Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsReviewer PR
Reviewer PR
Uploaded by
Laisan SantosThis document discusses research design and methodology. It defines key terms like hypothesis, dependent and independent variables, experimental and non-experimental designs, sampling, data collection methods, and types of surveys/questionnaires. The main types of research design discussed are true experimental, quasi-experimental, descriptive, comparative, correlative, and ex post facto designs. Common sampling techniques include probability sampling methods like simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling and non-probability methods like quota, voluntary, purposive, availability, and snowball sampling. Quantitative data collection is discussed along with structured interviews, mail questionnaires, and computer-assisted surveys.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Psych 2220 Exam 1 Review GuideDocument16 pagesPsych 2220 Exam 1 Review GuideSalil MahajanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Research (PART 1) G11Document6 pagesReviewer in Research (PART 1) G11aeiaeiuao100% (1)
- Chapter Eight: Answer: BDocument10 pagesChapter Eight: Answer: Bamelia_chairunnisa_1No ratings yet
- STATPSY ReviewerDocument15 pagesSTATPSY ReviewerVincent Miguel BastieroNo ratings yet
- Experimental Psychology Notes: by DanigürlDocument7 pagesExperimental Psychology Notes: by DanigürlMikko AlbanoNo ratings yet
- MMW ReviewerDocument9 pagesMMW ReviewerLiajhi ManubaNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument2 pagesResearch ReviewerJoseline SisonNo ratings yet
- Research Quiz 1Document5 pagesResearch Quiz 1Ellen CatedralNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PRDocument8 pagesReviewer in PRCatherine SalasNo ratings yet
- PR Notes Unit 1Document4 pagesPR Notes Unit 1Alyssa MacamayNo ratings yet
- PR Module 1Document18 pagesPR Module 1Aprilyn Martelino ObregonNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Approach: 3. Quasi-Experimental DesignDocument3 pagesQuantitative Approach: 3. Quasi-Experimental DesignDior EstrellaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Research MethodsDocument10 pagesCH 2 Research Methodskabelolesufi77No ratings yet
- Field Methods 1Document6 pagesField Methods 1Angelika PadawanNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument10 pagesPractical ResearchJeyceeNo ratings yet
- Experimental Research: Azuma, Mariquit, Soco, TusoDocument36 pagesExperimental Research: Azuma, Mariquit, Soco, TusoTonette ArlesNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ReviwerDocument7 pagesPractical Research 2 Reviwerselwyn duroNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS ANALYSIS - Reviewer Week 1Document5 pagesSTATISTICS ANALYSIS - Reviewer Week 1Lovely De SalasNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument5 pagesStatisticsMachi KomacineNo ratings yet
- Terms To Learn: Notes in StatisticsDocument13 pagesTerms To Learn: Notes in StatisticsMichael JubayNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument2 pagesResearch ReviewerGizelle AnteneroNo ratings yet
- Lessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative ResearchDocument17 pagesLessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative Researchjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Nature of Research Design and MethodsDocument10 pagesChapter 10: Nature of Research Design and MethodsVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Document4 pagesReviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Jv OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Exam SummaryDocument15 pagesExam SummaryLaurin KnödlerNo ratings yet
- M9-M10 Research Lec Rev.Document13 pagesM9-M10 Research Lec Rev.Shobi ShobsNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Chapter 3 - Research MethodologyDocument7 pagesPractical Research Chapter 3 - Research MethodologyBernadette ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document6 pagesPractical Research 2Jihane TanogNo ratings yet
- Group 5-Comprehensive OutlineDocument15 pagesGroup 5-Comprehensive OutlineNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Research Midterm ReviewerDocument22 pagesResearch Midterm ReviewerdonajinegarsulaNo ratings yet
- Types of ResearchDocument8 pagesTypes of ResearchYuhaniz AnuarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quiz 1Document3 pagesLesson 3 Quiz 1VANESSA MOLUDNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR 2Document2 pagesReviewer PR 2jet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 - Chap.3Document28 pagesPractical Research 2 - Chap.3wendell john medianaNo ratings yet
- 4q Capstone ReviewerDocument14 pages4q Capstone Reviewerlheyne lopezNo ratings yet
- 2802 Key PointsDocument34 pages2802 Key PointssethtwardNo ratings yet
- Research-L11 Quantitative Research DesignDocument21 pagesResearch-L11 Quantitative Research DesignVevienne Canta100% (1)
- Research ReviewerDocument3 pagesResearch ReviewerCris Antonette AbataNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument4 pagesResearch Reviewerroemloriega18No ratings yet
