Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Grade 9 Scheme of Work
New Grade 9 Scheme of Work
Uploaded by
ramloghun veerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Grade 9 Scheme of Work
New Grade 9 Scheme of Work
Uploaded by
ramloghun veerCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOLOGY SCHEME OF WORK 2023
GRADE 9
FIRST TERM (9th Jan- 31st March) a. Correct homework and announce assessment for next
week.
First Term comprises 12 weeks. UNITS B1 AND B2 can be
covered: BLOOD CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND Week 6
REPRODUCTION b. Class assessment 1st period (5 multiple choice questions
and 2 structured questions)
UNIT 1: BLOOD CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (pg. 195- 223) c. Correction of assessment in 2nd period.
Week 1: Blood Circulatory System (pg 195) Week 7: BIODIVERSITY
Learning objectives: a. Explain biodiversity and its importance to mankind
• State that the human circulatory system consists of the
blood, the heart and the blood vessels Values: Explain how it is important to preserve nature in order to
• Show an awareness that the heart is a pumping organ maintain balance. If it is destroyed by our selfishness then
distributing blood throughout the body problems will arise in terms of natural calamities. Avoid being
• List the four main components of blood as plasma, red selfish and think for the welfare of all organisms.
blood cells, white blood cells and platelets
Week 8: BIODIVERSITY
Learning Activities: a. Outline the threats (pollution, deforestation and
Activity 1.1 – locating the position of the heart (pg 196) degradation of habitat, invasive alien species) towards
biodiversity
Week 2: Red Blood Cells, White blood cells and blood patelets
Learning objective: Week 9: BIODIVERSITY
• Outline briefly the function(s) of red blood cells, white a. Formulate solutions to these threats mentioned above
blood cells, platelets and plasma (including conservation)
b. Explain why tropical rainforest has the richest
Learning Activities: biodiversity?
Activity 1.2 – Examining blood under a microscope (pg.
198) Values: To err is human. It should be realized whenever mistakes
Test yourself (pg. 198) are committed it is the duty of each and everyone to correct it.
Activity 1.3 – Exploring the structure and main function of Explain how tropical rainforest teaches unity in diversity.
red blood cells (RBCs) (pg. 199)
Activity 1.4 – Exploring the importance of platelets in the Project work
body (pg. 202) Ask students to design a poster containing five most endangered
organisms and the ways to protect them.
Week 3: BLOOD VESSELS
Learning objectives: Assignment and homework: pg 24-27
• Compare the structure of the different blood vessels:
arteries, veins and capillaries Week 10: BIODIVERSITY
• Relate the functions of different blood vessels to their Correction of homework
structures
Week 11
Learning Activities: Class assessment
Activity 1.5 – Comparing the structure of an artery, vein
and capillary (pg. 204) Week 12
a. Remedial work and revision
Test yourself (pg. 198)
b. Collection of assignment
Activity 1.3 – Exploring the structure and main function of
red blood cells (RBCs) (pg. 199)
Activity 1.4 – Exploring the importance of platelets in the
body (pg. 202)
Week 4: THE NUCLEUS AND ITS ROLE (PRACTICAL)
a. Carry out Teachers demonstration on page 7.
b. Demonstrate mitosis in onion or broad bean root tip
under the microscope or using a projector.
Homework
End of chapter questions on page 8-12.
Week 5: CORRECTION OF HOMEWORK
d. plasma – transport of blood cells, ions, soluble
food substances, carbon dioxide, urea,
vitamins and plasma proteins etc.
Values: Explain how each and every part of the blood carry out
their specific function for the welfare of the body. Learn how to
cooperate for the welfare of society. Whenever there is a problem
learn to defend.
Week 6: TRANSPORT IN MAN
a. Outline the structure and function of the blood vessels
(arteries, veins and capillaries)
b. Compare the structure and function of arteries, veins
and capillaries.
