Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIO Ch01 LQ e
BIO Ch01 LQ e
Uploaded by
hexu wangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIO Ch01 LQ e
BIO Ch01 LQ e
Uploaded by
hexu wangCopyright:
Available Formats
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
Structured questions
|!|BCELA0010000001|!| SI NOS
In the past, scurvy was a common disease among sailors and its cause was unknown. A
doctor called James Lind designed an experiment to investigate the cause of scurvy.
During one of his sailing trips, he divided 12 sailors suffering from scurvy into six pairs
and gave additional food on their basic diet. He then observed whether the pairs
recovered from scurvy. He maintained the same environmental conditions and diet
among all pairs. The type of additional food and the results are tabulated as below:
Pair Additional food Results
1 cider Symptoms did not disappear.
2 sulphuric acid Symptoms did not disappear.
3 seawater Symptoms did not disappear.
4 garlic, mustard Symptoms did not disappear.
5 vinegar Symptoms did not disappear.
6 oranges and lemons Symptoms disappeared.
(a) How did James Lind manipulate the control variables? (2 marks)
(b) Lind drew a conclusion that a lack of citric fruits, such as oranges and lemons in
the diet could cause scurvy. Suggest why the design of his experiment was not
adequate to demonstrate a lack of citric fruits in diet could cause scurvy. (3 marks)
(c) Scientific knowledge relies heavily on rational arguments and skepticism. After
reading the story of James Lind, a scientist was skeptical about his conclusion and
wrote down the following argument:
‘Citric fruits should be the cure of scurvy. It is not reasonable to
conclude that a lack of citric fruits is a cause of scurvy.’
Justify the scientist’s claim. (3 marks)
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 1
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
##
(a) He allocated same number of sailors in each pair. (1)
He maintained the same environmental conditions and diet among all pairs. (1)
(b) The sample size of each group is not large enough. (1) /
Feeding sulphuric acid or seawater to sailors would cause health problems, which
may deteriorate scurvy. (1) /
There is no controlled experiment, i.e. pairs of sailors having normal diet. (1) /
Sailors were not randomly allocated into each group receiving different additional
food. (1) (Max. 3)
(c) The scientist’s claim is correct. (1)
Symptoms in sailors disappeared after having citric fruits, showing that citric fruits
could be a cure of scurvy. (1)
There was no evidence on the deficiency of citric fruits of sailors shown. (1)
________
(8 marks)
##
Skills assessed Marks
(a) Applying concepts 2
(b) Applying concepts 3
(c) Critical thinking 3
|!|BCELA0010000002|!| SI
Tooth decay is caused by the action of bacteria in our mouth. After a meal, the bacteria
and food debris form a sticky and invisible layer called plaque on the surface of the
teeth. Bacteria in the plaque act on the sugar in food debris to produce acid. The acid
will dissolve the enamel and make a hole. Tooth decay begins.
(a) Describe one method to show that the bacteria in plaque are living organisms.
(4 marks)
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 2
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
(b) The student carried out an experiment to investigate the action of plaque bacteria.
He used vinegar to simulate the acid produced by plaque bacteria and a piece of
chicken bone to simulate a tooth. The diagram below shows the set-up.
vinegar
tooth
(i) State the assumption that should be made in order to make a valid
investigation. (1 mark)
(ii) Suggest a control set-up for the above experiment. (1 mark)
(c) Consider the pH value of saliva, explain the role of saliva in protecting our teeth
from plaque bacteria. (2 marks)
##
(a) Any one set of the following: (Max. 4)
Characteristic
Testing method Expected observation
tested
Growth (1) Culture plaque bacteria on Increase in number of
an agar plate for a period bacteria / colonies (1)
of time (1)
Observe the change in the
number of plaque bacteria
(1)
Respiration (1) Culture plaque bacteria in Hydrogencarbonate
a closed system, e.g. a indicator turns from red
stoppered test tube or a to yellow / limewater
syringe, for a period of turns milky (1)
time (1)
Use hydrogencarbonate
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 3
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
indicator or limewater, to
test for carbon dioxide, a
product of respiration (1)
Nutrition (1) Add a known amount of The amount of glucose
glucose solution to the decreases (less brick-
plaque bacteria culture (1) red precipitate is
Detect the change in the formed in the
amount of glucose with Benedict’s test) (1)
the Benedict’s test (1)
(b) (i) The acid produced by the plaque bacteria is the only cause of enamel damage.