- Research Techniques - Reference Notes: HypothesisDocument6 pagesResearch Techniques - Reference Notes: HypothesisHarshitBabooNo ratings yet
- (Trochim, 2006) (EBSCO Help, 2017)Document3 pages(Trochim, 2006) (EBSCO Help, 2017)왕JΔIRΩNo ratings yet
- Res - NotesDocument14 pagesRes - NotesYuri YapNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Mathematics in Modern WorldDocument5 pagesReviewer in Mathematics in Modern WorldMaria Luiza DeleonNo ratings yet
- Terminologies in ResearchDocument5 pagesTerminologies in ResearchRJEREENo ratings yet
- Research 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchAbie Joyce RemoNo ratings yet
- PR ReviwerDocument5 pagesPR ReviwerMichelle CailaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research Lecture Notes # 4Document1 pageNursing Research Lecture Notes # 4Jesamin PacquiaoNo ratings yet
- Epekto NG Tahong Sa TaoDocument5 pagesEpekto NG Tahong Sa Taojshua slNo ratings yet
- Unit 02 Word Wall - Research MethodsDocument23 pagesUnit 02 Word Wall - Research MethodsJayNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument8 pagesResearch Reviewerelecgabrielr.123No ratings yet
- Research Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchLerie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Mid TermDocument9 pagesStudy Guide For Mid Term455.lorenzoNo ratings yet
- WK 1 3Document5 pagesWK 1 3LorrieNo ratings yet
- Lectures Ni SheineDocument42 pagesLectures Ni SheineZedekiah HaloNo ratings yet
- 4410Document4 pages4410KATE CORPUZNo ratings yet
- METHODOLOGYDocument66 pagesMETHODOLOGYElon MuskNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2ND Quarter ModuleDocument21 pagesPractical Research 2ND Quarter ModuleJerome PascualNo ratings yet
- Math 4 ReviewerDocument2 pagesMath 4 ReviewerSh17sNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Key Data Analysis Terms - 2Document2 pagesGlossary of Key Data Analysis Terms - 2SocialNo ratings yet
- PSYC - 1001 - Chapter 2Document5 pagesPSYC - 1001 - Chapter 2Alaina PalmaNo ratings yet
- Venn DiagramDocument1 pageVenn DiagramLaisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 06 Activity 1Document5 pages06 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- Santos06 Quiz 1Document2 pagesSantos06 Quiz 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 1Document1 page01 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- Abm ArticleDocument2 pagesAbm ArticleLaisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 02 Worksheet 1Document1 page02 Worksheet 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Worksheet 1Document1 page01 Worksheet 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- Santos - 03 Quiz 1Document3 pagesSantos - 03 Quiz 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 1Document1 page01 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Essential Question 1Document1 page01 Essential Question 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 2Document4 pages01 Activity 2Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Giving InstructionsDocument1 page01 Giving InstructionsLaisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 1Document1 page01 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 1Document1 page01 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- PRELIMDocument16 pagesPRELIMchobiipiggy26No ratings yet
- SHS Fundamentals of Statistics PDFDocument210 pagesSHS Fundamentals of Statistics PDFRose Anne CaringalNo ratings yet
- Sample Sizes CalculationDocument5 pagesSample Sizes CalculationNewhame DagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - Statistical Quality ControlDocument82 pages15 - Statistical Quality Controlvega_nanthaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics - Numerical MeasuresDocument102 pagesDescriptive Statistics - Numerical MeasuresKautik ShahNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Statistical Inference Estimation of Parameters Lesson 1 Estimation of Parameters Part 1.pDocument5 pagesModule 4 Statistical Inference Estimation of Parameters Lesson 1 Estimation of Parameters Part 1.pLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- Properties of Arithmetic MeanDocument3 pagesProperties of Arithmetic MeandeepakNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Wk2Document10 pagesPractical Research 2 Wk2jaslorNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Consumer Interest in Choosing A Coffee Store in Tangerang DistrictDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting Consumer Interest in Choosing A Coffee Store in Tangerang Districtriro farNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression: Presented by Tayyab Pervaiz 19011507-093Document11 pagesSimple Linear Regression: Presented by Tayyab Pervaiz 19011507-093Mg HNo ratings yet
- MetaDocument5 pagesMetaAby MathewNo ratings yet
- Probability and Stochastic Process Chap 4 Exercise by Nguyễn Thị Thu Thủy (Sami-Hust)Document73 pagesProbability and Stochastic Process Chap 4 Exercise by Nguyễn Thị Thu Thủy (Sami-Hust)Doanh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- CI and HT PDFDocument8 pagesCI and HT PDFshama vidyarthyNo ratings yet
