Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsREACTION PAPER - VIdeo 14A and 15A
REACTION PAPER - VIdeo 14A and 15A
Uploaded by
Chilton John DuatThe document discusses chemical and biological wastewater treatment processes. It describes how Grundfos provides dosing pumps for chemical treatments like coagulation, flocculation, and disinfection in primary, secondary, and tertiary wastewater treatment. The biological process uses microorganisms to break down dissolved substances and removes nitrogen through nitrification and denitrification. Sludge is also treated, with the goal of biological treatment being to easily collect and dispose of decomposition results.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Biology Project On Sewage Treatment PlantDocument26 pagesBiology Project On Sewage Treatment Plantjananipriya84% (122)
- Lecture 4 - Liberalism and Bourbon Impacts Rizal's EraDocument1 pageLecture 4 - Liberalism and Bourbon Impacts Rizal's EraChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Secondary TreatmentDocument14 pagesSecondary TreatmentNasirNo ratings yet
- How Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisFrom EverandHow Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- V2i4 1160Document8 pagesV2i4 1160Ajay Kumar GantiNo ratings yet
- Wastewater TrainDocument3 pagesWastewater TrainLester Mercado100% (1)
- Wastewater Treatment MethodsDocument8 pagesWastewater Treatment MethodszzzamrNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment ProcessDocument4 pagesWaste Water Treatment ProcessDengAwutNo ratings yet
- Conventional Waste Water Treatment Process - Water ReuseDocument2 pagesConventional Waste Water Treatment Process - Water ReuseGeraldNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument3 pagesWaste Water TreatmentShiladitya ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Water PurificationDocument13 pagesWater PurificationKanchanNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument10 pagesWaste Water TreatmentPriyank LashkariNo ratings yet
- Secondary and Tertiary TreatmentDocument5 pagesSecondary and Tertiary TreatmentTerence VergaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Water TreatmentDocument4 pagesLecture 3 - Water TreatmentCorazon Francisco AustriaNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument14 pagesWaste Water TreatmentYash jadhavNo ratings yet
- LEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDocument5 pagesLEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDysmas100% (1)
- Lecture 3.Waste-Water-TreatmentDocument6 pagesLecture 3.Waste-Water-TreatmentDivya DiyaNo ratings yet
- Sewage Water TreatmentDocument8 pagesSewage Water Treatmentsivani rayavarapuNo ratings yet
- Industrial Wastewater TreatmentDocument7 pagesIndustrial Wastewater Treatmenthamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Textile Waste Water Management: Course: Introduction To General Chemistry Course Code: CHE 101Document7 pagesTextile Waste Water Management: Course: Introduction To General Chemistry Course Code: CHE 101Ishtiaq Ahmed MugdhaNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Document3 pagesBiological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument15 pagesWater727822tucv025No ratings yet
- Biological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Document4 pagesBiological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture-06: Sludge Treatment and Disposal: Ce 333: Environmental Engineering IiDocument6 pagesLecture-06: Sludge Treatment and Disposal: Ce 333: Environmental Engineering IiMirza Md. Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Lecture Iii Cve 503 Biological Treatment of Wastewater1Document41 pagesLecture Iii Cve 503 Biological Treatment of Wastewater1James Korbla Dodzi Hills100% (1)
- Haldia Institute of Technology Presentation For Environmental Sciences (MC - 401)Document12 pagesHaldia Institute of Technology Presentation For Environmental Sciences (MC - 401)subarna maitiNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT Environmental ChemistryDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT Environmental ChemistryAyesha MalikNo ratings yet
- Report of Educational VisitDocument5 pagesReport of Educational VisitHARSHADNo ratings yet
- Methods of Water PurificationDocument12 pagesMethods of Water PurificationjyotiNo ratings yet
- Sewage Wastewater Treatment GP 6Document9 pagesSewage Wastewater Treatment GP 6njsy02No ratings yet
- Water Waste Treatment: Prepared by Group 2Document41 pagesWater Waste Treatment: Prepared by Group 2Niman100% (1)
- VII. Water Treatment: A. Treatment of Wastewater and B. Treatment of Drinking WaterDocument33 pagesVII. Water Treatment: A. Treatment of Wastewater and B. Treatment of Drinking WaterMantha100% (1)
- Principles of Wastewater TreatmentDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Wastewater Treatmentaldren amigoNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument67 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantSWATHI ACHARNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument9 pagesExamDileepa NeranjanaNo ratings yet
- Sewage and SewerageDocument11 pagesSewage and SewerageStephen KaranNo ratings yet
