Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class XII Biomolecules
Class XII Biomolecules
Uploaded by
vartikasingh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views4 pagesThe document is a test sheet for Class XII Chemistry students assessing their knowledge of biomolecules. It contains multiple choice questions, assertion-reasoning questions, and matching questions testing students understanding of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins and nucleic acids. It also contains short answer and very short answer questions requiring students to define key terms, describe structures and properties of biomolecules, explain processes like hydrolysis, and differentiate between different types of biomolecules.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document is a test sheet for Class XII Chemistry students assessing their knowledge of biomolecules. It contains multiple choice questions, assertion-reasoning questions, and matching questions testing students understanding of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins and nucleic acids. It also contains short answer and very short answer questions requiring students to define key terms, describe structures and properties of biomolecules, explain processes like hydrolysis, and differentiate between different types of biomolecules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views4 pagesClass XII Biomolecules
Class XII Biomolecules
Uploaded by
vartikasinghThe document is a test sheet for Class XII Chemistry students assessing their knowledge of biomolecules. It contains multiple choice questions, assertion-reasoning questions, and matching questions testing students understanding of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins and nucleic acids. It also contains short answer and very short answer questions requiring students to define key terms, describe structures and properties of biomolecules, explain processes like hydrolysis, and differentiate between different types of biomolecules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
SRINIVASA RAMANUJAN PUBLIC SCHOOL, PRAYAGRAJ
TEST SHEET
Class – XII
Subject – Chemistry
TOPIC – Biomolecules
Name of the Student: __________________________ Roll No. - ____ Max Time: 01 Hr.
Q1. Multiple Choice Questions
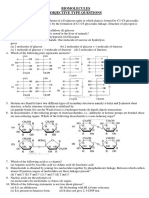
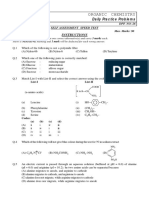
1. Which of the following statement is not true about glucose?
(a) it is an aldohexose (b) on heating with HI it forms n-hexane
(c) it is present in furanose form (d) it does not give 2, 4-DNP test
2. Which of the following acids is a vitamin?
(a) aspartic acid (b) ascorbic acid
(c) aoiphic acid (d) saccharic acid
3. Which of the following base is not present in RNA?
(a) adenine (b) uracil
(c) thymine (d) cytosine
4. Which of the following vitamins can be stored in our body?
(a) vitamin B1 (b) vitamin B2
(c) vitamin B6 (d) vitamin B12
5. Which one given below is non-reducing sugar?
(a) glucose (b) sucrose
(c) maltose (d) lactose
6. In a protein molecule amino acids are linked together by:
(a) peptide bond (b) dative bond
(c) glycosidic bond (d) phospodiestes bond
7. In DNA1 the complementary bases are:
(a) adenine and thynine ; guanine and eytosine
(b) adenine and thymine; guanine and uracil
(c) adenine and guanine; thymine and cytosine
(d) uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine
8. Deficiency of vitamin B1 , cause the disease:
(a) convulsions (b) beri-beri
(c) cheilosis (d) sterility
9. The correct statement regarding RNA and DNA is:
(a) The sugar component RNA is arabinose and sugar in DNA is ribose
(b) The sugar component in RNA is 2'deoxyribose and the sugar component in DNA is
arabinose.
(c) The sugar component in RNA is arabinose and the sugar component in DNA is 2'-
deoxyribose.
(d) The sugar component in RNA is ribose and sugar component in DNA is 2'-
deoxyribose.
10. Which of the following vitamin given below is water soluble?
(a) vitamin C (b) vitamin D
(c) vitamin K (d) vitamin E
11. The two functional groups present in a typical carbohydrates are:
(a) —OH and —COOH (b) —CHO and —COOH
(c) > C==O and —OH (d) —CHO and —COCl
12. Which of the following is called invert sugar
(a) lactose (b) sucrose
(c) maltose (d) glucose
13. Carbohydrates which give two molecules of mono-saccharides are called disaccharides.
These are:
(a) maltose (b) cellulose
(c) maltase (d) lactose
14. Starch is a mixture of:
(a) amylom (b) amylopectin
(c) amylose (d) β-D-glucose
15. Which of the following contain transition metal?
(a) Vitamin B-12 (b) Chlorophyl
(c) Haemoglobin (d) RNA
16. Which of the following has glycosidic linkage?
(a) Maltose (b) Anylose
(c) galactose (d) sucrose
17. Fibrous proteins are present in:
(a) myosin (b) albumin
(c) collagen (d) fibroin
Q2. Assertion and Reasoning Type
The question given below consist of an Assertion and the Reason. Use the following key to
choose the appropriate answer.
(a) Assertion and reason both are CORRECT and reason is the CORRECT explanation of the
assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(e) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reasson is not correct explanation of
assertion.
1. Assertion : A solution of sucrose in water is dextro rotatory but on hydrolysis in presence
of little HCl it becomes laevorotatory.
Reason : Sucrose on hydrolysis gives unequal amount of glucose and fructose as a result
sign of rotation changes.
2. Assertion : Fructose does not contain aldehyde group but still reduce Tollen's reagent.
Reason : In the presence of base, fructose undergoes rearrangement to form glucose and
mannose.
Q3. Matching Column Type
1. Match the carbohydrate in Column I with its characteristic given in Column II
Column-I Column-II
(A) Lactose (p) Ketohexose
(B) Starch (q) Disaccharide
(C) Sucrose (r) Polysaccharide
(D) Fructose (s) on hydrolysis gives β-D-glucose and β-D-galactose
(a) A–s, B–r, C–p, D–q (b) A–p, B–q, C–r, D–s
(c) A–r, B–s, C–p, D–q (d) A–s, B–r, C–q, D–p
2. Match the carbohydrate in Column I with its characteristic given in Column II
Column-I Column-II
(A) Keratin (p) protein
(B) Haemoglobin (q) β-pleated protein
(C) Riboflavin (r) α-amino acid
(D) Glycine (s) Water soluble vitamin
(a) A–p, B–q, C–s, D–r (b) A–q, B–p, C–s, D–r
(c) A–q, B–p, C–r, D–s (d) A–s, B–r, C–q, D–p
Q4. Very short answer type questions
1. What structural feature is required for a carbohydrate to behave as reducing sugar?
2. Give the significance of (+) sign in the name D-(+)-glucose.
3. Why is sucrose called invert sugar?
4. Which forces are responsible for the stability of α-helical structure of proteins?
5. What type of linkage holds together the monomers of DNA and RNA?
6. Give the Howarth projection of D-glucopyranose.
7. Name the vitamin responsible for coagulation of blood.
8. Give one example of:
(a) water soluble,
(b) fat soluble vitamins.
9. Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?
10. What are the products of hydrolysis of lactose?
11. What are monosaccharides?
12. What is the difference between native protein and denatured protein?
13. Amino acids are amphoteric in nature. Explain
Q5. Short answer type questions
1. Define the following terms in relation to proteins :
(i) Peptide linkage (ii) Denaturation
2. Explain the following terms :
(i) Invert sugar
(ii) Polypeptides
(iii) Glycosidic linkage
3. Name the product of hydrolysis of sucrose. Why is sucrose not a reducing sugar?
4. Describe what do you understand by primary structure and secondary structure of
proteins.
5. What is essentially the difference between α-form of glucose and β-form of glucose ?
Explain.
6. What are anomers ? Give the structures of two anomers of glucose.
7. . Write the hydrolysed product of :
(i) Maltose (ii) Cellulose
8. What are vitamins? How are they classified?
9. State two main differences between globular and fibrous proteins.
10. Name the constituents of starch and what is the difference between them?
11. What are essential and non-essential amino acid ? Give two examples of each type.
12. Give reasons:
(i) On electrolysis in acidic solution amino acids migrate towards cathode while in
alkaline solution these migrate towards anode.
(ii) The monoamino monocarboxylic acids have two pKa values.