- 1361 6793 1 PBDocument12 pages1361 6793 1 PBSheLyNo ratings yet
- Tabel Stat Baru PDFDocument19 pagesTabel Stat Baru PDFKenim MuhamdNo ratings yet
- A Novel Approach To Deriving The Lower Confidence Limit of Indices Cpu CPL and CPK in Assessing Process Capability - IJPR - 2017 PDFDocument20 pagesA Novel Approach To Deriving The Lower Confidence Limit of Indices Cpu CPL and CPK in Assessing Process Capability - IJPR - 2017 PDFCarlos Dario CristianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 QMT 554-Jul10Document59 pagesChapter 3 QMT 554-Jul10Umi Afiqah Amalin AzhishamNo ratings yet
- Validity of The World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS) Screener in A Representative Sample of Health Plan MembersDocument14 pagesValidity of The World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS) Screener in A Representative Sample of Health Plan MembersCloudcynaraaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques Assignment #1Document5 pagesQuantitative Techniques Assignment #1XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXNo ratings yet
- BES - R Lab 9Document5 pagesBES - R Lab 9Ngọc BíchNo ratings yet
- Null Hypothesis Significance TestingDocument9 pagesNull Hypothesis Significance Testingkash1080No ratings yet
- Incremental and Marginal VaR Plus Infiniti 4 Moment Version No VBADocument14 pagesIncremental and Marginal VaR Plus Infiniti 4 Moment Version No VBAPeter UrbaniNo ratings yet
- Correlation and Regression: Fathers' and Daughters' HeightsDocument43 pagesCorrelation and Regression: Fathers' and Daughters' HeightsI-51 GAURAV RANALKARNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 - Spring 2014 - Chapter 6 - KeyDocument8 pagesWorksheet 9 - Spring 2014 - Chapter 6 - KeyKatrina ManalaysayNo ratings yet
- Sioco LAS Stat&ProbDocument9 pagesSioco LAS Stat&ProbMark Anthony Montesa SiocoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document11 pagesChapter 5Mrcharming JadraqueNo ratings yet
- Blastam Statistics CheatsheetDocument1 pageBlastam Statistics CheatsheetHanbali Athari100% (1)
- Clinical Research Curriculum Critical Appraisal of The Medical LiteratureDocument36 pagesClinical Research Curriculum Critical Appraisal of The Medical LiteratureArkipus PamuttuNo ratings yet
Reviewer PR
Reviewer PR
Uploaded by
Laisan Santos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesThis document discusses research design and methodology. It defines key terms like hypothesis, dependent and independent variables, experimental and non-experimental designs, sampling, data collection methods, and types of surveys/questionnaires. The main types of research design discussed are true experimental, quasi-experimental, descriptive, comparative, correlative, and ex post facto designs. Common sampling techniques include probability sampling methods like simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling and non-probability methods like quota, voluntary, purposive, availability, and snowball sampling. Quantitative data collection is discussed along with structured interviews, mail questionnaires, and computer-assisted surveys.
Original Description:
pr
Original Title
Reviewer pr
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses research design and methodology. It defines key terms like hypothesis, dependent and independent variables, experimental and non-experimental designs, sampling, data collection methods, and types of surveys/questionnaires. The main types of research design discussed are true experimental, quasi-experimental, descriptive, comparative, correlative, and ex post facto designs. Common sampling techniques include probability sampling methods like simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling and non-probability methods like quota, voluntary, purposive, availability, and snowball sampling. Quantitative data collection is discussed along with structured interviews, mail questionnaires, and computer-assisted surveys.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesReviewer PR
Reviewer PR
Uploaded by
Laisan SantosThis document discusses research design and methodology. It defines key terms like hypothesis, dependent and independent variables, experimental and non-experimental designs, sampling, data collection methods, and types of surveys/questionnaires. The main types of research design discussed are true experimental, quasi-experimental, descriptive, comparative, correlative, and ex post facto designs. Common sampling techniques include probability sampling methods like simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling and non-probability methods like quota, voluntary, purposive, availability, and snowball sampling. Quantitative data collection is discussed along with structured interviews, mail questionnaires, and computer-assisted surveys.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Hypothesis Dependent variable
- Is the condition that you measure in
- a logical supposition, a reasonable the experiment.
