Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pasco Antibiotics PDF
Pasco Antibiotics PDF
Uploaded by
Nicole Obispo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views7 pagesThis document summarizes information about four antibiotics: amoxicillin, cephalexin, cefotetan, and cefepime. It provides the name, mode of action, common indications, potential side effects, and important nursing considerations for each drug. The antibiotics are all in the penicillin and cephalosporin classes and work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. Their indications include respiratory, skin, urinary tract, and other infections. Common side effects are gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and nausea. Nurses should monitor for side effects and assess renal, hepatic, and other organ function during treatment.
Original Description:
Original Title
PASCO_ANTIBIOTICS (2).pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes information about four antibiotics: amoxicillin, cephalexin, cefotetan, and cefepime. It provides the name, mode of action, common indications, potential side effects, and important nursing considerations for each drug. The antibiotics are all in the penicillin and cephalosporin classes and work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. Their indications include respiratory, skin, urinary tract, and other infections. Common side effects are gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and nausea. Nurses should monitor for side effects and assess renal, hepatic, and other organ function during treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views7 pagesPasco Antibiotics PDF
Pasco Antibiotics PDF
Uploaded by
Nicole ObispoThis document summarizes information about four antibiotics: amoxicillin, cephalexin, cefotetan, and cefepime. It provides the name, mode of action, common indications, potential side effects, and important nursing considerations for each drug. The antibiotics are all in the penicillin and cephalosporin classes and work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. Their indications include respiratory, skin, urinary tract, and other infections. Common side effects are gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and nausea. Nurses should monitor for side effects and assess renal, hepatic, and other organ function during treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Julianne Ninchie P.
Pasco
BSN 2A
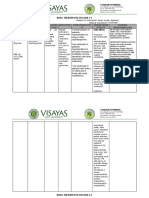
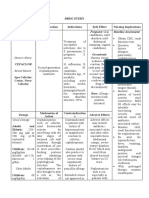
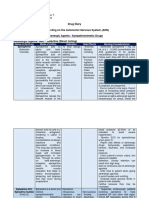
Antibiotics: Penicillins
Name of the Mode of Action Indication Side effects Nursing
drug considerations
1. amoxicillin It acts through Susceptible Oral suspension: Monitor signs of
the inhibition of infections diarrhea diarrhea,
cell wall including rash abdominal pain,
biosynthesis that ear/nose/throat vomiting fever, mucus in
leads to the (ENT), nausea stool, nausea,
death of the genitourinary Triple therapy: vomiting, and
bacteria. tract, skin and diarrhea heartburn.
skin structures, headache
lower taste
respiratory, perversion
acute Dual therapy
uncomplicated diarrhea
gonorrhea. headache
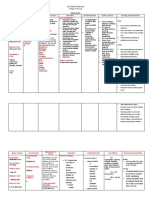
Antibiotics: Cephalosporins
Name of the Mode of Action Indication Side effects Nursing
drug considerations
1. cephalexin A bactericidal Treatment for: nausea Assess if the
agent that acts Respiratory diarrhea patient is
by the inhibition tract vomiting allergic to
of bacterial cell- infections heartburn penicillin or
wall synthesis. otitis media stomach pain cephalosporin, if
skin and soft rectal or genital pregnant or
tissue itching lactating
infections dizziness
bone and extreme Do a renal
joint infection tiredness function tests,
genitourinary agitation respiratory
infections status, skin
confusion
acute prostitis status
headache
dental assessment. And
joint pain
infections culture and
sensitivity tests
of infected area.
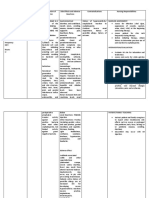
2. cefotetan Inhibits the third For prophylaxis diarrhea Determine
and final stage of and treatment of nausea history of
bacterial cell bacterial hepatic enzyme hypersensitivity
wall synthesis by infections like: elevation to
preferentially urinary tract hypersensitivity cephalosporins
binding to infections reaction and penicillins,
specific lower phlebitis and other drug
penicillin-binding respiratory nephrotoxicity allergies, before
proteins that are tract fever therapy begins.
located inside infections
the bacterial cell skin and skin Perform culture
wall. structure and sensitivity
infections studies before
gynecologic initiation of
infections therapy and
intra- during therapy,
abdominal as indicated.
infections
bone and Report onset of
joints loose stools or
infections diarrhea.
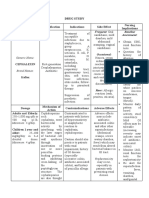
3. cefotaxime Inhibiting the bacteria and injection site Observe site
mucopeptide sepsis reactions (pain, closely for
synthesis in the bacterial irritation, hard extravasation
bacterial cell meningitis lump, or during
wall. Binding to and inflammation) administration
an enzymes vetriculitis rash
causing to lose gonorrhea itching Observe for
activity, disseminated hives signs of adverse
therefore, the gonococcal fever effects,
bacteria produce infection nausea especially those
defective cell surgical vomiting suggesting a
walls causing cell infection stomach pain superinfection
death. prophylaxis headache
urinary tract Observe for
diarrhea
infection signs of renal,
vaginal itching
intra- hepatic, or
or discharge
abdominal haematological
colitis
infections dysfunction
Less common:
skin and skin during
arrythmias
structure prolonged
low white blood therapy.
infections (i.e. cell levels
animal bite low blood
wounds) platelet levels
bone and yeast infection
joint
infections
gynecologic
infections
disseminated
Lyme disease
entric
infection
severe
leptospirosis
acute
bacterial
sinusitis
lower
respiratory
tract
infections
severe
typhoid fever
4. cefepime Inhibits bacterial pneumonia headache Watch for
cell wall febrile fever seizures; notify
synthesis by neutropenia neurotoxicity physician
covalently urinary tract nausea immediately if
binding enzymes infections vomiting patients
responsible for skin and skin abdominal pain develops or
the final step in structure hepatic injury increases
transpeptidation infections colitis seizure activity.
during Intra- vaginitis
peptidoglycan abdominal renal injury
wall synthesis. infections local site
This caused
injection
defects in the
irritation
cell wall leading
positive Coombs
to autolysis and
test without
subsequent
hemolysis
death of the
pancytopenia
organism.
anaplastic
anemia
Antibiotics: Aminoglycosides
Name of the Mode of Action Indication Side effects Nursing
drug considerations
1. neomycin Inhibits use in nausea Monitor signs of
sulfate bacterial protein preoperative vomiting hypersensitivity
synthesis bowel diarrhea reactions,
through preparation nephrotoxicity including
irreversible for patients ototoxicity pulmonary
binding to the undergoing neuromuscular symptoms or
30 S ribosomal colorectal blockage skin reactions.
subunit of surgery
susceptible suppression
bacteria. of intestinal
bacteria
hepatic coma
(portal-
systemic
encephalopat
hy)
infectious
diarrhea
Antibiotics: Macrolides
Name of the Mode of Action Indication Side effects Nursing
drug considerations
1. azithromycin Inhibits bacterial community - diarrhea Observe for
protein acquired nausea signs and
synthesis, pneumonia abdominal symptoms of
quorum-sensing pharyngitis or pain anaphylaxis.
and reduces the tonsilitis stomach
formation of uncomplicated upset Assess patient
biofilm. skin/skin vomiting skin for rash
structure constipation frequently
genital ulcer dizziness during therapy.
disease tiredness
pelvic headache
inflammatory sleep
disease problems
skin rash or
itching
ringing in the
ears
decreased
sense of taste
or smell
Antibiotics: Tetracyclines
Name of the Mode of Action Indication Side effects Nursing
drug considerations
1.demeclocycline Inhibits cell Lyme disease nausea Ask if the client is
growth by acne vomiting pregnant or
inhibiting bronchitis diarrhea lactating.
translation. It urinary loss of Pregnant woman
binds to the infections appetite cannot use it and
ribosomal gum diseas darkened skin it can pass into
subunit and malaria color breast milk and
prevent amino- gonorrhea swollen may affect bone
acyl tRNA from chlamydia tongue and tooth
binding to the A trouble development in
site of the swallowing an infant.
ribosome, which excessive
impairs protein thirst
synthesis by frequent
bacteria. irritation
severe
stomach pain
Antibiotics: Fluoroquinolons
Name of the Mode of Action Indication Side effects Nursing
drug considerations
1. moxifloxacin Inhibition of the acute sinusitis abdominal Watch for
enzymes chronic discomfort seizures.
topoisomerase II bronchitis diarrhea
and community- nausea Be alert for
topoisomerase acquired vomiting anxiety,
IV required for pneumonia mouth sores agitation, or
bacterial DNA complicated headaches other alterations
replication, skin and skin dizziness in mental status.
transcription, structure blurred vision
repair, and infections skin itching
recombination. bacterial agitation
conjunctivitis anxiety
insomia
Antibiotics: Sulfonamides
Name of the Mode of Action Indication Side effects Nursing
drug considerations
1. sulfadiazine It inhibits chancroid headache Monitor renal
formation of trachoma depression and liver
tetrahydrofolic inclusion seizures function test
acid from conjunctivitis hallucinations results.
paraminobenzoic nocardiosis nausea
(PABA), urinary tract vomiting Monitor patient
preventing infection diarrhea for signs of
bacterial cell (secondaary abdominal pain blood dyscrasia.
synthesis of folic therapy) toxic nephrosis
acid. toxoplasmosis Bee alet for
jaundice
ncephalitis signs of
hypersensitivity
meningococcal leukopenia,
reactions
menigitis including
acute otitis feever, sore
media throat, and
rheumatic signs of
fever infection.
Antibiotics: Anti TB
Name of the Mode of Action Indication Side effects Nursing
drug considerations
1. streptomycin Binds to four mycobacterium nausea Report any
nucleotides for tuberculosis vomiting muscle
16S rRNA and Yersinia pestis stomach weakness or
and a single Francisella upset paralysis that
amino acid of tularensis loss of occurs following
protein S12. This Brucella appetite injection of high
leads to H.influenza vertigo doses.
interference K. pneumoniae injection site
with the E. coli reactions Monitor signs of
initiation tingling or low magnesium
complex. prickling levels, such as
sensation in lethargy,
the face irritability,
rash insomnia,
fever muscle tremors,
hives and confusion.
edema
2. capreomycin Inhibit protein tuberculosis in black, tarry Observe
synthesis by combination stools injection sites
binding to the with other blood in the for signs of
70S ribosomal drugs urine excessive
unit. It also change in the bleeding and
binds to frequency of inflammation
components in urintion
the bacterial cell chest pain Evaluate hearing
which result in chills and balance by
the production cough audiometric
of abnormal difficulty in measurement
proteins. These breathing and test
proteins are dizziness vestibular
necessary for feeling of function.
the bacteria's fullness in
survival. the ears
fever
loss of
balance
loss of
hearing
nausea
vomiting
unusual
bleeding or
bruising
unusual
tiredness or
weakness
You might also like
- UntitledDocument996 pagesUntitledy100% (4)
- EssayDocument3 pagesEssayDavid RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Drug StudyDocument1 pageCephalexin Drug StudyAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanjamieboyRN91% (32)
- Name of Drug: Ceftazidime Therapeutic Class: Pharmacologic Class: CephalosporinsDocument20 pagesName of Drug: Ceftazidime Therapeutic Class: Pharmacologic Class: CephalosporinsianNo ratings yet
- Drug Study, NCP, and Concept MapDocument8 pagesDrug Study, NCP, and Concept MapMj BollenaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Ceftriaxone)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Ceftriaxone)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime 260 MG Ivttq 8 HRS AnstDocument2 pagesCefuroxime 260 MG Ivttq 8 HRS AnstKate TergaNo ratings yet
- AsncudDocument2 pagesAsncudJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MugnaDocument7 pagesDrug Study Mugnakint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Rabia Drug StudyDocument6 pagesRabia Drug StudyMonmon BagarinaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDrug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityGilianne JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RyDocument30 pagesDrug Study RyRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesYamatoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Darunday Rotation 3 - DarundayDocument5 pagesDrug Study Darunday Rotation 3 - DarundayEzra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJIREH MAE NOTARTENo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Matthew SuperioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudySofia CartallaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCase Pres Drug StudyMark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime GonzagaDocument3 pagesCefuroxime GonzagaSheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- 5drug StudyDocument7 pages5drug StudyPALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyJessica Pacris MaramagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefazolinDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefazolinNichole DancelNo ratings yet
- Name of Patient: E.J.P Ward/Room/Bed #: Pedia Ward/G.I./Bed 1 Age & Sex: 2 Y.o/ Female Diagnosis: Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pageName of Patient: E.J.P Ward/Room/Bed #: Pedia Ward/G.I./Bed 1 Age & Sex: 2 Y.o/ Female Diagnosis: Urinary Tract InfectionSALMA M. TUANONo ratings yet
- ... Drug Study...Document2 pages... Drug Study...Chona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyJanzelvine Lee MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeDocument2 pagesDrug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- Kardex, Drug Study and CheckDocument12 pagesKardex, Drug Study and CheckJemina Rafanan RacadioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drug/Classification Dose/Route Mechanism of Action Common Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Drug/Classification Dose/Route Mechanism of Action Common Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLiiza G-GsprNo ratings yet
- CERAME, CLARISSE B. - NUR 146 DRUG STUDY - Antibiotic ProphylaxisDocument3 pagesCERAME, CLARISSE B. - NUR 146 DRUG STUDY - Antibiotic ProphylaxisClarisse Biagtan CerameNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Cephalexin)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Cephalexin)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Cefoxitin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- Drug Study CeftriaxioneDocument2 pagesDrug Study CeftriaxioneJulie LesmorasNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeDocument3 pagesDrug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- Banaag Antibacterial MedsDocument5 pagesBanaag Antibacterial MedsPrince JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyECHO-FOXTROT-Mananing, Princess C.No ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Cefaclor)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Cefaclor)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Penicillin G Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPenicillin G Drug StudyRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Penicillin G Benza Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPenicillin G Benza Drug StudyRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug AlgeDocument1 pageName of Drug Algealgerich_delacuestaNo ratings yet
- Galang-D SDocument3 pagesGalang-D Sgalang.andrea.mNo ratings yet
- Drugsstudy Different ObDocument8 pagesDrugsstudy Different ObElvis DuotNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- History: Allergy To CiprofloxacinDocument1 pageHistory: Allergy To CiprofloxacinShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJanah PagayNo ratings yet
- Adults: 1-4 G/Day in Divided Doses 250 Mgpoq6 HR Usual DoseDocument3 pagesAdults: 1-4 G/Day in Divided Doses 250 Mgpoq6 HR Usual Dosemylene dabucolNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Class Summary TableDocument6 pagesAntibiotic Class Summary TableuserherwwweNo ratings yet
- VILLAMIN - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesVILLAMIN - Drug StudyAzizah VillaminNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesDocument3 pagesDrug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudygabbyNo ratings yet
- DS - Mod9Document2 pagesDS - Mod9designericlelynsoronioNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Outhwestern NiversityDocument22 pagesCollege of Nursing: Outhwestern NiversityMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument2 pagesCefuroximekristine_camerinoNo ratings yet
- Sev Ere Infe Ctio Ns Cau Sed by Sen Siti Ve Org Anis Ms (STRDocument16 pagesSev Ere Infe Ctio Ns Cau Sed by Sen Siti Ve Org Anis Ms (STRJAMES PATRICK MONTEMAYORNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of OxytocinDocument4 pagesDrug Study of OxytocinNichole DancelNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University: Institute of NursingDocument3 pagesFar Eastern University: Institute of Nursingshendae cosmianoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Insights into Acute Cystitis: Understanding, Management, and Future DirectionsFrom EverandComprehensive Insights into Acute Cystitis: Understanding, Management, and Future DirectionsNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children - Classification, Diagnosis and TreatmentFrom EverandUrinary Tract Infection in Children - Classification, Diagnosis and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Zalameda ANSDocument32 pagesZalameda ANSNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Subiaga Antiparkinsonismmuscle-RelaxantsDocument15 pagesSubiaga Antiparkinsonismmuscle-RelaxantsNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Pasco AntiviralsDocument2 pagesPasco AntiviralsNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Calara, KylaAnne BSN2A Nutrition LEC PDFDocument4 pagesCalara, KylaAnne BSN2A Nutrition LEC PDFNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Zalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingDocument16 pagesZalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Zalameda CNS-PNSDocument43 pagesZalameda CNS-PNSNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Subiaga - Bsn3-A - Activity#1Document1 pageSubiaga - Bsn3-A - Activity#1Nicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Zalameda - Hypothalamic and Pituitary Agents Adrenocortical Agents Thyroid and Parathyroid Anti Diabetic AgentsDocument55 pagesZalameda - Hypothalamic and Pituitary Agents Adrenocortical Agents Thyroid and Parathyroid Anti Diabetic AgentsNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Marcellana BSN2A NCPDocument3 pagesMarcellana BSN2A NCPNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Globalization - Alanzalon, Mary Grace L.Document1 pageGlobalization - Alanzalon, Mary Grace L.Nicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations and Symbols of Medical TermsDocument16 pagesAbbreviations and Symbols of Medical TermsRainida Catherine Romatho100% (1)
- Vitamin K: Adjunct To Vitamin DDocument7 pagesVitamin K: Adjunct To Vitamin DBeena WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Substance Abuse Among Adolescents in India: An OverviewDocument6 pagesAssessment of Substance Abuse Among Adolescents in India: An OverviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Secondary SyphilisDocument2 pagesSecondary SyphilisRoberto López MataNo ratings yet
- Ecg Findings in Pulmonary Embolism: Acute Cor PulmonaleDocument1 pageEcg Findings in Pulmonary Embolism: Acute Cor PulmonaleSuci Dika UtariNo ratings yet
- Stephanie Duran, BSN, RN: 12445 Paseo Lindo Drive El Paso, Texas 79928 (915) 328-1303Document1 pageStephanie Duran, BSN, RN: 12445 Paseo Lindo Drive El Paso, Texas 79928 (915) 328-1303api-418681616No ratings yet
- What Is Four Handed DentistryDocument7 pagesWhat Is Four Handed DentistryMahardhika PutriNo ratings yet
- SMM Review Form 6-28-2016 LongDocument8 pagesSMM Review Form 6-28-2016 Longahmad abadaNo ratings yet
- Howtohelpsomeonewithaneatingdisorderwebquest MegankleinDocument3 pagesHowtohelpsomeonewithaneatingdisorderwebquest Megankleinapi-299839434No ratings yet
- All About Introduction To URPDocument36 pagesAll About Introduction To URPFaria HossainNo ratings yet
- مهم للمزاولةDocument13 pagesمهم للمزاولةbelal nurseNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing Spondylitis Symptoms, Causes, Treatments (1161)Document2 pagesAnkylosing Spondylitis Symptoms, Causes, Treatments (1161)Saad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Common Drug Side Effects - Drug Interactions - Elderly - Primary Care - 2017Document8 pagesCommon Drug Side Effects - Drug Interactions - Elderly - Primary Care - 2017opulgarNo ratings yet
- Printed in FranceDocument23 pagesPrinted in FranceNina MarliatiNo ratings yet
- Influence of Food-Derived Advanced Glycation End Products On HealthDocument5 pagesInfluence of Food-Derived Advanced Glycation End Products On Healthjose venaNo ratings yet
- Liver Failure: Lyn CrellinDocument39 pagesLiver Failure: Lyn CrellinTran Ngoc Hoang PhapNo ratings yet
- Volunteer Opportunities: Aarp-Oregon State OfficeDocument16 pagesVolunteer Opportunities: Aarp-Oregon State OfficeJimee PhanNo ratings yet
- The Physician AssistantDocument12 pagesThe Physician AssistantThe Physician Assistant LifeNo ratings yet
- Nursing InterventionsDocument1 pageNursing InterventionsTancred UyNo ratings yet
- TLA On Nutrition in Late AdulthoodDocument4 pagesTLA On Nutrition in Late AdulthoodEdda Marie PidutNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Month Narrative IIIDocument2 pagesNutrition Month Narrative IIIRod Dumala GarciaNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support CPR and First AidDocument112 pagesBasic Life Support CPR and First AidArthur LimNo ratings yet
- Case Note Template Group ProjectDocument3 pagesCase Note Template Group Projectnatalie forsythNo ratings yet
- 2022 Hjy SPLKPM Sinopsisbuku 2Document2 pages2022 Hjy SPLKPM Sinopsisbuku 2smile2jing100% (1)
- Prevention of Catheter Associated Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument61 pagesPrevention of Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infectionsdex99No ratings yet
- Bab 2Document16 pagesBab 2jihan febriyantiNo ratings yet
- BCMJ Vol58 No 3 Cardiorespiratory FitnessDocument7 pagesBCMJ Vol58 No 3 Cardiorespiratory FitnessJuanMa Correa SanabriaNo ratings yet