13. Describe two important functions of nucleic acids.
14. Differentiate between the following :
(i) Secondary and tertiary structure of protein
(ii) α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure of protein
(iii) Fibrous and globular protein
You might also like
- Coursebook Answers Chapter 25 Asal ChemistryDocument4 pagesCoursebook Answers Chapter 25 Asal ChemistryAditiNo ratings yet
- BP203T Bichemistry 100 MCQsDocument16 pagesBP203T Bichemistry 100 MCQsShubhrat MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesEvans DionNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument5 pagesBio MoleculesKashvi BachyasNo ratings yet
- Question Chap 10 BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesQuestion Chap 10 BiomoleculesakshayorbgkapapaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument6 pagesBIOMOLECULESkavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Excel Educational Centre, Al-Thumama: Chemistry - BiomoleculesDocument4 pagesExcel Educational Centre, Al-Thumama: Chemistry - BiomoleculesteenaNo ratings yet
- MCQ CHAPTE 13 BIOMOLECULE CBSE Reduced SyllabusDocument2 pagesMCQ CHAPTE 13 BIOMOLECULE CBSE Reduced SyllabusSavien BrandanNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules 1Document5 pagesBiomolecules 1Bhumisht JatiNo ratings yet
- CPP (Biomolecules) : Part - I: Subjective QuestionsDocument15 pagesCPP (Biomolecules) : Part - I: Subjective QuestionsFalgun SoniNo ratings yet
- BIO MOLECULE MCQsDocument8 pagesBIO MOLECULE MCQsdk390381No ratings yet
- Biomolecules - DPP 01 - DPP - 1 - Biomolecues - Chemistry Vishal Sir - 08112021 - HussainDocument2 pagesBiomolecules - DPP 01 - DPP - 1 - Biomolecues - Chemistry Vishal Sir - 08112021 - Hussainanurag palNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 12 Chemistry Mcqs For BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesCbse Class 12 Chemistry Mcqs For BiomoleculeskarthikNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument4 pagesBio Moleculestimepass CreationNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules MCQs - 01Document24 pagesBiomolecules MCQs - 01Types100% (1)
- 12 Chem CH 10 MCQSDocument12 pages12 Chem CH 10 MCQSSaran.kNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentmehakNo ratings yet
- XII Biomolecules OrganizedDocument9 pagesXII Biomolecules OrganizedKazi afroz SultanNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument10 pagesBio Moleculesdivya divyaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules MCQ-1Document4 pagesBiomolecules MCQ-1BikashNo ratings yet
- 10 QP BiomoleculeDocument5 pages10 QP BiomoleculePREM SINGHNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Without Answer - 12945790 - 2024 - 03 - 26 - 12 - 20Document5 pagesBiomolecules Without Answer - 12945790 - 2024 - 03 - 26 - 12 - 20Dhirendra Kumar ChauhanNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Biology Biomolecules-2Document20 pagesNEET UG Biology Biomolecules-2VyjayanthiNo ratings yet
- DPP-41 Text Solution 20230717101012Document3 pagesDPP-41 Text Solution 20230717101012ansarinaved8920No ratings yet
- Biomolecules PrintDocument3 pagesBiomolecules Printbegrash5No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Test BankDocument24 pagesChapter 5 Test Bank陳禹誌No ratings yet
- Biomolecules 10+2, 2021-22, 30 QuestionDocument2 pagesBiomolecules 10+2, 2021-22, 30 QuestionArshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 12.10 Biomolecules WorksheetDocument5 pages12.10 Biomolecules Worksheetnivasininiva0No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesBiomoleculesAditya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULESAarushi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsDocument12 pagesRespiration in Plants: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsAditya DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class Xii Unit - 6 Biomolecules Multiple Choice Question BankDocument19 pagesChemistry Class Xii Unit - 6 Biomolecules Multiple Choice Question BankSahilNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and PolymersDocument17 pagesBiomolecules and PolymersAmogh R.GowdaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Class 12Document8 pagesBiomolecules Class 12manishachatterjee912No ratings yet
- Ch-14 Class-XII (ENG)Document8 pagesCh-14 Class-XII (ENG)rahulverma186425No ratings yet
- Biochemistry MLT EXAMDocument8 pagesBiochemistry MLT EXAMLeonel Nkweti100% (1)
- Marking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 176 Time: 1 HR 30 MinDocument9 pagesMarking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 176 Time: 1 HR 30 MinAbdulaziz-- SHNo ratings yet
- 1210 Biomolecules Worksheet 240418 103920Document4 pages1210 Biomolecules Worksheet 240418 103920nivasininiva0No ratings yet
- Biomolecules 2Document8 pagesBiomolecules 2fardeenriazahamedNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet 2Document8 pagesRevision Worksheet 2Rakesh BhutaniNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Exercises ResonanceDocument21 pagesBiomolecules Exercises Resonancehorn blowNo ratings yet
- 10 MCQsDocument1 page10 MCQsTanveer AhmedNo ratings yet
- MCQ Biochemistry CarbohydrateDocument21 pagesMCQ Biochemistry Carbohydratestuff100% (2)
- Biochemistry Gpat Exam Question PaperDocument9 pagesBiochemistry Gpat Exam Question PaperPadmavathi C100% (1)
- Organic Final PracticeDocument28 pagesOrganic Final PracticeKaushikNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Practice2 ANSWERSDocument11 pagesBiochemistry Practice2 ANSWERSmuhammadnewhuss2No ratings yet
- Biomolecule (MCQ)Document8 pagesBiomolecule (MCQ)ΑᲫげφα Κυ๓αན ᄋ1No ratings yet
- JEE Main Biomolecules Practice Paper With Solutions Download PDFDocument7 pagesJEE Main Biomolecules Practice Paper With Solutions Download PDFravirmanoj1No ratings yet
- Fssai: Previous Year PaperDocument16 pagesFssai: Previous Year PaperSuraj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Question Bank (Subjective)Document10 pagesBiomolecules Question Bank (Subjective)Rajendra SahaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules AssignmentDocument31 pagesBiomolecules AssignmentudaysrinivasNo ratings yet
- Romeo Batch GS FM-05Document16 pagesRomeo Batch GS FM-05KanishkaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Biological Basics: Sample QuestionsDocument8 pagesAn Overview of Biological Basics: Sample QuestionsJanine Abiegale PeraltaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES Ncert Class 12 Most Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesBIOMOLECULES Ncert Class 12 Most Important QuestionsRamNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Test - PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Answers On Last Page)Document4 pagesBiochemistry Test - PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Answers On Last Page)EceNo ratings yet
- DPP BiomoleculesDocument7 pagesDPP BiomoleculesKisna guptaNo ratings yet
- X CH 4 TestDocument2 pagesX CH 4 TestHadi BuxNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Past PapersDocument2 pagesBiomolecules Past Papersharshiiiii352No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument29 pagesBiomoleculeswavodak821No ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Polymers-03 - Assignments (New)Document11 pagesBiomolecules and Polymers-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Speed Test (26-30)Document30 pagesSelf Assessment Speed Test (26-30)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Dihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives: A Modern Comprehensive TreatiseFrom EverandDihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives: A Modern Comprehensive TreatiseNo ratings yet
- Class X Sulphuric AcidDocument3 pagesClass X Sulphuric AcidvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Class XII Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesClass XII Chemical KineticsvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Class X Nitric AcidDocument2 pagesClass X Nitric AcidvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Class X Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesClass X Chemical BondingvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Class XII Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument5 pagesClass XII Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Class XII Alcohols Phenols EthersDocument7 pagesClass XII Alcohols Phenols EthersvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Class X ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesClass X ElectrolysisvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Class XII HaloalkanesDocument3 pagesClass XII HaloalkanesvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Class X Acids BasesDocument6 pagesClass X Acids BasesvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Cret SyllabusDocument6 pagesCret SyllabusvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Inter Imun Dan Lemak 1Document5 pagesJurnal Inter Imun Dan Lemak 1Regitaand PutNo ratings yet
- Amine and Nitro CompundsDocument30 pagesAmine and Nitro CompundsDima MasadehNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review of The Structure Elucidation and Biological Activity of Triterpenoids From Ganoderma SPPDocument58 pagesA Comprehensive Review of The Structure Elucidation and Biological Activity of Triterpenoids From Ganoderma SPPAchilleas CallergisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 PracticeQDocument20 pagesChapter 8 PracticeQKevin Peng0% (1)
- Wa0097.Document41 pagesWa0097.amel elabassNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Kinetic Isotope EffectDocument11 pagesLecture 6 Kinetic Isotope EffectcsnNo ratings yet
- Use of ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy To Detect The Changes in Extra Virgin Olive Oil by Adulteration With Soybean Oil and High Temperature Heat TreatmentDocument10 pagesUse of ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy To Detect The Changes in Extra Virgin Olive Oil by Adulteration With Soybean Oil and High Temperature Heat TreatmentKiruthick DonNo ratings yet
- Student Special Study Material: Class 12 Chemistry (Theory)Document63 pagesStudent Special Study Material: Class 12 Chemistry (Theory)Varanasi Anil0% (1)
- Microwave in Organic SynthesisDocument20 pagesMicrowave in Organic Synthesisdr_cutecatNo ratings yet
- Friedel-Crafts AlkylationDocument7 pagesFriedel-Crafts AlkylationSalmaAlhasanNo ratings yet
- Oxiranes and Oxirenes: Monocyclic: Ihsan ErdenDocument48 pagesOxiranes and Oxirenes: Monocyclic: Ihsan ErdencapdesuroNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Teaching SchemeDocument60 pagesPart 3 - Teaching Schemeanon-741352100% (1)
- Direction: Identify The Type of Reaction Involved in Each Alkene. Predict The Major Product/s Formed in Each Equation. Draw and Name These Products. Use Only Permanent BLUE Ink Pen. Total: 30 PointsDocument1 pageDirection: Identify The Type of Reaction Involved in Each Alkene. Predict The Major Product/s Formed in Each Equation. Draw and Name These Products. Use Only Permanent BLUE Ink Pen. Total: 30 PointsKYLA MORALESNo ratings yet
- WO2015026689A1 - OBS IngevityDocument55 pagesWO2015026689A1 - OBS IngevityelenitabastosNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part BDocument247 pagesUnit 1 Part BhairtNo ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument16 pagesAlkenesVijay Kumar NatteyNo ratings yet
- Reactions, Rearrangements and Reagents (PDFDrive)Document276 pagesReactions, Rearrangements and Reagents (PDFDrive)Simone Singh100% (1)
- A1 Halogenoalkanes WS1Document15 pagesA1 Halogenoalkanes WS1chantellelimNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Novel Fluorobenzothiazole Linked Thiadiazole Compounds: As Possible Anti-Tubercular AgentsDocument2 pagesSynthesis of Novel Fluorobenzothiazole Linked Thiadiazole Compounds: As Possible Anti-Tubercular AgentsVINODNo ratings yet
- Classification of Essential OilDocument1 pageClassification of Essential OilElizabelth Woan Chyi75% (4)
- Fatty Acid Degradation and Biosynthesis: Department of BiochemistryDocument55 pagesFatty Acid Degradation and Biosynthesis: Department of Biochemistrydentcu70No ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms-I ApspDocument15 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanisms-I ApspGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document42 pagesChapter 14NayLinNo ratings yet
- Allen Guided Revision Organic ChemistryDocument74 pagesAllen Guided Revision Organic ChemistrymemepepedankNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 2Document87 pages11 Chapter 2pathanabjal12No ratings yet
- Chem 153 Problem Set 1Document2 pagesChem 153 Problem Set 1wanglixiangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - CarbohydratesDocument16 pagesChapter 18 - CarbohydratesPrince John Divinagracia BarnalNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Class XII Chemistry: ITL Public SchoolDocument14 pagesHoliday Homework Class XII Chemistry: ITL Public SchoolNisith Kr DasNo ratings yet