guess and an educated conjecture that - You test how it reacts to a change
provides a tentative explanation to in the independent variable.
formulated questions - It is also known as the responding
- It is used to define the relationship of a variable.
variable to another variable.
Types of Research Designs
Two (2) categories of hypothesis
Experimental
Null hypothesis - a variable or group variables are
manipulated or controlled to know
- Symbolized by Ho and the alternative
if a formulated hypothesis is valid
hypothesis id denoted by Ha, H1, or Em.
or displays truthfulness
- States the relationship between the
variables. It somewhat disproves that
Two (2) types of experimental research:
the independent variable has a direct
reaction or effect to the dependent
variable 1. True Experimental Design
- Uses random selection of
Alternative hypothesis participants.
- It is free from bias and ensures
- Employed to challenge the null objectivity of results.
hypothesis by giving statements, which - It is the best design to use when
claim that the independent variable examining causal relationships.
does effect the dependent variable.
- Is often tested first. 2. Quasi-Experimental Design
- The term quasi means pseudo,
There are two (2) types of variables important partly, or almost.
to any given research: - This design is prone to bias since
the researcher purposely selects
Independent variable
the participants.
- Is the condition that you change in
- It is incapable of determining cause
an experiment or study.
and relationships.
- This is the variable that you can
control.
- Its value is not affected and does
not depend on the state of any other
variable in an experiment.
Non-Experimental Sampling
- a method of acquiring representatives
- Capable of providing qualitative and of a certain population to gain and
quantitative data but more on determine parameters of the whole
qualitative data. group
- It is often used in the field of social
sciences. Population
- Non-experimental designs do away - used in research that denotes a huge
with manipulating variables. group of people where you can choose
a sample
Five (5) types of non-experimental research:
Sample
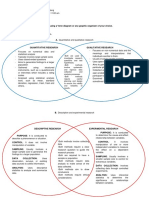
1. Descriptive
- represents the entire group
- Shows an image or picture of an
individual or group.
3. Comparative
- Tells the differences or similarities 1. Probability Sampling
among individuals, groups, - this method relies on the
occurrences, and others. researcher’s selection of
4. Correlative respondents on pure chance thus,
- Shows the extent of relationship everybody in the population
of people, occurrences, places, participates.
and others whether if it is negative
of positive. a. Simple-random Sampling
5. Survey - the selection of respondents is
- Describes the behavior, based on pure chance.
preferences, opinions, views, b. Systematic Sampling
stand, or attitudes of a huge - this is a type of probability sampling
amount of people. scheme in which sample members
6. Ex Post Facto
from a larger population are chosen
- Derives data from stuff that
normally occurs as is. No according to a random starting point
alterations whatsoever are done and a fixed, periodic interval.
to not influence the reactions of - This interval, called the sampling
variables. This is done to explain interval, is calculated by dividing the
about past events. It means “that population size by the desired
which is done afterwards” in sample size.
English.
c. Stratified Sampling Data
- this type of method chooses a - various kinds of information
sample that later on be subdivided formatted in a particular way.
into- sub-groups during the stage
of data analysis Types of quantitative data
d. Cluster Sampling
- this is choosing respondents in Descriptive data
clusters, rather than in separate - statistics allows you to easily quantify a
individuals. variable (or variables) for a target
group.
2. Non-Probability Sampling Comparative data
- allows a comparison two or more target
- this technique is prone to bias
groups based on one or more variable.
due to the pre-selection of
Relationship data
respondents.
- data highlights trends, associations
and relationships between two or
a. Quota Sampling
more variables.
- selecting specific samples that the
researcher knows will correspond
to the population in terms of one Interviews
(1), two (2), or even more
characteristics. - Interviewing people is a standard
b. Voluntary Sampling method used for data collection.
