Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Yr11 t3 2021
Physics Yr11 t3 2021
Uploaded by
Luke FleriCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Scienceclinic Smartprep GR11 Dbe Eng 1 PDFDocument44 pagesScienceclinic Smartprep GR11 Dbe Eng 1 PDFCayden Davids100% (4)
- Foundation Certificate FC312 Physics (B) End of Module Open Book Examination (Practice) Question Book Time Allowed: 120 MinutesDocument11 pagesFoundation Certificate FC312 Physics (B) End of Module Open Book Examination (Practice) Question Book Time Allowed: 120 MinutesNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- LTE ATOL RF PlannningDocument78 pagesLTE ATOL RF PlannningNikhil SwadiaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of IlluminationDocument12 pagesFundamental of IlluminationMinerva AbantoNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr11 t3 2020Document16 pagesPhysics Yr11 t3 2020Luke FleriNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr11 t3 2019Document12 pagesPhysics Yr11 t3 2019Luke FleriNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Physics TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools - SAMPLE PAPERDocument13 pagesYear 11 Physics TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools - SAMPLE PAPERtrical27 tricalNo ratings yet
- PH 2023Document14 pagesPH 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Yr 12 2.7 Int Nature Q 03Document10 pagesYr 12 2.7 Int Nature Q 03trubriteNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr10 t3 2021Document12 pagesPhysics Yr10 t3 2021Rebecca SciberrasNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr10 t3 2017Document11 pagesPhysics Yr10 t3 2017Rebecca SciberrasNo ratings yet
- Chap.1 NoteDocument37 pagesChap.1 NoteRachell RequellNo ratings yet
- Paper-2 With Solution PhysicsDocument19 pagesPaper-2 With Solution Physicsanunay.mishra4141No ratings yet
- 24 June 2022 Shift I PhysicsDocument6 pages24 June 2022 Shift I PhysicsArav IyerNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities Units & DimensionsDocument8 pagesPhysical Quantities Units & DimensionsVictor OduorNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample (17th Nov 2023)Document8 pagesPhysics Sample (17th Nov 2023)shamimshafeb2005No ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument24 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelGaneshNo ratings yet
- 2 Hours and 30 Minutes: List of Physical ConstantsDocument11 pages2 Hours and 30 Minutes: List of Physical ConstantsAdam mahabirNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument13 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelShashwat ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr10 t3 2019Document12 pagesPhysics Yr10 t3 2019Rebecca SciberrasNo ratings yet
- Percubaan Negeri Melaka 2020 (K2)Document7 pagesPercubaan Negeri Melaka 2020 (K2)FATIN FARHANAH BINTI HALIDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Exam Vibrations and NoiseDocument6 pagesExam Vibrations and NoisejoaoftabreuNo ratings yet
- Nurture Course (Phase: MNC) : Pattern / Type: Neet / Minor Answer Key Pre-Medical 2021 24-11-2019Document6 pagesNurture Course (Phase: MNC) : Pattern / Type: Neet / Minor Answer Key Pre-Medical 2021 24-11-2019VadoNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Units and DimensionsDocument12 pagesPhysical Quantities, Units and Dimensionsdavid ama100% (1)
- Fis 24Document6 pagesFis 24syafrina novitaNo ratings yet
- Units & DimensionsDocument6 pagesUnits & DimensionsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Name - Summer Assignment - Part 1 Fall 2021 - Spring 2022Document11 pagesAP Physics 1 Name - Summer Assignment - Part 1 Fall 2021 - Spring 2022Pradyun GREEN CELL VOLUNTEERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelhassanNo ratings yet
- This Exam Is Formed of Four Obligatory Exercises in Two Pages Non Programmable Calculators Are AllowedDocument3 pagesThis Exam Is Formed of Four Obligatory Exercises in Two Pages Non Programmable Calculators Are AllowedMJ TarhiniNo ratings yet
- Skull Crusher-1 - Class XI - JEE (Adv) - PhysicsDocument3 pagesSkull Crusher-1 - Class XI - JEE (Adv) - Physicslootera715No ratings yet
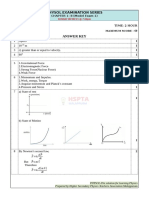
- Physol Examination Series: PESM01 Answer KeyDocument23 pagesPhysol Examination Series: PESM01 Answer Keykapil sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22nattawat10720No ratings yet
- hw8 PDFDocument44 pageshw8 PDFShaya Nirenberg0% (3)
- Exam Vibrations and NoiseDocument5 pagesExam Vibrations and NoisejoaoftabreuNo ratings yet
- MECHANICSDocument65 pagesMECHANICSDr. Unoma OkoraforNo ratings yet
- Pundra University of Science & Technology: Assignment On: PhysicsDocument8 pagesPundra University of Science & Technology: Assignment On: PhysicsSYED FARHAN REZANo ratings yet