Week 7: TRANSPORT IN MAN
a. Outline the structure and function of the heart (the
chambers, valves and associated blood vessels)
b. State examples of cardiovascular diseases such as
stroke, heart attack and hypertension
c. List preventive measures for cardiovascular diseases
SECOND TERM Practical investigation
Carry out practical investigation on page 53 & correction of
Second Term normally comprises 13 weeks. Here 2 topics can be homework.
covered: TRANSPORT IN MAN AND PLANTS & BREATHING
AND GAS EXCHANGE Homework
End of chapter questions
Week 1: DIFFUSION, OSMOSIS AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT
(a) Describe the movement of substances in living organisms Week 9:
(diffusion, osmosis and active transport) Class assessment.
(b) Define and give importance of diffusion, osmosis and active
transport in living organisms. Weeks 10, 11 & 12: Revision and Second term exams.
Week 2: Practical Demonstration
a. Demonstrate diffusion and osmosis in the lab.
b. Refer to teacher’s demonstration pg 34.
Week 3: TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
a. Outline the role of xylem and phloem in transport of
materials in a plant
b. Identify xylem and phloem in root, stem and leaf
Practical demonstration: Demonstrate movement of dye in celery
from page 38.
Homework: End of chapter questions 1, 2 and 5.
Week 4: Class assessment and Correction of homework.
Week 5: TRANSPORT IN MAN
a. Describe the double circulation of blood through the
heart.
b. Outline the different components of the circulatory
system (blood, blood vessel and heart)
c. List the components of blood and state the function of
red blood cell, white blood cells, platelets and blood
plasma
d. State the functions of blood:
a. red blood cells – haemoglobin and oxygen
transport;
b. white blood cell – phagocytosis, antibody
formation;
c. platelets – causing clotting;
Week 4
Assessment on Breathing and gas exchange
Week 5: HEALTH AND SAFETY
a. Recall definition of infectious disease.
b. Outline malaria and influenza as examples of
infectious/communicable diseases that involve causative
agent, their mode of transmission and host
c. State the signs and symptoms and treatment (preventive
and curative) of influenza.
Week 6: HEALTH AND SAFETY
a. State the signs and symptoms and treatment (preventive
and curative) of malaria.
Homework
End of chapter questions
Values: Like disease causing organisms there will be many
problems in life. Learn how to find an antidote against them. There
is always a solution for every problem. No problem is big enough
to make us desperate. Learn to tolerate and accept atrocities in
life. Tolerance is a great virtue in man.
Week 7:
THIRD TERM Correction of homework and class assessment
This term comprises 12 weeks. In this term 2 topics at most can be Homework
covered: BREATHING AND GAS EXCHANGE & HEALTH AND Specimen paper 1
SAFETY.
Week 8: correction of specimen paper
Week 1: BREATHING AND GAS EXCHANGE
(a) State breathing as the process of exchange of gases in living Homework
organisms Specimen paper 2 & 3
(b) Outline the structure and function of the major parts of the
respiratory system (nostrils, pharynx, larynx, trachea, Week 9: correction of specimen papers and past exam papers.
bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli)
(c) outline the mechanism of breathing (inspiration and Weeks 10, 11 & 12: Revision an 3rd term exams
expiration)
Project work
Design a working model of the chest and lungs [pg 72]
Week 2: BREATHING AND GAS EXCHANGE
a. State the differences in the percentages of the gases in
inhaled air exhaled air.