(1)
(ii) Leave a chicken bone exposed to air. / Immerse a chicken bone in distilled
water. (1)
(c) Saliva is slightly alkaline, (1)
which helps neutralize the acid produced by plaque bacteria. (1)
________
(8 marks)
##
Skills assessed Marks
(a) Applying concepts 4
(b)(i) Practical skills 1
(b)(ii) Practical skills 1
(c) Applying concepts 2
|!|BCELB0010000003|!| SI
For centuries, many people believed in spontaneous generation, the idea that living
organisms could arise from non-living substances.
In 1745, John Needham carried out the following experiment.
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 4
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
The broth was The flask was left The opening of Microorganisms
briefly boiled. open for the broth the flask was grew in the broth
to cool. sealed. after a few days.
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 5
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
(a) Needham concluded that microorganisms had arisen from the non-living
substances in the broth. How did Needham arrive at this conclusion? (2 marks)
(b) However, Needham’s findings were suspected to be due to experimental errors.
Give one possible error in Needham’s experiment. (1 mark)
In 1767, Lazzaro Spallanzani modified Needham’s experiment as follows.
Set-up 1
The broth was The flask was Microorganisms grew
heated to boil. left open. in the broth after a
few days.
Set-up 2
opening sealed by
melting the glass
over a flame
The broth was The flask was No microorganisms
heated to boil. sealed quickly. grew in the broth even
after a long time.
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 6
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
(c) Suggest two control variables in set-ups 1 and 2. (2 marks)
(d) While Spallanzani claimed his own experiment as a disproval of spontaneous
generation, proponents of spontaneous generation did not agree. Suggest a reason
against Spallanzani’s claim. (2 marks)
##
(a) Needham reasoned that boiling had killed any living things in the broth (1)
and that the sealed opening prevented any living thing from entering. (1)
Thus, the microorganisms must have arisen from the non-living substances in the
broth.
(b) Any one of the following: (1)
The broth might not be sufficiently boiled to kill all organisms inside.
The broth might be contaminated when the flask remained open for cooling.
(c) The same type of broth / the same length of time of boiling / the same type of flask
(or other reasonable answers) (Any two, 2)
(d) Spallanzani had prevented air (oxygen) from entering the flask. (1)
It was thought that air (oxygen) was necessary for spontaneous generation /
The experiment only showed that microorganisms appeared when air could come
into contact with the broth. (1)
________
(7 marks)
##
Skills assessed Marks
(a) Applying concepts 2
(b) Practical skills 1
(c) Practical skills 2
(d) Applying concepts 2
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 7
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
|!|BCELB0010000004|!| SI
A disease causes the formation of black spots on the leaves of rose bushes.
John investigated the emergence of black spots in rose bushes in two areas. He picked
30 leaves at random from rose bushes growing in area A where air pollution is severe.
He counted the number of leaves with black spots as follows.
Number of spots per leaf Number of leaves
0 3
1 3
2 5
3 8
4 7
5 3
6 1
Table 1
John also picked 30 leaves at random from rose bushes growing in area B where the air
is clean. The table below shows the results.
Number of spots per leaf Number of leaves
3 1
4 1
5 2
6 3
7 8
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 8
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
8 9
9 6
Table 2
(a) Construct a bar chart to show the data in Table 1 and Table 2. (5 marks)
(b) With reference to the results, describe the effect of air pollution on this
disease. (2 marks)
(c) Suggest one way to increase the reliability of the above investigation. (1 mark)
##
(a) Correct title (1)
Correct choice of axes (1)
Axes with labels and units (1)
Correct drawing of bars for the two sets of data (1, 1)
(b) More spots in non-polluted area. Reference to data, e.g. most leaves had 3 or 4
spots in area A, while most leaves had 7 to 9 spots in area B. (1)
The disease is less widespread in the area with more air pollution.