- Exercises 2Document7 pagesExercises 2andre130912No ratings yet
- 9702 w17 QP 42 PDFDocument28 pages9702 w17 QP 42 PDFSabeha KhanNo ratings yet
- SPHL Sample ProblemsDocument20 pagesSPHL Sample ProblemsĐức TiếnNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 05 01Document2 pagesWorksheet 05 01BadeekhNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Week 1 Lesson 2Document4 pagesGrade 10 Physics Week 1 Lesson 2Daniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving I: Mathematical Techniques: 1 Dimensional AnalysisDocument27 pagesProblem Solving I: Mathematical Techniques: 1 Dimensional AnalysisTest EmailNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 AnswerDocument10 pagesTutorial 1 AnswerHafizuddin AdzharNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/04Document26 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/04sinting lim100% (1)
- Topic 1: Measurement and UncertaintiesDocument4 pagesTopic 1: Measurement and UncertaintiesHoa Dinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 2016 HW PDFDocument38 pagesAP Physics 1 2016 HW PDFAnika KimNo ratings yet
- 9702 w16 QP 43 PDFDocument24 pages9702 w16 QP 43 PDFSajidAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ExamplesDocument11 pagesChapter 6 ExamplesSurya NarasimanNo ratings yet
- Dimensions & Units: Q MC (TDocument2 pagesDimensions & Units: Q MC (TS1S0334 苏熙文SOO XI WENNo ratings yet
- Break-Up of Questions: Mechanics Sound Heat Electromagnetism Optics Modern Physics 6 2 2 5 2 3Document12 pagesBreak-Up of Questions: Mechanics Sound Heat Electromagnetism Optics Modern Physics 6 2 2 5 2 3Jasbir MaanNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Week 8: Learning Activity Sheet 1 Solve Problems Involving Logarithmic Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesDocument6 pagesQuarter 1 - Week 8: Learning Activity Sheet 1 Solve Problems Involving Logarithmic Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesJiwon ParkNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/22Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/22王涛No ratings yet
- Dimensional Anaylsis - Part 2Document11 pagesDimensional Anaylsis - Part 2khosatintswalo1010No ratings yet
- Physics Assignment NewDocument7 pagesPhysics Assignment NewSYED FARHAN REZANo ratings yet
- Paper 2 With Solution PhysicsDocument19 pagesPaper 2 With Solution PhysicsMuhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22LINH DUONGNo ratings yet
- November 2016 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Physics A-LevelDocument24 pagesNovember 2016 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Physics A-LevelcamaralckinNo ratings yet
- Dimension of Physical QuantitiesDocument2 pagesDimension of Physical QuantitiesPriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- The Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64From EverandThe Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64No ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lesson 2b Fractions To Percent WorksheetDocument1 pageLesson 2b Fractions To Percent WorksheetLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2c Decimal To Fractions Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pageLesson 2c Decimal To Fractions Worksheet Answer KeyLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2c Decimal To Fractions WorksheetDocument1 pageLesson 2c Decimal To Fractions WorksheetLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1a Decimal Terminating Nonterminating and Repeating WorksheetDocument1 pageLesson 1a Decimal Terminating Nonterminating and Repeating WorksheetLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2b Fractions To Percent Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pageLesson 2b Fractions To Percent Worksheet Answer KeyLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2a Converting Fraction To Decimal Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pageLesson 2a Converting Fraction To Decimal Worksheet Answer KeyLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1a Decimal Terminating Nonterminating and Repeating Vocabularies Lecture NoteDocument1 pageLesson 1a Decimal Terminating Nonterminating and Repeating Vocabularies Lecture NoteLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr11 t3 2020Document16 pagesPhysics Yr11 t3 2020Luke FleriNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr11 t3 2019Document12 pagesPhysics Yr11 t3 2019Luke FleriNo ratings yet
- Results Reporter: QUIZ RESULTS FOR Tippens: Physics: Chapter 21: Mechanical Waves: QuizDocument5 pagesResults Reporter: QUIZ RESULTS FOR Tippens: Physics: Chapter 21: Mechanical Waves: QuizAnniaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Wave MechanicsDocument4 pagesActivity 1 Wave MechanicsAeriel May PliegoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AcousticsDocument180 pagesFundamentals of Acousticscastro100% (8)