- choosing samples who are very - However, the interviews conducted to
much willing to participate as collect quantitative data are more
respondents. structured, wherein the researchers ask
c. Purposive Sampling only a standard set of questionnaires
- selecting respondents who are and nothing more than that.
deemed by the researcher as
samples with good background There are three major types of interviews
and knowledgeable about the conducted for data collection
study being conducted.
d. Availability Sampling Telephone interviews
- choosing respondents who are
- interviews ruled the charts of data
easy to find and willing to
collection methods.
communicate with the researcher.
- However, nowadays, there is a
e. Snowball Sampling
- also known as chain sampling, is significant rise in conducting video
used when the respondents interviews using the internet, Skype, or
cannot be easily located like similar online video calling platforms
homeless individuals or street
children
Face-to-face interviews Mail Questionnaire
- It is a proven technique to collect data - the survey is mailed out to a host of the
directly from the participants. sample population, enabling the
- It helps in acquiring quality data as it researcher to connect with a wide
provides a scope to ask detailed range of audiences.
questions and probing further to collect
rich and informative data.
Computer-Assisted Personal Interviewing
(CAPI)
- It is nothing but a similar setup of the
face-to-face interview where the
interviewer carries a desktop or laptop
along with him at the time of interview
to upload the data obtained from the
interview directly into the database.
Surveys/questionnaires
- questionnaires created using online
survey software are playing a pivotal
role in online data collection be is
quantitative or qualitative research
Two significant types of survey questionnaires
used to collect online data for quantitative
market research
Web-based questionnaire
- This is one of the ruling and most
trusted methods for internet-based
research or online research.
- In a web-based questionnaire, the
receive an email containing the survey
link, clicking on which takes the
respondent to a secure online survey
tool from where he/she can take the
survey or fill in the survey
questionnaire.
You might also like
- Psych 2220 Exam 1 Review GuideDocument16 pagesPsych 2220 Exam 1 Review GuideSalil MahajanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Research (PART 1) G11Document6 pagesReviewer in Research (PART 1) G11aeiaeiuao100% (1)
- Chapter Eight: Answer: BDocument10 pagesChapter Eight: Answer: Bamelia_chairunnisa_1No ratings yet
- STATPSY ReviewerDocument15 pagesSTATPSY ReviewerVincent Miguel BastieroNo ratings yet
- Experimental Psychology Notes: by DanigürlDocument7 pagesExperimental Psychology Notes: by DanigürlMikko AlbanoNo ratings yet
- MMW ReviewerDocument9 pagesMMW ReviewerLiajhi ManubaNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument2 pagesResearch ReviewerJoseline SisonNo ratings yet
- Research Quiz 1Document5 pagesResearch Quiz 1Ellen CatedralNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PRDocument8 pagesReviewer in PRCatherine SalasNo ratings yet
- PR Notes Unit 1Document4 pagesPR Notes Unit 1Alyssa MacamayNo ratings yet
- PR Module 1Document18 pagesPR Module 1Aprilyn Martelino ObregonNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Approach: 3. Quasi-Experimental DesignDocument3 pagesQuantitative Approach: 3. Quasi-Experimental DesignDior EstrellaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Research MethodsDocument10 pagesCH 2 Research Methodskabelolesufi77No ratings yet
- Field Methods 1Document6 pagesField Methods 1Angelika PadawanNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument10 pagesPractical ResearchJeyceeNo ratings yet
- Experimental Research: Azuma, Mariquit, Soco, TusoDocument36 pagesExperimental Research: Azuma, Mariquit, Soco, TusoTonette ArlesNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ReviwerDocument7 pagesPractical Research 2 Reviwerselwyn duroNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS ANALYSIS - Reviewer Week 1Document5 pagesSTATISTICS ANALYSIS - Reviewer Week 1Lovely De SalasNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument5 pagesStatisticsMachi KomacineNo ratings yet
- Terms To Learn: Notes in StatisticsDocument13 pagesTerms To Learn: Notes in StatisticsMichael JubayNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument2 pagesResearch ReviewerGizelle AnteneroNo ratings yet
- Lessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative ResearchDocument17 pagesLessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative Researchjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Nature of Research Design and MethodsDocument10 pagesChapter 10: Nature of Research Design and MethodsVero SteelNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Document4 pagesReviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Jv OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Exam SummaryDocument15 pagesExam SummaryLaurin KnödlerNo ratings yet
- M9-M10 Research Lec Rev.Document13 pagesM9-M10 Research Lec Rev.Shobi ShobsNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Chapter 3 - Research MethodologyDocument7 pagesPractical Research Chapter 3 - Research MethodologyBernadette ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document6 pagesPractical Research 2Jihane TanogNo ratings yet
- Group 5-Comprehensive OutlineDocument15 pagesGroup 5-Comprehensive OutlineNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Research Midterm ReviewerDocument22 pagesResearch Midterm ReviewerdonajinegarsulaNo ratings yet
- Types of ResearchDocument8 pagesTypes of ResearchYuhaniz AnuarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quiz 1Document3 pagesLesson 3 Quiz 1VANESSA MOLUDNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR 2Document2 pagesReviewer PR 2jet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 - Chap.3Document28 pagesPractical Research 2 - Chap.3wendell john medianaNo ratings yet
- 4q Capstone ReviewerDocument14 pages4q Capstone Reviewerlheyne lopezNo ratings yet
- 2802 Key PointsDocument34 pages2802 Key PointssethtwardNo ratings yet
- Research-L11 Quantitative Research DesignDocument21 pagesResearch-L11 Quantitative Research DesignVevienne Canta100% (1)
- Research ReviewerDocument3 pagesResearch ReviewerCris Antonette AbataNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument4 pagesResearch Reviewerroemloriega18No ratings yet
- Research Techniques - Reference Notes: HypothesisDocument6 pagesResearch Techniques - Reference Notes: HypothesisHarshitBabooNo ratings yet
- (Trochim, 2006) (EBSCO Help, 2017)Document3 pages(Trochim, 2006) (EBSCO Help, 2017)왕JΔIRΩNo ratings yet
- Res - NotesDocument14 pagesRes - NotesYuri YapNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Mathematics in Modern WorldDocument5 pagesReviewer in Mathematics in Modern WorldMaria Luiza DeleonNo ratings yet
- Terminologies in ResearchDocument5 pagesTerminologies in ResearchRJEREENo ratings yet
- Research 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchAbie Joyce RemoNo ratings yet
- PR ReviwerDocument5 pagesPR ReviwerMichelle CailaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research Lecture Notes # 4Document1 pageNursing Research Lecture Notes # 4Jesamin PacquiaoNo ratings yet
- Epekto NG Tahong Sa TaoDocument5 pagesEpekto NG Tahong Sa Taojshua slNo ratings yet
- Unit 02 Word Wall - Research MethodsDocument23 pagesUnit 02 Word Wall - Research MethodsJayNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument8 pagesResearch Reviewerelecgabrielr.123No ratings yet
- Research Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchLerie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Mid TermDocument9 pagesStudy Guide For Mid Term455.lorenzoNo ratings yet
- WK 1 3Document5 pagesWK 1 3LorrieNo ratings yet
- Lectures Ni SheineDocument42 pagesLectures Ni SheineZedekiah HaloNo ratings yet
- 4410Document4 pages4410KATE CORPUZNo ratings yet
- METHODOLOGYDocument66 pagesMETHODOLOGYElon MuskNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2ND Quarter ModuleDocument21 pagesPractical Research 2ND Quarter ModuleJerome PascualNo ratings yet
- Math 4 ReviewerDocument2 pagesMath 4 ReviewerSh17sNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Key Data Analysis Terms - 2Document2 pagesGlossary of Key Data Analysis Terms - 2SocialNo ratings yet
- PSYC - 1001 - Chapter 2Document5 pagesPSYC - 1001 - Chapter 2Alaina PalmaNo ratings yet
- Venn DiagramDocument1 pageVenn DiagramLaisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 06 Activity 1Document5 pages06 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- Santos06 Quiz 1Document2 pagesSantos06 Quiz 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 1Document1 page01 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- Abm ArticleDocument2 pagesAbm ArticleLaisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 02 Worksheet 1Document1 page02 Worksheet 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Worksheet 1Document1 page01 Worksheet 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- Santos - 03 Quiz 1Document3 pagesSantos - 03 Quiz 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 1Document1 page01 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Essential Question 1Document1 page01 Essential Question 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 2Document4 pages01 Activity 2Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Giving InstructionsDocument1 page01 Giving InstructionsLaisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 1Document1 page01 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- 01 Activity 1Document1 page01 Activity 1Laisan SantosNo ratings yet
