Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Graduate International Trade Theory: Mjyu@ Ccer - Pku.edu - CN /mjyu - Ccer.edu - Cn/courses/phdtrade - HTML
Graduate International Trade Theory: Mjyu@ Ccer - Pku.edu - CN /mjyu - Ccer.edu - Cn/courses/phdtrade - HTML
Uploaded by
Reema LuciaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Graduate International Trade Theory: Mjyu@ Ccer - Pku.edu - CN /mjyu - Ccer.edu - Cn/courses/phdtrade - HTML
Graduate International Trade Theory: Mjyu@ Ccer - Pku.edu - CN /mjyu - Ccer.edu - Cn/courses/phdtrade - HTML
Uploaded by
Reema LuciaCopyright:
Available Formats
Beijing University Dr.
Miaojie
Yu
China Center for Economic Research Fall 2009
Graduate International Trade Theory
Thursday 14:40-17:40
Lecture Hall, No. 3, Room 407
Course Description
This course will cover the causes and consequences of international trade, including
the determinants of the trade pattern, increasing returns, gains from trade, trade policy,
the role of multinational corporations, and the relationship between trade and growth.
Contact Information
Instructor: Dr. Miaojie Yu
Office: Rm. 621, Langrun Yuan
Email: mjyu@ccer.pku.edu.cn
Telephone: 6275-3109 (ext.5-3109)
Office Hours: Monday 3:30-4:30(or by appointment)
Course Website: http://mjyu.ccer.edu.cn/courses/phdtrade.html
Course Prerequisites
Prerequisites for this course are advanced microeconomics (I and II) or equivalent. For
those who didn’t take such courses but have strong interest in international trade could
contact me directly before registration.
Teaching Languages
Lectures, homework and exams will be delivered in English
Required Textbook:
Feenstra, Robert C., Advanced International Trade: Theory and Evidence, 2003,
Princeton University Press.
Recommended Books:
These books are not required but very helpful for future research. Those intending to
do research in this field may want to have them in their personal libraries.
Bhagwati, Jagdish, International Trade: Selected Readings, 2nd edition, 1987.
Dixit, Avinash and Victor Norman, Theory of International Trade, 1980
Grossman, Gene, Imperfect Competition and International Trade, 1991
Grossman, Gene and Ken Rogoff, Handbook of International Economics, vol (3),
1995
Dr. Yu, CCER, page 1 of 4
Helpman Elhanan and Paul Krugman, Market Structure and Foreign Trade, 1985.
Krugman, Paul, Rethinking International Trade, 1992
Course Grading:
Problem Sets Due dates as announced 10%
Literature Review TBA 10%
Final Exam/Term Paper TBA 80%
Course Outline:
This is tentative and subject to change. Check back at http://mjyu.ccer.edu.cn for
periodic updates and direct links to papers. Please read the assigned readings before
the lecture. Lectures will follow Feenstra’s book quite closely. Papers list here are
highly recommended but not required.
1. Ricardian Trade Theory
Dornbusch, R., S. Fischer and P.A. Samuelson, “Comparative advantage, trade
and payments in a Ricardian model with a continuum of goods”, AER, 1977,
823-39.
Eaton, J. and S. Kortum, “Technology, Geography, and Trade”, Econometria,
Sep. 2002, 70(5), 1741-1779.
2. Preliminaries: Two-Sector Models
Feenstra, Chapter 1
3. The Heckscher-Ohlin Model
Feenstra, Chapter 2
Dixit and Norman, 1980, Chapter 4.
“Higher Dimensional Issues in Trade Theory”, in Jones and Kenen,1984.
Leamer, E.E., “The Leontief Paradox , Reconsidered”, Journal of Political
Economy,1980, 88(3) 495-503.
Bowen, H.P., E.E. Leamer and L. Sveikauskas, “Multicountry, Multi-factor Tests
of the Factor Abundance Theory”, American Economic Review, 1987, 77(5),
791-809.
Trefler, D., “International Factor Price Differences: Leontief was Right!”,
Journal of Political Economy, December, 1993, 101(6), 961-87.
Trefler, D., “The Case of the Missing Trade and Other Mysteries”, American
Economic Review, December 1995, 85(5), 1029-46.