b. State examples of respiratory diseases such as
bronchitis, emphysema, asthma and tuberculosis
Practical
Investigate an experiment to compare carbon dioxide content
between inspired and expired air [pg 72]
Homework
End of chapter questions
Week 3: RESPIRATION
a. Explain the need for energy in living organisms
b. Define respiration as the chemical breakdown of food to
release of energy
c. Write a word equation for respiration
(glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy)
Homework
End of chapter questions
You might also like
- Internet Book of Critical Care (IBCC) : Rapid ReferenceDocument1 pageInternet Book of Critical Care (IBCC) : Rapid Referenceian porterNo ratings yet
- The Customer Experience Book - How To Design, Measure and Improve Customer Experience in Your Business (PDFDrive)Document233 pagesThe Customer Experience Book - How To Design, Measure and Improve Customer Experience in Your Business (PDFDrive)Vera Pratiwi Goenfi100% (1)
- DLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 .DocxDocument17 pagesDLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 .Docxjoan100% (4)
- Science ViDocument96 pagesScience ViLiel Yxan VelardeNo ratings yet
- Sbi 0112Document2 pagesSbi 0112api-279841346No ratings yet
- RPT Biology Form 5 2020Document21 pagesRPT Biology Form 5 2020izeliwaniismailNo ratings yet
- LP9th - Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesLP9th - Cardiovascular SystemOliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Performance Task q1Document2 pagesQuiz Performance Task q1Haise GTNo ratings yet
- Week 2-Day 2 I. Objectives: S9LT-lab-26Document5 pagesWeek 2-Day 2 I. Objectives: S9LT-lab-26GinalynMaacNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Grade 9 2023Document2 pagesScheme of Work Grade 9 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Science G7 Q2 W3 MODDocument9 pagesScience G7 Q2 W3 MODAveCorpuz BioCornerNo ratings yet
- Human Body WorkbookDocument25 pagesHuman Body Workbookjk centralNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMDocument4 pagesMIDTERMArchon BanzonNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY MODEL PAPER 9thDocument3 pagesBIOLOGY MODEL PAPER 9thHasnain Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan 2020 Biology Form 5 SMK Convent IpohDocument23 pagesYearly Lesson Plan 2020 Biology Form 5 SMK Convent IpohIZWAHANE BINTI IBRAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Final Lesson Plan Day 6Document3 pagesFinal Lesson Plan Day 6Sheila May Tapales TabonNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN in SCIENCE 6 RecoveredDocument4 pagesLESSON PLAN in SCIENCE 6 RecoveredApril Grace Genobatin BinayNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Lesson ExemplarDocument6 pagesCirculatory System Lesson ExemplarAilee Mae Artajo - Villo100% (1)
- Science Week 1 - Q2Document11 pagesScience Week 1 - Q2chona redillasNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan 2007Document13 pagesYearly Plan 2007Masitah AmzalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Holes Human Anatomy Physiology Shier 13th Edition Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Holes Human Anatomy Physiology Shier 13th Edition Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterdominiecabasfsa28100% (23)
- UG022524 International GCSE in Human Biology 4HB0 For PrintDocument42 pagesUG022524 International GCSE in Human Biology 4HB0 For PrintHosni ShowikeNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W3Document5 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W3Louie Raff Michael EstradaNo ratings yet
- Holes Human Anatomy Physiology Shier 13th Edition Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesHoles Human Anatomy Physiology Shier 13th Edition Solutions Manualunstockallegoric9n60100% (41)
- UNIT 4 Transport in Humans and RespirationDocument7 pagesUNIT 4 Transport in Humans and RespirationDilan Hiroshana MendisNo ratings yet
- DAY: 4 I. Objectives: S9LT-lab-26Document6 pagesDAY: 4 I. Objectives: S9LT-lab-26GinalynMaacNo ratings yet
- LP - Day 4 and 5Document2 pagesLP - Day 4 and 5JENNY MAY SUDAYNo ratings yet
- Keystone Biology ReviewDocument53 pagesKeystone Biology ReviewTalia GelmanNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W3Document5 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W3john.borbonNo ratings yet