(or vice versa) (1)
(c) Any one of the following: (1)
larger sample / collect more leaves
compare leaves of same age / same size / same position on the plants
all leaves from the same species
(or other reasonable answers)
________
(8 marks)
##
Skills assessed Marks
(a) Presenting information 5
(b) Analysing data 2
(c) Practical skills 1
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 9
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
|!|BCELA0010000005|!| Cross topic SI
Edexcel GCE AL Biology Unit 5 Jun 2012 Q3
(a) An investigation was carried out to study the ability of rats to learn. A number of
rats were divided into two groups, P and Q.
The rats in group P were deprived of food for twenty hours and then released into a
cage. The cage contained hidden food and the rats were left in this cage for four
hours each day. This was repeated each day for fourteen days.
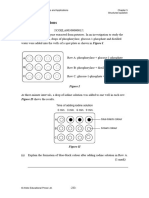
The diagram below shows the cage. In the cage, the floors A, B, C, D and E had
hidden food, water, wooden blocks, freshly cut wood chips, branches, fresh leaves,
plastic containers and paper bags.
(i) The rats in group Q were used as a control. Describe how the rats in control
group Q would have been treated. (2 marks)
(ii) Explain why the rats were not fed for twenty hours each day. (1 mark)
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 10
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
(b) During each four-hour period in the cage, the number of floors visited by the rats in
group P was recorded as a percentage of the total number of floors. The graph
below shows the results of this experiment.
Using the information in the graph, describe the behaviour of the rats in group P
over the fourteen-day period during this investigation. (3 marks)
(c) In a second experiment, the two groups of rats were placed in a maze containing
hidden food. The percentage of rats from each group that found the food in a short
period of time was recorded. The results are shown in the table below.
Group Percentage of rats finding food (%)
P 85
Q 0
Explain the effect of the first experiment on the ability of rats to find food in a short
period of time. (2 marks)
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 11
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
(d) The brains of both groups of rats were examined. The mean spine density per
neurone for each group was calculated.
Spine density represents a measure of the number of synapses per neurone.
The results are shown in the table below.
Group Mean spine density / arbitrary units
P 1.96
Q 1.78
Suggest how these results explain the effect of the first experiment on the ability of
rats to find food using the cage. (2 marks)
##
(a) (i) Group Q should be put in the same cage but with no enrichment. (1)
They should be treated the same as group P, e.g. same length of starvation
time, feeding time, time kept in the cage, etc. (1)
(ii) Starvation encourages them to look for food. (1)
(b) The percentage number of floors visited increases. (1) /
Rapid increase occurred during the first five days. (1) /
After the 5th day, the increase slowed down / levelled off. (1) /
The rats did not visit all the floors (on each day), e.g. 100% of the floors never
achieved. (1) (Max. 3)
(c) In the first experiment, hidden food in the cage encouraged the rats to explore the
environment. (1)
They learned to look for food, so they visit more of the maze. (1)
(d) More synapses allow more connections between neurones. (1)
The learning capacity of group P improved. (1)
________
(10 marks)
##
Skills assessed Marks
(a)(i) Practical skills 2
(a)(ii) Applying concepts 1
(b) Analysing data 3
(c) Analysing data 1
Applying concepts 1
(d) Analysing data 1
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 12
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
Applying concepts 1
|!|BCELC0010000006|!|
Excretion is a common characteristic of living organisms.
(a) State two other common characteristics of living organisms. (2 marks)
(b) Like other living organisms, plants also need to excrete metabolic wastes.
Describe how the waste product produced in respiration is removed from a leaf.
(2 marks)
(c) During the cold winter, some plants shed their leaves. This can be described as an
excretory mechanism. Suggest two other reasons why plants shed their leaves
during winter. (2 marks)
(d) State one excretory organ in humans, and the metabolic waste it excretes. (2 marks)
##
(a) Any two of the following: (2)
nutrition / respiration / movement / sensitivity / growth / reproduction
(b) The carbon dioxide produced in respiration diffuses out (1)
of the leaf through the stomata (along the concentration gradient). (1)
(c) To reduce water loss (1)
To conserve energy (1)
(Or other reasonable answers)
(d) Any one set of the following: (2)
The lungs (1) excrete carbon dioxide. (1)
The kidneys (1) excrete urea. (1)
The skin (1) excretes urea. (1)
________
(8 marks)
##
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 13
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
Skills assessed Marks
(a) Understanding basic concepts 2
(b) Understanding basic concepts 2
(c) Understanding basic concepts 2
(d) Understanding basic concepts 2
|!|BCELB0010000007|!| SI
Studying biology involves carrying out scientific investigations.
(a) Scientific investigation involves several steps as shown below.
Making a hypothesis Analysing the results
Making observation Carrying out an experiment
(i) Arrange the above steps of scientific investigation in the correct order.
(2 marks)
(ii) What will biologists do if the experimental results
(1) support the hypothesis? (1 mark)
(2) do not support the hypothesis? (1 mark)
(b) Amy works in a small and crowded office with many colleagues. She finds that her
potted plant in her office grows larger than the one in her home. She wants to find
out why this occurs by carrying out a scientific investigation.
(i) What is Amy’s observation in her scientific investigation? (1 mark)
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 14
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
(ii) Suggest how Amy may carry out the following steps. (3 marks)
1. Making a hypothesis:
2. Making a prediction:
3. Conducting an experiment:
(iii) State two control variables in her scientific investigation. (2 marks)
##
(a) (i) 1. Making observation
2. Making a hypothesis
3. Carrying out an experiment
4. Analysing the results
(Maximum 2 marks, deduct 1 mark for each wrong answer) (2)
(ii) (1) If the experimental results support the hypothesis, the biologists will
repeat the experiment many times for confirmation. (1)
(2) If the experimental results do not support the hypothesis, the biologists
have to revise the hypothesis. (1)
(b) (i) She observes that her potted plant in the office grows larger than that in her
home. (1)
(ii) 1. Making hypothesis: Plants grow better in an environment with more people
(or higher carbon dioxide concentration). (1)
2. Making a prediction: If a plant is grown in an environment with more
people, then it will grow larger than a plant grown in an environment with
fewer people. (1)
3. Conducting an experiment: Grow five plants in five rooms with different
numbers of people (e.g. 0, 2, 4, 6 and 8 people) (1)
(iii) Any two of the following: (2)
species of the plant / light intensity / nutrient content in the soil
(Or other reasonable answers)
_________
(10 marks)
##
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 15
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
Skills assessed Marks
(a)(i) Understanding basic concepts 2
(a)(ii) Understanding basic concepts 2
(b)(i) Applying concepts 1
(b)(ii) Applying concepts 3
(b) Practical skills 2
(iii)
|!|BCELA0010000008|!| SI NOS STSE
In the past, doctors believed that gastric ulcer was caused by excessive secretion of
stomach acid induced by stress. However, many patients developed gastric ulcer again
after being treated with medicines for neutralizing stomach acid. In the 1980s, the
Australian doctor Barry Marshall observed that patients with gastric ulcers had a type of
bacterium called Helicobacter pylori in their stomach. He therefore put forward a
hypothesis about gastric ulcer. Based on this hypothesis, he treated his patients with
antibiotics. Many of the patients recovered and did not develop gastric ulcer again.
(a) Suggest the hypothesis made by Marshall about gastric ulcer. (1 mark)
(b) Based on the hypothesis you answered in (a), describe how you would test whether
it is correct or not. (2 marks)
(c) Explain why many doctors were surprised about Marshall’s observation. (1 mark)
Scientists study how Helicobacter pylori survives in the stomach. To avoid the acidic
environment of the stomach, H. pylori uses its flagella to burrow into the mucus lining
of the stomach to reach the epithelial cells underneath, where it is less acidic. H. pylori
is able to detect the pH gradient in the mucus and move towards the less acidic region.
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 16
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
(d) Give two characteristics of organisms demonstrated by Helicobacter pylori in the
passage above. (2 marks)
(e) Elaborate on how the events above demonstrate the following aspect of the nature
of science: Scientific knowledge is tentative and subject to change. (2 marks)
##
(a) Helicobacter pylori causes gastric ulcer. (1)
(b) Introduce Helicobacter pylori into the stomach of healthy mammals. (1)
If the hypothesis is correct, the mammals will develop gastric ulcer. (1)
(c) They thought that the acidic environment in the stomach is unfavourable to the
survival of bacteria. (1)
(d) Movement, sensitivity (1, 1)
(e) Barry Marshall’s new findings provide evidence that gastric ulcer is caused by
Helicobacter pylori. (1)
His findings corrected the previous misconception that gastric ulcer was caused by
excessive secretion of stomach acid. (1)
________
(8 marks)
##
Skills assessed Marks
(a) Applying concepts 1
(b) Practical skills 2
(c) Applying concepts 1
(d) Applying concepts 2
(e) Applying concepts 2
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 17
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
|!|BCELB0010000009|!| SI NOS
Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow:
Power plants emit sulphur dioxide which is a type of air pollutant. A farmer whose
fields are near to a power plant thinks that the yield of soybeans is reduced because
of the emission of sulphur dioxide. To find out whether this is true, scientists
worked with farmers to study the effect of sulphur dioxide concentration on the
growth of soybeans.