Helpman, E. “The Structure of Foreign Trade,” Journal of Economic
Perspectives, Spring 1999, 13(2), 121-44.
Davis, D.R. and D.W. Weinstein, “An Account of Global Factor Trade,”
American Economic Review, December 2001, 91(5), 1423-53.
4. Many Goods and Factors
Feenstra, Chapter 3
5. Trade in Intermediate Inputs and Wages
Feenstra, Chapter 4
Feenstra, R.C. and Hanson, G.H., “The Impact of Outsourcing and High-
Technology Capital on Wages: Estimates for the United States, 1979-1990,”
Quarterly Journal of Economics, August 1999, 114(3), 907-40.
Leamer, E.E., “What’s the Use of Factor Contents,?” Journal of International
Dr. Yu, CCER, page 2 of 4
Economics, February 2000, 50(1): 17-49.
Krugman, P.R., “Technology, Trade and Factor Prices,” Journal of International
Economics, February 2000, 50(1): 51-71.
6. Increasing Returns to scale and Firm Heterogeneity
Feenstra, Chapter 5
Helpman and Krugman, 1985, Chapters 3-4.
Krugman, P.R. and A. Venables, “Globalization and the Inequality of Nations”,
Quarterly Journal of Economics, November 1995, CX(4), 857-80.
Melitz, M.J., “The Impact of Trade on Intra-Industry Reallocations and
Aggregate Industry Productivity,” Econometrica, 2003, 1695-1725
Channey, Thomas (2005), "Liquidity Constrained Exporters", mimeo, University
of Chicago.
7.The Gravity Equation
Anderson, James and van Wincoop, Eric (2003), "Gravity with Gravitas: A
Solution to the Border Puzzle," American Economic Review 93(1), pp. 170-192.
Baier, Scott L. and Bergstrand, Jeffrey H.(2001), "The Growth of World Trade:
Tariffs, Transport Costs, and Income Similarity," Journal of International
Economics 53, pp. 1-27.
Rose, Andrew K. (2004), "Do We Really Know That the WTO Increases Trade?"
American Economic Review 94(1), pp. 98-114.
Yu, Miaojie (2009), “Trade, Democracy, and the Gravity Equation,” Journal of
Development Economics, forthcoming
8. Gains from Trade and Preferential Trade Agreements
Feenstra, Chapter 6
9. Import Tariffs and Dumping
Feenstra, Chapter 7
10. Import Quotas and Export Subsidies
Feenstra, Chapter 8
11. International Political Economy
Feenstra, Chapter 9
Grossman, G.M. and E. Helpman, “Protection for Sale,” American Economic
Review, September 1994, 84(4), 833-50.
Grossman, G.M. and E. Helpman, “The Politics of Free Trade Agreements,”
American Economic Review, September 1995, 84(4), 667-90.
Koujianou Goldberg, P. and G. Maggi, “Protection for Sale: An Empirical
Investigation,” American Economic Review 89(5): 1135-55, December 1999.
Yu, Miaojie (2009), “Trade Protectionism and Electoral Outcome,” CATO
Journal, forthcoming
12. Trade and Endogenous Growth
Feenstra, Chapter 10
Brezis, E., P.R. Krugman and D. Tsiddon, “Leapfrogging in International
Competition”,American Economic Review, December 1993, 83(5), 1211-19.
Coe, David T. and Helpman, Elhanan, “International R&D Spillovers”, European
Economic Review, May 1995, 39(5), 859-887.
Bayoumi, Tamim, Coe, David T. and Helpman, Elhanan, “R&D Spillovers and
Global Growth”, Journal of International Economics, April 1999, 47(2), 399-428.
Frankel, Jeff;rey A. and Romer, David, “Does Trade Cause Growth?” American
Economic Review, June 1999, 89(3), 379-399.
Dr. Yu, CCER, page 3 of 4
13. Multinational and Organization of the Firm
Feenstra, Chapter 11
Helpman and Krugman, 1985, Chapter 12.
Markusen, J.R. and A.J. Venables, “The Theory of Endowment, Intra-Industry
and Multinational Trade,” Journal of International Economics, December 2000,
52, 209-234.
Helpman, M. Melitz, and S. Yeaple, “Export versus FDI with heterogeneous
firms,” AER 2004, 300-316.
14. Trade and Environment (If time allowed)
Copeland Brian and M. Scott Taylor, “North-South Trade and the
Environment”, QJE, 1994, 755-787.
Copeland Brian and M. Scott Taylor, “Trade and Transboundary
Pollution”, AER, 1995, 716-737
Copeland Brian and M. Scott Taylor, “Trade, Tragedy, and the
Commons,” AER, 2009, 725-749
Dr. Yu, CCER, page 4 of 4
You might also like
- Fine 707Document6 pagesFine 707Anonymous NOSL188B0% (1)
- Crocs Inc. STRAMA PaperDocument22 pagesCrocs Inc. STRAMA PaperAnne Marieline Buenaventura100% (2)
- Ec122 PaderonDocument5 pagesEc122 PaderonArn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lone Pine CaféDocument3 pagesLone Pine Caféchan_han123No ratings yet
- Ec 876 Syl 12Document9 pagesEc 876 Syl 12driftkingfighterNo ratings yet
- International Economics (HSL714) Aug2022Document5 pagesInternational Economics (HSL714) Aug2022RashulNo ratings yet
- Topics in International Trade: Prof. Dr. Dalia Marin SS 2009Document6 pagesTopics in International Trade: Prof. Dr. Dalia Marin SS 2009Sikandar KhattakNo ratings yet
- 10710econ612100 PDFDocument5 pages10710econ612100 PDFJeffwei WeiNo ratings yet
- EF8931 W 18Document3 pagesEF8931 W 18Guang Lin WangNo ratings yet
- 137d PDFDocument3 pages137d PDFNorhaini D. TampogaoNo ratings yet
- 1 - 研究生经典阅读与讨论-reading listDocument2 pages1 - 研究生经典阅读与讨论-reading listelodie leeNo ratings yet
- Econ 5601wDocument8 pagesEcon 5601wBrooke ParkerNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets Structure, Institutions and Regulations: ECON 412Document7 pagesFinancial Markets Structure, Institutions and Regulations: ECON 412Miguel MaNo ratings yet
- ECON 871 - Advanced International EconomicsDocument11 pagesECON 871 - Advanced International EconomicsTanmoy Pal ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- International Trade (DEEQA) SyllabusDocument15 pagesInternational Trade (DEEQA) SyllabusHector Perez SaizNo ratings yet
- Pure TheoryDocument3 pagesPure TheoryAshima MishraNo ratings yet
- MQF Syllabus 26 220 501Document4 pagesMQF Syllabus 26 220 501Economiks PanviewsNo ratings yet
- MRP Topics 2018-19: Topic 1: Fiscal SustainabilityDocument31 pagesMRP Topics 2018-19: Topic 1: Fiscal SustainabilityGuang Lin WangNo ratings yet
- Sposi ECO 7332Document7 pagesSposi ECO 7332qixinyiNo ratings yet
- Outline Dev EconDocument10 pagesOutline Dev EconAmara AshfaqNo ratings yet
- ECON 269 Nternational Acroeconomics: Fmilani@uci - EduDocument8 pagesECON 269 Nternational Acroeconomics: Fmilani@uci - EduMatias CanoNo ratings yet
- Development Economic SyllabusDocument6 pagesDevelopment Economic SyllabusTran KahnNo ratings yet
- 2015 Winter ECON 571 LECTURE B2Document12 pages2015 Winter ECON 571 LECTURE B2jgordon2No ratings yet
- MECS 475 Teaching Notes Apr 18 2014Document110 pagesMECS 475 Teaching Notes Apr 18 2014bgates123456No ratings yet
- TECS Assignment 1 BriefDocument4 pagesTECS Assignment 1 Brief3081245716No ratings yet
- Advanced Macroeconomics - Mersin Ve Çukurova 2017 FallDocument17 pagesAdvanced Macroeconomics - Mersin Ve Çukurova 2017 FallAyat SalimNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument12 pagesReferencesBilal RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Economics 235: Course DescriptionDocument4 pagesEconomics 235: Course Descriptionbilllin12345No ratings yet
- Syllabus Fall 2023 0Document8 pagesSyllabus Fall 2023 0rribeiro70No ratings yet
- Syllabus: Economic Development II, Ph.D. Course, Spring 2010Document7 pagesSyllabus: Economic Development II, Ph.D. Course, Spring 2010Merlita TuralbaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus DEEQA Finance TSEDocument3 pagesSyllabus DEEQA Finance TSENatalia KovalevaNo ratings yet
- POLI3080Document7 pagesPOLI3080Eil00NNo ratings yet
- Course Monetary and Nancial MacroeconomicsDocument5 pagesCourse Monetary and Nancial MacroeconomicsmangreNo ratings yet
- AQR Value Research BibliographyDocument6 pagesAQR Value Research BibliographyArchana ShahuNo ratings yet
- Recommended Reading For A Basic But Excellent Description of Mean Variance Optimisation (MVO)Document3 pagesRecommended Reading For A Basic But Excellent Description of Mean Variance Optimisation (MVO)champakNo ratings yet
- MGT3033 Winter07Document12 pagesMGT3033 Winter07hatemNo ratings yet
- 14 773Document19 pages14 773Johannes ArdiantNo ratings yet
- 14.773: Political Economy of Institutions and Development: Daron Acemoglu and Benjamin Olken January 29, 2010Document18 pages14.773: Political Economy of Institutions and Development: Daron Acemoglu and Benjamin Olken January 29, 2010Sounman HongNo ratings yet
- International Business Environment Article List - FinalversionDocument6 pagesInternational Business Environment Article List - FinalversiontesfaNo ratings yet
- Kyle Market Microstructure SyllabusDocument7 pagesKyle Market Microstructure SyllabusssdebNo ratings yet
- EndnotesDocument4 pagesEndnotesRey2202No ratings yet
- Macro Theory II - SyllabusDocument6 pagesMacro Theory II - SyllabusThích Nem NướngNo ratings yet
- Labour EconomicsDocument6 pagesLabour EconomicsNitin Singh100% (1)
- Relationship Between Inflation and Stock Prices in ThailandDocument6 pagesRelationship Between Inflation and Stock Prices in ThailandEzekiel WilliamNo ratings yet
- John SyllabusDocument10 pagesJohn SyllabusAli SharifiNo ratings yet
- IO Reading ListDocument3 pagesIO Reading ListDat NguyenNo ratings yet
- Asset Pricing PuzzlesDocument6 pagesAsset Pricing Puzzlesgr8fun5052No ratings yet
- BFDocument11 pagesBFTaher JamilNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomía I 2017Document3 pagesMacroeconomía I 2017mauro monterosNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance SyllabusDocument10 pagesBehavioral Finance Syllabusidontneedaman_060% (1)
- Rajan Course Outline Asymmetric Information Ba865 - Syll2011Document8 pagesRajan Course Outline Asymmetric Information Ba865 - Syll2011Adriana GarciaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Political EconomyDocument10 pagesSyllabus Political EconomyNapat PorNo ratings yet
- Reading List: Macro-Finance: Review 102 (2) : 1029Document4 pagesReading List: Macro-Finance: Review 102 (2) : 1029Micheal GoNo ratings yet
- ReadinglistDocument25 pagesReadinglistsaghNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Syllabus 2018Document5 pagesEconomic Development Syllabus 2018Mohammad Khaerul AzisNo ratings yet
- Acemoglu Short Course 2014.24Document7 pagesAcemoglu Short Course 2014.24Tanya SonkarNo ratings yet
- Frieden SyllabusDocument10 pagesFrieden SyllabusPedro ZFNo ratings yet
- EC 585 - Special Topics in Dynamic Macroeconomic Modeling Spring 2011Document5 pagesEC 585 - Special Topics in Dynamic Macroeconomic Modeling Spring 2011su11674No ratings yet
- Monetary+Thoery+and+Policy PHDDocument2 pagesMonetary+Thoery+and+Policy PHDhm512771No ratings yet
- FI 9400 Syllabus 2016Document11 pagesFI 9400 Syllabus 2016Qianlong LiuNo ratings yet
- Lista de LecturaDocument17 pagesLista de LecturaRoberto Paez100% (1)
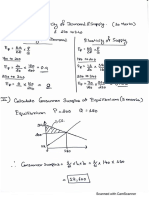
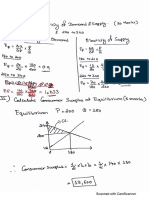
- H-O Numerical PDFDocument4 pagesH-O Numerical PDFReema LuciaNo ratings yet
- Solution 5Document4 pagesSolution 5Reema LuciaNo ratings yet
- Demand FunctionDocument2 pagesDemand FunctionReema LuciaNo ratings yet
- Q1A - Revised SolutionDocument1 pageQ1A - Revised SolutionReema LuciaNo ratings yet
- HElloDocument8 pagesHElloReema LuciaNo ratings yet
- Negen Capital PMS Feb 22 FactsheetDocument5 pagesNegen Capital PMS Feb 22 Factsheetjeevan gangavarapuNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements: Overheads - Accounting and ControlDocument11 pagesClassification of Elements: Overheads - Accounting and ControlAyushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Trainee'S Record Book: Technical Education and Skills Development AuthorityDocument10 pagesTrainee'S Record Book: Technical Education and Skills Development AuthorityVirgil Keith Juan PicoNo ratings yet
- Engineeringinterviewquestions Mcqs On Requirement Engineering AnswersDocument6 pagesEngineeringinterviewquestions Mcqs On Requirement Engineering Answersdevid mandefroNo ratings yet
- SAP.C TS4CO 1909.v2020-05-21.q63Document16 pagesSAP.C TS4CO 1909.v2020-05-21.q63Vladimir Jovanovic0% (1)
- Tax Invoice: Description of Services HSN Code Taxable Amount Igst Rate AmountDocument2 pagesTax Invoice: Description of Services HSN Code Taxable Amount Igst Rate AmountSunil PatelNo ratings yet
- 2023.07.07 HS PaeDocument2 pages2023.07.07 HS Paehanis0% (1)
- MGT305 Ass1Document5 pagesMGT305 Ass1Trần Phước Diễm TrangNo ratings yet
- Sample Questionnaire For Job AnalysisDocument4 pagesSample Questionnaire For Job AnalysisJinal DamaniNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4Document1 pageCase Study 4Aeilin AgotoNo ratings yet
- Chap 007Document36 pagesChap 007Lee FeiNo ratings yet
- AKT-SIP-SOP-004 SIP Management PlantDocument39 pagesAKT-SIP-SOP-004 SIP Management PlantSHES BBPNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management (BEG499 SM) (Elective)Document2 pagesStrategic Management (BEG499 SM) (Elective)Anil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Amex Billie Statement FULLDocument2 pagesAmex Billie Statement FULLleovaideuberNo ratings yet
- Doing Deals in PEDocument139 pagesDoing Deals in PEHarjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Problems GeneralDocument9 pagesProblems GeneralAmal BharaliNo ratings yet
- Ecolean Customer StoryDocument2 pagesEcolean Customer StorypasanNo ratings yet
- Joshua Greenberg 9 1 12Document3 pagesJoshua Greenberg 9 1 12api-239860330No ratings yet
- Status of Kendu Leaves Sale: Jharkhand State Forest Development Corporation LTDDocument11 pagesStatus of Kendu Leaves Sale: Jharkhand State Forest Development Corporation LTDmdNo ratings yet
- EY The New Case For Shared ServicesDocument12 pagesEY The New Case For Shared ServicesRahul MandalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Max Newyork Life InsuranceDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Max Newyork Life Insurancedhruvpatel_bca2010No ratings yet
- Enhancing Employee Performance PDFDocument26 pagesEnhancing Employee Performance PDFSnigdhangshu BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Intensive SBR (INT) 4 WeekDocument9 pagesIntensive SBR (INT) 4 WeekBellaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Problem Solving Cases in Microsoft Access and Excel 13th Edition Monk Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument19 pagesFull Download Problem Solving Cases in Microsoft Access and Excel 13th Edition Monk Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterwestmostlabent.zdqs2e100% (20)
- FINALDocument20 pagesFINALShubhangi BishnoiNo ratings yet
- BT India Factsheet - NewDocument2 pagesBT India Factsheet - NewsunguntNo ratings yet
- (I) Statement of Changes in Working Capital (Ii) Fund Flow StatementDocument3 pages(I) Statement of Changes in Working Capital (Ii) Fund Flow StatementShailendrasingh DikitNo ratings yet
- What Is SAP (Systems Applications Products) ?Document2 pagesWhat Is SAP (Systems Applications Products) ?satya narayanaNo ratings yet