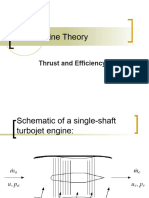
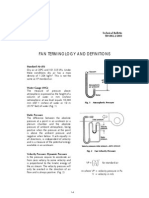
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Derivation
Derivation
Uploaded by
George GomezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Derivation
Derivation
Uploaded by
George GomezCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
The static pressure and total pressure of a fan are important because they determine the
amount of air that the fan can move through a system. The higher the static pressure and total
pressure, the more air the fan can move through the system.
2. Air horsepower (AH) is a unit of power used to measure the performance of a fan or blower that
moves air through a system. It is a measure of the amount of work that a fan can do to move a
given amount of air through a system.
Air horsepower is defined as the power required to move a certain volume of air at a specific
pressure through a system. The formula for calculating air horsepower is:
AH = (Q x P) / (6356 x EFF)
Where:
Q = airflow rate in cubic feet per minute (CFM)
P = pressure in inches of water column (inWC)
EFF = fan efficiency (expressed as a decimal)
In this formula, the values for airflow rate and pressure are measured by the fan, while the fan
efficiency is typically provided by the manufacturer.
Air horsepower is an important parameter used to select and size fans and blowers for specific
applications. By calculating the required air horsepower, engineers can determine the
appropriate size and type of fan needed to meet the airflow and pressure requirements of a
particular system.
The ideal gas law can be rearranged to solve for the density (ρ) of an ideal gas, which is defined
as the mass of the gas per unit volume.
Starting from the ideal gas law:
PV = nRT
We can solve for the density by rearranging this equation as follows:
PV = mRT/M
Where:
P = pressure of the gas (in Pa)
V = volume of the gas (in m³)
n = number of moles of the gas
R = gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K)
T = temperature of the gas (in K)
m = mass of the gas (in kg)
M = molar mass of the gas (in kg/mol)
We can then solve for the density by dividing both sides by V:
m/V = P/RT × M
ρ = P/RT × M
where ρ is the density of the gas (in kg/m³).
Therefore, to equate the ideal gas law equation to density, we simply divide the pressure (P) by
the gas constant (R) times the temperature (T) and the molar mass (M) of the gas. This gives us
the density of the gas at the given pressure, temperature, and molar mass
You might also like
- Fans and Blowers Part I ModuleDocument26 pagesFans and Blowers Part I ModuleCharlyn Flores67% (3)
- Aircraft Propulsion Systems: Dr. Anmar H. AliDocument10 pagesAircraft Propulsion Systems: Dr. Anmar H. AliAlmukhtar AlkinanyNo ratings yet
- Steam Flow Compensation Equations - For DCSDocument10 pagesSteam Flow Compensation Equations - For DCSLTE0020% (1)
- The Myth About Fan Static PressureDocument5 pagesThe Myth About Fan Static Pressurebetos013No ratings yet
- Analysis of A Regenerative Gas Turbine Cycle For Performance EvaluationDocument10 pagesAnalysis of A Regenerative Gas Turbine Cycle For Performance EvaluationbensouiciNo ratings yet
- Axial Fan AssignmentDocument7 pagesAxial Fan AssignmentMorgana RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines For Aircraft Propulsion Chapter 9.9-10Document49 pagesGas Turbines For Aircraft Propulsion Chapter 9.9-10Dk DamoNo ratings yet
- Work Per Cycle PcmaiDocument12 pagesWork Per Cycle PcmaiSchiopu George0% (1)
- Cermak AMCA Web FanDocument6 pagesCermak AMCA Web Fanbigi1234No ratings yet
- Analysis of Rocket NozzleDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Rocket NozzleleulmathersNo ratings yet
- Modern Cooling System TheoryDocument4 pagesModern Cooling System TheorySporkyNo ratings yet
- Solutions Solutions EquationsDocument2 pagesSolutions Solutions EquationsJohn OlivierNo ratings yet
- Lect 01 Introduction02Document21 pagesLect 01 Introduction02Salman KhalilNo ratings yet
- Design of Ventilation Systems: Example - Removing Moisture From A RoomDocument18 pagesDesign of Ventilation Systems: Example - Removing Moisture From A RoomshakebmailNo ratings yet
- Vapor Flow To Equivalent Air Flow Conversion EquationsDocument2 pagesVapor Flow To Equivalent Air Flow Conversion EquationsAnonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet
- Example 6 - Cal Supply Air Quantity FCUDocument11 pagesExample 6 - Cal Supply Air Quantity FCUHo Dac ThanhNo ratings yet
- Principal Technical Particulars : V QV 3.600 - ADocument7 pagesPrincipal Technical Particulars : V QV 3.600 - Ahalder_kalyan9216No ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About FansDocument10 pagesAll You Need To Know About FansgertibajNo ratings yet
- Thrust and EfficiencyDocument60 pagesThrust and EfficiencyDenyseNo ratings yet
- Compressors Version 3Document4 pagesCompressors Version 3elpidiozr8229No ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument19 pagesConversion of UnitsAnurag TripathyNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Solution For The CrossflowDocument17 pagesTheoretical Solution For The CrossflowAndriano Suryawan UtamaNo ratings yet
- Turbo Machinery Unit 1Document50 pagesTurbo Machinery Unit 1Temesgen ErenaNo ratings yet
- Influencias Caracteristicas VentiladorDocument19 pagesInfluencias Caracteristicas VentiladorSebastian LopezNo ratings yet
- Numerical of MVDocument14 pagesNumerical of MVshivam raiNo ratings yet
- MECH2410 Fan PracticalDocument7 pagesMECH2410 Fan Practicalbgrin7No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine ExperimentDocument7 pagesSteam Turbine ExperimentEnriv Yasilad100% (1)
- AnAnalysisofCombined CyclePowerPlantData - Docx 0Document32 pagesAnAnalysisofCombined CyclePowerPlantData - Docx 0nabilaNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Concept of Compressible Flow - Sae1301Document172 pagesUnit - I Concept of Compressible Flow - Sae1301Divy KaravdiyaNo ratings yet
- Assosa University: Compressible FlowDocument74 pagesAssosa University: Compressible FlowWillky FrezerNo ratings yet
- Gas ConstantDocument3 pagesGas ConstantArdhendu SamantaNo ratings yet
- Parag Fan WriteupDocument9 pagesParag Fan Writeuprashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Ventilator Characteristic Determination by Thomas CylinderDocument6 pagesVentilator Characteristic Determination by Thomas Cylindercapricorno4694No ratings yet
- Applying Psychrometric RelationshipsDocument6 pagesApplying Psychrometric Relationshipssaifuddin722No ratings yet
- The Average Output Power of A Wind Turbine in Turbulant WindDocument16 pagesThe Average Output Power of A Wind Turbine in Turbulant WindKausihan SelvamNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document13 pagesLab 4Dilshad S FaisalNo ratings yet
- Vent Axia Vent GuideDocument23 pagesVent Axia Vent GuideblasderNo ratings yet
- Boiling: TB TsDocument5 pagesBoiling: TB TsPhilip ShihNo ratings yet
- Fans - Volume Flow, Pressure Head and Power Consumption vs. Air Temperature and DensityDocument11 pagesFans - Volume Flow, Pressure Head and Power Consumption vs. Air Temperature and DensitykaustavNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Measurement ParametersDocument11 pagesNatural Gas Measurement ParametersmounirakermaniNo ratings yet
- Fan BasicsDocument6 pagesFan BasicsPankaj Patil100% (1)
- Trade Study: Stirling Engine: Phillip M. Hicks February 28, 2008Document12 pagesTrade Study: Stirling Engine: Phillip M. Hicks February 28, 2008Timothy MathisNo ratings yet
- Wind Tunnel Experiments Procedure in UPMDocument5 pagesWind Tunnel Experiments Procedure in UPMMohd AnuarNo ratings yet
- Fan Terminology and Definitions: Technical Bulletin TBN002.2/2003Document4 pagesFan Terminology and Definitions: Technical Bulletin TBN002.2/2003Ngoc Vũ TrầnNo ratings yet
- Aiaa 2007 7848 764Document12 pagesAiaa 2007 7848 764Opteron K.No ratings yet
- 2.6 Wind Energy TheoryDocument6 pages2.6 Wind Energy TheoryAlaa TamimiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report No.05Document11 pagesLab Report No.05Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Practical Lab # 8. Finding Pressure Distribution Over An Aerofoil at Different Velocity and AnglesDocument3 pagesPractical Lab # 8. Finding Pressure Distribution Over An Aerofoil at Different Velocity and Anglesamanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- ALUP Compressed Air Fundamentals-Part1 - GBDocument50 pagesALUP Compressed Air Fundamentals-Part1 - GBmbrijbhushan75% (4)
- Summed With The Wind Opposing The Forward Velocity of The Airfoil. This Combined Velocity Is Known As The Relative WindDocument6 pagesSummed With The Wind Opposing The Forward Velocity of The Airfoil. This Combined Velocity Is Known As The Relative WindAshok JohnNo ratings yet
- Calcul UkDocument5 pagesCalcul UkJeremyNo ratings yet
- Adii Quest BankDocument13 pagesAdii Quest Bankvinod kumarNo ratings yet
- Giải 1 - mergedDocument13 pagesGiải 1 - mergedsy.buitienNo ratings yet
- Nickel Industry: Heavy Metal (Loid) S Contamination - Sources, Environmental Impacts and Recent Advances On Waste ValorizationDocument9 pagesNickel Industry: Heavy Metal (Loid) S Contamination - Sources, Environmental Impacts and Recent Advances On Waste ValorizationGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- EM 206 System and DynamicsDocument5 pagesEM 206 System and DynamicsGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Mineral Processing Lecture NotesDocument943 pagesMineral Processing Lecture NotesGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Fire Assaying IVDocument27 pagesFire Assaying IVGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Carlos Sierra - Mine Ventilation - A Concise Guide For Students-Springer International Publishing - Springer (2020)Document372 pagesCarlos Sierra - Mine Ventilation - A Concise Guide For Students-Springer International Publishing - Springer (2020)George GomezNo ratings yet
- CHEM 5 03 Protein DenaturationPurificationCharacterizationDocument19 pagesCHEM 5 03 Protein DenaturationPurificationCharacterizationGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Fire AssayingDocument28 pagesFire AssayingGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- DEM PPT-Template2Document13 pagesDEM PPT-Template2George GomezNo ratings yet
- CHEM 5 04 EnzymesDocument45 pagesCHEM 5 04 EnzymesGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- CHEM 5 02 Protein Amino Acids Peptide BondDocument53 pagesCHEM 5 02 Protein Amino Acids Peptide BondGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Syllabus2021 - 1stsem - EM 101 Underground MiningDocument7 pagesSyllabus2021 - 1stsem - EM 101 Underground MiningGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 (Week 1)Document19 pagesTopic 1 (Week 1)George GomezNo ratings yet
- Cover LetterDocument1 pageCover LetterGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Syllabus2021 - 1stsem - EM 103 Mine SafetyDocument20 pagesSyllabus2021 - 1stsem - EM 103 Mine SafetyGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Met 101: Mineral Processing: Course OrientationDocument25 pagesMet 101: Mineral Processing: Course OrientationGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Project 1: Quantitative ResultsDocument2 pagesProject 1: Quantitative ResultsGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- Chemical TechnicianDocument1 pageChemical TechnicianGeorge GomezNo ratings yet