- Serway Chapter - 41Document36 pagesSerway Chapter - 41Lujain TamimiNo ratings yet
- Ultra Sonic TestingDocument160 pagesUltra Sonic TestingKarina bautista ramon100% (1)
- Practice Usapho X: Kevin ZhouDocument5 pagesPractice Usapho X: Kevin ZhouAkshat goyalNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam 50 60% LegitDocument20 pagesPhysics Exam 50 60% Legitrajiel bautista50% (4)
- CNS Est4Document8 pagesCNS Est4Jesther Liwag100% (1)
- Activity 2 LP Radio WavesDocument6 pagesActivity 2 LP Radio Wavesapi-313517608100% (1)
- Comsol y Ondas UltrasonicasDocument7 pagesComsol y Ondas UltrasonicasCelesteCebedioNo ratings yet
- The Abbe Principle Revisited by Bryan 1979Document4 pagesThe Abbe Principle Revisited by Bryan 1979ASHOKNo ratings yet
- Experiment On LaserDocument4 pagesExperiment On LaserSiddharth GautamNo ratings yet
- Prelim/Midterm Examination I. Multiple ChoiceDocument1 pagePrelim/Midterm Examination I. Multiple ChoiceMaria Deborah Vivas BaluranNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Beginner S Guide Universe 8th Edition Chaisson Test BankDocument37 pagesAstronomy Beginner S Guide Universe 8th Edition Chaisson Test Bankworkdayembolism7ldf5100% (13)
- Planning of Line-Of-Sight Radio Relay Systems - Part 1Document118 pagesPlanning of Line-Of-Sight Radio Relay Systems - Part 1aezzat100% (1)
- Soal Seleksi Tahap I A. Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesSoal Seleksi Tahap I A. Multiple Choice QuestionsAgung PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation: Question BankDocument6 pagesUnit 7: Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation: Question BankNathanianNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Sound WavesDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Sound Wavespdtgpuplg100% (1)
- 1.6 Sound WavesDocument14 pages1.6 Sound Wavespanitiafiziksmkb100% (1)
- Sir Saqib 10th Physics Full Book-2 2016-17Document2 pagesSir Saqib 10th Physics Full Book-2 2016-17ahsanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12Document253 pagesChemistry 12mukesh_mlb100% (1)
- Reflection and Transmission Spectra of Multimode Interference Devices With Bragg GratingsDocument8 pagesReflection and Transmission Spectra of Multimode Interference Devices With Bragg GratingsPaola GongoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Quantum Mechanics - Part I: Institute of Theoretical Physics, Shanxi UniversityDocument36 pagesLecture Notes On Quantum Mechanics - Part I: Institute of Theoretical Physics, Shanxi Universitydpoudel1No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Em Waves Part 2 Activity SheetDocument2 pagesEm Waves Part 2 Activity SheetDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 5 - Engineering Mechanics-PhysicsDocument2 pagesProblem Set 5 - Engineering Mechanics-Physicsdaryl malolosNo ratings yet
- Jam PH2021Document20 pagesJam PH2021Rahul Satapathy100% (1)
- Phys HW17Document1 pagePhys HW17Adam LiangNo ratings yet
Physics Yr11 t3 2021
Physics Yr11 t3 2021
Uploaded by
Luke FleriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Yr11 t3 2021
Physics Yr11 t3 2021
Uploaded by
Luke FleriCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT FOR CURRICULUM,
LIFELONG LEARNING AND EMPLOYABILITY
Directorate for Learning and Assessment Programmes
Educational Assessment Unit Track 3
Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2021
YEAR 11 PHYSICS TIME: 2h
Name: _____________________________________ Class: _______________
Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided on the Examination Paper.
All working must be shown. The use of a calculator is allowed.
Where necessary take the acceleration due to gravity g = 10 m/s .
Density m=ρV
Pressure P=ρgh F=PA
Moments Moment = F × perpendicular distance
1
PE = m g h KE = mv Work Done = F s
Energy 2
Work Done = Energy Converted E=Pt
Force F=ma W = mg
total distance (u + v) t 1
Average Speed = s= s = ut + at
Motion total time 2 2
v = u + at v = u + 2as Momentum = m v
Q = It V = IR E = QV
L
P = IV R∝ E = IVt
Electricity A
1 1 1
R =R +R +R = +
R R R
N V
Electromagnetism =
N V
Heat ΔQ = m c Δθ
real depth the speed of light in air
η= η=
apparent depth the speed of light in medium
Waves v = f λ h image distance
1 m= =
f= h object distance
T
Radioactivity A = Z + N
Final Mark
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Theory
(Theory X 0.8)
Mark 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 15 15 15 125 100
Score
Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021 Page 1 of 16
SECTION A
This section has 8 questions. Each question carries 10 marks.
After being weighed, a lump of metal is
lowered into a measuring cylinder
containing 12 cm3 of water.
lump of
Name the instrument used to find the metal
mass of the lump of metal.
_______________________________ [1]
Using Figure 1, calculate the following Figure 1
quantities of the lump of metal:
the volume of the lump of metal.
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
the density of the metal.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Three liquids P, Q and R, are poured in a measuring
cylinder and allowed to settle. A small block is then
dropped into the measuring cylinder and this comes to
rest as shown in Figure 2. R
Underline the correct statement about the density Q
Block
of the block: [1]
P
A. It is equal to the density of R.
B. It is larger than the density of P.
Figure 2
C. It is larger than the density of Q.
Explain your answer in ci).
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
The block is divided into two unequal pieces. State if two pieces will have the
same density. Explain.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Page 2 of 16 Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021
Kayne decides to buy a new desk as shown in Figure 3. The mass of the new desk
is 45 kg.
Figure 3
Find the weight of the desk. _______________________________________ [1]
Name the upward force acting on each leg of the desk. _________________ [1]
The base of each leg is 3 cm by 3 cm. Find the total contact area in m2 of the desk’s
4 legs with the floor.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Calculate the pressure exerted on the floor by the desk.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
State two factors on which the pressure made by the desk on the floor depends.
1. ___________________________________________________________ [1]
2. ___________________________________________________________ [1]
Kayne is worried that the desk might damage
the parquet (wooden) flooring, so he decides to
buy a desk with two legs as shown in Figure 4.
State whether his reasoning is correct.
_______________________________________ [1] Figure 4
Explain your answer, assuming the mass of the desk remains the same.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021 Page 3 of 16
Tammy uses a ripple tank to study waves. She obtained the Displacement – Time
graph for waves as shown in Figure 5.
Displacement / mm
10
0
0.15 0.30 0.45 0.60 Time / s
−5
−10
Figure 5
For the waves shown in Figure 5, state the value of:
the amplitude: _______________________________________________ [1]
the periodic time: _____________________________________________ [1]
Calculate:
the frequency of the wave.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
the velocity of the wave if its wavelength is 15 mm.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Tammy observes that when water waves travel from deep to shallow at an angle,
the direction of travel changes. This is called __________________________ [1]
State what happens to the following, when a wave travels from a deep to a shallow
region:
velocity _____________________________________________ [1]
frequency ____________________________________________ [1]
wavelength __________________________________________ [1]
Page 4 of 16 Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021
Dwayne decides to observe the behaviour of light through prisms.
He sets up the apparatus as shown in Figure 6 to observe dispersion of white light.
White light
Screen
Prism
Figure 6
Explain the term ‘dispersion of white light’.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Continue the ray of white light to show how a spectrum is formed on the screen.
[2]
Mark where the colours violet and red are formed on the screen. [2]
Dwayne has two 45°–45°–90° prisms and
sets them up to make a periscope as shown A
Periscope
in Figure 7.
Draw two rays of light on Figure 7, one Object O B
from the top and the other from the
bottom of the object O, which pass
through the periscope to the eye. Assume Prism
that the critical angle of glass is 42°. [3]
Fill in: Total internal reflection occurs at Eye
surface AB since the angle of incidence is
____________ than the critical angle.
[1]
State one property of the image formed. Figure 7
___________________________________
[1]
Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021 Page 5 of 16
Jade takes part in a 100 m race. She starts from rest and reaches a velocity of 10
m/s in 10 s. She continues the race to the finish line at this speed.
Calculate Jade’s acceleration in the first 10 s.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Find the distance moved in the first 10 s.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Find the total time Jade takes to complete the 100 m race.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [3]
Sketch the graph of Jade’s motion in the grid below. [2]
A graph of velocity against time
12
10
8
Velocity in m/s
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
Time in s
Find Jade’s average velocity for the whole race.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Page 6 of 16 Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021
Figure 8 represents the orbits of several bodies in our solar Sun
system.
Earth
Explain the term ‘orbit’. B
C
________________________________________________ D
A
________________________________________________
_____________________________________________ [2] Figure 8
Name the largest planet in our solar system.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Underline the correct letter: In Figure 8, point (A, B, C) is not a planet but a comet
orbiting the Sun. [1]
Name the body at point D.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Number from 1 to 4, the list on the right in order of size
Earth
starting with the smallest. [1]
Milky Way
Figure 9 shows the Earth’s orbit.
Universe
Saturn
Earth
Sun
Figure 9
Name the force that keeps the Earth orbiting the Sun.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
On Figure 9, mark with an X the side of the Earth which is in daylight. Explain.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
The distance between the Sun and the Earth is 1.58 × 10−5 light years. Explain
the term ‘light year’.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021 Page 7 of 16
Figure 10 shows three
nuclei A, B and C of
different atoms.
Figure 10
Two of the nuclei are isotopes of each other.
Define the term ‘isotopes’.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
From Figure 10, identify which nuclei are isotopes of each other.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Write the proton number and nucleon number of element B.
Proton number: ______________________________________________ [1]
Nucleon number: _____________________________________________ [1]
The graph shows how the corrected
Corrected count rate /
counts per minute
count rate of a radioactive element
changes over a few days.
Define the term ‘half-life’.
_________________________________
_________________________________
_________________________________
Time / days
______________________________ [1]
Figure 11
Find the half-life of this radioactive element from Figure 11.
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
When the radioactive source is removed, the counter detects background radiation.
Explain the term ‘background radiation’ and give a source of such radiation.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Page 8 of 16 Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021
Figure 12 shows a fork lifter being used to lift barrels a height of 0.8 m onto a
lorry.
0.8 m
Figure 12
The upward force produced by the lifter is 2250 N. Calculate the work done on a
barrel to lift it on the lorry.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
The lifter is powered by batteries.
State the form of energy stored in the batteries.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Mention one advantage of using a battery-operated engine over a fuel engine.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
The lifting mechanism raises a barrel onto the lorry in 2 s.
Calculate the power of the lifting mechanism.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
The efficiency of the system is 65%. Find the input power.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Unfortunately, one of the barrels falls from the lorry. Calculate the velocity with
which it hits the ground.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021 Page 9 of 16
SECTION B
There are 3 questions in this section. Each question carries 15 marks.
This question is about electricity.
Figure 13 shows a circuit consisting of three appliances R, S and T connected to a
240 V electrical supply. Appliance R has a resistance of 60 Ω while S has a
resistance of 120 Ω.
X Y
9A
4A 2A
R
R S T
240 V ~
=
Figure 13
A fuse is required to protect the appliances from high currents.
On Figure 13, draw the symbol of a fuse that would protect all the three
appliances. [2]
State a suitable value for the fuse rating to be used.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Appliance T has an outer metal casing. Name another safety measure required
for this appliance.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
State the way in which the three appliances are connected.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Using the values given in Figure 13, calculate:
the current at point X.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
the current at point Y.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Page 10 of 16 Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021
the resistance of appliance T.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
the combined resistance of appliances R and S.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
the power developed by appliance R.
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
the energy converted by appliance S in 2 minutes.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
This question is about electromagnetism.
A bar magnet is freely suspended using a spring and is held over a coil as shown in
Figure 14.
Spring
S Bar
magnet
N
Centre zero
galvanometer
Coil
Figure 14
Draw the magnetic field around the bar magnet shown in Figure 14. [2]
Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021 Page 11 of 16
The lower end of the magnet is moved towards the coil and held at rest inside
the coil. As a result, the needle of the galvanometer deflects momentarily to
one side as a current is induced in the coil. Explain why this happens.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
The lower end of the magnet is then released. The magnet moves repeatedly
up and down over the coil due to the action of the spring. Describe what is
observed on the galvanometer and state the type of current induced in this case.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
State two ways by which a higher current can be induced.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
The coil shown in Figure 14 has 575 turns. It is used as the primary coil of a
transformer as shown in Figure 15. When a bulb is connected to the secondary coil,
an output current of 2.3 A flows through the bulb.
2.3 A
230 V
a.c. 4.6 W
supply
Primary coil Secondary coil
575 turns
Laminated iron core
Figure 15
Page 12 of 16 Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021
Explain in detail how a transformer produces an output current in the bulb.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [3]
Assume the transformer is an ideal transformer (100% efficient), calculate the
number of turns in the secondary coil if the power of the bulb is 4.6 W.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
A student doubles the number of turns in the secondary coil. State how this will
change the current and voltage in the bulb.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
In reality the transformer is not 100% efficient. Explain.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021 Page 13 of 16
This question is about heat transfer.
In 1945, Maria Telkes, an American physicist, developed a portable air inflated
plastic solar still like the one shown in Figure 16. It can be used in emergency life
rafts. The black container in the solar still is filled with seawater and it provides
fresh water in case of emergency.
Solar Still
Transparent dome
Infra-red rays
from the sun
Condensed water
flows in the rim
Seawater
Sea Fresh water
container
Layer of air Black container
Figure 16
Julian and Krissa tested one of these solar stills. They measured the temperature
of seawater while the solar still was left for 4 hours in the sun.
Time (hrs) 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Temperature (°C) 25.0 26.0 27.5 30.0 33.5 38.0 44.0 53.0 70.0
Plot a graph of Temperature (oC) on the y-axis against Time (hrs) on the x-axis.
[5]
Page 14 of 16 Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021
Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021 Page 15 of 16
The seawater is placed in a black container. Suggest why the container is black.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Julian suggests that the transparent dome manages to trap infrared radiation.
Explain how this takes place.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Krissa suggests that the layer of air below the black container reduces heat transfer.
Explain.
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
In terms of Kinetic theory, explain how evaporation of seawater takes place.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [2]
Julian and Krissa want to test two different models of solar stills to check which one
generates more fresh water.
Describe the procedure they should follow.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [3]
Mention one aspect they should take into consideration to ensure fair testing.
____________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ [1]
Page 16 of 16 Physics – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2021
You might also like
- Scienceclinic Smartprep GR11 Dbe Eng 1 PDFDocument44 pagesScienceclinic Smartprep GR11 Dbe Eng 1 PDFCayden Davids100% (4)
- Foundation Certificate FC312 Physics (B) End of Module Open Book Examination (Practice) Question Book Time Allowed: 120 MinutesDocument11 pagesFoundation Certificate FC312 Physics (B) End of Module Open Book Examination (Practice) Question Book Time Allowed: 120 MinutesNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- LTE ATOL RF PlannningDocument78 pagesLTE ATOL RF PlannningNikhil SwadiaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of IlluminationDocument12 pagesFundamental of IlluminationMinerva AbantoNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr11 t3 2020Document16 pagesPhysics Yr11 t3 2020Luke FleriNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr11 t3 2019Document12 pagesPhysics Yr11 t3 2019Luke FleriNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Physics TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools - SAMPLE PAPERDocument13 pagesYear 11 Physics TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools - SAMPLE PAPERtrical27 tricalNo ratings yet
- PH 2023Document14 pagesPH 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Yr 12 2.7 Int Nature Q 03Document10 pagesYr 12 2.7 Int Nature Q 03trubriteNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr10 t3 2021Document12 pagesPhysics Yr10 t3 2021Rebecca SciberrasNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr10 t3 2017Document11 pagesPhysics Yr10 t3 2017Rebecca SciberrasNo ratings yet
- Chap.1 NoteDocument37 pagesChap.1 NoteRachell RequellNo ratings yet
- Paper-2 With Solution PhysicsDocument19 pagesPaper-2 With Solution Physicsanunay.mishra4141No ratings yet
- 24 June 2022 Shift I PhysicsDocument6 pages24 June 2022 Shift I PhysicsArav IyerNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities Units & DimensionsDocument8 pagesPhysical Quantities Units & DimensionsVictor OduorNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample (17th Nov 2023)Document8 pagesPhysics Sample (17th Nov 2023)shamimshafeb2005No ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument24 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelGaneshNo ratings yet
- 2 Hours and 30 Minutes: List of Physical ConstantsDocument11 pages2 Hours and 30 Minutes: List of Physical ConstantsAdam mahabirNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument13 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelShashwat ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr10 t3 2019Document12 pagesPhysics Yr10 t3 2019Rebecca SciberrasNo ratings yet
- Percubaan Negeri Melaka 2020 (K2)Document7 pagesPercubaan Negeri Melaka 2020 (K2)FATIN FARHANAH BINTI HALIDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Exam Vibrations and NoiseDocument6 pagesExam Vibrations and NoisejoaoftabreuNo ratings yet
- Nurture Course (Phase: MNC) : Pattern / Type: Neet / Minor Answer Key Pre-Medical 2021 24-11-2019Document6 pagesNurture Course (Phase: MNC) : Pattern / Type: Neet / Minor Answer Key Pre-Medical 2021 24-11-2019VadoNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Units and DimensionsDocument12 pagesPhysical Quantities, Units and Dimensionsdavid ama100% (1)
- Fis 24Document6 pagesFis 24syafrina novitaNo ratings yet
- Units & DimensionsDocument6 pagesUnits & DimensionsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Name - Summer Assignment - Part 1 Fall 2021 - Spring 2022Document11 pagesAP Physics 1 Name - Summer Assignment - Part 1 Fall 2021 - Spring 2022Pradyun GREEN CELL VOLUNTEERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelhassanNo ratings yet
- This Exam Is Formed of Four Obligatory Exercises in Two Pages Non Programmable Calculators Are AllowedDocument3 pagesThis Exam Is Formed of Four Obligatory Exercises in Two Pages Non Programmable Calculators Are AllowedMJ TarhiniNo ratings yet
- Skull Crusher-1 - Class XI - JEE (Adv) - PhysicsDocument3 pagesSkull Crusher-1 - Class XI - JEE (Adv) - Physicslootera715No ratings yet
- Physol Examination Series: PESM01 Answer KeyDocument23 pagesPhysol Examination Series: PESM01 Answer Keykapil sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22nattawat10720No ratings yet
- hw8 PDFDocument44 pageshw8 PDFShaya Nirenberg0% (3)
- Exam Vibrations and NoiseDocument5 pagesExam Vibrations and NoisejoaoftabreuNo ratings yet
- MECHANICSDocument65 pagesMECHANICSDr. Unoma OkoraforNo ratings yet
- Pundra University of Science & Technology: Assignment On: PhysicsDocument8 pagesPundra University of Science & Technology: Assignment On: PhysicsSYED FARHAN REZANo ratings yet
- Exercises 2Document7 pagesExercises 2andre130912No ratings yet
- 9702 w17 QP 42 PDFDocument28 pages9702 w17 QP 42 PDFSabeha KhanNo ratings yet
- SPHL Sample ProblemsDocument20 pagesSPHL Sample ProblemsĐức TiếnNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 05 01Document2 pagesWorksheet 05 01BadeekhNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Week 1 Lesson 2Document4 pagesGrade 10 Physics Week 1 Lesson 2Daniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving I: Mathematical Techniques: 1 Dimensional AnalysisDocument27 pagesProblem Solving I: Mathematical Techniques: 1 Dimensional AnalysisTest EmailNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 AnswerDocument10 pagesTutorial 1 AnswerHafizuddin AdzharNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/04Document26 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/04sinting lim100% (1)
- Topic 1: Measurement and UncertaintiesDocument4 pagesTopic 1: Measurement and UncertaintiesHoa Dinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 2016 HW PDFDocument38 pagesAP Physics 1 2016 HW PDFAnika KimNo ratings yet
- 9702 w16 QP 43 PDFDocument24 pages9702 w16 QP 43 PDFSajidAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ExamplesDocument11 pagesChapter 6 ExamplesSurya NarasimanNo ratings yet
- Dimensions & Units: Q MC (TDocument2 pagesDimensions & Units: Q MC (TS1S0334 苏熙文SOO XI WENNo ratings yet
- Break-Up of Questions: Mechanics Sound Heat Electromagnetism Optics Modern Physics 6 2 2 5 2 3Document12 pagesBreak-Up of Questions: Mechanics Sound Heat Electromagnetism Optics Modern Physics 6 2 2 5 2 3Jasbir MaanNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Week 8: Learning Activity Sheet 1 Solve Problems Involving Logarithmic Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesDocument6 pagesQuarter 1 - Week 8: Learning Activity Sheet 1 Solve Problems Involving Logarithmic Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesJiwon ParkNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/22Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/22王涛No ratings yet
- Dimensional Anaylsis - Part 2Document11 pagesDimensional Anaylsis - Part 2khosatintswalo1010No ratings yet
- Physics Assignment NewDocument7 pagesPhysics Assignment NewSYED FARHAN REZANo ratings yet
- Paper 2 With Solution PhysicsDocument19 pagesPaper 2 With Solution PhysicsMuhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/22LINH DUONGNo ratings yet
- November 2016 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Physics A-LevelDocument24 pagesNovember 2016 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Physics A-LevelcamaralckinNo ratings yet
- Dimension of Physical QuantitiesDocument2 pagesDimension of Physical QuantitiesPriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- The Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64From EverandThe Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64No ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lesson 2b Fractions To Percent WorksheetDocument1 pageLesson 2b Fractions To Percent WorksheetLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2c Decimal To Fractions Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pageLesson 2c Decimal To Fractions Worksheet Answer KeyLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2c Decimal To Fractions WorksheetDocument1 pageLesson 2c Decimal To Fractions WorksheetLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1a Decimal Terminating Nonterminating and Repeating WorksheetDocument1 pageLesson 1a Decimal Terminating Nonterminating and Repeating WorksheetLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2b Fractions To Percent Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pageLesson 2b Fractions To Percent Worksheet Answer KeyLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2a Converting Fraction To Decimal Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pageLesson 2a Converting Fraction To Decimal Worksheet Answer KeyLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1a Decimal Terminating Nonterminating and Repeating Vocabularies Lecture NoteDocument1 pageLesson 1a Decimal Terminating Nonterminating and Repeating Vocabularies Lecture NoteLuke FleriNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr11 t3 2020Document16 pagesPhysics Yr11 t3 2020Luke FleriNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr11 t3 2019Document12 pagesPhysics Yr11 t3 2019Luke FleriNo ratings yet
- Results Reporter: QUIZ RESULTS FOR Tippens: Physics: Chapter 21: Mechanical Waves: QuizDocument5 pagesResults Reporter: QUIZ RESULTS FOR Tippens: Physics: Chapter 21: Mechanical Waves: QuizAnniaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Wave MechanicsDocument4 pagesActivity 1 Wave MechanicsAeriel May PliegoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AcousticsDocument180 pagesFundamentals of Acousticscastro100% (8)
- Serway Chapter - 41Document36 pagesSerway Chapter - 41Lujain TamimiNo ratings yet
- Ultra Sonic TestingDocument160 pagesUltra Sonic TestingKarina bautista ramon100% (1)
- Practice Usapho X: Kevin ZhouDocument5 pagesPractice Usapho X: Kevin ZhouAkshat goyalNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam 50 60% LegitDocument20 pagesPhysics Exam 50 60% Legitrajiel bautista50% (4)
- CNS Est4Document8 pagesCNS Est4Jesther Liwag100% (1)
- Activity 2 LP Radio WavesDocument6 pagesActivity 2 LP Radio Wavesapi-313517608100% (1)
- Comsol y Ondas UltrasonicasDocument7 pagesComsol y Ondas UltrasonicasCelesteCebedioNo ratings yet
- The Abbe Principle Revisited by Bryan 1979Document4 pagesThe Abbe Principle Revisited by Bryan 1979ASHOKNo ratings yet
- Experiment On LaserDocument4 pagesExperiment On LaserSiddharth GautamNo ratings yet
- Prelim/Midterm Examination I. Multiple ChoiceDocument1 pagePrelim/Midterm Examination I. Multiple ChoiceMaria Deborah Vivas BaluranNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Beginner S Guide Universe 8th Edition Chaisson Test BankDocument37 pagesAstronomy Beginner S Guide Universe 8th Edition Chaisson Test Bankworkdayembolism7ldf5100% (13)
- Planning of Line-Of-Sight Radio Relay Systems - Part 1Document118 pagesPlanning of Line-Of-Sight Radio Relay Systems - Part 1aezzat100% (1)
- Soal Seleksi Tahap I A. Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesSoal Seleksi Tahap I A. Multiple Choice QuestionsAgung PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation: Question BankDocument6 pagesUnit 7: Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation: Question BankNathanianNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Sound WavesDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Sound Wavespdtgpuplg100% (1)
- 1.6 Sound WavesDocument14 pages1.6 Sound Wavespanitiafiziksmkb100% (1)
- Sir Saqib 10th Physics Full Book-2 2016-17Document2 pagesSir Saqib 10th Physics Full Book-2 2016-17ahsanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12Document253 pagesChemistry 12mukesh_mlb100% (1)
- Reflection and Transmission Spectra of Multimode Interference Devices With Bragg GratingsDocument8 pagesReflection and Transmission Spectra of Multimode Interference Devices With Bragg GratingsPaola GongoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Quantum Mechanics - Part I: Institute of Theoretical Physics, Shanxi UniversityDocument36 pagesLecture Notes On Quantum Mechanics - Part I: Institute of Theoretical Physics, Shanxi Universitydpoudel1No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Em Waves Part 2 Activity SheetDocument2 pagesEm Waves Part 2 Activity SheetDebbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 5 - Engineering Mechanics-PhysicsDocument2 pagesProblem Set 5 - Engineering Mechanics-Physicsdaryl malolosNo ratings yet
- Jam PH2021Document20 pagesJam PH2021Rahul Satapathy100% (1)
- Phys HW17Document1 pagePhys HW17Adam LiangNo ratings yet