Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BZ Lab 2
BZ Lab 2
Uploaded by
Alexa Jean D. HonrejasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BZ Lab 2
BZ Lab 2
Uploaded by
Alexa Jean D. HonrejasCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet # 2
Animal Cells and tissues
Name: ALEXA JEAN D. HONREJAS Date Performed: 03-15-22
Group & Section: BIOL 102 ABM1 Date Submitted: 03-21-22
I. A. Draw and label the structures of the cheek cell of a human organism.
Magnification: 40x
Source/s: _________________________________________________________
General Zoology Laboratory Exercise #2 Page 1
B. Fill in the appropriate parts/functions of the animal cell below
D. Illu
General Zoology Laboratory Exercise #2 Page 2
C. illustrate the three major parts of sperm
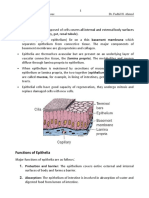
D. illustrate at least one (1) epithelial and connective tissue and label the drawing
appropriately.
General Zoology Laboratory Exercise #2 Page 3
Magnification: 40x Magnification: 40x
Source/s:
__________________________________________________________________
E. Fill in the needed informations in the table below.
Types Epithelial Location/s Function/s
Tissues
Simple squamous Air sacs of lungs and the Allows materials to pass through by
epithelium lining of the heart, blood diffusion and filtration, and secretes
vessels, and lymphatic lubricating substance.
vessels.
Simple cuboidal In ducts and secretory Secretes and absorbs
epithelium portions of small glands
and in kidney tubules.
Simple columnar Ciliated tissues are in Absorbs; it also secretes mucous
epithelium bronchi, uterine tubes, and enzymes
uterus; smooth (non-
ciliated tissues) are in the
digestive tract, bladder.
Pseudostratified Ciliated tissue lines the Secretes mucus; ciliated tissue
columnar trachea and much of the moves mucus
epithelium upper respiratory tract.
Lines the esophagus,
Stratified mouth, and vagina.
squamous FUNCTION: protects
epithelium against abrasion.
Stratified cuboidal Sweat glands, salivary Protective tissue
epithelium glands, and the
mammary glands.
Stratified columnar The male urethra and Secretes and protects
epithelium the ducts of some glands.
General Zoology Laboratory Exercise #2 Page 4
Transitional Lines the bladder, Allows the urinary organs to
epithelium urethra, and the ureters. expand and stretch
F. Fill in the needed information in the table below.
Types MuscleTissue Voluntary/involuntary Striated/Non-striated
Cardiac Involuntary Striated
Smooth Involuntary Striated
Skeletal Voluntary Non - Striated
G. Illustrate the morphology of neuron showing the four regions.
Source/s: ____________________________________________________
General Zoology Laboratory Exercise #2 Page 5
Guide Questions:
1. Name the organelles of an animal cell that are absent in a plant cell.
Lysosomes, centrosomes/centrioles, cilia, and desmosomes.
2. What is the function of flagellum in a mature spermatozoa?
The sperm used the flagellum to move towards the egg cell.
3. Give the reason/s why warm distilled water and slide are used during semen wet
mount preparation.
Temperature is critical. In tap and distilled water, sperm cells can be found after a longer
period of time than in sea and fresh water. If you put sperm in a hot water, the temperature
would kill the sperm in seconds.
4. Identify the location and major function of each of these cells:
a) Astrocyte
Found in central nervous system, perform a number of functions, including axon
guidance and synaptic support, as well as blood brain barrier and blood flow
regulation.
b) Schwann Cell
The myelin sheath is formed by glial cells in the peripheral nervous system
wrapping around the axons of motor and sensory neurons. I
c) Oligodendrocyte
Located in central nervous system. Invertebrates and vertebrates have a form of
neuroglia that produces myelin, an insulating covering on the axons of nerve
fibres.
d) Ependymal Cell
Develop from radial glia along the surface of the ventricles of the brain and the
spinal canal. The cerebrospinal fluid that fills the ventricles of the central
nervous system is secreted, circulated, and maintained in equilibrium by this
organ.
General Zoology Laboratory Exercise #2 Page 6
e) Microglia
Located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Regulate brain development,
maintenance of neuronal networks, and injury repai
f) Satellite Cell
Located in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. Satellite cells were
mononucleated cells jammed between the muscle fiber's basement membrane
and plasma membrane. They function as stem cells and are in charge of skeletal
muscle growth and development.
References:
Reece, J.B., Urry, L.A., Cain, M.L., Wasserman, S.A., Minorsky, P.V., Jackson, R.B., 2011.
Campbell Biology 9th Ed. Pearson Education Inc., Pearson Benjamin Cummings. P 100.
Biologycorner, Histology Virtual Lab - Epithelial Tissues Retrieved 19 August 2019, from
https://biologycorner.com/anatomy/histology/
Connective Tissue lab, Histology @ Yale, Retrieved 19 August 2019, from
http://medcell.med.yale.edu/histology/connective_tissue_lab.php
Muscle lab, Histology @ Yale, Retrieved 19 August 2019,
from
http://medcell.med.yale.edu/histology/connective_tissue_lab.php
Nervous system lab, Histology @ Yale, Retrieved 19 August 2019, from
http://medcell.med.yale.edu/histology/connective_tissue_lab.php
General Zoology Laboratory Exercise #2 Page 7
You might also like
- Lab Exercise 2Document4 pagesLab Exercise 2Angela Robles0% (1)
- Year 10 Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology Cells Unit 1 NotesDocument49 pagesYear 10 Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology Cells Unit 1 NotesZoonieFR0% (1)
- Lab 6 Tissue Answers PDFDocument9 pagesLab 6 Tissue Answers PDFJameson Ephisson Ferguson Forson100% (3)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument10 pagesCell Structure and FunctionKanaga ValliNo ratings yet
- Tissues and CellsDocument14 pagesTissues and Cellsstormigirl017No ratings yet
- Histology 2018 1Document38 pagesHistology 2018 1Marvin Ndashimye100% (1)
- Lab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesPia CincoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellAllyson CruzNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueDocument16 pagesMicroscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueSinger Rahul Sharma100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4100% (1)
- Lab1 Histology Bios E1b 2016cDocument13 pagesLab1 Histology Bios E1b 2016cwekrjbhweiuNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Body TissueDocument59 pagesBody TissueAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY Edited 2020Document44 pagesHISTOLOGY Edited 2020lifeeternaltointerveneNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Document10 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Saurav Soni100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueSagar GavasNo ratings yet
- Education Notes 2Document6 pagesEducation Notes 2Rwynn MemoryNo ratings yet
- Mirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Document5 pagesMirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Kiana MiradorNo ratings yet
- Epithelium SummaryDocument7 pagesEpithelium SummaryElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIDocument110 pagesAnimal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIYash Soneji100% (2)
- Histo 1Document9 pagesHisto 1carloNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocument20 pagesAnimal TissuesRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- Tissue WorksheetDocument4 pagesTissue WorksheetFAITH ALBAÑEZNo ratings yet
- Bio Presentation Week 2.1Document53 pagesBio Presentation Week 2.1NormanNo ratings yet
- Elementary TissuesDocument32 pagesElementary TissuesManjunath100% (1)
- Lesson 4 - Activity 2 1 TBHDocument6 pagesLesson 4 - Activity 2 1 TBHLoraine Andrei DeLeonNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument20 pagesTissueJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument39 pagesHistologyHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Session No. 1.2. Cell Types and ModificationsDocument48 pagesSession No. 1.2. Cell Types and ModificationsShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Lec 1-2Document7 pagesLec 1-2Monenus KedirNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Epithelial TissueDocument6 pagesExercise 1: Epithelial TissueTherese RiveraNo ratings yet
- Q1 GenBio1 SLKWeek2 EditDocument21 pagesQ1 GenBio1 SLKWeek2 EditInele Ellia AgRe100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - 2013 Animal TissuesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - 2013 Animal TissuesSiti Juwairiah ZainurinNo ratings yet
- Ciliated EpitheliumDocument26 pagesCiliated EpitheliumdeepasanmughamNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsDocument16 pagesCH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsREENA GULERIANo ratings yet
- Expeeriment 2Document4 pagesExpeeriment 2Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Btec Biology New RevisionDocument53 pagesBtec Biology New RevisionGemma WrigleyNo ratings yet
- AnaPhyLec Midterms TissueDocument4 pagesAnaPhyLec Midterms TissueSoul YuNo ratings yet
- Crissman Epithelial ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCrissman Epithelial Objectiveskkonci01No ratings yet
- Cells 22-23Document7 pagesCells 22-23hiNo ratings yet
- Q 0h7jscpou, 2s6nvoDocument14 pagesQ 0h7jscpou, 2s6nvoJosh SalengNo ratings yet
- Lecture One - PPTX - 20231008 - 142421 - 0000Document40 pagesLecture One - PPTX - 20231008 - 142421 - 0000Wll NasiibNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument10 pagesNcert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsdrathod4653No ratings yet
- TissueDocument22 pagesTissueRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument11 pagesEpithelial TissueFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Epithelial-Tissues Lect.Document13 pagesEpithelial-Tissues Lect.adelbaneen31No ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Stations 1-3Document4 pagesEpithelial Tissue Stations 1-3api-692335939No ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 Epitheliel ConnectiveDocument2 pagesWorksheet 5 Epitheliel ConnectiveMel TrincaNo ratings yet