- MARKOVNIKOVDocument23 pagesMARKOVNIKOVWamorena Bruno LucasNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W3Document8 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W3TERESITA DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work-Biology (Form5) Theme: Physiology of Living Things Learning Area: 1.0 TransportDocument52 pagesYearly Scheme of Work-Biology (Form5) Theme: Physiology of Living Things Learning Area: 1.0 TransportSyakirah Abdullah100% (1)
- Weekly Learning Plan 2Document6 pagesWeekly Learning Plan 2Nova Gracia Amor OdivilasNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 First Trinal ExaminationDocument7 pagesBio 1 First Trinal ExaminationZERILLE ANNE INSON AGREGADONo ratings yet
- RPT Sains Ting. 3 2016Document20 pagesRPT Sains Ting. 3 2016NorSafarien RahimNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Cells and Cell Processes: Recommended Prior KnowledgeDocument5 pagesUNIT 1 Cells and Cell Processes: Recommended Prior KnowledgeDilan Hiroshana MendisNo ratings yet
- Exercise of Final Test 1 Plus DiscussionsDocument7 pagesExercise of Final Test 1 Plus Discussions9H17 makaylaNo ratings yet
- Science (Code No. 086) Classes: IX and X (2020-21) : General InstructionsDocument12 pagesScience (Code No. 086) Classes: IX and X (2020-21) : General InstructionsAbhishekNo ratings yet
- S11 12LT IIIaj 17Document3 pagesS11 12LT IIIaj 17Evangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Human OrganismDocument18 pagesChapter 1 The Human OrganismJURADO, Lady Brittany G.No ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W3Document5 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W3Cristina Tumanguil Ramos-BonodeNo ratings yet
- The Human BodyDocument17 pagesThe Human BodyRuthie MendozaNo ratings yet
- First Nine Weeks ReviewDocument19 pagesFirst Nine Weeks Reviewsuper novaNo ratings yet
- BIO315116 Biology Information SheetDocument18 pagesBIO315116 Biology Information SheettobdenosixNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology (5090) : Unit 5: Coordination, Response, Movement and HomeostasisDocument8 pagesO Level Biology (5090) : Unit 5: Coordination, Response, Movement and HomeostasissureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Bio Form5Document30 pagesYearly Plan Bio Form5maieyNo ratings yet
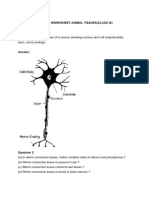
- BIOLOGY WORKSHEET-ANIMAL TISSUES (Launch Pad 1)Document11 pagesBIOLOGY WORKSHEET-ANIMAL TISSUES (Launch Pad 1)RaashiNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Tahunan Bio T5Document36 pagesRancangan Tahunan Bio T5riyashreeNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT FOR Annual EXAMINATIONS Class IX BiologyDocument3 pagesASSIGNMENT FOR Annual EXAMINATIONS Class IX BiologyhashikaNo ratings yet
- Explain How The Organs of Each Organ System Work Together (S6Lt-Lia-B-1) Describe The Structure and Function of The Parts of The Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesExplain How The Organs of Each Organ System Work Together (S6Lt-Lia-B-1) Describe The Structure and Function of The Parts of The Skeletal SystemAloha Mae ImbagNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing 4th QuarterDocument5 pagesReading and Writing 4th Quarterminkyu moviesNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument5 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogMICHELE PEREZNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument5 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayRuth Charmaine SalvatusNo ratings yet
- Final Answer Key-WebsiteDocument6 pagesFinal Answer Key-Websiteapi-292258241No ratings yet
- 15 FY11FE Biology Detailed Solution Rkedit2Document35 pages15 FY11FE Biology Detailed Solution Rkedit2Peter MayNo ratings yet
- Good Hand Written Notes Chapter WiseDocument8 pagesGood Hand Written Notes Chapter Wisesantunaskar948No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Animal Physiology 2nd Edition SherwoodDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Animal Physiology 2nd Edition Sherwoodspousessvirgerm4sq100% (46)