- 9.6.2023 - Shorthand Notes On Sewage Sludge Treatment and DisposalDocument17 pages9.6.2023 - Shorthand Notes On Sewage Sludge Treatment and DisposalLucas AgumbaNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument9 pagesWaste Water Treatment MethodsAmira El GendyNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Technology in Sewage Waste WaterDocument4 pagesFermentation Technology in Sewage Waste Waterfama18No ratings yet
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocument48 pagesActivated Sludge Processrozma khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction-au-traitement-secondaireDocument8 pagesIntroduction-au-traitement-secondairesalma17052003No ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Water Waster Characteristics and Sewage TreatmentDocument2 pagesReaction Paper - Water Waster Characteristics and Sewage TreatmentChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Water Traetment Lecture 3Document41 pagesWater Traetment Lecture 3romanbrock991No ratings yet
- Hope Seminar 2Document9 pagesHope Seminar 2SOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Potable Water Purification: Water Treatment Describes Those Industrial-Scale Processes Used To MakeDocument7 pagesPotable Water Purification: Water Treatment Describes Those Industrial-Scale Processes Used To MakeKay RenNo ratings yet
- Finals NotesDocument4 pagesFinals NotescherriebaekkiebbhNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment Plant: Theni Kammavar Sangam Public SchoolDocument26 pagesSewage Treatment Plant: Theni Kammavar Sangam Public SchoolAritra Bag100% (1)
- Waste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementDocument27 pagesWaste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementSujith KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1Document11 pagesLecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1negaathanipalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Process Wastewater CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesProcess Wastewater CharacteristicsYeAsin AraFatNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Methods Physical Unit Operations Chemical Unit Operations Biological Unit OperationsDocument34 pagesWastewater Treatment Methods Physical Unit Operations Chemical Unit Operations Biological Unit OperationsNuman100% (1)
- Lesson 15 - Trickling FiltersDocument10 pagesLesson 15 - Trickling FiltersShane RodriguezNo ratings yet
- A MICRO PROJECT ON "Prepare Report On Household Water Filtrations Unit"Document9 pagesA MICRO PROJECT ON "Prepare Report On Household Water Filtrations Unit"pmali1408No ratings yet
- Unit Operations & Processes in Waste Water TreatmentDocument16 pagesUnit Operations & Processes in Waste Water Treatmentbefkadu ayalkieNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Works... The BasicsDocument6 pagesWastewater Treatment Works... The BasicsOboy KristantoNo ratings yet
- 3213 Activity 1Document3 pages3213 Activity 1Gen UntalanNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Plant: Chlorination AerationDocument6 pagesWater Treatment Plant: Chlorination AerationGladylyn MirandaNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment EnviBiotechDocument8 pagesSewage Treatment EnviBiotechAbdul KabirNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument2 pagesWaste Water TreatmentMuhammad HumaidNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment PlantDocument2 pagesWastewater Treatment PlantJerson RicafortNo ratings yet
- How Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial ROFrom EverandHow Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial RORating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Environmental Engineering Introduction PDFDocument84 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Introduction PDFChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- EM4 Assignment 5 AnswerDocument5 pagesEM4 Assignment 5 AnswerChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- BES 12 Reviewer For PrelimDocument5 pagesBES 12 Reviewer For PrelimChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Water CycleDocument2 pagesReaction Paper - Water CycleChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Assignment 3 (Lec 3 - Video A, B, C)Document2 pagesReaction Paper - Assignment 3 (Lec 3 - Video A, B, C)Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Video 12A, B, C Sources of Wastewater and How It Is Treated in The Wastewater PlantDocument3 pagesReaction Paper - Video 12A, B, C Sources of Wastewater and How It Is Treated in The Wastewater PlantChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Video 13A and 13BDocument1 pageReaction Paper - Video 13A and 13BChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Water Waster Characteristics and Sewage TreatmentDocument2 pagesReaction Paper - Water Waster Characteristics and Sewage TreatmentChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Integrals by Partial DecompositionDocument8 pagesIntegrals by Partial DecompositionChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES 7 - First Order Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesLECTURE NOTES 7 - First Order Differential EquationsChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 8 - The Bernoulli EquationDocument7 pagesLECTURE 8 - The Bernoulli EquationChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 11 - Physical Application - Exponential DecayDocument11 pagesLECTURE 11 - Physical Application - Exponential DecayChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY 20 - Locating Sounding (Answers)Document4 pagesLABORATORY 20 - Locating Sounding (Answers)Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 - Types of Solution To A Differential Equation EM4Document4 pagesLECTURE 2 - Types of Solution To A Differential Equation EM4Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - CRITIQUING NEOLIBERALISMDocument3 pagesGlobalization - CRITIQUING NEOLIBERALISMChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - CHAPTER SUMMARY Chapter 2Document4 pagesGlobalization - CHAPTER SUMMARY Chapter 2Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 5 - Homogeneous Differential EquationsDocument21 pagesLECTURE 5 - Homogeneous Differential EquationsChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - POPULAR NEOLIBERAL "THEORY" - THE CASE OF THOMAS FRIEDMANDocument5 pagesGlobalization - POPULAR NEOLIBERAL "THEORY" - THE CASE OF THOMAS FRIEDMANChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - NEOLIBERALISM - AN EXEMPLARYDocument5 pagesGlobalization - NEOLIBERALISM - AN EXEMPLARYChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - NEOLIBERALISM AS EXCEPTIONDocument3 pagesGlobalization - NEOLIBERALISM AS EXCEPTIONChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Definition and Classifications of Differential EquationsDocument5 pagesLECTURE 1 - Definition and Classifications of Differential EquationsChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - BROADER, MORE RECENT CHANGESDocument4 pagesGlobalization - BROADER, MORE RECENT CHANGESChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - IF THERE IS SUCH A THING AS GLOBALIZAT ION, WHEN DID IT BEGINDocument4 pagesGlobalization - IF THERE IS SUCH A THING AS GLOBALIZAT ION, WHEN DID IT BEGINChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - GLOBALIZAT ION AND RELATE D PROCESSESDocument5 pagesGlobalization - GLOBALIZAT ION AND RELATE D PROCESSESChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization Chapter 3 SummaryDocument4 pagesGlobalization Chapter 3 SummaryChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Sur Lab 24 - Layout of Compound CurveDocument2 pagesSur Lab 24 - Layout of Compound CurveChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - NEOLIBERALISM AN EXEMPLARY STATEMENT AND THE BASIC PRINCIPLESDocument5 pagesGlobalization - NEOLIBERALISM AN EXEMPLARY STATEMENT AND THE BASIC PRINCIPLESChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Sur Lab 21 Assignment (Answer)Document2 pagesSur Lab 21 Assignment (Answer)Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY 25-Lay Out of Reversed CurveDocument5 pagesLABORATORY 25-Lay Out of Reversed CurveChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Polyaluminium Chloride MSDSDocument6 pagesPolyaluminium Chloride MSDSNandhakumarNo ratings yet
- OHSP LM Week 9 10 7 ScienceDocument2 pagesOHSP LM Week 9 10 7 ScienceLA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Polymer-Derived Ceramics and Their Space ApplicationsDocument107 pagesPolymer-Derived Ceramics and Their Space ApplicationsRAHUL BHASKARNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions PPT AlcoholsDocument43 pagesOrganic Reactions PPT Alcoholssmithsashay74No ratings yet
- Nurdr Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesNurdr Practice QuestionsSHEENA MAE DE LOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Astm D971Document4 pagesAstm D971JORGE SANTANDERNo ratings yet
- Banana Pseudo Stem CHAPTER 1 3Document53 pagesBanana Pseudo Stem CHAPTER 1 3mizzpain CabuyadaoNo ratings yet
- Flux Decline in Skim Milk UltrafiltrationDocument19 pagesFlux Decline in Skim Milk Ultrafiltrationpremnath.sNo ratings yet
- SAES-Q-001 (Criteria For The Design & Construction of Concrete Structures)Document5 pagesSAES-Q-001 (Criteria For The Design & Construction of Concrete Structures)Nino Celso Astillero100% (1)
- Advanced Materials - 2022 - Nair - 2D MBenes A Novel Member in The FlatlandDocument14 pagesAdvanced Materials - 2022 - Nair - 2D MBenes A Novel Member in The FlatlandVinay ThakurNo ratings yet
- Company Profil - PT Multan Kusuma SaktiDocument32 pagesCompany Profil - PT Multan Kusuma SaktiMariana LopNo ratings yet
- Fugalite Bio IN 2020Document8 pagesFugalite Bio IN 2020aasifNo ratings yet
- Water Report 17 JanDocument3 pagesWater Report 17 Janansar aliNo ratings yet
- Soldering Basic GuideDocument6 pagesSoldering Basic GuidechchuanNo ratings yet
- Forced Degradation - Mass BalanceDocument8 pagesForced Degradation - Mass BalanceppiccoliniNo ratings yet
- WM GSC MFL70761362 00 200526 00 WebDocument36 pagesWM GSC MFL70761362 00 200526 00 WebMaeNo ratings yet
- Guar ReportDocument44 pagesGuar ReportSatendra Singh GurjarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 BioGeoChemical CyclesDocument25 pagesModule 2 BioGeoChemical CyclesPonce GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Beach Babies WO Sunscreen SPF50+ SC-587-1Document1 pageBeach Babies WO Sunscreen SPF50+ SC-587-1ajitbadboy2No ratings yet
- Schmidt + Clemens: Weld Repair Practices in High Temperature MaterialsDocument46 pagesSchmidt + Clemens: Weld Repair Practices in High Temperature MaterialsmanojballaNo ratings yet
- 14 54 Namat Upvc DrainageDocument22 pages14 54 Namat Upvc DrainageImtiyaz KhanNo ratings yet
- STK1211 Practical Analytical ChemistryDocument39 pagesSTK1211 Practical Analytical Chemistrylox agencyNo ratings yet
- A320 - SRM - MSN - 05234 - 01-Aug-2019 - TASK 57-53-00-300-029 - Zone 1 - Skin Covered With Metal Strap RepairDocument20 pagesA320 - SRM - MSN - 05234 - 01-Aug-2019 - TASK 57-53-00-300-029 - Zone 1 - Skin Covered With Metal Strap Repairjr primeNo ratings yet
- RANGER - Rescue Davit Kit Shoring - Operating Manual CertificationDocument38 pagesRANGER - Rescue Davit Kit Shoring - Operating Manual CertificationAmr Adel HameedNo ratings yet
- Organic Peroxides PresentationDocument24 pagesOrganic Peroxides Presentationtatarey790% (1)
- Trace Impurities in Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Gas Chromatography and Effective Carbon NumberDocument13 pagesTrace Impurities in Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Gas Chromatography and Effective Carbon NumberAngel Cambero100% (1)
- Lett 8b04147Document5 pagesLett 8b04147Alane Priscilla AméricoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Rate of ReactionDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Rate of ReactionMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- For Teachers' Use Only: with 弋 mark eπ0Document22 pagesFor Teachers' Use Only: with 弋 mark eπ0Copper ShortswordNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - DLL For July 16 2019Document2 pagesMicrosoft Word - DLL For July 16 2019Marilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
REACTION PAPER - VIdeo 14A and 15A
REACTION PAPER - VIdeo 14A and 15A
Uploaded by
Chilton John Duat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesThe document discusses chemical and biological wastewater treatment processes. It describes how Grundfos provides dosing pumps for chemical treatments like coagulation, flocculation, and disinfection in primary, secondary, and tertiary wastewater treatment. The biological process uses microorganisms to break down dissolved substances and removes nitrogen through nitrification and denitrification. Sludge is also treated, with the goal of biological treatment being to easily collect and dispose of decomposition results.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses chemical and biological wastewater treatment processes. It describes how Grundfos provides dosing pumps for chemical treatments like coagulation, flocculation, and disinfection in primary, secondary, and tertiary wastewater treatment. The biological process uses microorganisms to break down dissolved substances and removes nitrogen through nitrification and denitrification. Sludge is also treated, with the goal of biological treatment being to easily collect and dispose of decomposition results.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesREACTION PAPER - VIdeo 14A and 15A
REACTION PAPER - VIdeo 14A and 15A
Uploaded by
Chilton John DuatThe document discusses chemical and biological wastewater treatment processes. It describes how Grundfos provides dosing pumps for chemical treatments like coagulation, flocculation, and disinfection in primary, secondary, and tertiary wastewater treatment. The biological process uses microorganisms to break down dissolved substances and removes nitrogen through nitrification and denitrification. Sludge is also treated, with the goal of biological treatment being to easily collect and dispose of decomposition results.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
NAME: Chilton John C.
Duat
COURSE/YEAR: BSCE – 2nd Year
Subject/Offer Number: BES 12_24324
REACTION PAPER
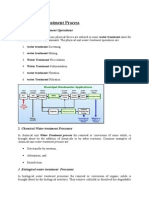
Chemical Treatment for the Waste Water Treatment Plant
In the Video, Grundfos was introduced as a water pump company that provides a big range of dosing
pumps – digital and mechanical dosing pumps that cover the entire treatment process at the wastewater
treatment plant. This includes including primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment, coagulation and
flocculation, substrate dosing, and alkalinity correction in sludge treatment. In their advanced primary
treatment process, which offer pumps with a flocculation process or coagulation. The flocculant's primary
use is to bind and agglomerate suspended particles in water to form large particles to assist in their
settling and facilitate removal through particle and water separation processes. The primary purpose of
the coagulation/flocculation process is the removal of turbidity from the water. In secondary treatment,
they provide alum dosing which is used as a flocculant to remove unwanted color and turbidity from
water supplies. Also, they can provide the removal of phosphorous by means of dosing ferric chloride, ph
correction, and substrate dosing. Tertiary treatment is the same as secondary treatment, like Flocculation,
coagulation, alkalinity, or ph correction with lime milk and chlorine solution for water disinfection
treatment. Also, have a powder-activated carbon dosing to eliminate undesired substances. Finally, sludge
treatment has a polymer to dose for the flocculation process.