- ORALHISTNIKIZESDocument7 pagesORALHISTNIKIZESKizes Irah Marie YsitNo ratings yet
- 3 Tissue of Human Body NotesDocument11 pages3 Tissue of Human Body Notesghanshyam agnihotryNo ratings yet
- 6 - Histology Lecture, Structure of The Epithelium 1Document52 pages6 - Histology Lecture, Structure of The Epithelium 1AMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Answer Key-TissuesDocument10 pagesCh05 Answer Key-TissuesGaveen CoatesNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues - Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesLAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues - Integumentary SystemMickey Ayle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument27 pagesNothingyoussef zareaNo ratings yet
- Ep It HeliumDocument75 pagesEp It HeliumSahin mollickNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review TissueDocument4 pagesChapter Review TissueGeorge IvyNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Experiment No.2 Animal CellDocument18 pagesGen Bio 1 Experiment No.2 Animal CellIan Karlo NuñezNo ratings yet
- Activity: Nomenclature of Organic Compounds: HYDROCARBONSDocument10 pagesActivity: Nomenclature of Organic Compounds: HYDROCARBONSAlexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab 2Document5 pagesChem Lab 2Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 7Document7 pagesBZ Lab 7Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 4.0Document7 pagesBZ Lab 4.0Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 5Document8 pagesBZ Lab 5Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 3Document11 pagesBZ Lab 3Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and PhenolsDocument1 pageAlcohol and PhenolsAlexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 1Document10 pagesBZ Lab 1Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Alexa Jean D. HonrejasDocument1 pageAlexa Jean D. HonrejasAlexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology & Organisation: Body/what-Cells-In-The-Human-Body-Live-The-LongestDocument17 pagesCell Biology & Organisation: Body/what-Cells-In-The-Human-Body-Live-The-LongestDewi SallehNo ratings yet
- Histology 1Document5 pagesHistology 1raphaelNo ratings yet
- (L-2) - Cell - Mar 03, 2020Document52 pages(L-2) - Cell - Mar 03, 2020puneetlokwani04No ratings yet
- Cells Andtissues Power PointDocument92 pagesCells Andtissues Power Point46bwilsonNo ratings yet
- Cells 2 FDocument10 pagesCells 2 FEANo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Cell StructureDocument62 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Cell StructureElyse LeeNo ratings yet
- BrainstormingDocument2 pagesBrainstormingashrafbiology333No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Structure 1) Capsule: Spirillum (Spiral) - Mycoplasmas Are BacteriaDocument4 pagesBacterial Cell Structure 1) Capsule: Spirillum (Spiral) - Mycoplasmas Are BacteriaTLCRNo ratings yet
- Biol 309 Question Bank CytoskeletonDocument6 pagesBiol 309 Question Bank CytoskeletonsharventhiriNo ratings yet
- 3D. Muscle TissueDocument47 pages3D. Muscle Tissuejaf123xyNo ratings yet
- Epithelium IDocument33 pagesEpithelium IUmerNo ratings yet
- An Awareness Session On Blood Donation and Its ImportanceDocument40 pagesAn Awareness Session On Blood Donation and Its Importancekushi krishnaNo ratings yet
- CBC LalpathDocument2 pagesCBC Lalpathmoyic39272No ratings yet
- Specialised CellsDocument1 pageSpecialised CellsMr. TigerNo ratings yet
- Blood Component Fractionation: Manual Versus Automatic ProceduresDocument6 pagesBlood Component Fractionation: Manual Versus Automatic ProceduresAngelNo ratings yet
- Muscle and MovementDocument5 pagesMuscle and MovementRabiaNo ratings yet
- 3 CellsDocument7 pages3 CellsCaviles, Jasmin S.No ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Physio Ex) IntroductionDocument1 pageSkeletal Muscle Physiology (Physio Ex) IntroductionCamille ButacNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2210L Unit 2: Tissues: Terms To Know For Unit 2Document15 pagesBIOL 2210L Unit 2: Tissues: Terms To Know For Unit 2iuventasNo ratings yet
- 9744 H2 Biology Lecture Notes - JC 1: Organelles and Cellular StructuresDocument34 pages9744 H2 Biology Lecture Notes - JC 1: Organelles and Cellular StructuresTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- BONE TissueDocument16 pagesBONE TissuePotini AdityaNo ratings yet
- The Giemsa Stain Its History and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesThe Giemsa Stain Its History and ApplicationsMaritza GranadilloNo ratings yet
- Muscle Contraction MechanismDocument57 pagesMuscle Contraction MechanismRatih AnandayuNo ratings yet
- A Epithelial Tissue1!16!12 14Document32 pagesA Epithelial Tissue1!16!12 14Noor SinghNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Protein LocalizationDocument54 pagesPowerpoint Protein LocalizationJoseph BenaiahNo ratings yet
- Review On Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesReview On Animal and Plant CellLadymae GalolaNo ratings yet
- AHS 131 Lecture 4 MusclesDocument60 pagesAHS 131 Lecture 4 MusclesBikash MainaliNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus HistopathDocument11 pagesCourse Syllabus HistopathRudy Quismorio100% (2)
- CELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonDocument19 pagesCELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet