Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GEN CHEM Reviewer
GEN CHEM Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ruth Caroline Dela CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GEN CHEM Reviewer
GEN CHEM Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ruth Caroline Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTER 1.
Matter is composed of discrete
● All kinds of matter are particulates in nature. These particles.
particles may be in the form of molecules, atoms, or 2. There is an empty space between
ions. Atoms are the building blocks of matter. particles of matter.
3. The particles of matter are in
ION constant motion.
● Refers to a charged particle or a set of charged 4. There are forces that act between
particles. the particles.
● Either positively or negatively charged atoms or
molecules. PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTER
● A block of wood can be easily observed as hard, and
ATOMS based on its internal composition, it is made up of
● These are the building blocks of matter. compact particles.
MOLECULES EMPTY
● Combinations of two or more atoms.
MATTER
● Made up of particles which may be atoms, molecules,
or ions. SPACES BETWEEN PARTICLES
● Matter is anything that has mass and volume. ● The particles that make up matter have spaces in
● Ancient Greek philosophers were the first to between them.
speculate the nature of matter. ● These spaces may be little or huge, depending on the
● They only speculate on the nature of materials around kind of matter.
them as they were not able to conduct experiments
that will validate their assumptions. MOTION OF PARTICLES
● The spaces between particles dictate the kind of
○ Materials are made up of one primal movement that particles in matter can do.
matter. ● Particles that are close to one another move in
vibratory motion while particles that are far apart
move fast and in random directions.
● As the temperature increases, particles gain kinetic
energy which results in their fast movement. (Heat
and Kinetic Energy Increases)
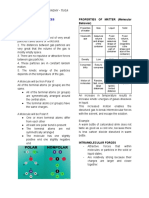
FORCES BETWEEN PARTICLES
1. Air
2. Fire INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
3. Water ● Forces that exist between particles may be attractive
4. Earth or repulsive.
● The water particles (inside) attract one another.
ANCIENT VIEWS ON MATTER ● The glass particles and
● Aristotle suggested that all space is filled up with the water particles
matter, thus, implying that there are no empty spaces. (outside) repel one
● He described each element as a balance between another.
two qualities. ● example: formation of
water droplets in cold
CONTINUITY OF MATTER glass of water.
● Since matter is not void, this means that it is divisible
and can be cut into pieces over and over again.
● This started the principle of continuity of matter,
wherein matter can be broken down into pieces and PARTICULATE NATURE OF
as you do so, you will not be able to obtain its THE THREE STATES OF MATTER
smallest parts
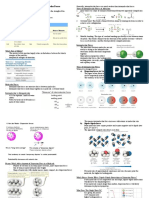
SOLID
THE GREEK CONCEPT OF ATOM ● Arrangement of particles: compact and arranged in an
● Leucippus and Democritus thought that all materials orderly manner; very little spaces between particles.
are made up of tiny bits of matter which cannot be ● Intermolecular Forces: strong
divided further. ● Motion of Particles: vibrating in fixed positions
● Greeks referred to this as atom (Greek word atomos, ● Energy of Particles: low
meaning indivisible).
LIQUID
HOW DOES THE IDEA OF DEMOCRITUS RESULT IN THE ● Arrangement of particles: close together but not
FORMULATION OF THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF arranged in an orderly manner; moderate spaces
MATTER? between particles
● The idea of Democritus paved the way in establishing ● Intermolecular Forces: moderate
that matter is made up of particles instead of a primal ● Motion of Particles: sliding past one another
material. ● Energy of Particles: moderate
DISCONTINUITY OF MATTER GAS
● Matter is made up of particles instead of primal ● Arrangement of particles: far apart and arranged
material.\ randomly; huge spaces between particles.
● Intermolecular Forces: very minimal
○ Four Main Ideas: ● Motion of Particles: move quickly and randomly
● Energy of Particles: high
The arrangement of particles, its motion, and intermolecular Separation techniques on homogeneous and heterogeneous
forces dictate the kind of state in which matter exists. mixtures play an important role in several industrial processes.
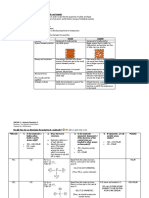
HOMOGENEOUS AND HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURES ● Homogeneous solid-liquid mixtures may be
separated by evaporation or by recrystallization.
● MIXTURE ○ Evaporation is the phase transition from
○ It is a blend of two or more substances liquid to vapor. It is done by heating the
combined together through a physical solution to dry up the solvent and crystallized
process. the substance of interest.
● Recrystallization is a separation technique
● HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE based on the difference in solubilities of
○ It is a combination of two or more substances in an appropriate solvent at an
substances that cannot be distinguished elevated temperature.
from one another. It has uniform composition
and properties. Homogeneous mixtures are ● Homogeneous liquid-liquid mixtures may be
also called solutions. separated by distillation or by chromatography.
○ Distillation is a separation technique based
● HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE on the difference of boiling points between
○ It is a combination of two or more two liquid components.
substances that can be distinguished from ○ Chromatography is a separation technique
one another. It has varying composition and that relies on the differential partition of the
properties. components between the two important
○ A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture phases in chromatography: the mobile phase
whose solutes do not completely dissolve. and the stationary phase.
The insoluble particles settle into clumps or
layers when left undisturbed. ● Different methods can be used to separate
○ A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture whose heterogeneous solid-solid mixtures. Components
solute-like particles are dispersed in a of some mixtures of this type can be separated by
medium. manual picking, sieving or by using a magnet.
● COMPOUNDS ● Different methods can be used to separate
○ consist of atoms of different elements that heterogeneous solid-liquid mixtures such as
are chemically combined together in a fixed filtration, sedimentation, decantation, and
ratio. centrifugation.
○ Mixtures are combinations of two or more ○ Filtration is a process of separating solids
substances where there is no chemical from liquids by allowing the mixture to pass
combination or reaction. through a filtering material.
■ Compounds have their own specific ○ Sedimentation is the process in which
chemical and physical properties suspended solids will eventually separate
that are distinct from their from liquids by gravity.
constituent elements. Mixtures do ○ Decantation is the removal of the liquid
not. They reflect the properties of component from the solid sediment by
their constituent substances, which pouring the liquid out of the container gently
retain their original properties. to avoid the solid particles to suspend again.
■ Compounds have specific mass ○ Centrifugation is a process in which the
ratios. Mixtures have variable mass suspension is rotated at very high speeds,
ratios. allowing the components to separate into
■ Compounds are created by layers based on their densities or particle
chemical reactions. Mixtures are size.
made by physically combining pure
substances whether they be solids, ● Combustibility
liquids or gases. ○ Refers to the ability of a material to combust
■ Mixtures can be homogeneous or or burn.
heterogeneous. Compounds can be
separated into simpler substances
by chemical methods or reactions. ● Malleability
Mixtures can be separated into ○ Capability of being shaped or extended by
simpler substances by physical hammering, forging, etc.
methods. ○ Example: Metal can be flattened into thin
sheets due to its malleability.
● Solvent
SEPARATION OF MIXTURES ○ It is the dissolving medium.
Homogeneous mixtures or solutions are mixtures composed of ○ Example: water
two or more substances combined together in a manner that ● Solute
the components are indistinguishable from each other. ○ The substance that is being dissolved.
They appear in only one phase. Many commercial products ○ Example: salt, sugar
that we use in our everyday lives are solutions.
Heterogeneous mixtures are mixtures whose composition and
appearance is not consistent all throughout since components
of a are visually distinct from each other. It can have two or
more phases. They can be further classified as suspensions or
colloids. Many commercial products that we use in our
everyday lives are heterogeneous mixtures.
You might also like
- Spec Section 05-05-19 For Post-Installed Concrete Anchors Specification Text ASSET DOC LOC 1614384Document8 pagesSpec Section 05-05-19 For Post-Installed Concrete Anchors Specification Text ASSET DOC LOC 1614384Marcus de AssisNo ratings yet
- HK Training Plan-2019Document10 pagesHK Training Plan-2019Lian stwn100% (1)
- Manual Tecnico Daewoo DWC 300MDocument52 pagesManual Tecnico Daewoo DWC 300MMaurilio CaetanoNo ratings yet
- Failures and Repair of Silo and BunkersDocument51 pagesFailures and Repair of Silo and BunkersBalan-Nogi Dan100% (1)
- PopwerpointDocument31 pagesPopwerpointLhyn DE Leon DumayaNo ratings yet
- ' ' SdsaDocument34 pages' ' SdsaUD ATNo ratings yet
- Sci ReviewersDocument9 pagesSci ReviewersCrane BigwavebigwavepihajjmaNo ratings yet
- VarunoutlineDocument80 pagesVarunoutlineDheekshith KumarNo ratings yet
- Particle Model of Matter and Atomic structureDocument11 pagesParticle Model of Matter and Atomic structure22kuriangNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes (Midterms)Document7 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes (Midterms)John Henry PahilangaNo ratings yet
- Chem 1st FinDocument333 pagesChem 1st Finjzjz14324No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDuke FaciolNo ratings yet
- Midterm Week 1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument15 pagesMidterm Week 1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryLealyn OlunanNo ratings yet
- GENERALESSON1234Document13 pagesGENERALESSON1234Carmina BesarioNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The AtomDocument57 pagesThe Structure of The AtomGranville RegalarioNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Particle Nature of MatterDocument67 pagesUnit 9 Particle Nature of Mattermiguelcastillo212301No ratings yet
- Folio Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document34 pagesFolio Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Nurul Syafiqa MahadhirNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument38 pages1.1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryKéiNo ratings yet
- Sci-States of MatterDocument1 pageSci-States of MatterClaude de alger ObeliaNo ratings yet
- 1st Semester Q1 General Chemistry (Notes)Document10 pages1st Semester Q1 General Chemistry (Notes)vince.resultay07No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesCHEMISTRYGeorgia LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionDocument27 pagesThermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionSaad BBNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 3rd Quarter Unit 1 PT 1Document99 pagesChem 2 3rd Quarter Unit 1 PT 1Yzabelle RemataNo ratings yet
- MLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyDocument15 pagesMLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyfuckyouNo ratings yet
- Particle Model of Matter and Atomic Structure (2)Document11 pagesParticle Model of Matter and Atomic Structure (2)22kuriangNo ratings yet
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0101 AkDocument4 pagesCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0101 AkKyla Dave LiganNo ratings yet
- PHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFDocument28 pagesPHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFanton petrovNo ratings yet
- 6resource 131602210601 53Document156 pages6resource 131602210601 53No ExcuseNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 1: Chapter 1: Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 1: Chapter 1: Kinetic Particle TheoryKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document31 pagesChapter 10oninNo ratings yet
- C07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)Document22 pagesC07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)a m i rNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2Document20 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2Jin LianNo ratings yet
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0101 FDDocument12 pagesCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0101 FDJerome ManriqueNo ratings yet
- LeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1Document4 pagesLeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1John michael EstradaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Theory PDFDocument38 pagesKinetic Particle Theory PDFMuhammad Darrel Keefa100% (1)
- INTERMOLECULAR-FORCES-Part-I_050842 (1)Document30 pagesINTERMOLECULAR-FORCES-Part-I_050842 (1)kilameshkingNo ratings yet
- GNCHM 2 1st Quarter Exam ReviewerDocument19 pagesGNCHM 2 1st Quarter Exam ReviewerDani AlmanzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Medical ChemistryDocument165 pagesLecture 1 Medical ChemistryCypher Soth ViNo ratings yet
- All About Matter: November 20, 2017Document2 pagesAll About Matter: November 20, 2017Aaliyah Joize LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Matter STD 8Document13 pagesMatter STD 8sohail.shaikh5065No ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument37 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJohnnardBelenNo ratings yet
- Particle Theory Q&aDocument2 pagesParticle Theory Q&aNancy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument53 pagesKinetic Particle TheoryAaditya MKNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction (Study Guide)Document22 pagesLesson 1.2 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction (Study Guide)Wilmark Rivera Official100% (2)
- Tro 3rded Chapter1 CH FA14Document14 pagesTro 3rded Chapter1 CH FA14tamaraNo ratings yet
- Chap-2 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument23 pagesChap-2 - Kinetic Particle TheoryMin HanbyeolNo ratings yet
- States of Matter: Hi My Dear Students! I Am On The Chat For Answer Any QuestionDocument9 pagesStates of Matter: Hi My Dear Students! I Am On The Chat For Answer Any QuestionAna Maria Robayo JiménezNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 MidtermDocument18 pagesChem 1 MidtermIsabel SantosNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceandreacaswNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Document28 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Fern Baldonaza100% (1)
- Week 1: Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument31 pagesWeek 1: Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsCrizza Mae CuregNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: DR en C. Abril Ivett P. Gómez Guzmán MailDocument18 pagesChemistry: DR en C. Abril Ivett P. Gómez Guzmán Mailjesus gomezNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document23 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2St. DymphaMaralit, Joyce Anne L.No ratings yet
- Changes in The States of Matter: Chapter 4 Matter and Substance 4.1Document11 pagesChanges in The States of Matter: Chapter 4 Matter and Substance 4.1Jia JiaNo ratings yet
- Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesDocument6 pagesLiquids and Intermolecular Forcessofia tolentinoNo ratings yet
- Notes MatterDocument5 pagesNotes Mattertaha imranNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetDocument2 pagesStates of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM II Kulang PaDocument12 pagesGEN CHEM II Kulang Pasara joyce pinedaNo ratings yet
- Particle Theory & WorksheetsDocument6 pagesParticle Theory & WorksheetsaamarahyousafNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ReviewerDocument23 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewerKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- Genchem ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenchem ReviewerKarylle PingolNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterDocument39 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterSilhouette DreamNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument2 pagesGen Chem ReviewerayonnahreesedeveraNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Philo EssayDocument2 pagesPhilo EssayRuth Caroline Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Q4 Written Work MUSICDocument1 pageQ4 Written Work MUSICRuth Caroline Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Q4 Written Work HEALTHDocument1 pageQ4 Written Work HEALTHRuth Caroline Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ruth Dela Cruz - Portfolio Sa Araling PanlipunanDocument25 pagesRuth Dela Cruz - Portfolio Sa Araling PanlipunanRuth Caroline Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Cam Vice ReportDocument40 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Cam Vice ReportSendhilNathan67% (3)
- Synthesis of PolycarboxilateDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Polycarboxilatejhon smithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Test QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Test QuestionsBestswimmer2011No ratings yet
- 5.6 SpecDocument9 pages5.6 Specz32No ratings yet
- 10 Building Stones & MasonryDocument47 pages10 Building Stones & MasonryMohamedNo ratings yet
- Precon Sewerage SystemDocument10 pagesPrecon Sewerage SystemArdiPratomoNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Methanol Synthesis in Packed Bed Reactor Based On Gas From Biomass GasificationDocument9 pagesSimulation of Methanol Synthesis in Packed Bed Reactor Based On Gas From Biomass GasificationHaris Surya HidayatNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug 75 TDocument2 pagesLifting Lug 75 Trustamriyadi0% (1)
- MAS-Access Panel by Saint Gobain GyprocDocument43 pagesMAS-Access Panel by Saint Gobain GyprocPunk GowthamanNo ratings yet
- Bomba Dosificadora Serie VDocument12 pagesBomba Dosificadora Serie VMartin AndradeNo ratings yet
- An II - DG 250KVA Tech SpecificationsDocument19 pagesAn II - DG 250KVA Tech SpecificationsMary HarrisonNo ratings yet
- c2 PDFDocument48 pagesc2 PDFSantiago UrgilesNo ratings yet
- Bajrang Wire & Infra Credentials 2024Document257 pagesBajrang Wire & Infra Credentials 2024SM AreaNo ratings yet
- 05 Repair of Concrete Super&Substructure by RecyDocument65 pages05 Repair of Concrete Super&Substructure by RecyErika BanguilanNo ratings yet
- Designing With Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) : J. R. Keough and K. L. Hayrynen G. L. PioszakDocument15 pagesDesigning With Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) : J. R. Keough and K. L. Hayrynen G. L. PioszakDouglas RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Materials Used in Tropical and Temperate Zones7Document7 pagesMaterials Used in Tropical and Temperate Zones7LKP GhNo ratings yet
- E-WASTE MANAGEMENT (Autosaved)Document19 pagesE-WASTE MANAGEMENT (Autosaved)Bijay Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Altium Rigid Flex GuidebookDocument40 pagesAltium Rigid Flex GuidebookKiran Jot Singh100% (1)
- C50 Tablet Hardness Tester HandbookDocument53 pagesC50 Tablet Hardness Tester HandbookaustoziNo ratings yet
- E 1729 - XX - Rte3mjkDocument4 pagesE 1729 - XX - Rte3mjkEric GozzerNo ratings yet
- pts830 DatasheetDocument4 pagespts830 DatasheetteehoweNo ratings yet
- Mine Ventilation RisksDocument23 pagesMine Ventilation RisksMinangkabau BreederNo ratings yet
- 42Document8 pages42Syed Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Kda - Factory Ii (Gen - Trias, Cavite) Design of MicropilesDocument4 pagesKda - Factory Ii (Gen - Trias, Cavite) Design of MicropilesRoda Cadiz100% (4)
- Fluid Mechanics-Statics: Topics ReviewedDocument57 pagesFluid Mechanics-Statics: Topics Reviewedسيد ميثم علويNo ratings yet
- Short Notes Chapter 6Document2 pagesShort Notes Chapter 6alinNo ratings yet