- Biology Form TwoDocument7 pagesBiology Form TwoteramindgreatnessNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay State University: Lesson Plan On Science 4 Major Ogrgans of The Body: Parts and FuctionsDocument9 pagesPresident Ramon Magsaysay State University: Lesson Plan On Science 4 Major Ogrgans of The Body: Parts and FuctionsEli AmagnaNo ratings yet
- RPT Biology Form4Document50 pagesRPT Biology Form4Nadiah BorhanNo ratings yet
- BIO 1 - Module 3Document25 pagesBIO 1 - Module 3mtalquisola2002No ratings yet
- Science A/Biology Foundation Tier: P.M. WEDNESDAY, 15 June 2016 1 HourDocument19 pagesScience A/Biology Foundation Tier: P.M. WEDNESDAY, 15 June 2016 1 Hourramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- NSSBIO3E Skills Sci Investigation Identify Variables Ts&Ss eDocument8 pagesNSSBIO3E Skills Sci Investigation Identify Variables Ts&Ss eramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- NSSBIO3E Skills Data Handling Intrepret Line Graph Ts&Ss eDocument8 pagesNSSBIO3E Skills Data Handling Intrepret Line Graph Ts&Ss eramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/63Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/63ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE ™: Biology 0610/61 October/November 2022Document9 pagesCambridge IGCSE ™: Biology 0610/61 October/November 2022ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Biology Module Bi1: General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary/AdvancedDocument14 pagesBiology Module Bi1: General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary/Advancedramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE ™: Biology 0610/62 October/November 2022Document10 pagesCambridge IGCSE ™: Biology 0610/62 October/November 2022ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Scheme of Work 2023Document3 pagesGrade 7 Scheme of Work 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE ™: Biology 0610/63 October/November 2022Document8 pagesCambridge IGCSE ™: Biology 0610/63 October/November 2022ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- GCE AS/A Level 311/01 Biology - Bi1: A.M. TUESDAY, 3 June 2008 1 HoursDocument15 pagesGCE AS/A Level 311/01 Biology - Bi1: A.M. TUESDAY, 3 June 2008 1 Hoursramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Sequencing Cards For The Story of M Ambarish Yr 3 & 4Document1 pageSequencing Cards For The Story of M Ambarish Yr 3 & 4ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Biology Module Bi1Document14 pagesBiology Module Bi1ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- ExcerptDocument12 pagesExcerptramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- GCE AS/A Level 1071/01 Biology/Human Biology - By1: A.M. MONDAY, 16 May 2011 1 HoursDocument12 pagesGCE AS/A Level 1071/01 Biology/Human Biology - By1: A.M. MONDAY, 16 May 2011 1 Hoursramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Practical SkillsDocument22 pagesPractical Skillsramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 1 QPDocument13 pagesEukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 1 QPramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesMark Schemeramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- BSE2 Nandapriya Devi Dasi UNIT 1 OBA PDFDocument4 pagesBSE2 Nandapriya Devi Dasi UNIT 1 OBA PDFramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Grdae 8 Scheme of Work 2023Document3 pagesGrdae 8 Scheme of Work 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Scheme of WorkDocument25 pagesForm 5 Scheme of Workramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Labeling Pictures & Diagrams WorksheetDocument80 pagesLabeling Pictures & Diagrams Worksheetramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 (P) Scheme of Work 2023Document14 pagesGrade 12 (P) Scheme of Work 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Grade 13 (P) Scheme of Work 2023Document2 pagesGrade 13 (P) Scheme of Work 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 (P) Scheme of Work 2023 NewDocument15 pagesGrade 12 (P) Scheme of Work 2023 Newramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Scheme of Work 2023Document5 pagesGrade 9 Scheme of Work 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Grade 12:13 (S) Scheme of Work 2023Document15 pagesGrade 12:13 (S) Scheme of Work 