In one of their studies, the scientists grew soybean plants in a greenhouse. They
divided the soybean plants into two groups:
1. The plants were subject to sulphur dioxide gas for a few hours per day to
simulate the emission of sulphur dioxide from power plants.
2. The plants were left to grow in the greenhouse normally and without sulphur
dioxide treatment.
The growth of the two groups of soybean plants was monitored for a year. During
this period, the local scientists worked with other scientists from foreign countries
on the sulphur dioxide emission issue.
(a) Identify the hypothesis of this investigation. (1 mark)
(b) Suggest two variables that the scientists can measure to represent growth. (2 marks)
(c) Identify the control group of the study. Explain the purpose of including the control
group. (2 marks)
(d) What are control variables? Suggest two control variables in this study. (3 marks)
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 18
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
(e) Suggest what aspects of the nature of science are reflected from the following:
‘The local scientists worked with other scientists from foreign countries on the
sulphur dioxide emission issue.’ (1 mark)
##
(a) Sulphur dioxide lowers the yield of soybeans. (1)
(b) Any two of the following: (2)
the number of bean pods in each plant
the number of seeds per pod in each plant
the dry mass of the pods in each plant
(Or other reasonable answers)
(c) The group that was left to grow in the greenhouse normally and without sulphur
dioxide treatment. (1)
It is used to show that any reduction of the yield of soybean is due to sulphur
dioxide. (1)
(d) Variables that have to be kept constant. (1)
Any two of the following: (2)
age of the soybean plants
species of the soybean plants
number of soybean plants in each group
water supply
light intensity
temperature
(Or other reasonable answers)
(e) Scientists collaborate with each other. (1)
________
(9 marks)
##
Skills assessed Marks
(a) Applying concepts 1
(b) Applying concepts 2
(c) Applying concepts 2
(d) Understanding basic concepts 1
Applying concepts 2
(e) Applying concepts 1
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 19
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
|!|BCELA0010000010|!| SI
The beet caterpillar is an insect pest that feeds on the leaves of tomato plants. When beet
caterpillars feed on the leaves of a tomato plant, the leaves will release a chemical X.
In an investigation, some scientists suggest that chemical X attracts wasps to the tomato
plants attacked by caterpillars.
(a) What is the hypothesis of this investigation? (1 mark)
(b) The scientists design an experiment to test the hypothesis.
