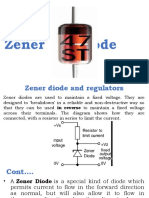
PROOF Circuit Protection
PROOF Circuit Protection
Uploaded by
sabCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cahier Technique: Discrimination With LV Power Circuit BreakersDocument10 pagesCahier Technique: Discrimination With LV Power Circuit BreakersAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 3.2 PN Junction Diode - CKT AnalysisDocument20 pages3.2 PN Junction Diode - CKT AnalysisLaurent VitugNo ratings yet
- Surge Arrester SizingDocument3 pagesSurge Arrester Sizingoadipphone7031100% (1)
- DIN Fuses 7.2kV - 36kVDocument124 pagesDIN Fuses 7.2kV - 36kVlarryNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Diode, SCR, TriacDocument67 pages1.1 Diode, SCR, Triac727721eumt082No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices in Mechatronics: U G Dilusha Duminda Cot Galle. MechatronicsDocument45 pagesSemiconductor Devices in Mechatronics: U G Dilusha Duminda Cot Galle. MechatronicsugdilushaNo ratings yet
- Transient Overvoltages and Insulation CoordinationDocument9 pagesTransient Overvoltages and Insulation CoordinationCristian Santana Rodriguez0% (1)
- ArresterWorks ArresterFacts-001 ArresterLeadLengthDocument11 pagesArresterWorks ArresterFacts-001 ArresterLeadLengthShung Tak ChanNo ratings yet
- ArresterWorks Facts-001 Arrester Lead LengthDocument11 pagesArresterWorks Facts-001 Arrester Lead Lengthnshj196No ratings yet
- Power DiodesDocument46 pagesPower DiodesJay R BallonNo ratings yet
- EDS Day 3 - 15-02-24Document20 pagesEDS Day 3 - 15-02-24Swarnaprabha JenaNo ratings yet
- @6 - Power Electronics - Thyristors - Part I - v2 - ReducedDocument258 pages@6 - Power Electronics - Thyristors - Part I - v2 - ReducedKhanh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- TVS Diode Applications Training: Version01 - 100407Document33 pagesTVS Diode Applications Training: Version01 - 100407Adrian TestareNo ratings yet
- EE450: High Voltage Engineering: January 25, 2017Document33 pagesEE450: High Voltage Engineering: January 25, 2017Ehtisham RajpootNo ratings yet
- Week2 - Lecture2 - Uncontrolled Rectifier 1 - 1phaseDocument36 pagesWeek2 - Lecture2 - Uncontrolled Rectifier 1 - 1phasex TommyNo ratings yet
- Deutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Document15 pagesDeutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Modesto Marcos Calderon CruzNo ratings yet
- The H.V Measurements-3Document21 pagesThe H.V Measurements-3Alfred OkacheNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeMD. Abdullah Al NomanNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection-2Document49 pagesPower System Protection-2IsaacNo ratings yet
- Over Current ProtectionDocument22 pagesOver Current ProtectionnihkinwejkbNo ratings yet
- Over Current ProtectionDocument22 pagesOver Current Protectionnihkinwejkb100% (1)
- 3VL 1706-1dd36-0aa0Document4 pages3VL 1706-1dd36-0aa0Omkar ThakurNo ratings yet
- WP276 - Switching Transients and Surge Protection For MV Transformers in Data CentersDocument26 pagesWP276 - Switching Transients and Surge Protection For MV Transformers in Data CenterscachiletNo ratings yet
- De Zener DiodeDocument17 pagesDe Zener Dioderemember sundayNo ratings yet
- Power Diode - Lecture 2Document29 pagesPower Diode - Lecture 2Akpata SamuelNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection and Switchgear: Fundamentals of Protective Relaying IvDocument24 pagesPower System Protection and Switchgear: Fundamentals of Protective Relaying IvSampath AnbuNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-Diode ApplicationsDocument55 pagesUnit 3-Diode ApplicationsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Physical Explanation RectifiersDocument3 pagesPhysical Explanation RectifiersmixilopotstlyNo ratings yet
- ResistorsDocument8 pagesResistorsVinilda MercurioNo ratings yet
- EPO630 - Chapter 4b - Measurements of HV and CurrentsDocument28 pagesEPO630 - Chapter 4b - Measurements of HV and CurrentsfajrinaNo ratings yet
- I. Diode Equivalent CircuitsDocument5 pagesI. Diode Equivalent CircuitsJohn RivasNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeNeal John VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Transient Voltage Suppression Diodes: Echnical RticleDocument3 pagesTransient Voltage Suppression Diodes: Echnical Rticlezero cloudNo ratings yet
- DiodeApplications 1spDocument32 pagesDiodeApplications 1spHakkı AKYÜZNo ratings yet
- Insulation Co OrdinationDocument4 pagesInsulation Co OrdinationVasudha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Hve PPT NotesDocument131 pagesUnit 4 Hve PPT Notesjaihind 3048No ratings yet
- Littelfuse TVS Diode SMAJ Datasheet PDFDocument6 pagesLittelfuse TVS Diode SMAJ Datasheet PDFAENo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document31 pagesLab 3張博翔No ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To Semiconductor DiodesDocument50 pages2 Introduction To Semiconductor DiodesKurt PalacioNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodesDocument12 pagesZener DiodesnardnardNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDocument19 pagesDiode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEHarshith TsNo ratings yet
- Power Diodes: BY: Ronald Brion Angel Fel Burlat RJ CanoyDocument15 pagesPower Diodes: BY: Ronald Brion Angel Fel Burlat RJ CanoyAngel Fel BurlatNo ratings yet
- Varistor Tutorial: Register To Download Premium Content!Document10 pagesVaristor Tutorial: Register To Download Premium Content!a_calabreseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Fuses and ArrestersDocument23 pagesLecture 5 Fuses and ArrestersSyed KhizarNo ratings yet
- ALSTOM Instntneous Voltage Relay VAGM HighRes PDFDocument4 pagesALSTOM Instntneous Voltage Relay VAGM HighRes PDFnadhsai3No ratings yet
- Sizing Neutral Grounding ResistorDocument5 pagesSizing Neutral Grounding ResistorRueban AntonyNo ratings yet
- Switchgear and ProtectionDocument17 pagesSwitchgear and Protection002Pradeep002No ratings yet
- EE450: High Voltage Engineering: Lecture 20, 21Document37 pagesEE450: High Voltage Engineering: Lecture 20, 21Syed KumailNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Topic 2 Diodes - Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument30 pagesUnit IV Topic 2 Diodes - Characteristics and Applicationssherinjoanna2006No ratings yet
- UEEA3993 Topic 3 03Document67 pagesUEEA3993 Topic 3 03RyanNo ratings yet
- Active Magnetic AntennasDocument53 pagesActive Magnetic AntennaslazarosNo ratings yet
- 4CAE000328 A en High Burden Tripping RelayDocument11 pages4CAE000328 A en High Burden Tripping RelayDave ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Measurement of High VoltageDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Measurement of High VoltageTeh chia NienNo ratings yet
- Lec2 Power-DiodeDocument33 pagesLec2 Power-DiodeSaqib ButtNo ratings yet
- Electrical ComponentsDocument12 pagesElectrical ComponentsAna MaryanaNo ratings yet
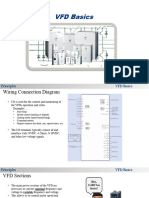