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Scheme of Work 2023Document13 pagesGrade 11 Scheme of Work 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- NEW GRADE 10 Scheme of WorkDocument28 pagesNEW GRADE 10 Scheme of Workramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Scheme of Wrok 2023Document11 pagesGrade 10 Scheme of Wrok 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Grade 9 2023Document2 pagesScheme of Work Grade 9 2023ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- A Study of The Aggressiveness Behavior of Senior High School Students of de La Salle Lipa As Predicted by The Perceived Parenting Styles of Their ParentsDocument32 pagesA Study of The Aggressiveness Behavior of Senior High School Students of de La Salle Lipa As Predicted by The Perceived Parenting Styles of Their ParentsVince Catapang100% (1)
- Standard Estimating Summary SpreadsheetDocument192 pagesStandard Estimating Summary SpreadsheetRon SantosNo ratings yet
- State Centric Theories of International Relations Belong To The Past in Security StudiesDocument3 pagesState Centric Theories of International Relations Belong To The Past in Security StudiesshoufiiNo ratings yet
- What I Need To Know? What I Need To Know?: Quarter 1Document16 pagesWhat I Need To Know? What I Need To Know?: Quarter 1Aileen gay PayunanNo ratings yet
- Coping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionDocument12 pagesCoping Strategies, Optimism, and Life SatisfactionNurulAtiqahAbRajiNo ratings yet
- Test Oil Compressor #4067 (06-12-22)Document1 pageTest Oil Compressor #4067 (06-12-22)albertoNo ratings yet
- Mastering Sketching S11 BLAD Print2Document8 pagesMastering Sketching S11 BLAD Print2Interweave0% (1)
- ENIE - 100 Technical Communication Skills Week-1 Lecture # 1 & 2Document7 pagesENIE - 100 Technical Communication Skills Week-1 Lecture # 1 & 2HIMANo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet: A. Grammar Exercise 1: Fill in Where, Whose, Who, Which, When and WhyDocument6 pagesExercise Sheet: A. Grammar Exercise 1: Fill in Where, Whose, Who, Which, When and WhyArthasNo ratings yet
- Cse320 MCQDocument12 pagesCse320 MCQAnsh Gulati ji100% (1)
- MatrixDocument30 pagesMatrixauras2065No ratings yet
- 10 Honey Bee NutritionDocument35 pages10 Honey Bee NutritionJasper Diaz DagaleNo ratings yet
- Polycab Solar PDFDocument6 pagesPolycab Solar PDFVivek RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Company / Project Title: Overview - The Quick PitchDocument3 pagesCompany / Project Title: Overview - The Quick PitchMauro Domingo'sNo ratings yet
- AICTE Model - Digital Electronics and Systems - Abhishek Bhatt - 17-01-2024Document539 pagesAICTE Model - Digital Electronics and Systems - Abhishek Bhatt - 17-01-2024matey.tushar5646No ratings yet
- 4.contour Flow Conditioner PDFDocument14 pages4.contour Flow Conditioner PDFFIRMANSYAHNo ratings yet
- HERQA QA Auditor Note BookDocument36 pagesHERQA QA Auditor Note Booktebebe solomonNo ratings yet
- RINA NCC92 - Rules For The Type Approval CertificationDocument9 pagesRINA NCC92 - Rules For The Type Approval CertificationMarianoNo ratings yet
- Cash Out With WhatsappDocument22 pagesCash Out With WhatsappIDRIS JAMIUNo ratings yet
- Physica Medica: Slobodan Devic, Nada Tomic, David LewisDocument16 pagesPhysica Medica: Slobodan Devic, Nada Tomic, David LewisFrederico GomesNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document91 pagesCH 11Putri AsmeliaNo ratings yet
- Fausto Romitelli Six Keywords PDFDocument4 pagesFausto Romitelli Six Keywords PDFNachinsky von FriedenNo ratings yet
- Blockchain For Iot: The Challenges and A Way Forward: July 2018Document13 pagesBlockchain For Iot: The Challenges and A Way Forward: July 2018ronicaNo ratings yet
- BEE301Document4 pagesBEE301cshohil300No ratings yet
- Ethylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process BrochureDocument4 pagesEthylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process Brochurerkapoor584199No ratings yet
- Tyler Street News November 2010Document4 pagesTyler Street News November 2010tsumcNo ratings yet
- Part B Unit 3 DBMSDocument4 pagesPart B Unit 3 DBMSkaran.1888kNo ratings yet
- Report On VSATDocument19 pagesReport On VSATchinu meshramNo ratings yet