Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Syllabus Science 10 B Physics
Course Syllabus Science 10 B Physics
Uploaded by
Nard Emsoc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesThis course syllabus outlines a Thermodynamics and Modern Physics course that is worth 0.6 credits and meets for 2 hours per week. The course covers key topics in thermodynamics like temperature, heat, the first and second laws of thermodynamics, as well as modern physics topics like special and general relativity, quantum mechanics, and nuclear physics. Students are assessed through participation, assignments, projects, and exams.
Original Description:
Original Title
Course-Syllabus-Science-10-B-Physics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis course syllabus outlines a Thermodynamics and Modern Physics course that is worth 0.6 credits and meets for 2 hours per week. The course covers key topics in thermodynamics like temperature, heat, the first and second laws of thermodynamics, as well as modern physics topics like special and general relativity, quantum mechanics, and nuclear physics. Students are assessed through participation, assignments, projects, and exams.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesCourse Syllabus Science 10 B Physics
Course Syllabus Science 10 B Physics
Uploaded by
Nard EmsocThis course syllabus outlines a Thermodynamics and Modern Physics course that is worth 0.6 credits and meets for 2 hours per week. The course covers key topics in thermodynamics like temperature, heat, the first and second laws of thermodynamics, as well as modern physics topics like special and general relativity, quantum mechanics, and nuclear physics. Students are assessed through participation, assignments, projects, and exams.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
COURSE SYLLABUS
Course Title: THERMODYNAMICS AND MODERN PHYSICS
Credits Earned: 0.6
No. of Hours/Week: 2
Course Requirements:
Regular and punctual attendance
Exemplary performance in portfolio assessment which include paper-and-pencil works, mid-quarter and final quarter
assessments/examinations, quizzes, board works and performance tasks
Active participation in class
Project-making
Passing of assignment
Pass on time a good quality project
Course Description:
This course aims to give the students an advanced background of the important topics in the field of Physics particularly in
Thermodynamics and Modern Physics.
Course Outline:
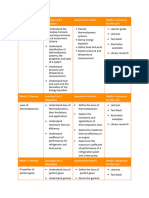
Period Coverage Learning Competencies
FIRST QUARTER TEMPERATURE AND HEAT The learner…
Temperature and Zeroth Law of Define temperature.
TEMPERATURE, HEAT, Thermodynamics State the zeroth law of
AND FIRST LAW OF Temperature Scales thermodynamics.
THERMODYNAMICS Thermal Expansion Compare the different temperature
Heat Quantity scales.
Calorimetry and Phase Changes Describe how temperature change
Heat Transfer Mechanism
affects an object’s dimension.
Differentiate heat and temperature.
Discuss and solve word problems
involving the quantity of heat,
calorimetry and phase changes.
Explain the concepts behind
mechanisms of heat transfer.
FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Thermodynamic Systems
Internal Energy and First Law of Explain the importance of
Thermodynamics thermodynamic systems.
Different Thermodynamic Processes State the first law of thermodynamics.
Some Applications of the First Law of
Enumerate and analyze thermodynamic
Thermodynamics
processes.
SECOND QUARTER SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Differentiate reversible and irreversible
Directions of Thermodynamic Processes processes.
SECOND LAW OF Heat Engines and the Second Law of State the second law of
THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics thermodynamics.
Heat Pumps and Refrigerators Define heat engine.
Carnot Cycle Enumerate types of engines.
Entropy Calculate the efficiency of a heat
engine.
Analyze the performance of
refrigerator.
Discuss Carnot cycle.
Explain how entropy is used in
analyzing thermodynamic processes.
Elaborate the relationship between
entropy and microscopic states.
THIRD QUARTER SPECIAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY Compare Galilean-Newtonian relativity
RELATIVITY AND Galilean-Newtonian Relativity from Einstein’s relativity theory.
QUANTUM MECHANICS Postulates of Special Theory of Describe the postulates of special
Relativity theory of relativity.
Relativity of Simultaneity
Solve for relativistic values of time,
Time Dilation and Length Contraction
length, momentum, mass, and energy.
Relativistic Momentum
Mass – Energy Equivalence Explain mass-energy equivalence.
GENERAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY Explain the principle of equivalence.
Principle of Equivalence Discuss how gravity bends light
Bending of Light by Gravity according to the general theory of
Gravitational Red Shift
relativity.
Gravitational Waves
Describe the geometry of space-time
according to the general theory of
relativity.
Discuss how gravitation waves are
formed.
QUANTUM MECHANICS
Blackbody Radiation and Planck’s
Hypothesis Describe blackbody radiation.
Photoelectric Effect Explain Planck’s hypothesis.
Compton Effect Discuss wave-particle duality.
Wave-Particle Duality Solve problems about photoelectric
De Broglie Wavelength and Compton effect.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Solve problems about De Broglie
wavelength Heisenberg uncertainty
principle.
FOURTH QUARTER NUCLEAR PHYSICS AND RADIOACTIVITY Differentiate between nuclear fission
Nuclear Fission and nuclear fusion.
NUCLEAR PHYSICS Nuclear Fusion Identify radiation measurements.
Biological Effects of Radiation Discuss radiation hazards.
Enumerate industrial and medical
applications of radiation.
You might also like
- Physics Grade 12 Student TextBook PDFDocument356 pagesPhysics Grade 12 Student TextBook PDFjairo mesa93% (15)
- When I Was A Puerto RicanDocument2 pagesWhen I Was A Puerto RicanNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Sessional - 100 100 Final - Total - 100 100Document3 pagesSessional - 100 100 Final - Total - 100 100Sagar AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Thermodynamics SyllabusDocument4 pagesBasic Thermodynamics SyllabusKrish RobertsNo ratings yet
- TD SylabusDocument5 pagesTD SylabusNenu Na RakshasiNo ratings yet
- Semester Plan of Physics-2Document7 pagesSemester Plan of Physics-2Istyeak AhmmedNo ratings yet
- CHEM 114 PRELIM Module 1 1st Sem 2020 2021revisedDocument24 pagesCHEM 114 PRELIM Module 1 1st Sem 2020 2021revisedJULLIE MAE SAULON100% (1)
- Modeling of Heat Conduction Through Rate Equations: Claudio Giorgi, Angelo Morro, Federico ZulloDocument26 pagesModeling of Heat Conduction Through Rate Equations: Claudio Giorgi, Angelo Morro, Federico ZulloDaniele MarconiNo ratings yet
- 2023 Unification of The First Law of Quantum ThermodynamicsDocument43 pages2023 Unification of The First Law of Quantum ThermodynamicsWI TONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Document36 pagesChapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Ng Kee NainNo ratings yet
- Physics XIIDocument255 pagesPhysics XIIQulb e AbbasNo ratings yet
- First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesFirst Law of ThermodynamicsewannnkobaNo ratings yet
- 1 Concepts of Thermodynamics HoDocument9 pages1 Concepts of Thermodynamics HoFilipe Gama FreireNo ratings yet
- THERMODocument1 pageTHERMOamireddysugunaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical MeasurementsMechanical MeasurementsDocument2 pagesMechanical MeasurementsMechanical MeasurementsNenu Na RakshasiNo ratings yet
- PhyCompulsory & Elective Part-Revised Curriculum-20151211 PDFDocument29 pagesPhyCompulsory & Elective Part-Revised Curriculum-20151211 PDFonlineyykNo ratings yet
- Heat & EnergyDocument45 pagesHeat & EnergyImran UnarNo ratings yet
- Basic-Thermodynamics 1Document4 pagesBasic-Thermodynamics 1Kawie AñeroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To ThermodynamicsjaiqcooNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Thermo - NewDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Thermo - Newविशाल पुडासैनीNo ratings yet
- CHEM F111 GChem Handout 2023-24-2nd Sem AnDocument5 pagesCHEM F111 GChem Handout 2023-24-2nd Sem Anf20230424No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 14 Weeks of HellDocument7 pagesThermodynamics 14 Weeks of HellseirphenyoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics - Term 3Document8 pagesGrade 10 Physics - Term 3Trevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 0Document41 pagesChapter 1 - 0Tsiye TekleyohanisNo ratings yet
- PhysRevE 91 012104Document8 pagesPhysRevE 91 012104Aditi MisraNo ratings yet
- XE SampleDocument31 pagesXE SampleJerome HarinaNo ratings yet
- Silabus Mata Kuliah FI2282 Termodinamika BDocument2 pagesSilabus Mata Kuliah FI2282 Termodinamika B008 - Jihan AlfiraNo ratings yet
- Physics: Chapter 4 Motion in A PlaneDocument4 pagesPhysics: Chapter 4 Motion in A Planeandrilyazhini25No ratings yet
- CHEM F111 - I Sem 2020-21 - HandoutDocument6 pagesCHEM F111 - I Sem 2020-21 - HandoutTejaswi ReddyNo ratings yet
- ME ThermodynamicsDocument22 pagesME ThermodynamicsVishesh DwivediNo ratings yet
- Atd Course HandoutDocument5 pagesAtd Course Handoutmaaz ahmadNo ratings yet
- Basic ThermodynamicsDocument284 pagesBasic Thermodynamicsikneo100% (10)
- Basic Thermodynamics SyllabusDocument284 pagesBasic Thermodynamics SyllabusSecretNo ratings yet
- Jhep04 (2015) 123Document66 pagesJhep04 (2015) 12312banmathNo ratings yet
- Heat and Thermodynamics Course OutlineDocument2 pagesHeat and Thermodynamics Course Outlinekirabirasteven81No ratings yet
- Chem 145Document5 pagesChem 145Omar QasimNo ratings yet
- Thermo 02 00007Document6 pagesThermo 02 00007RunkitoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 2Document8 pagesAssignment Unit 2samar sultanNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusTMedhin MisganawNo ratings yet
- COMEDK Important Topics and Revised SyllabusDocument49 pagesCOMEDK Important Topics and Revised SyllabusVishal VermaNo ratings yet
- High Temperature Gas Dynamics - Synopsis - Himanshu BanaitDocument53 pagesHigh Temperature Gas Dynamics - Synopsis - Himanshu BanaitHimanshu BanaitNo ratings yet
- TD Lesson Plan and SyllabusDocument7 pagesTD Lesson Plan and Syllabuschandrasekhar reddyNo ratings yet
- Classical and Geometrical Theory of Chemical and Phase ThermodynamicsFrom EverandClassical and Geometrical Theory of Chemical and Phase ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- The Thermodynamic Universe and Beyond: How Nature's Laws Reveal the Secrets of Time, Biology, Information, and Quantum RealityFrom EverandThe Thermodynamic Universe and Beyond: How Nature's Laws Reveal the Secrets of Time, Biology, Information, and Quantum RealityNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: A Dynamical Systems ApproachFrom EverandThermodynamics: A Dynamical Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Treatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsFrom EverandTreatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Time's Arrow: The Origins of Thermodynamic BehaviorFrom EverandTime's Arrow: The Origins of Thermodynamic BehaviorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Finite Quantum Electrodynamics: The Causal Approach, Third EditionFrom EverandFinite Quantum Electrodynamics: The Causal Approach, Third EditionNo ratings yet
- Topics in the Foundations of General Relativity and Newtonian Gravitation TheoryFrom EverandTopics in the Foundations of General Relativity and Newtonian Gravitation TheoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Course Syllabus SCIENCEB Grade 8Document4 pagesCourse Syllabus SCIENCEB Grade 8Nard EmsocNo ratings yet
- 8B DarwinDocument1 page8B DarwinNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus English 10 BDocument4 pagesCourse Syllabus English 10 BNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus SCIENCEB Grade 9Document5 pagesCourse Syllabus SCIENCEB Grade 9Nard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus SCIENCEB Grade 7Document7 pagesCourse Syllabus SCIENCEB Grade 7Nard EmsocNo ratings yet
- 10B EnglishDocument1 page10B EnglishNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- 7B QuarterDocument1 page7B QuarterNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- GenscieDocument16 pagesGenscieNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- 9B QuarterDocument1 page9B QuarterNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Dear NanayDocument5 pagesDear NanayNard Emsoc100% (1)
- 10B QuarterDocument1 page10B QuarterNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Lorentz TransformationDocument7 pagesActivity 3 - Lorentz TransformationNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Readings in Philippine Literature Study GuideDocument6 pagesReadings in Philippine Literature Study GuideNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Activity 4&5: Relativistic Length Contraction and Time DilationDocument5 pagesActivity 4&5: Relativistic Length Contraction and Time DilationNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Activity 2: The Postulate of EinsteinDocument3 pagesActivity 2: The Postulate of EinsteinNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Selection 6Document1 pageSelection 6Nard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Galilean Transformation: Make A Compilation of Concepts in Your Classical Physics Focus OnDocument4 pagesActivity 1: Galilean Transformation: Make A Compilation of Concepts in Your Classical Physics Focus OnNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Module 8 ThermochemistryDocument33 pagesModule 8 ThermochemistryNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Urdaneta City UniversityDocument6 pagesUrdaneta City UniversityNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Calculations Involving SolutionsDocument14 pagesModule 6 Calculations Involving SolutionsNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Once Upon A Time by N. GordimerDocument3 pagesOnce Upon A Time by N. GordimerNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- 1 - Euramet Training On Hydraulic Pressure Balances, Feb 2017, Fredrik Arrhen RISE Sweden, DAY 1 PDFDocument37 pages1 - Euramet Training On Hydraulic Pressure Balances, Feb 2017, Fredrik Arrhen RISE Sweden, DAY 1 PDFkalibrasibbkkpNo ratings yet
- Iit Jam Physics 2016 PDFDocument13 pagesIit Jam Physics 2016 PDFKritiraj KalitaNo ratings yet
- Vibratingfeeder 150211110459 Conversion Gate01Document18 pagesVibratingfeeder 150211110459 Conversion Gate01ManekGorisNo ratings yet
- Sample Report Otdr YokogawaDocument26 pagesSample Report Otdr YokogawaKiarra gamingNo ratings yet
- Stability of Structures QuestionsDocument2 pagesStability of Structures QuestionsAnandkumar MukiriNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Extended Surface Heat TransferDocument19 pagesA Critical Review of Extended Surface Heat TransferJuan Fernando Cano LarrotaNo ratings yet
- Energy and Work 6Document21 pagesEnergy and Work 6Yash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Physics. Solutions Sheet 10.: Hi, Ji I JDocument8 pagesStatistical Physics. Solutions Sheet 10.: Hi, Ji I JJuan MondáNo ratings yet
- PASTEURISER Holding Section Holding Time CalculationDocument2 pagesPASTEURISER Holding Section Holding Time Calculationarenco100% (2)
- Physical Science Q2 Week 6 - 7 SLM 8Document15 pagesPhysical Science Q2 Week 6 - 7 SLM 8Romel Bayaban0% (1)
- Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, PatialaDocument2 pagesThapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, Patialaauro auroNo ratings yet
- Microwave Lab ManualDocument52 pagesMicrowave Lab ManualDhanish VijayanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Boussinesq ApproximationDocument1 pageUnderstanding Boussinesq ApproximationHsu Tien-YiaoNo ratings yet
- On Solar CellDocument17 pagesOn Solar CellMab Sharma100% (2)
- 12 Turbulent FlowDocument5 pages12 Turbulent FlowDavid KegayaNo ratings yet
- SolubilityDocument37 pagesSolubilityLalitha Sravani100% (1)
- Design of RC ShellsDocument9 pagesDesign of RC Shellscacrcarlos100% (1)
- An Introduction To Chemical Engineering Kinetics and Reactor Design PDFDocument603 pagesAn Introduction To Chemical Engineering Kinetics and Reactor Design PDFAnonymous lDX3QhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding A PDFDocument22 pagesChemical Bonding A PDFshubhammukriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Centrifugal CompressorsDocument11 pagesChapter 8: Centrifugal CompressorsAnonymous zb5O19SzkDNo ratings yet
- Phys 3 QPDocument18 pagesPhys 3 QPPhonxayNo ratings yet
- Sencore SG165 O&M ManualDocument70 pagesSencore SG165 O&M ManualDENIS BRIAND100% (2)
- Textbook Particle Physics Fourth Edition Edition Martin Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Particle Physics Fourth Edition Edition Martin Ebook All Chapter PDFkristine.webb574100% (12)
- Elec TechnDocument6 pagesElec TechnIsraelNo ratings yet
- Alternator Part I Eac ReviewDocument15 pagesAlternator Part I Eac ReviewKevin MaramagNo ratings yet
- Portescap Katalog Silniki GBDocument292 pagesPortescap Katalog Silniki GBpicmasterNo ratings yet
- Theory of Electrostatics: Electric ChargeDocument8 pagesTheory of Electrostatics: Electric ChargeAbrahamRubioNo ratings yet
- 1 Thin Shells PDFDocument16 pages1 Thin Shells PDFMarcus Vinicius FaleiroNo ratings yet
- Small Bore Orifice For Gas FlowDocument4 pagesSmall Bore Orifice For Gas FlowMarc EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Van Der WallsDocument24 pagesVan Der WallsAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBNo ratings yet