- VFD BasicsDocument18 pagesVFD Basicsabinash pradhanNo ratings yet
- Littelfuse - TVS - Diode - SMBJ - Datasheet PDFDocument6 pagesLittelfuse - TVS - Diode - SMBJ - Datasheet PDFsamuelborgesNo ratings yet
- 4 Diode Applications Part 3 (Zener Diodes and Voltage Multipliers)Document17 pages4 Diode Applications Part 3 (Zener Diodes and Voltage Multipliers)Kurt PalacioNo ratings yet
- Special Purpose Diodes PDFDocument19 pagesSpecial Purpose Diodes PDFJhoanna Dacatimbang0% (1)
- Analog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5From EverandAnalog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1446 AschsdDocument1 page1446 AschsdsabNo ratings yet
- Urdu A Brief History of Time Stephen Hawking PDFDocument234 pagesUrdu A Brief History of Time Stephen Hawking PDFsabNo ratings yet
- NEC Article 501 Class 1 HazardousDocument3 pagesNEC Article 501 Class 1 HazardoussabNo ratings yet
- Cheap AVR51 Development BoardDocument7 pagesCheap AVR51 Development BoardsabNo ratings yet
- Creating Smartlinks (Deep Links) : Product Page Promotional Links in 4 Steps!Document16 pagesCreating Smartlinks (Deep Links) : Product Page Promotional Links in 4 Steps!sabNo ratings yet
- ESP MX (V1 - 3)Document17 pagesESP MX (V1 - 3)sabNo ratings yet
- 2020-07 QST Product Review Midnight Design Solutions Phaser Digital Mode Transceiver KitDocument4 pages2020-07 QST Product Review Midnight Design Solutions Phaser Digital Mode Transceiver KitsabNo ratings yet
- Hajj Wa Umra Ki Purnoor DuainDocument183 pagesHajj Wa Umra Ki Purnoor DuainsabNo ratings yet
- Arduino Basic Connection PDFDocument39 pagesArduino Basic Connection PDFsabNo ratings yet
- SMS To Moving Message Display With An 8051: Technology Workshop Craft Home Food Play Outside CostumesDocument4 pagesSMS To Moving Message Display With An 8051: Technology Workshop Craft Home Food Play Outside CostumessabNo ratings yet
- LookDocument1 pageLooksabNo ratings yet
- At 25080Document21 pagesAt 25080sabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Arduino: by Alan G. Smith September 30, 2011Document172 pagesIntroduction To Arduino: by Alan G. Smith September 30, 2011sabNo ratings yet
- KeywordsDocument1 pageKeywordssabNo ratings yet
- IPTV New Update With All Adress 06.04.2020...Document2 pagesIPTV New Update With All Adress 06.04.2020...sabNo ratings yet
- IPTV New Update With All Adress 05.04.2020Document2 pagesIPTV New Update With All Adress 05.04.2020sabNo ratings yet
- Analog Vls I ProjectDocument8 pagesAnalog Vls I ProjectLakshmi Sri Ram GannavarapuNo ratings yet
- GV2 ManualDocument3 pagesGV2 ManualDrMahmoud AbbasNo ratings yet
- Pages From NFPA 70E - Standard For Electrical Safety in The Workplace-3Document1 pagePages From NFPA 70E - Standard For Electrical Safety in The Workplace-3MohamedSaidNo ratings yet
- Centre-Break Disconnectors: Types SGF 72.5Document2 pagesCentre-Break Disconnectors: Types SGF 72.5Ionut - CristianNo ratings yet
- Coffing EC1 ManualDocument44 pagesCoffing EC1 ManualJESUSCALVILLONo ratings yet
- EcodialAdvanceCalculation HelpDocument33 pagesEcodialAdvanceCalculation HelpChàng NgốcNo ratings yet
- 7 - Hysteresis MotorDocument22 pages7 - Hysteresis MotorFariba IslamNo ratings yet
- FAC-008-1 FKE Facility Rating Methodology r5Document13 pagesFAC-008-1 FKE Facility Rating Methodology r5Dave SchlageterNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 2Document2 pagesDatasheet 2Kike VillasurNo ratings yet
- 12-24 KV Umc Series Metal Clad Switchgear: User ManualDocument8 pages12-24 KV Umc Series Metal Clad Switchgear: User ManualAngeloNo ratings yet