In my view, the discussed chemical wastewater treatment processes include chemical precipitation
(coagulation, flocculation), ion exchange, neutralization, adsorption, and disinfection (chlorination). This
chemical wastewater treatment process works in a similar fashion as chemical oxidation. Sludge is treated
with a large amount of a given oxidant, such as chlorine. The introduction of the oxidant slows down the
rate of biological growth within the sludge and also helps deodorize the mixture. The water is then
removed from the sludge. Chlorine is the chemical most often used in treating sewage and other types of
wastewater. The process is called chlorination. This is the most effective means of destroying a variety of
viruses and bacteria.
Biological Process in Wastewater Treatment
The biological wastewater treatment method, also known as the conventional method, is a common and
widely used method of treatment. It takes into account biodegradation bleaching by taking the aid of
several microorganisms, fungi, bacteria, yeasts, and algae. The biological treatment stage comprises
called activated sludge tank and a final clarification tank. The activated sludge is the place of the
nitrification and denitrification process. In larger wastewater treatment plants, the additional step of
phosphate elimination is carried out before these processes. The biological treatment, here micro-
organisms – anaerobic, anoxic, and aerobic bacteria – serve to decompose dissolved substances contained
in the wastewater. The process is divided into 2 steps: Denitrification and nitrification phase and Final
Clarification. Nitrification under aerobic conditions. Nitrification is a biochemical reaction that occurs
inside bacteria. The most widespread process for nitrogen removal from wastewater is the activated
sludge process, which uses nitrification-denitrification to remove nitrate. The last stage is the sludge
treatment. This sludge comprises primary sludge, secondary sludge, and grease. Primary sludge is mainly
composed of feces. The terms secondary or excess sludge define excess micro-organisms that are
removed from the treated water after the final clarification stage. The different types of sludge can either
be treated together or separately.
The goal of biological wastewater treatment is to create a system in which the results of decomposition
are easily collected for proper disposal. Biological treatment is used worldwide because it's effective and
more economical than many mechanical or chemical processes.
Further, biological treatment can be used to reduce the volume of waste materials, destruct human
pathogens, and produce biogas for energy use. Biological treatment can be operated both aerobically and
anaerobically. Composting is the aerobic decomposition of biodegradable organic matter and toxic
compounds.
Compared to other treatment methods, biological methods have certain advantages such as (1) treatment
technology is traditional and well understood; (2) enhanced efficiency in terms of organic content
removal; (3) cost-effective; and (4) environment-friendly and safe.
You might also like
- Biology Project On Sewage Treatment PlantDocument26 pagesBiology Project On Sewage Treatment Plantjananipriya84% (122)
- Lecture 4 - Liberalism and Bourbon Impacts Rizal's EraDocument1 pageLecture 4 - Liberalism and Bourbon Impacts Rizal's EraChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Secondary TreatmentDocument14 pagesSecondary TreatmentNasirNo ratings yet
- How Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisFrom EverandHow Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- V2i4 1160Document8 pagesV2i4 1160Ajay Kumar GantiNo ratings yet
- Wastewater TrainDocument3 pagesWastewater TrainLester Mercado100% (1)
- Wastewater Treatment MethodsDocument8 pagesWastewater Treatment MethodszzzamrNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment ProcessDocument4 pagesWaste Water Treatment ProcessDengAwutNo ratings yet
- Conventional Waste Water Treatment Process - Water ReuseDocument2 pagesConventional Waste Water Treatment Process - Water ReuseGeraldNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument3 pagesWaste Water TreatmentShiladitya ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Water PurificationDocument13 pagesWater PurificationKanchanNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument10 pagesWaste Water TreatmentPriyank LashkariNo ratings yet
- Secondary and Tertiary TreatmentDocument5 pagesSecondary and Tertiary TreatmentTerence VergaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Water TreatmentDocument4 pagesLecture 3 - Water TreatmentCorazon Francisco AustriaNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument14 pagesWaste Water TreatmentYash jadhavNo ratings yet
- LEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDocument5 pagesLEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDysmas100% (1)