- PRELIMDocument16 pagesPRELIMchobiipiggy26No ratings yet
- SHS Fundamentals of Statistics PDFDocument210 pagesSHS Fundamentals of Statistics PDFRose Anne CaringalNo ratings yet
- Sample Sizes CalculationDocument5 pagesSample Sizes CalculationNewhame DagneNo ratings yet
- 15 - Statistical Quality ControlDocument82 pages15 - Statistical Quality Controlvega_nanthaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics - Numerical MeasuresDocument102 pagesDescriptive Statistics - Numerical MeasuresKautik ShahNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Statistical Inference Estimation of Parameters Lesson 1 Estimation of Parameters Part 1.pDocument5 pagesModule 4 Statistical Inference Estimation of Parameters Lesson 1 Estimation of Parameters Part 1.pLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- Properties of Arithmetic MeanDocument3 pagesProperties of Arithmetic MeandeepakNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Wk2Document10 pagesPractical Research 2 Wk2jaslorNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Consumer Interest in Choosing A Coffee Store in Tangerang DistrictDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting Consumer Interest in Choosing A Coffee Store in Tangerang Districtriro farNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression: Presented by Tayyab Pervaiz 19011507-093Document11 pagesSimple Linear Regression: Presented by Tayyab Pervaiz 19011507-093Mg HNo ratings yet
- MetaDocument5 pagesMetaAby MathewNo ratings yet
- Probability and Stochastic Process Chap 4 Exercise by Nguyễn Thị Thu Thủy (Sami-Hust)Document73 pagesProbability and Stochastic Process Chap 4 Exercise by Nguyễn Thị Thu Thủy (Sami-Hust)Doanh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- CI and HT PDFDocument8 pagesCI and HT PDFshama vidyarthyNo ratings yet
- 1361 6793 1 PBDocument12 pages1361 6793 1 PBSheLyNo ratings yet
- Tabel Stat Baru PDFDocument19 pagesTabel Stat Baru PDFKenim MuhamdNo ratings yet
- A Novel Approach To Deriving The Lower Confidence Limit of Indices Cpu CPL and CPK in Assessing Process Capability - IJPR - 2017 PDFDocument20 pagesA Novel Approach To Deriving The Lower Confidence Limit of Indices Cpu CPL and CPK in Assessing Process Capability - IJPR - 2017 PDFCarlos Dario CristianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 QMT 554-Jul10Document59 pagesChapter 3 QMT 554-Jul10Umi Afiqah Amalin AzhishamNo ratings yet
- Validity of The World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS) Screener in A Representative Sample of Health Plan MembersDocument14 pagesValidity of The World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS) Screener in A Representative Sample of Health Plan MembersCloudcynaraaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques Assignment #1Document5 pagesQuantitative Techniques Assignment #1XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXNo ratings yet
- BES - R Lab 9Document5 pagesBES - R Lab 9Ngọc BíchNo ratings yet
- Null Hypothesis Significance TestingDocument9 pagesNull Hypothesis Significance Testingkash1080No ratings yet
- Incremental and Marginal VaR Plus Infiniti 4 Moment Version No VBADocument14 pagesIncremental and Marginal VaR Plus Infiniti 4 Moment Version No VBAPeter UrbaniNo ratings yet
- Correlation and Regression: Fathers' and Daughters' HeightsDocument43 pagesCorrelation and Regression: Fathers' and Daughters' HeightsI-51 GAURAV RANALKARNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 - Spring 2014 - Chapter 6 - KeyDocument8 pagesWorksheet 9 - Spring 2014 - Chapter 6 - KeyKatrina ManalaysayNo ratings yet
- Sioco LAS Stat&ProbDocument9 pagesSioco LAS Stat&ProbMark Anthony Montesa SiocoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document11 pagesChapter 5Mrcharming JadraqueNo ratings yet
- Blastam Statistics CheatsheetDocument1 pageBlastam Statistics CheatsheetHanbali Athari100% (1)
- Clinical Research Curriculum Critical Appraisal of The Medical LiteratureDocument36 pagesClinical Research Curriculum Critical Appraisal of The Medical LiteratureArkipus PamuttuNo ratings yet