- BurdenResistorCalculator CalculoDocument5 pagesBurdenResistorCalculator CalculoFredman Carlos de MoraesNo ratings yet
- Gate-Diffusion Input (GDI) A Power Efficient Method For Digital Combinatorial CircuitsDocument16 pagesGate-Diffusion Input (GDI) A Power Efficient Method For Digital Combinatorial Circuitsmdzakir_hussainNo ratings yet
- Banner Sensor ManualDocument8 pagesBanner Sensor ManualPumzile FaleniNo ratings yet
- Vol 2 Sec 5.2 - Generator Bus Ducts Neutral Grounding EquipmentDocument14 pagesVol 2 Sec 5.2 - Generator Bus Ducts Neutral Grounding EquipmentBijaya Kumar MohantyNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Bill Validator With StackerDocument2 pagesUser Guide: Bill Validator With StackerBruce TidswellNo ratings yet
- BS 159 1992Document16 pagesBS 159 1992Kalaimany ArumuggamNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Diodes SKN 20 SKR 20 Skna 20 SKN 26 SKR 26: RSM Frms RRMDocument4 pagesRectifier Diodes SKN 20 SKR 20 Skna 20 SKN 26 SKR 26: RSM Frms RRMDurodola TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Kist Seminar On Automatic Solar Tracking: Presented by Biswaranjan Panda REGN - NO.-0801214272 7 Sem, Ele - EnggDocument16 pagesKist Seminar On Automatic Solar Tracking: Presented by Biswaranjan Panda REGN - NO.-0801214272 7 Sem, Ele - EnggDev KumarNo ratings yet
- 74VHC123A Dual Retriggerable Monostable Multivibrator: General DescriptionDocument10 pages74VHC123A Dual Retriggerable Monostable Multivibrator: General DescriptionKuni KazeNo ratings yet
- Medium-Pressure Accel Valves-Celeris (MKT-0277) UnLckDocument6 pagesMedium-Pressure Accel Valves-Celeris (MKT-0277) UnLckBiji PaulNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: KV-21FW150 KV-21FW150Document53 pagesService Manual: KV-21FW150 KV-21FW150Alex Villa AredoNo ratings yet
- An-6076 - Design and Application Guide of Bootstrap Circuit ForDocument13 pagesAn-6076 - Design and Application Guide of Bootstrap Circuit ForwxapazmiNo ratings yet
- SENTERA - Instructiuni Instalare ITRSDocument8 pagesSENTERA - Instructiuni Instalare ITRSAlex IuziNo ratings yet
- Diode BrakesDocument1 pageDiode BrakesClaudio Lima Lopes FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 986K Wheel Loader Electrical System (Cab) 486-0964 Chassis and Engine (486-0965)Document6 pages986K Wheel Loader Electrical System (Cab) 486-0964 Chassis and Engine (486-0965)abduallah muhammadNo ratings yet
- Datasheet WT160-F450 6022804 enDocument6 pagesDatasheet WT160-F450 6022804 enamin radNo ratings yet
- MOD 3000-9000TL3-X DatasheetDocument2 pagesMOD 3000-9000TL3-X DatasheetZain RizviNo ratings yet
- EN ACS800 MD El Plan E Screen 3AXD00000273236 FDocument42 pagesEN ACS800 MD El Plan E Screen 3AXD00000273236 FDaniel AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Basis ReportDocument9 pagesElectrical Safety Basis ReportRaj KumaranNo ratings yet
- RCOM Consumables Master ListDocument44 pagesRCOM Consumables Master ListRaju KumarNo ratings yet
PROOF Circuit Protection
PROOF Circuit Protection
Uploaded by
sabOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PROOF Circuit Protection
PROOF Circuit Protection
Uploaded by
sabCopyright:
Available Formats
mouser.
com
Circuit Protection Reference Guide
This reference guide outlines the basic circuits for protection, and the major protective
systems based on these basic circuits. It is the ideal memory aid to help you select the
optimum protection solution for your design!
Protective circuit with diode Recovery diode Circuit breaker
• Suitable only for DC and low switching loads Automatic switch that protects an electrical
• High reliability circuit from damage by excess current caused
• Limits peak of self-induction voltage to the by overload or short circuit. Interrupts the
diode’s threshold voltage current flow when an overload detected
Protective circuit with diode Breakdown diode TVS Diode
and Zener diode
• Suitable only for DC Protects ICs from voltage spikes induced in
• No suppression of voltages below connected wires
Zener voltage
• Limits induction voltage to diode’s threshold
voltage + Zener voltage
Fuse
Protects an electrical circuit from overcurrents
Protective circuit with varistor Short-circuit to self-induction
• Suitable for AC and DC
• Voltage-dependent resistor, used to protect
V
against excess transient voltages
• No suppression of voltages below Varistor’s
threshold voltage
• Suppression of self-induction voltage
Surge suppressor
depends on Varistor characteristic
Protects ICs from AC voltage spikes
Snubber RC Filter
• Suitable for AC
• Mainly used for switching contacts
• RF suppression Thermal cut-off
• Voltage peak depends on R and C
• Contact voltage depends on R Interrupts electrical currents when the
temperature reaches a specified value.
Protective circuit with resistor Simple protection circuit
• Suitable for AC and DC Thermistor
• Voltage peak direct proportional to R
Temperature-dependent resistor, used to limit
V inrush currents.
Circuit protection
You might also like
- Cahier Technique: Discrimination With LV Power Circuit BreakersDocument10 pagesCahier Technique: Discrimination With LV Power Circuit BreakersAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 3.2 PN Junction Diode - CKT AnalysisDocument20 pages3.2 PN Junction Diode - CKT AnalysisLaurent VitugNo ratings yet
- Surge Arrester SizingDocument3 pagesSurge Arrester Sizingoadipphone7031100% (1)
- DIN Fuses 7.2kV - 36kVDocument124 pagesDIN Fuses 7.2kV - 36kVlarryNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Diode, SCR, TriacDocument67 pages1.1 Diode, SCR, Triac727721eumt082No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices in Mechatronics: U G Dilusha Duminda Cot Galle. MechatronicsDocument45 pagesSemiconductor Devices in Mechatronics: U G Dilusha Duminda Cot Galle. MechatronicsugdilushaNo ratings yet
- Transient Overvoltages and Insulation CoordinationDocument9 pagesTransient Overvoltages and Insulation CoordinationCristian Santana Rodriguez0% (1)
- ArresterWorks ArresterFacts-001 ArresterLeadLengthDocument11 pagesArresterWorks ArresterFacts-001 ArresterLeadLengthShung Tak ChanNo ratings yet
- ArresterWorks Facts-001 Arrester Lead LengthDocument11 pagesArresterWorks Facts-001 Arrester Lead Lengthnshj196No ratings yet
- Power DiodesDocument46 pagesPower DiodesJay R BallonNo ratings yet
- EDS Day 3 - 15-02-24Document20 pagesEDS Day 3 - 15-02-24Swarnaprabha JenaNo ratings yet
- @6 - Power Electronics - Thyristors - Part I - v2 - ReducedDocument258 pages@6 - Power Electronics - Thyristors - Part I - v2 - ReducedKhanh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- TVS Diode Applications Training: Version01 - 100407Document33 pagesTVS Diode Applications Training: Version01 - 100407Adrian TestareNo ratings yet
- EE450: High Voltage Engineering: January 25, 2017Document33 pagesEE450: High Voltage Engineering: January 25, 2017Ehtisham RajpootNo ratings yet
- Week2 - Lecture2 - Uncontrolled Rectifier 1 - 1phaseDocument36 pagesWeek2 - Lecture2 - Uncontrolled Rectifier 1 - 1phasex TommyNo ratings yet
- Deutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Document15 pagesDeutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Modesto Marcos Calderon CruzNo ratings yet
- The H.V Measurements-3Document21 pagesThe H.V Measurements-3Alfred OkacheNo ratings yet
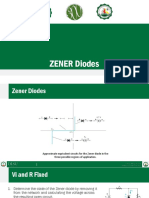
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeMD. Abdullah Al NomanNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection-2Document49 pagesPower System Protection-2IsaacNo ratings yet
- Over Current ProtectionDocument22 pagesOver Current ProtectionnihkinwejkbNo ratings yet
- Over Current ProtectionDocument22 pagesOver Current Protectionnihkinwejkb100% (1)
- 3VL 1706-1dd36-0aa0Document4 pages3VL 1706-1dd36-0aa0Omkar ThakurNo ratings yet
- WP276 - Switching Transients and Surge Protection For MV Transformers in Data CentersDocument26 pagesWP276 - Switching Transients and Surge Protection For MV Transformers in Data CenterscachiletNo ratings yet
- De Zener DiodeDocument17 pagesDe Zener Dioderemember sundayNo ratings yet
- Power Diode - Lecture 2Document29 pagesPower Diode - Lecture 2Akpata SamuelNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection and Switchgear: Fundamentals of Protective Relaying IvDocument24 pagesPower System Protection and Switchgear: Fundamentals of Protective Relaying IvSampath AnbuNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-Diode ApplicationsDocument55 pagesUnit 3-Diode ApplicationsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Physical Explanation RectifiersDocument3 pagesPhysical Explanation RectifiersmixilopotstlyNo ratings yet
- ResistorsDocument8 pagesResistorsVinilda MercurioNo ratings yet
- EPO630 - Chapter 4b - Measurements of HV and CurrentsDocument28 pagesEPO630 - Chapter 4b - Measurements of HV and CurrentsfajrinaNo ratings yet
- I. Diode Equivalent CircuitsDocument5 pagesI. Diode Equivalent CircuitsJohn RivasNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeNeal John VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Transient Voltage Suppression Diodes: Echnical RticleDocument3 pagesTransient Voltage Suppression Diodes: Echnical Rticlezero cloudNo ratings yet
- DiodeApplications 1spDocument32 pagesDiodeApplications 1spHakkı AKYÜZNo ratings yet
- Insulation Co OrdinationDocument4 pagesInsulation Co OrdinationVasudha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Hve PPT NotesDocument131 pagesUnit 4 Hve PPT Notesjaihind 3048No ratings yet
- Littelfuse TVS Diode SMAJ Datasheet PDFDocument6 pagesLittelfuse TVS Diode SMAJ Datasheet PDFAENo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document31 pagesLab 3張博翔No ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To Semiconductor DiodesDocument50 pages2 Introduction To Semiconductor DiodesKurt PalacioNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodesDocument12 pagesZener DiodesnardnardNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDocument19 pagesDiode Circuits Perspective: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEHarshith TsNo ratings yet
- Power Diodes: BY: Ronald Brion Angel Fel Burlat RJ CanoyDocument15 pagesPower Diodes: BY: Ronald Brion Angel Fel Burlat RJ CanoyAngel Fel BurlatNo ratings yet
- Varistor Tutorial: Register To Download Premium Content!Document10 pagesVaristor Tutorial: Register To Download Premium Content!a_calabreseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Fuses and ArrestersDocument23 pagesLecture 5 Fuses and ArrestersSyed KhizarNo ratings yet
- ALSTOM Instntneous Voltage Relay VAGM HighRes PDFDocument4 pagesALSTOM Instntneous Voltage Relay VAGM HighRes PDFnadhsai3No ratings yet
- Sizing Neutral Grounding ResistorDocument5 pagesSizing Neutral Grounding ResistorRueban AntonyNo ratings yet
- Switchgear and ProtectionDocument17 pagesSwitchgear and Protection002Pradeep002No ratings yet
- EE450: High Voltage Engineering: Lecture 20, 21Document37 pagesEE450: High Voltage Engineering: Lecture 20, 21Syed KumailNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Topic 2 Diodes - Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument30 pagesUnit IV Topic 2 Diodes - Characteristics and Applicationssherinjoanna2006No ratings yet
- UEEA3993 Topic 3 03Document67 pagesUEEA3993 Topic 3 03RyanNo ratings yet
- Active Magnetic AntennasDocument53 pagesActive Magnetic AntennaslazarosNo ratings yet
- 4CAE000328 A en High Burden Tripping RelayDocument11 pages4CAE000328 A en High Burden Tripping RelayDave ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Measurement of High VoltageDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Measurement of High VoltageTeh chia NienNo ratings yet
- Lec2 Power-DiodeDocument33 pagesLec2 Power-DiodeSaqib ButtNo ratings yet
- Electrical ComponentsDocument12 pagesElectrical ComponentsAna MaryanaNo ratings yet
- VFD BasicsDocument18 pagesVFD Basicsabinash pradhanNo ratings yet
- Littelfuse - TVS - Diode - SMBJ - Datasheet PDFDocument6 pagesLittelfuse - TVS - Diode - SMBJ - Datasheet PDFsamuelborgesNo ratings yet
- 4 Diode Applications Part 3 (Zener Diodes and Voltage Multipliers)Document17 pages4 Diode Applications Part 3 (Zener Diodes and Voltage Multipliers)Kurt PalacioNo ratings yet
- Special Purpose Diodes PDFDocument19 pagesSpecial Purpose Diodes PDFJhoanna Dacatimbang0% (1)
- Analog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5From EverandAnalog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1446 AschsdDocument1 page1446 AschsdsabNo ratings yet
- Urdu A Brief History of Time Stephen Hawking PDFDocument234 pagesUrdu A Brief History of Time Stephen Hawking PDFsabNo ratings yet
- NEC Article 501 Class 1 HazardousDocument3 pagesNEC Article 501 Class 1 HazardoussabNo ratings yet
- Cheap AVR51 Development BoardDocument7 pagesCheap AVR51 Development BoardsabNo ratings yet
- Creating Smartlinks (Deep Links) : Product Page Promotional Links in 4 Steps!Document16 pagesCreating Smartlinks (Deep Links) : Product Page Promotional Links in 4 Steps!sabNo ratings yet
- ESP MX (V1 - 3)Document17 pagesESP MX (V1 - 3)sabNo ratings yet
- 2020-07 QST Product Review Midnight Design Solutions Phaser Digital Mode Transceiver KitDocument4 pages2020-07 QST Product Review Midnight Design Solutions Phaser Digital Mode Transceiver KitsabNo ratings yet
- Hajj Wa Umra Ki Purnoor DuainDocument183 pagesHajj Wa Umra Ki Purnoor DuainsabNo ratings yet
- Arduino Basic Connection PDFDocument39 pagesArduino Basic Connection PDFsabNo ratings yet
- SMS To Moving Message Display With An 8051: Technology Workshop Craft Home Food Play Outside CostumesDocument4 pagesSMS To Moving Message Display With An 8051: Technology Workshop Craft Home Food Play Outside CostumessabNo ratings yet
- LookDocument1 pageLooksabNo ratings yet
- At 25080Document21 pagesAt 25080sabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Arduino: by Alan G. Smith September 30, 2011Document172 pagesIntroduction To Arduino: by Alan G. Smith September 30, 2011sabNo ratings yet
- KeywordsDocument1 pageKeywordssabNo ratings yet
- IPTV New Update With All Adress 06.04.2020...Document2 pagesIPTV New Update With All Adress 06.04.2020...sabNo ratings yet
- IPTV New Update With All Adress 05.04.2020Document2 pagesIPTV New Update With All Adress 05.04.2020sabNo ratings yet
- Analog Vls I ProjectDocument8 pagesAnalog Vls I ProjectLakshmi Sri Ram GannavarapuNo ratings yet
- GV2 ManualDocument3 pagesGV2 ManualDrMahmoud AbbasNo ratings yet
- Pages From NFPA 70E - Standard For Electrical Safety in The Workplace-3Document1 pagePages From NFPA 70E - Standard For Electrical Safety in The Workplace-3MohamedSaidNo ratings yet
- Centre-Break Disconnectors: Types SGF 72.5Document2 pagesCentre-Break Disconnectors: Types SGF 72.5Ionut - CristianNo ratings yet
- Coffing EC1 ManualDocument44 pagesCoffing EC1 ManualJESUSCALVILLONo ratings yet
- EcodialAdvanceCalculation HelpDocument33 pagesEcodialAdvanceCalculation HelpChàng NgốcNo ratings yet
- 7 - Hysteresis MotorDocument22 pages7 - Hysteresis MotorFariba IslamNo ratings yet
- FAC-008-1 FKE Facility Rating Methodology r5Document13 pagesFAC-008-1 FKE Facility Rating Methodology r5Dave SchlageterNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 2Document2 pagesDatasheet 2Kike VillasurNo ratings yet
- 12-24 KV Umc Series Metal Clad Switchgear: User ManualDocument8 pages12-24 KV Umc Series Metal Clad Switchgear: User ManualAngeloNo ratings yet
- BurdenResistorCalculator CalculoDocument5 pagesBurdenResistorCalculator CalculoFredman Carlos de MoraesNo ratings yet
- Gate-Diffusion Input (GDI) A Power Efficient Method For Digital Combinatorial CircuitsDocument16 pagesGate-Diffusion Input (GDI) A Power Efficient Method For Digital Combinatorial Circuitsmdzakir_hussainNo ratings yet
- Banner Sensor ManualDocument8 pagesBanner Sensor ManualPumzile FaleniNo ratings yet
- Vol 2 Sec 5.2 - Generator Bus Ducts Neutral Grounding EquipmentDocument14 pagesVol 2 Sec 5.2 - Generator Bus Ducts Neutral Grounding EquipmentBijaya Kumar MohantyNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Bill Validator With StackerDocument2 pagesUser Guide: Bill Validator With StackerBruce TidswellNo ratings yet
- BS 159 1992Document16 pagesBS 159 1992Kalaimany ArumuggamNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Diodes SKN 20 SKR 20 Skna 20 SKN 26 SKR 26: RSM Frms RRMDocument4 pagesRectifier Diodes SKN 20 SKR 20 Skna 20 SKN 26 SKR 26: RSM Frms RRMDurodola TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Kist Seminar On Automatic Solar Tracking: Presented by Biswaranjan Panda REGN - NO.-0801214272 7 Sem, Ele - EnggDocument16 pagesKist Seminar On Automatic Solar Tracking: Presented by Biswaranjan Panda REGN - NO.-0801214272 7 Sem, Ele - EnggDev KumarNo ratings yet
- 74VHC123A Dual Retriggerable Monostable Multivibrator: General DescriptionDocument10 pages74VHC123A Dual Retriggerable Monostable Multivibrator: General DescriptionKuni KazeNo ratings yet
- Medium-Pressure Accel Valves-Celeris (MKT-0277) UnLckDocument6 pagesMedium-Pressure Accel Valves-Celeris (MKT-0277) UnLckBiji PaulNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: KV-21FW150 KV-21FW150Document53 pagesService Manual: KV-21FW150 KV-21FW150Alex Villa AredoNo ratings yet
- An-6076 - Design and Application Guide of Bootstrap Circuit ForDocument13 pagesAn-6076 - Design and Application Guide of Bootstrap Circuit ForwxapazmiNo ratings yet
- SENTERA - Instructiuni Instalare ITRSDocument8 pagesSENTERA - Instructiuni Instalare ITRSAlex IuziNo ratings yet
- Diode BrakesDocument1 pageDiode BrakesClaudio Lima Lopes FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 986K Wheel Loader Electrical System (Cab) 486-0964 Chassis and Engine (486-0965)Document6 pages986K Wheel Loader Electrical System (Cab) 486-0964 Chassis and Engine (486-0965)abduallah muhammadNo ratings yet
- Datasheet WT160-F450 6022804 enDocument6 pagesDatasheet WT160-F450 6022804 enamin radNo ratings yet
- MOD 3000-9000TL3-X DatasheetDocument2 pagesMOD 3000-9000TL3-X DatasheetZain RizviNo ratings yet
- EN ACS800 MD El Plan E Screen 3AXD00000273236 FDocument42 pagesEN ACS800 MD El Plan E Screen 3AXD00000273236 FDaniel AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Basis ReportDocument9 pagesElectrical Safety Basis ReportRaj KumaranNo ratings yet
- RCOM Consumables Master ListDocument44 pagesRCOM Consumables Master ListRaju KumarNo ratings yet