Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Common Compressive Radiculopathies
Common Compressive Radiculopathies
Uploaded by
Phillip KarpatiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Common Compressive Radiculopathies
Common Compressive Radiculopathies
Uploaded by
Phillip KarpatiCopyright:
Available Formats
Describe the anatomy of common sites of nerve root compression (C6, C7, L5, S1)
Identify the common causes of radiculopathy
Describe the clinical features of common radiculopathies
Predict the outcome of common radiculopathies
Definition:
• radiculopathy is a pathologic process affecting the nerve root
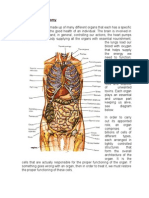
Anatomy:
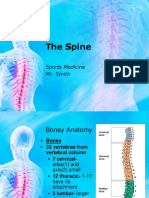
• The cervical spinal column is comprised of seven vertebral bodies.
• The vertebral bodies are separated by intervertebral discs, which provide support and
mobility.
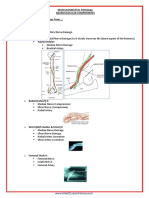
• The dorsal and ventral spinal nerve roots emerge from the spinal cord and travel
through the intervertebral foramina.
• There are seven cervical vertebrae but eight cervical nerve roots. As there is no C8
vertebra, the C8 nerve root exits through the C7 to T1 intervertebral foramen
Dorsal Root Ganglia
Pathogenesis
Compressive
• Spondylosis (degenerative change of spine)
- Osteoarthritis (uncovertebral join, facet joint)
- Disc space narrowing (degenerative changes)
- spondylolisthesis
• Disc prolapse/herniation
non-degenerative causes:
• Tumour infiltration
• nerve root infarction
• infection (herpes zoster)
• neurodegenerative causes
Cervical – nerve root comes out
above the vertebrae (C5 root
comes above C5 vetebrae)
Thoracic and lumbar – nerve root
comes out below the vertebrae
Common radiculopathies:
Cervical Lumbar
C7>C6>C7 L5>S1
Cervical Radiculopathies
• Strongly associated with lumbar radiculopathies (40%)
• Often relapsing course
Pathogenesis • spondylosis (70%)>disc herniation (20%)
• rarely associated w trauma (~15%)
Clinical manifestations • see below
Diagnosis History + clinical findings
Imaging:
• Imaging diagnostic not required with little or no motor deficits
• Imaging done if:
Progressive/severe motor deficits
Suspected neoplasm, myelopathy, epidural abscess
Bilateral signs and symptoms
• MRI imaging of choice
• CT myelography good for foraminal compression
Electromyography:
• may provide information regarding both ongoing axon loss and
compensatory reinnervation
Cervical radiculopathy symptoms:
• Neck pain, scapula pain
• upper arm pain
• difficulty with fine motor skills
• headache
• most common sign is depressed reflex
Root Pain Numbness Weakness Reflex affected
C5 Neck, scapula Lateral arm (axillary Shoulder abd. Biceps
(C4-5 shoulder nerve distribution) External rotation Brachioradialis
disc) Elbow flexion
Forearm sup.
C6 Neck, scapula, Lateral forearm Shoulder Abd. Biceps
(C5-6 shoulder Thumb External rotation brachioradialis
disc) lat. Arm Index finger Elbow flexion
lat. Forearm Forearm supination
lat. hand Forearm pronation
C7 Neck Index finger Elbow extension Triceps
(C6-7 Shoulder Middle finger Wrist extension
disc) Middle finger Palm (radial)
Hand Forearm pronation
Wrist flexion
C8 Neck Medial forearm Finger extension None
(C7- Shoulder Medial hand Wrist extension
T1 Medial forearm 4th/5th digit (ulnar)
disc) 4th/5th digit Distal finger
Medial hand flex./exten./abd./add.
Distal thumb flexion
T1 Neck Anterior arm Thumb abduction None
(T1-2 Medial Arm Medial forearm Distal thumb flexion
disc) Forearm Finger abd/add
Lumbar radiculopathy
• Lower back pain
• Pain worsening on lumbar flexion (intervertebral foramen narrower)
• benign prognosis (90% better in 3 months)
• L5 most common lumbar radiculopathy
• Aetiology: commonly: disc herniation
Roo Pain Numbness Weakness Reflex affected
t
L5 Back Paraesthesia outer Dorsiflexion Semitendinosus/
aspect of leg + top of semimembranosus
Radiating to foot Hip abduction, knee (internal hamstrings)
buttock, lateral flexion, foot tendon
thigh, lateral calf, Lateral calf, dorsum dorsiflexion, toe
dorsum of foot, foot, web space extension and flexion,
great toe between first and foot inversion and
second toe eversion
S1 Back Paraesthesia back of Unable to stand on Achilles tendon
leg + along outside tip toes on affected
radiating into of foot foot
buttock, lateral or
posterior thigh, Posterior calf, lateral Hip extension, knee
posterior calf, or plantar aspect of flexion, plantar
lateral or plantar foot flexion of the foot
foot
For L5:
You might also like
- Back Owners ManualDocument16 pagesBack Owners Manualonwuzuam100% (1)
- 3-Cervical RadiculopathyDocument7 pages3-Cervical RadiculopathyAmimul EhsanNo ratings yet
- Dermatomes and MyotomesDocument19 pagesDermatomes and MyotomesDaniela N Anghel100% (1)
- MCQS FatimaDocument8 pagesMCQS Fatimarawalian100% (2)
- Singh's OsceDocument466 pagesSingh's OsceShuaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Spine RehabilationDocument157 pagesSpine RehabilationSyeda Abida Hussain SheraziNo ratings yet
- Notes SC NeurologyDocument7 pagesNotes SC Neurology202213No ratings yet
- Upper Limb AnatomyDocument15 pagesUpper Limb AnatomyAjennyKinoNo ratings yet
- Cervical RadiculopathyDocument110 pagesCervical RadiculopathyShabana AfzalNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus ExaminationDocument7 pagesBrachial Plexus ExaminationMalvinder Singh DhillonNo ratings yet
- Radicular Syndrome: Darwin Amir BGN Ilmu Penyakit Saraf Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas AndalasDocument32 pagesRadicular Syndrome: Darwin Amir BGN Ilmu Penyakit Saraf Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Andalasdhilla_18No ratings yet
- Inbound 3572289752270573946Document92 pagesInbound 3572289752270573946Viola BlenteNo ratings yet
- ملزمة محمد مرعي الشاملهDocument98 pagesملزمة محمد مرعي الشاملهMuhammad FahmyNo ratings yet
- Neck Pain DDDocument50 pagesNeck Pain DDZuhaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuriesDocument109 pagesSpinal Cord InjuriesGurinder GillNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus InjuryDocument5 pagesBrachial Plexus InjurykadekNo ratings yet
- TrunkDocument86 pagesTrunkdr_asalehNo ratings yet
- Muscle of Upper LimbsDocument5 pagesMuscle of Upper LimbsFong Yu-heng100% (1)
- Manual TherapyDocument16 pagesManual TherapylecturioNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus Injury 1Document5 pagesBrachial Plexus Injury 1luthfi aziziNo ratings yet
- Approach To Low Back Pain (22 Oct)Document61 pagesApproach To Low Back Pain (22 Oct)Halawatul ImanNo ratings yet
- 20.nyeri PunggungDocument53 pages20.nyeri PunggungAy'oe Ithyu RezthuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Emergency ProceduresDocument59 pagesLecture 9 Emergency ProceduresAniqa AsgharNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury, DisordersDocument54 pagesSpinal Cord Injury, DisordersChananNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Review of Extreme TiesDocument65 pagesAnatomy Review of Extreme Tiesskihard0404749No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Vertebral Column: Your Subtitle Goes HereDocument54 pagesStructure and Function of The Vertebral Column: Your Subtitle Goes HereJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Back Spine AnatomyDocument3 pagesBack Spine AnatomyNinjaNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb 1Document31 pagesUpper Limb 1AnuNo ratings yet
- The Basics & OsteologyDocument15 pagesThe Basics & OsteologyHanneke Du PlessisNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Spinal Cord InjuriesDocument28 pagesTraumatic Spinal Cord Injuriesbibi bennyNo ratings yet
- PATH - Neurovascular Compromises (4p)Document4 pagesPATH - Neurovascular Compromises (4p)andreeaNo ratings yet
- Chest Cavity, Vertebral Column and Back Muscles. Respiratory MusclesDocument35 pagesChest Cavity, Vertebral Column and Back Muscles. Respiratory MusclesOr100% (2)
- Upper ExtremityDocument216 pagesUpper ExtremityChester VergilNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury: Barrios, Kevin George BDocument52 pagesSpinal Cord Injury: Barrios, Kevin George B乔治凯文No ratings yet
- The Thorax: Axial & Appendicular Skeleton Mammary Glands Surface AnatomyDocument28 pagesThe Thorax: Axial & Appendicular Skeleton Mammary Glands Surface AnatomyDr-Arsalan ZahidNo ratings yet
- RevalidaDocument192 pagesRevalidaJon De LeonNo ratings yet
- Spine Emergencies: Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) - The BasicsDocument67 pagesSpine Emergencies: Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) - The Basicsditya_madridistasNo ratings yet
- Unit4 DM - Vb.inddDocument31 pagesUnit4 DM - Vb.inddAlexNo ratings yet
- Elbow, Wrist and Hand Upper & Lower Quarter Neurological ScreenDocument3 pagesElbow, Wrist and Hand Upper & Lower Quarter Neurological ScreenAsad ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Spine Evaluation PowerpointDocument57 pagesSpine Evaluation PowerpointrexNo ratings yet
- Limbs 1b - Overview of Anatomy of Upper and Lower LimbsDocument5 pagesLimbs 1b - Overview of Anatomy of Upper and Lower LimbsTarmizi Md NorNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and TCM Treatment of Cervical Herniated Disc: East West Healing Center by Dr. Leon ChenDocument68 pagesPathogenesis and TCM Treatment of Cervical Herniated Disc: East West Healing Center by Dr. Leon ChenArtha PutuNo ratings yet
- Cervical SpineDocument3 pagesCervical SpineCherrie MaeNo ratings yet
- Neuropati Jepitan (Entrapment Neuropathy)Document38 pagesNeuropati Jepitan (Entrapment Neuropathy)Lukman HakimNo ratings yet
- Final IbcDocument26 pagesFinal IbcAngeliitha Tqm Ramos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Spine Exam Lecture - Shaffer 2006Document65 pagesSpine Exam Lecture - Shaffer 2006মোহাম্মদ আবীরNo ratings yet
- Brachium, Cubital Fossa and UmDocument24 pagesBrachium, Cubital Fossa and UmartikslennonNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument4 pagesMusclesJoesph HallNo ratings yet
- Week 6 PCP Workbook QsDocument6 pagesWeek 6 PCP Workbook Qsapi-479849199No ratings yet
- Cervical DisordersDocument89 pagesCervical DisordersAbdallah Samir Mostafa٢٠١٩٠٢١٥٩No ratings yet
- DR - Rieva Kuliah 7 November - 2018Document38 pagesDR - Rieva Kuliah 7 November - 2018Nisrina100% (1)
- 2nd Order (Unit 1 - B)Document5 pages2nd Order (Unit 1 - B)uberjunk426801No ratings yet
- Entrapment Syndrom of Neck Shoulder and ElbowDocument111 pagesEntrapment Syndrom of Neck Shoulder and ElbowHaikal ZainolNo ratings yet
- Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction and Piriformis Syndrome PDFDocument37 pagesSacroiliac Joint Dysfunction and Piriformis Syndrome PDFDevi SiswaniNo ratings yet
- Kaye - Cervical Disc DiseaseDocument6 pagesKaye - Cervical Disc DiseaseAlina AndreiNo ratings yet
- Hill Sachs Lesion: Anterior Shoulder DislocationDocument3 pagesHill Sachs Lesion: Anterior Shoulder DislocationmakananlezatNo ratings yet
- EktremitasDocument40 pagesEktremitasBram wijayaNo ratings yet
- CRS Cervical RadiculopathyDocument57 pagesCRS Cervical RadiculopathyBackup WA ORINo ratings yet
- Anatomia Da ColunaDocument59 pagesAnatomia Da ColunaPaula Duarte MarquesNo ratings yet
- Muscle NotesDocument2 pagesMuscle NotesGrace YNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Limb NervesDocument6 pagesUpper and Lower Limb NervesTaimoor DogarNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandOrthopedics Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- What Are Spinal Tracts?Document2 pagesWhat Are Spinal Tracts?Ahsan JamilNo ratings yet
- Basic Human AnatomyDocument6 pagesBasic Human AnatomySuman KumarNo ratings yet
- Peifu Tang (Editor), Hua Chen (Editor) - Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery - Volume 3 - Axial Skeleton Fractures and Nonunion (2023, Springer) - Libgen - LiDocument226 pagesPeifu Tang (Editor), Hua Chen (Editor) - Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery - Volume 3 - Axial Skeleton Fractures and Nonunion (2023, Springer) - Libgen - LiThiago Longo MoraesNo ratings yet
- ASIA ScoreDocument14 pagesASIA Scorezloncar3No ratings yet
- Thesis Reza Salman Roghani PDFDocument76 pagesThesis Reza Salman Roghani PDFscoopyNo ratings yet
- Spinocerebelar Tract-2Document20 pagesSpinocerebelar Tract-2Vijayasekhar VempalliNo ratings yet
- fINAL of Octeochondroma in C - SpineDocument1 pagefINAL of Octeochondroma in C - SpineadilNo ratings yet
- Spine: Junior Intern - Csu College of MedicineDocument22 pagesSpine: Junior Intern - Csu College of MedicineCris Soliven DucosNo ratings yet
- Activity For Nervous System 2019Document10 pagesActivity For Nervous System 2019Jughead JonesNo ratings yet
- HAPL 3 & 4 - The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesHAPL 3 & 4 - The Nervous SystemwelpNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PowerpointDocument45 pagesNervous System Powerpointabisantiago613175% (4)
- CH 41 LBP - Braddom's Physical Medicine & RehabilitationDocument46 pagesCH 41 LBP - Braddom's Physical Medicine & RehabilitationPyrectic WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PainDocument52 pagesPathophysiology of PainTahta Pambudi100% (3)
- Degenerative Spinal DisordersDocument2 pagesDegenerative Spinal DisordersjabolbolNo ratings yet
- Cerebrum +pons LectureDocument53 pagesCerebrum +pons LectureIsrael Olusegun100% (1)
- Nervous System 1 (Viva)Document53 pagesNervous System 1 (Viva)Mohammed shabekNo ratings yet
- Quiz Neuroscience Part 1 of 4Document55 pagesQuiz Neuroscience Part 1 of 4MedShare80% (5)
- Anatomy One LinersDocument10 pagesAnatomy One Linersridin007100% (2)
- 1.1 Musculoskeletal Care Modalities PDFDocument20 pages1.1 Musculoskeletal Care Modalities PDFDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Roles of Axon Guidance MoleculesDocument17 pagesRoles of Axon Guidance MoleculesDaoud IssaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Ns-Reeves and SwensonDocument112 pagesDisorders of Ns-Reeves and SwensonSuganya BalachandranNo ratings yet
- Group 38 CaseDocument73 pagesGroup 38 CaseMarjune DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System: Dr. Catherine C. SiosonDocument43 pagesNeurologic System: Dr. Catherine C. Siosonwieka mawieNo ratings yet
- Bio MCQ TestDocument23 pagesBio MCQ TestMalay ParikhNo ratings yet
- Effects of Kinesio Taping in Rectus Femoris Activity and Sit-To-Stand Movement in Children With Unilateral Cerebral Palsy - Placebo-Controlled, Repeated-Measure Design 2018Document12 pagesEffects of Kinesio Taping in Rectus Femoris Activity and Sit-To-Stand Movement in Children With Unilateral Cerebral Palsy - Placebo-Controlled, Repeated-Measure Design 2018Maria Del Mar Marulanda GrizalesNo ratings yet
- Scientific American - Changing FacesDocument45 pagesScientific American - Changing FacesQuod AntichristusNo ratings yet
- AV UWorld EOs (Rough Draft) - Data - Repeat LandscapeDocument139 pagesAV UWorld EOs (Rough Draft) - Data - Repeat LandscapeJonathan AiresNo ratings yet