(i) Outline how the scientists would carry out the experiment. (4 marks)
(ii) Predict the experimental results that would support the hypothesis. (1 mark)
(c) Explain an advantage for the plant to release chemical X when its leaves are being
eaten by caterpillars. (1 mark)
##
(a) Chemical X attracts wasps. (1)
(b) (i) Prepare two groups of tomato plants that are of the same age and state of
health. (1)
One group is affected with beet caterpillars, the other is unaffected. (1)
Place both groups in the same environment (e.g. the temperature and water
availability are kept constant). (1)
Release wasps and observe their activity. (1)
(ii) The hypothesis is supported when more wasps visit the plants eaten by
caterpillars than the unaffected group. (1)
(c) Chemical X attracts wasps which kill / eat beet caterpillars. (1)
________
(7 marks)
##
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 20
HKDSE BIOLOGY: Connecting Concepts Chapter 1
Question bank Structured questions
Skills assessed Marks
(a) Applying concepts 1
(b)(i) Applying concepts 4
(b)(ii) Applying concepts 1
(c) Applying concepts 1
© 2019 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 21
You might also like
- CSEC Biology - Digestion TestDocument3 pagesCSEC Biology - Digestion TestTamicka Bonnick100% (6)
- 2000 CXC Biology Paper 3 - May-JunDocument4 pages2000 CXC Biology Paper 3 - May-JunSaintm101100% (2)
- BIO Ch01 SQ eDocument15 pagesBIO Ch01 SQ eGaming BeeNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam Practice: Chapter 1 Introduction To BiologyDocument25 pagesAnswers To Exam Practice: Chapter 1 Introduction To BiologyGaming BeeNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam Practice: Chapter 1 Introduction To BiologyDocument23 pagesAnswers To Exam Practice: Chapter 1 Introduction To BiologyHiiiNo ratings yet
- Ujian Mac 2020, Sains Tingkatan 5: Animal ProteinDocument3 pagesUjian Mac 2020, Sains Tingkatan 5: Animal Proteinhuda186No ratings yet
- 2020-2021-F3 Bio Mid Year Exam Paper GC ANSDocument4 pages2020-2021-F3 Bio Mid Year Exam Paper GC ANSs192438No ratings yet
- Topic Test: Oxfordaqa International Gcse Biology 9201Document26 pagesTopic Test: Oxfordaqa International Gcse Biology 9201Novanolo Christovori ZebuaNo ratings yet
- 2000-11 & 2012 Hkcee + Al LQDocument180 pages2000-11 & 2012 Hkcee + Al LQArthur ChoiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-AND-HEALTH-SCIENCES-THEORY-AND-PRACTICAL-EXAMINATION-S2 (1)Document16 pagesBIOLOGY-AND-HEALTH-SCIENCES-THEORY-AND-PRACTICAL-EXAMINATION-S2 (1)JEAN Fred ISHIMWENo ratings yet
- M 10TH Phys Fa 1Document2 pagesM 10TH Phys Fa 1Aditay SinghNo ratings yet
- S4 2021 Half Yearly Exam (Paper 1 & 2) Marking Scheme V4Document4 pagesS4 2021 Half Yearly Exam (Paper 1 & 2) Marking Scheme V4dream oNo ratings yet
- Diseases & Immunity 3 QPDocument6 pagesDiseases & Immunity 3 QPLia lylNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 - LQ - eDocument27 pagesChapter 05 - LQ - eYoyo HelenNo ratings yet
- Bio PP2 S.6 ST. MARY - S KITENDE 2020Document4 pagesBio PP2 S.6 ST. MARY - S KITENDE 2020Batuuse George WilliamNo ratings yet
- Microbes in Human Welfare: SolutionsDocument24 pagesMicrobes in Human Welfare: SolutionsRana GhoshNo ratings yet
- ROLL NO .. RKDF UniversityDocument2 pagesROLL NO .. RKDF UniversityAhmad AslamNo ratings yet
- F.3 1st Term Bio Exam (16-17) - TV ShortDocument2 pagesF.3 1st Term Bio Exam (16-17) - TV Shortjonas hoNo ratings yet
- MM 10 Phy Fa 1 Set BDocument2 pagesMM 10 Phy Fa 1 Set BAditay SinghNo ratings yet
- Bio 4.4Document8 pagesBio 4.4zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- CXC Jan - 2015 - HSB 002 - AnswersDocument3 pagesCXC Jan - 2015 - HSB 002 - AnswersKyñg ShākëëlNo ratings yet
- Shyann Kirk - CSEC Food and Nutrition June 2005 P2Document5 pagesShyann Kirk - CSEC Food and Nutrition June 2005 P2shyannNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme PapeDocument14 pagesMark Scheme Papehasan memosNo ratings yet
- 2020 Year 7 Science Cyclic Test Four - Acids and Bases + Microbes MARK SCHEMEDocument9 pages2020 Year 7 Science Cyclic Test Four - Acids and Bases + Microbes MARK SCHEMEsyu055No ratings yet
- Answers To The Cambridge Checkpoint Science 2Document28 pagesAnswers To The Cambridge Checkpoint Science 2Nur Dina ZaulkifleeNo ratings yet