- Lecture 3.Waste-Water-TreatmentDocument6 pagesLecture 3.Waste-Water-TreatmentDivya DiyaNo ratings yet
- Sewage Water TreatmentDocument8 pagesSewage Water Treatmentsivani rayavarapuNo ratings yet
- Industrial Wastewater TreatmentDocument7 pagesIndustrial Wastewater Treatmenthamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Textile Waste Water Management: Course: Introduction To General Chemistry Course Code: CHE 101Document7 pagesTextile Waste Water Management: Course: Introduction To General Chemistry Course Code: CHE 101Ishtiaq Ahmed MugdhaNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Document3 pagesBiological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument15 pagesWater727822tucv025No ratings yet
- Biological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Document4 pagesBiological Treatment of Waste Water Unit 4Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture-06: Sludge Treatment and Disposal: Ce 333: Environmental Engineering IiDocument6 pagesLecture-06: Sludge Treatment and Disposal: Ce 333: Environmental Engineering IiMirza Md. Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Lecture Iii Cve 503 Biological Treatment of Wastewater1Document41 pagesLecture Iii Cve 503 Biological Treatment of Wastewater1James Korbla Dodzi Hills100% (1)
- Haldia Institute of Technology Presentation For Environmental Sciences (MC - 401)Document12 pagesHaldia Institute of Technology Presentation For Environmental Sciences (MC - 401)subarna maitiNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT Environmental ChemistryDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT Environmental ChemistryAyesha MalikNo ratings yet
- Report of Educational VisitDocument5 pagesReport of Educational VisitHARSHADNo ratings yet
- Methods of Water PurificationDocument12 pagesMethods of Water PurificationjyotiNo ratings yet
- Sewage Wastewater Treatment GP 6Document9 pagesSewage Wastewater Treatment GP 6njsy02No ratings yet
- Water Waste Treatment: Prepared by Group 2Document41 pagesWater Waste Treatment: Prepared by Group 2Niman100% (1)
- VII. Water Treatment: A. Treatment of Wastewater and B. Treatment of Drinking WaterDocument33 pagesVII. Water Treatment: A. Treatment of Wastewater and B. Treatment of Drinking WaterMantha100% (1)
- Principles of Wastewater TreatmentDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Wastewater Treatmentaldren amigoNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument67 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantSWATHI ACHARNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument9 pagesExamDileepa NeranjanaNo ratings yet
- Sewage and SewerageDocument11 pagesSewage and SewerageStephen KaranNo ratings yet
- 9.6.2023 - Shorthand Notes On Sewage Sludge Treatment and DisposalDocument17 pages9.6.2023 - Shorthand Notes On Sewage Sludge Treatment and DisposalLucas AgumbaNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument9 pagesWaste Water Treatment MethodsAmira El GendyNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Technology in Sewage Waste WaterDocument4 pagesFermentation Technology in Sewage Waste Waterfama18No ratings yet
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocument48 pagesActivated Sludge Processrozma khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction-au-traitement-secondaireDocument8 pagesIntroduction-au-traitement-secondairesalma17052003No ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Water Waster Characteristics and Sewage TreatmentDocument2 pagesReaction Paper - Water Waster Characteristics and Sewage TreatmentChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Water Traetment Lecture 3Document41 pagesWater Traetment Lecture 3romanbrock991No ratings yet
- Hope Seminar 2Document9 pagesHope Seminar 2SOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Potable Water Purification: Water Treatment Describes Those Industrial-Scale Processes Used To MakeDocument7 pagesPotable Water Purification: Water Treatment Describes Those Industrial-Scale Processes Used To MakeKay RenNo ratings yet
- Finals NotesDocument4 pagesFinals NotescherriebaekkiebbhNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment Plant: Theni Kammavar Sangam Public SchoolDocument26 pagesSewage Treatment Plant: Theni Kammavar Sangam Public SchoolAritra Bag100% (1)
- Waste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementDocument27 pagesWaste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementSujith KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1Document11 pagesLecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1negaathanipalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Process Wastewater CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesProcess Wastewater CharacteristicsYeAsin AraFatNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Methods Physical Unit Operations Chemical Unit Operations Biological Unit OperationsDocument34 pagesWastewater Treatment Methods Physical Unit Operations Chemical Unit Operations Biological Unit OperationsNuman100% (1)