- Lyceum International School: Monthly Test January 2018Document7 pagesLyceum International School: Monthly Test January 2018mohamed rahilNo ratings yet
- Expt 33&34 ReqDocument11 pagesExpt 33&34 ReqBlack WidowNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 15 16 XIII Bot Study Package 5 Set 1 Chapter 18 PDFDocument24 pagesCLS Aipmt 15 16 XIII Bot Study Package 5 Set 1 Chapter 18 PDFMoumita SarkarNo ratings yet
- Topper 2 110 7 1 Biology Question Up201711171731 1510920087 7276Document5 pagesTopper 2 110 7 1 Biology Question Up201711171731 1510920087 7276UMANo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2005 P3Document4 pagesCSEC Biology January 2005 P3Makayla AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Csec Biology Digestion Test PDF FreeDocument3 pagesCsec Biology Digestion Test PDF FreeSay DavidNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologyGlennNo ratings yet
- BioK QQ 6.1 QPDocument3 pagesBioK QQ 6.1 QPesteban1013264503No ratings yet
- Olympiad and Quiz QuestionsDocument19 pagesOlympiad and Quiz Questionslucksonmkandawire111No ratings yet
- AugustDocument4 pagesAugustNamraNo ratings yet
- Biology New Sample PaperDocument5 pagesBiology New Sample PaperSuvham Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Nutrition & Digestion WorksheetDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Nutrition & Digestion WorksheetthanunovaisnoNo ratings yet
- Nabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursDocument10 pagesNabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursCecilia KhaombiNo ratings yet
- CSSC Ms Science 10 CSSC Set1Document8 pagesCSSC Ms Science 10 CSSC Set11770No ratings yet
- Kelm 317Document11 pagesKelm 317Prince SoniNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam Practice: Chapter 6 Food and HumansDocument5 pagesAnswers To Exam Practice: Chapter 6 Food and Humansan ChiNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Science - Final Examination 2023-24 - Model PaperDocument7 pagesClass 7 - Science - Final Examination 2023-24 - Model Paperuttam biswasNo ratings yet
- IX HalfYearly Dec21Document5 pagesIX HalfYearly Dec21Hasna Hena SarkerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) Past Paper Questions and NswersDocument9 pagesCambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) Past Paper Questions and NswersIonela HoteaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Answers Biological MoleculesDocument2 pagesWorksheet Answers Biological MoleculesNatalja BoultingNo ratings yet
- CBSE Schools and KV Class VII SA I Science Model Question Paper 2015Document4 pagesCBSE Schools and KV Class VII SA I Science Model Question Paper 2015Amrita SenNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their Elimination - DPP 09 - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Alpha)Document2 pagesExcretory Products and Their Elimination - DPP 09 - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Alpha)kutties kitchenNo ratings yet
- Salt Making 1 Salt Making 1Document1 pageSalt Making 1 Salt Making 1Mr BobNo ratings yet
- Ch4 LQDocument16 pagesCh4 LQMomoNo ratings yet
- 4bi1 1br Rms 20230824Document29 pages4bi1 1br Rms 20230824ep1c19No ratings yet
- SSC Public Examination - 2017 Model Paper - 1Document7 pagesSSC Public Examination - 2017 Model Paper - 1ThirupathaiahNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII (2019-20) BIOLOGY (044) Sample Paper-3: Section ADocument5 pagesCLASS XII (2019-20) BIOLOGY (044) Sample Paper-3: Section AKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- 2024 LS GR 11 Assignment MG 14 May 2024Document5 pages2024 LS GR 11 Assignment MG 14 May 2024nomvulamathipaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam Practice: Chapter 6 Food and HumansDocument17 pagesAnswers To Exam Practice: Chapter 6 Food and HumansHiiiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Answers Biological MoleculesDocument2 pagesWorksheet Answers Biological MoleculesCally ChewNo ratings yet
- Name of Candidate: . . Date: Subject: Biology / 5090 Total MarksDocument5 pagesName of Candidate: . . Date: Subject: Biology / 5090 Total MarksAhmed Kaleem Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Biology 2004 Paper 1 Marking SchemeDocument4 pagesMarking Scheme Biology 2004 Paper 1 Marking Schemeapi-381289475% (4)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualNo ratings yet
- Anomalous Retinal Correspondence - Diagnostic Tests and TherapyDocument5 pagesAnomalous Retinal Correspondence - Diagnostic Tests and TherapySumon SarkarNo ratings yet
- The Health and Care System Explained - GOV - UKDocument5 pagesThe Health and Care System Explained - GOV - UKkaidNo ratings yet
- Extra, Extra On Wachter Cease and Desist OrderDocument7 pagesExtra, Extra On Wachter Cease and Desist OrderConflict GateNo ratings yet
- Pengisian Tanggal3Document32 pagesPengisian Tanggal3gusrina simamoraNo ratings yet
- THI THỬ QG LẦN 1 (2020 - 2021)Document5 pagesTHI THỬ QG LẦN 1 (2020 - 2021)buitinhNo ratings yet
- S StoryDocument24 pagesS StoryApril Anne MaguadNo ratings yet
- Hospital Design Module 8 - 13Document107 pagesHospital Design Module 8 - 13At Sa Wakas Ay100% (6)
- Biophysical ProfileDocument7 pagesBiophysical ProfileFloid Tortogo SibbalucaNo ratings yet
- Influencing Factors Behind Customers Attending Fitness CentreDocument10 pagesInfluencing Factors Behind Customers Attending Fitness CentreHum92reNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Dengue Viral Infections Among Febrile Patients in Mombasa County, KenyaDocument95 pagesPrevalence of Dengue Viral Infections Among Febrile Patients in Mombasa County, KenyaMuhammad AyazNo ratings yet
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ceja, Philippines ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIEDDocument1 pageNueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ceja, Philippines ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIEDKei VienaNo ratings yet
- Epilepsia Levotiracetam Vs PhenobabytalDocument9 pagesEpilepsia Levotiracetam Vs PhenobabytalBYRON RENE MALDONADO CABRERANo ratings yet
- Week-2 - Environmental Problems-Causes and Sustainability Part-1Document72 pagesWeek-2 - Environmental Problems-Causes and Sustainability Part-1Saloni ShawNo ratings yet
- Activity I IIDocument3 pagesActivity I IItristanjancisarnesto172No ratings yet
- Prof Univ DR Ion C.Tintoiu FESC Centrul de Cardiologie Al Armatei Universitatea Titu MaiorescuDocument719 pagesProf Univ DR Ion C.Tintoiu FESC Centrul de Cardiologie Al Armatei Universitatea Titu MaiorescuVioleta Malina Bîrsan HodivoianuNo ratings yet
- BEPZA Act 2019 EnglishDocument66 pagesBEPZA Act 2019 Englishfahad100% (1)
- Tools Ipe, Interprofesional Education, QuestionnaireDocument70 pagesTools Ipe, Interprofesional Education, QuestionnaireRosikhah Al-MarisNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Clinical Records PDFDocument2 pagesHeart Failure Clinical Records PDFana lucia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Vector Control and Prevention OF Aedes Aegypti: Uma RaghavDocument19 pagesVector Control and Prevention OF Aedes Aegypti: Uma RaghavAdarshRaghavNo ratings yet
- Far 1 - Statement of Appropriations, Allotment, Obligations, Disbursements and Balances As of December 31, 2022Document4 pagesFar 1 - Statement of Appropriations, Allotment, Obligations, Disbursements and Balances As of December 31, 2022Whenng LopezNo ratings yet
- Form A15 - Application For Seafarers DocumentsDocument3 pagesForm A15 - Application For Seafarers DocumentsMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Labor Law-Q&ADocument8 pagesLabor Law-Q&AAldin Lucena AparecioNo ratings yet
- Conclusion: Ryngoscope 1983 93:220 - 231Document1 pageConclusion: Ryngoscope 1983 93:220 - 231SamNo ratings yet
- Administrative Officer Duties and ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesAdministrative Officer Duties and ResponsibilitiesJOEL ESPENIDANo ratings yet
- Infection Control BasicsDocument10 pagesInfection Control BasicsAlan Amato100% (1)
- Vilda MetDocument28 pagesVilda Metnaeem186No ratings yet
- Sample Test Executive MBA 2020Document8 pagesSample Test Executive MBA 2020iftikharhassanNo ratings yet
- Land Surveying Course in HydDocument2 pagesLand Surveying Course in HydAnkush NayarNo ratings yet
- LegendsDocument2 pagesLegendsEnrique Serrano VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Media Manual Book PDFDocument81 pagesMedia Manual Book PDFsteldyNo ratings yet