- Lesson 15 - Trickling FiltersDocument10 pagesLesson 15 - Trickling FiltersShane RodriguezNo ratings yet
- A MICRO PROJECT ON "Prepare Report On Household Water Filtrations Unit"Document9 pagesA MICRO PROJECT ON "Prepare Report On Household Water Filtrations Unit"pmali1408No ratings yet
- Unit Operations & Processes in Waste Water TreatmentDocument16 pagesUnit Operations & Processes in Waste Water Treatmentbefkadu ayalkieNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Works... The BasicsDocument6 pagesWastewater Treatment Works... The BasicsOboy KristantoNo ratings yet
- 3213 Activity 1Document3 pages3213 Activity 1Gen UntalanNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Plant: Chlorination AerationDocument6 pagesWater Treatment Plant: Chlorination AerationGladylyn MirandaNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment EnviBiotechDocument8 pagesSewage Treatment EnviBiotechAbdul KabirNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument2 pagesWaste Water TreatmentMuhammad HumaidNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment PlantDocument2 pagesWastewater Treatment PlantJerson RicafortNo ratings yet
- How Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial ROFrom EverandHow Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial RORating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Environmental Engineering Introduction PDFDocument84 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Introduction PDFChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- EM4 Assignment 5 AnswerDocument5 pagesEM4 Assignment 5 AnswerChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- BES 12 Reviewer For PrelimDocument5 pagesBES 12 Reviewer For PrelimChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Water CycleDocument2 pagesReaction Paper - Water CycleChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Assignment 3 (Lec 3 - Video A, B, C)Document2 pagesReaction Paper - Assignment 3 (Lec 3 - Video A, B, C)Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Video 12A, B, C Sources of Wastewater and How It Is Treated in The Wastewater PlantDocument3 pagesReaction Paper - Video 12A, B, C Sources of Wastewater and How It Is Treated in The Wastewater PlantChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Video 13A and 13BDocument1 pageReaction Paper - Video 13A and 13BChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Water Waster Characteristics and Sewage TreatmentDocument2 pagesReaction Paper - Water Waster Characteristics and Sewage TreatmentChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Integrals by Partial DecompositionDocument8 pagesIntegrals by Partial DecompositionChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES 7 - First Order Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesLECTURE NOTES 7 - First Order Differential EquationsChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 8 - The Bernoulli EquationDocument7 pagesLECTURE 8 - The Bernoulli EquationChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 11 - Physical Application - Exponential DecayDocument11 pagesLECTURE 11 - Physical Application - Exponential DecayChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY 20 - Locating Sounding (Answers)Document4 pagesLABORATORY 20 - Locating Sounding (Answers)Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 - Types of Solution To A Differential Equation EM4Document4 pagesLECTURE 2 - Types of Solution To A Differential Equation EM4Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - CRITIQUING NEOLIBERALISMDocument3 pagesGlobalization - CRITIQUING NEOLIBERALISMChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - CHAPTER SUMMARY Chapter 2Document4 pagesGlobalization - CHAPTER SUMMARY Chapter 2Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 5 - Homogeneous Differential EquationsDocument21 pagesLECTURE 5 - Homogeneous Differential EquationsChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - POPULAR NEOLIBERAL "THEORY" - THE CASE OF THOMAS FRIEDMANDocument5 pagesGlobalization - POPULAR NEOLIBERAL "THEORY" - THE CASE OF THOMAS FRIEDMANChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - NEOLIBERALISM - AN EXEMPLARYDocument5 pagesGlobalization - NEOLIBERALISM - AN EXEMPLARYChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - NEOLIBERALISM AS EXCEPTIONDocument3 pagesGlobalization - NEOLIBERALISM AS EXCEPTIONChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Definition and Classifications of Differential EquationsDocument5 pagesLECTURE 1 - Definition and Classifications of Differential EquationsChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - BROADER, MORE RECENT CHANGESDocument4 pagesGlobalization - BROADER, MORE RECENT CHANGESChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - IF THERE IS SUCH A THING AS GLOBALIZAT ION, WHEN DID IT BEGINDocument4 pagesGlobalization - IF THERE IS SUCH A THING AS GLOBALIZAT ION, WHEN DID IT BEGINChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - GLOBALIZAT ION AND RELATE D PROCESSESDocument5 pagesGlobalization - GLOBALIZAT ION AND RELATE D PROCESSESChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization Chapter 3 SummaryDocument4 pagesGlobalization Chapter 3 SummaryChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Sur Lab 24 - Layout of Compound CurveDocument2 pagesSur Lab 24 - Layout of Compound CurveChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Globalization - NEOLIBERALISM AN EXEMPLARY STATEMENT AND THE BASIC PRINCIPLESDocument5 pagesGlobalization - NEOLIBERALISM AN EXEMPLARY STATEMENT AND THE BASIC PRINCIPLESChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Sur Lab 21 Assignment (Answer)Document2 pagesSur Lab 21 Assignment (Answer)Chilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY 25-Lay Out of Reversed CurveDocument5 pagesLABORATORY 25-Lay Out of Reversed CurveChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Polyaluminium Chloride MSDSDocument6 pagesPolyaluminium Chloride MSDSNandhakumarNo ratings yet
- OHSP LM Week 9 10 7 ScienceDocument2 pagesOHSP LM Week 9 10 7 ScienceLA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Polymer-Derived Ceramics and Their Space ApplicationsDocument107 pagesPolymer-Derived Ceramics and Their Space ApplicationsRAHUL BHASKARNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions PPT AlcoholsDocument43 pagesOrganic Reactions PPT Alcoholssmithsashay74No ratings yet
- Nurdr Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesNurdr Practice QuestionsSHEENA MAE DE LOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Astm D971Document4 pagesAstm D971JORGE SANTANDERNo ratings yet
- Banana Pseudo Stem CHAPTER 1 3Document53 pagesBanana Pseudo Stem CHAPTER 1 3mizzpain CabuyadaoNo ratings yet
- Flux Decline in Skim Milk UltrafiltrationDocument19 pagesFlux Decline in Skim Milk Ultrafiltrationpremnath.sNo ratings yet
- SAES-Q-001 (Criteria For The Design & Construction of Concrete Structures)Document5 pagesSAES-Q-001 (Criteria For The Design & Construction of Concrete Structures)Nino Celso Astillero100% (1)
- Advanced Materials - 2022 - Nair - 2D MBenes A Novel Member in The FlatlandDocument14 pagesAdvanced Materials - 2022 - Nair - 2D MBenes A Novel Member in The FlatlandVinay ThakurNo ratings yet
- Company Profil - PT Multan Kusuma SaktiDocument32 pagesCompany Profil - PT Multan Kusuma SaktiMariana LopNo ratings yet
- Fugalite Bio IN 2020Document8 pagesFugalite Bio IN 2020aasifNo ratings yet
- Water Report 17 JanDocument3 pagesWater Report 17 Janansar aliNo ratings yet
- Soldering Basic GuideDocument6 pagesSoldering Basic GuidechchuanNo ratings yet
- Forced Degradation - Mass BalanceDocument8 pagesForced Degradation - Mass BalanceppiccoliniNo ratings yet
- WM GSC MFL70761362 00 200526 00 WebDocument36 pagesWM GSC MFL70761362 00 200526 00 WebMaeNo ratings yet
- Guar ReportDocument44 pagesGuar ReportSatendra Singh GurjarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 BioGeoChemical CyclesDocument25 pagesModule 2 BioGeoChemical CyclesPonce GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Beach Babies WO Sunscreen SPF50+ SC-587-1Document1 pageBeach Babies WO Sunscreen SPF50+ SC-587-1ajitbadboy2No ratings yet
- Schmidt + Clemens: Weld Repair Practices in High Temperature MaterialsDocument46 pagesSchmidt + Clemens: Weld Repair Practices in High Temperature MaterialsmanojballaNo ratings yet
- 14 54 Namat Upvc DrainageDocument22 pages14 54 Namat Upvc DrainageImtiyaz KhanNo ratings yet
- STK1211 Practical Analytical ChemistryDocument39 pagesSTK1211 Practical Analytical Chemistrylox agencyNo ratings yet
- A320 - SRM - MSN - 05234 - 01-Aug-2019 - TASK 57-53-00-300-029 - Zone 1 - Skin Covered With Metal Strap RepairDocument20 pagesA320 - SRM - MSN - 05234 - 01-Aug-2019 - TASK 57-53-00-300-029 - Zone 1 - Skin Covered With Metal Strap Repairjr primeNo ratings yet
- RANGER - Rescue Davit Kit Shoring - Operating Manual CertificationDocument38 pagesRANGER - Rescue Davit Kit Shoring - Operating Manual CertificationAmr Adel HameedNo ratings yet
- Organic Peroxides PresentationDocument24 pagesOrganic Peroxides Presentationtatarey790% (1)
- Trace Impurities in Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Gas Chromatography and Effective Carbon NumberDocument13 pagesTrace Impurities in Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Gas Chromatography and Effective Carbon NumberAngel Cambero100% (1)
- Lett 8b04147Document5 pagesLett 8b04147Alane Priscilla AméricoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Rate of ReactionDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Rate of ReactionMarcTnnNo ratings yet
- For Teachers' Use Only: with 弋 mark eπ0Document22 pagesFor Teachers' Use Only: with 弋 mark eπ0Copper ShortswordNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - DLL For July 16 2019Document2 pagesMicrosoft Word - DLL For July 16 2019Marilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet