Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Os Assignment
Os Assignment
Uploaded by
Abel AbCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 7 Generations of ComputerDocument5 pages7 Generations of ComputerZeshan Munir78% (9)
- Handout - Grade 7 - ICT - Parts of A Computer PDFDocument0 pagesHandout - Grade 7 - ICT - Parts of A Computer PDFRodsil Czar Palma Sacmar100% (4)
- Computer GenerationsDocument3 pagesComputer Generationsdaniyalshakeel573No ratings yet
- Topic A Computer Generations - Key Concepts of Computer Studies 1700232042305Document9 pagesTopic A Computer Generations - Key Concepts of Computer Studies 1700232042305gozibartmutegekNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument10 pagesComputer GenerationsfidanmouradliNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1: Name: ID: SubjectDocument4 pagesAssignment No.1: Name: ID: SubjectJUNAID IRFANNo ratings yet
- Arba Minch University: DEPARTEMENT OF: Health Informatics Individual AssignmentDocument7 pagesArba Minch University: DEPARTEMENT OF: Health Informatics Individual AssignmentAgegnehu TakeleNo ratings yet
- кпізDocument8 pagesкпізMax SvirskyNo ratings yet
- Itc ReportDocument13 pagesItc ReportaleezaNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument4 pagesGenerations of Computerkhanburki701No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document11 pagesAssignment 1Atif HaiderNo ratings yet
- School of Information System: Addis Ababa UniversityDocument13 pagesSchool of Information System: Addis Ababa Universitymuhidinhawlet76No ratings yet
- Extra Period. Topic: Computer EvolutionDocument4 pagesExtra Period. Topic: Computer EvolutionAdila AhmedNo ratings yet
- Reading Activity 2 Generations of ComputersDocument4 pagesReading Activity 2 Generations of ComputersLance GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 1.3-1.4 Generations and Classifications of ComputerDocument51 pages1.3-1.4 Generations and Classifications of ComputerKipi Waruku BinisutiNo ratings yet
- Emergence of New TechnologyDocument19 pagesEmergence of New TechnologyLONEZOIDNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument15 pagesComputer Generationsirakozebruce329No ratings yet
- Generations of ComputersDocument4 pagesGenerations of ComputersprathisimhaNo ratings yet
- Genertation of ComputerDocument6 pagesGenertation of ComputerMuhammad OsamaNo ratings yet
- SBI Clerk Computer Awareness Pocket Knowledge HereDocument16 pagesSBI Clerk Computer Awareness Pocket Knowledge HerePKS_200No ratings yet
- Comp HistoryDocument2 pagesComp HistoryMugasira CalvinNo ratings yet
- It AssignmentDocument13 pagesIt AssignmentPriyanshu MishraNo ratings yet
- Module 1.2 Computer GenerationDocument48 pagesModule 1.2 Computer Generationnavi jaeNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument18 pagesComputer GenerationsDuggi Shanmukha ViharNo ratings yet
- CA UNIT 1 NotesDocument36 pagesCA UNIT 1 NotesAbsolutely NotNo ratings yet
- Generation of ComputersDocument4 pagesGeneration of ComputersAgrippa TemboNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 Computer EvolutionDocument26 pagesLesson3 Computer Evolutiontebelayhabitamu12No ratings yet
- Lesson3 Computer EvolutionDocument26 pagesLesson3 Computer EvolutionJennifer Diaz PendonNo ratings yet
- ICT Assignment 1Document8 pagesICT Assignment 1Abdullah KhosaNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument4 pagesComputer GenerationsJason YipNo ratings yet
- DAY 3 (Generation of Computer)Document12 pagesDAY 3 (Generation of Computer)Vneet ButolaNo ratings yet
- Computer EvolutionDocument20 pagesComputer EvolutionMUHAMMAD RAHEEL BSSE-FA20-100No ratings yet
- Muhammad HamzaDocument7 pagesMuhammad Hamzapxking6No ratings yet
- Generation of ComputersDocument16 pagesGeneration of ComputersAbhishek K.CNo ratings yet
- Computer Generations Generation in Computer Terminology Is A Change in Technology A Computer Is/wasDocument6 pagesComputer Generations Generation in Computer Terminology Is A Change in Technology A Computer Is/wasYogendra Rajavat100% (1)
- Generations of ComputersDocument5 pagesGenerations of ComputersTata Duero LachicaNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument12 pagesGenerations of ComputerVehleSinghNo ratings yet
- Generation of ComputersDocument9 pagesGeneration of ComputersMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument7 pagesGenerations of Computerdipankar.gede23No ratings yet
- Computer Brahmastra E-BOOKDocument99 pagesComputer Brahmastra E-BOOKSayantan MandalNo ratings yet
- Computer Brahmastra E-BOOKDocument99 pagesComputer Brahmastra E-BOOKrajNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputersDocument5 pagesGenerations of Computersmohammad shoaibNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationDocument10 pagesComputer Generationmuleya nchimunyaNo ratings yet
- Generation of Computer in DetailsDocument5 pagesGeneration of Computer in DetailsAbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- ICT Assigment-Generation of ComputerDocument9 pagesICT Assigment-Generation of ComputerABDUL HASEEBNo ratings yet
- Com Hardware1 EEC117Document62 pagesCom Hardware1 EEC117pdaramola344No ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument7 pagesComputer Generationsrakotogogo1No ratings yet
- Evolution of ComputingDocument26 pagesEvolution of ComputingIrish AmaroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Computerssindhu palanisamyNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument9 pagesHistoryJared LozadaNo ratings yet
- ParallelprocessingDocument36 pagesParallelprocessingவெ. விஷ்வாNo ratings yet
- History and Generations of Computers Group 7Document13 pagesHistory and Generations of Computers Group 7John Franklin Guliman MorenoNo ratings yet
- Lab Presentation-1Document8 pagesLab Presentation-1Fahad MalikNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument18 pagesGenerations of ComputerDynDyn DisenNo ratings yet
- Ict t1Document6 pagesIct t1tyjien.05No ratings yet
- By:Gourav Kumar Class:5 Section:B Subject:Computer: Evolution of ComputersDocument9 pagesBy:Gourav Kumar Class:5 Section:B Subject:Computer: Evolution of ComputersGracy RaikwarNo ratings yet
- Welcome To My Presentation: Evolution OF ComputersDocument13 pagesWelcome To My Presentation: Evolution OF ComputersSanzir Islam 191-23-5506No ratings yet
- Generation of ComputerDocument6 pagesGeneration of ComputerPratik KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Computers have-WPS OfficeDocument24 pagesComputers have-WPS OfficeisanguramaguNo ratings yet
- Class 5 ComputerDocument5 pagesClass 5 ComputerDr HussainNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer BookDocument113 pagesBasic Computer BookAnonde MauriceNo ratings yet
- Basic 7 Computer 2nd Term E-Notes-1Document17 pagesBasic 7 Computer 2nd Term E-Notes-1Funsho TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Dankbaar College of Applied Science and TechnologyDocument9 pagesDankbaar College of Applied Science and TechnologyBright Alike ChiwevuNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Unit Test-1 Study Material 2022-23Document53 pagesGrade 5 Unit Test-1 Study Material 2022-23ajay.parasharNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document30 pagesModule 1ehzanpklmNo ratings yet
- Computer EvolutionDocument34 pagesComputer EvolutionJovin MosesNo ratings yet
- DLD MaqterialDocument267 pagesDLD MaqterialmalyadriNo ratings yet
- Celestino - Jenny - (Module 2)Document3 pagesCelestino - Jenny - (Module 2)Jenny CelestinoNo ratings yet
- Five Generations of ComputersDocument3 pagesFive Generations of ComputersKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Field Technician - Computing - PeripheralsDocument398 pagesField Technician - Computing - Peripheralsardigital226No ratings yet
- Connect HardwareDocument23 pagesConnect HardwareYoni ManNo ratings yet
- JSS 1 First Term Lesson NoteDocument8 pagesJSS 1 First Term Lesson NoteHalifaxNo ratings yet
- Full Seminar Report On e BallDocument45 pagesFull Seminar Report On e BallLalit Bhagat100% (1)
- Introduction To Computer Skills For Uganda Christian UniversityDocument61 pagesIntroduction To Computer Skills For Uganda Christian UniversityvianneloroNo ratings yet
- UNIT2 Brief History of Number SystemDocument42 pagesUNIT2 Brief History of Number SystemLloyd RevesNo ratings yet
- Module 1-85206-1Document5 pagesModule 1-85206-1Erick MeguisoNo ratings yet
- CIT 213 - RevisedDocument127 pagesCIT 213 - RevisedDavid OmaguNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument71 pagesIntroduction To ComputerschristinaceciliaaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Computer Book Federal Board MergedDocument120 pagesClass 9 Computer Book Federal Board MergedMunib Ahmad100% (1)
- Intro To ComputingDocument3 pagesIntro To ComputingAntonio, Jachin Nicolai F.No ratings yet
- GE ELECTIVE 2 - History of ComputersDocument46 pagesGE ELECTIVE 2 - History of ComputersVincent BlancoNo ratings yet
- CAO Assignment 1 - SIMBAJONDocument5 pagesCAO Assignment 1 - SIMBAJONShaun Wesley SimbajonNo ratings yet
- Ict1 Lec 1Document13 pagesIct1 Lec 1mevam22No ratings yet
- Asma Computer AssignmentDocument4 pagesAsma Computer AssignmentUmaima NoorNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1 - Introdution To ComputerDocument72 pagesPresentation 1 - Introdution To ComputerRyan NguyaNo ratings yet
- Oliveboard Computer PDFDocument33 pagesOliveboard Computer PDFrrphysicsinstituteNo ratings yet
- Generation of ComputersDocument4 pagesGeneration of ComputersanshifhaarNo ratings yet
Os Assignment
Os Assignment
Uploaded by
Abel AbOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Os Assignment
Os Assignment
Uploaded by
Abel AbCopyright:
Available Formats
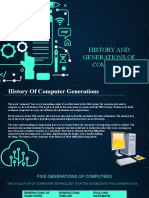
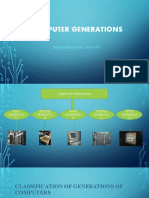
Five Generations of Computers
Generations of Generations
Evolving hardware
computers timeline
First generation 1940s-1950s Vacuum tube based
Second
1950s-1960s Transistor based
generation
Integrated circuit
Third generation 1960s-1970s
based
Fourth Microprocessor
1970s-present
generation based
The present and Artificial intelligence
Fifth generation
the future based
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s)
Main electronic component – vacuum tube
Main memory – magnetic drums and magnetic tapes
Programming language – machine language
Power – consume a lot of electricity and generate a lot of heat.
Speed and size – very slow and very large in size (often taking up entire room).
Input/output devices – punched cards and paper tape.
Examples – ENIAC, UNIVAC1, IBM 650, IBM 701, etc.
Quantity – there were about 100 different vacuum tube computers produced between 1942
and1963
Second Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of second generation of computers (1950s-1960s)
Main electronic component – transistor
Memory – magnetic core and magnetic tape / disk
Programming language – assembly language
Power and size – low power consumption, generated less heat, and smaller in size (in
comparison with the first generation computers).
Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the first generation
computers).
Input/output devices – punched cards and magnetic tape.
Examples – IBM 1401, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, etc.
Third Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of third generation of computers (1960s-1970s)
Main electronic component – integrated circuits (ICs)
Memory – large magnetic core, magnetic tape / disk
Programming language – high level language (FORTRAN, BASIC, Pascal, COBOL, C, etc.)
Size – smaller, cheaper, and more efficient than second generation computers (they were called
minicomputers).
Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the second generation
computers).
Input / output devices – magnetic tape, keyboard, monitor, printer, etc.
Examples – IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, UNIVAC 1108, etc.
Fourth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fourth generation of computers (1970s-present)
Main electronic component – very large-scale integration
(VLSI) and microprocessor.
VLSI– thousands of transistors on a single microchip.
Memory – semiconductor memory (such as RAM, ROM, etc.)
o RAM (random-access memory) – a type of data storage (memory element) used in
computers that temporary stores of programs and data (volatile: its contents are lost
when the computer is turned off).
o ROM (read-only memory) – a type of data storage
used in computers that permanently stores data and programs (non-volatile: its
contents are retained even when the computer is turned off).
Programming language – high level language (Python, C#, Java, JavaScript, Rust, Kotlin, etc.).
o A mix of both third- and fourth-generation languages
Size – smaller, cheaper and more efficient than third generation computers.
Speed – improvement of speed, accuracy, and reliability (in comparison with the third
generation computers).
Input / output devices – keyboard, pointing devices, optical
scanning, monitor, printer, etc.
Network – a group of two or more computer systems linked together.
Examples – IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, etc.
Fifth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fifth generation of computers (the present and the future)
Main electronic component: based on artificial intelligence,
uses the Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method.
o ULSI – millions of transistors on a single microchip
o Parallel processing method – use two or more microprocessors to run tasks
simultaneously.
Language – understand natural language (human language).
Power – consume less power and generate less heat.
Speed – remarkable improvement of speed, accuracy and reliability (in comparison with the
fourth generation computers).
Size – portable and small in size, and have a huge storage capacity.
Input / output device – keyboard, monitor, mouse, trackpad
(or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognise voice / speech), light scanner, printer,
etc.
Example – desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.
You might also like
- 7 Generations of ComputerDocument5 pages7 Generations of ComputerZeshan Munir78% (9)
- Handout - Grade 7 - ICT - Parts of A Computer PDFDocument0 pagesHandout - Grade 7 - ICT - Parts of A Computer PDFRodsil Czar Palma Sacmar100% (4)
- Computer GenerationsDocument3 pagesComputer Generationsdaniyalshakeel573No ratings yet
- Topic A Computer Generations - Key Concepts of Computer Studies 1700232042305Document9 pagesTopic A Computer Generations - Key Concepts of Computer Studies 1700232042305gozibartmutegekNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument10 pagesComputer GenerationsfidanmouradliNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1: Name: ID: SubjectDocument4 pagesAssignment No.1: Name: ID: SubjectJUNAID IRFANNo ratings yet
- Arba Minch University: DEPARTEMENT OF: Health Informatics Individual AssignmentDocument7 pagesArba Minch University: DEPARTEMENT OF: Health Informatics Individual AssignmentAgegnehu TakeleNo ratings yet
- кпізDocument8 pagesкпізMax SvirskyNo ratings yet
- Itc ReportDocument13 pagesItc ReportaleezaNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument4 pagesGenerations of Computerkhanburki701No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document11 pagesAssignment 1Atif HaiderNo ratings yet
- School of Information System: Addis Ababa UniversityDocument13 pagesSchool of Information System: Addis Ababa Universitymuhidinhawlet76No ratings yet
- Extra Period. Topic: Computer EvolutionDocument4 pagesExtra Period. Topic: Computer EvolutionAdila AhmedNo ratings yet
- Reading Activity 2 Generations of ComputersDocument4 pagesReading Activity 2 Generations of ComputersLance GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 1.3-1.4 Generations and Classifications of ComputerDocument51 pages1.3-1.4 Generations and Classifications of ComputerKipi Waruku BinisutiNo ratings yet
- Emergence of New TechnologyDocument19 pagesEmergence of New TechnologyLONEZOIDNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument15 pagesComputer Generationsirakozebruce329No ratings yet
- Generations of ComputersDocument4 pagesGenerations of ComputersprathisimhaNo ratings yet
- Genertation of ComputerDocument6 pagesGenertation of ComputerMuhammad OsamaNo ratings yet
- SBI Clerk Computer Awareness Pocket Knowledge HereDocument16 pagesSBI Clerk Computer Awareness Pocket Knowledge HerePKS_200No ratings yet
- Comp HistoryDocument2 pagesComp HistoryMugasira CalvinNo ratings yet
- It AssignmentDocument13 pagesIt AssignmentPriyanshu MishraNo ratings yet
- Module 1.2 Computer GenerationDocument48 pagesModule 1.2 Computer Generationnavi jaeNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument18 pagesComputer GenerationsDuggi Shanmukha ViharNo ratings yet
- CA UNIT 1 NotesDocument36 pagesCA UNIT 1 NotesAbsolutely NotNo ratings yet
- Generation of ComputersDocument4 pagesGeneration of ComputersAgrippa TemboNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 Computer EvolutionDocument26 pagesLesson3 Computer Evolutiontebelayhabitamu12No ratings yet
- Lesson3 Computer EvolutionDocument26 pagesLesson3 Computer EvolutionJennifer Diaz PendonNo ratings yet
- ICT Assignment 1Document8 pagesICT Assignment 1Abdullah KhosaNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument4 pagesComputer GenerationsJason YipNo ratings yet
- DAY 3 (Generation of Computer)Document12 pagesDAY 3 (Generation of Computer)Vneet ButolaNo ratings yet
- Computer EvolutionDocument20 pagesComputer EvolutionMUHAMMAD RAHEEL BSSE-FA20-100No ratings yet
- Muhammad HamzaDocument7 pagesMuhammad Hamzapxking6No ratings yet
- Generation of ComputersDocument16 pagesGeneration of ComputersAbhishek K.CNo ratings yet
- Computer Generations Generation in Computer Terminology Is A Change in Technology A Computer Is/wasDocument6 pagesComputer Generations Generation in Computer Terminology Is A Change in Technology A Computer Is/wasYogendra Rajavat100% (1)
- Generations of ComputersDocument5 pagesGenerations of ComputersTata Duero LachicaNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument12 pagesGenerations of ComputerVehleSinghNo ratings yet
- Generation of ComputersDocument9 pagesGeneration of ComputersMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument7 pagesGenerations of Computerdipankar.gede23No ratings yet
- Computer Brahmastra E-BOOKDocument99 pagesComputer Brahmastra E-BOOKSayantan MandalNo ratings yet
- Computer Brahmastra E-BOOKDocument99 pagesComputer Brahmastra E-BOOKrajNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputersDocument5 pagesGenerations of Computersmohammad shoaibNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationDocument10 pagesComputer Generationmuleya nchimunyaNo ratings yet
- Generation of Computer in DetailsDocument5 pagesGeneration of Computer in DetailsAbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- ICT Assigment-Generation of ComputerDocument9 pagesICT Assigment-Generation of ComputerABDUL HASEEBNo ratings yet
- Com Hardware1 EEC117Document62 pagesCom Hardware1 EEC117pdaramola344No ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument7 pagesComputer Generationsrakotogogo1No ratings yet
- Evolution of ComputingDocument26 pagesEvolution of ComputingIrish AmaroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Computerssindhu palanisamyNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument9 pagesHistoryJared LozadaNo ratings yet
- ParallelprocessingDocument36 pagesParallelprocessingவெ. விஷ்வாNo ratings yet
- History and Generations of Computers Group 7Document13 pagesHistory and Generations of Computers Group 7John Franklin Guliman MorenoNo ratings yet
- Lab Presentation-1Document8 pagesLab Presentation-1Fahad MalikNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument18 pagesGenerations of ComputerDynDyn DisenNo ratings yet
- Ict t1Document6 pagesIct t1tyjien.05No ratings yet
- By:Gourav Kumar Class:5 Section:B Subject:Computer: Evolution of ComputersDocument9 pagesBy:Gourav Kumar Class:5 Section:B Subject:Computer: Evolution of ComputersGracy RaikwarNo ratings yet
- Welcome To My Presentation: Evolution OF ComputersDocument13 pagesWelcome To My Presentation: Evolution OF ComputersSanzir Islam 191-23-5506No ratings yet
- Generation of ComputerDocument6 pagesGeneration of ComputerPratik KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Computers have-WPS OfficeDocument24 pagesComputers have-WPS OfficeisanguramaguNo ratings yet
- Class 5 ComputerDocument5 pagesClass 5 ComputerDr HussainNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer BookDocument113 pagesBasic Computer BookAnonde MauriceNo ratings yet
- Basic 7 Computer 2nd Term E-Notes-1Document17 pagesBasic 7 Computer 2nd Term E-Notes-1Funsho TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Dankbaar College of Applied Science and TechnologyDocument9 pagesDankbaar College of Applied Science and TechnologyBright Alike ChiwevuNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Unit Test-1 Study Material 2022-23Document53 pagesGrade 5 Unit Test-1 Study Material 2022-23ajay.parasharNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document30 pagesModule 1ehzanpklmNo ratings yet
- Computer EvolutionDocument34 pagesComputer EvolutionJovin MosesNo ratings yet
- DLD MaqterialDocument267 pagesDLD MaqterialmalyadriNo ratings yet
- Celestino - Jenny - (Module 2)Document3 pagesCelestino - Jenny - (Module 2)Jenny CelestinoNo ratings yet
- Five Generations of ComputersDocument3 pagesFive Generations of ComputersKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Field Technician - Computing - PeripheralsDocument398 pagesField Technician - Computing - Peripheralsardigital226No ratings yet
- Connect HardwareDocument23 pagesConnect HardwareYoni ManNo ratings yet
- JSS 1 First Term Lesson NoteDocument8 pagesJSS 1 First Term Lesson NoteHalifaxNo ratings yet
- Full Seminar Report On e BallDocument45 pagesFull Seminar Report On e BallLalit Bhagat100% (1)
- Introduction To Computer Skills For Uganda Christian UniversityDocument61 pagesIntroduction To Computer Skills For Uganda Christian UniversityvianneloroNo ratings yet
- UNIT2 Brief History of Number SystemDocument42 pagesUNIT2 Brief History of Number SystemLloyd RevesNo ratings yet
- Module 1-85206-1Document5 pagesModule 1-85206-1Erick MeguisoNo ratings yet
- CIT 213 - RevisedDocument127 pagesCIT 213 - RevisedDavid OmaguNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument71 pagesIntroduction To ComputerschristinaceciliaaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Computer Book Federal Board MergedDocument120 pagesClass 9 Computer Book Federal Board MergedMunib Ahmad100% (1)
- Intro To ComputingDocument3 pagesIntro To ComputingAntonio, Jachin Nicolai F.No ratings yet
- GE ELECTIVE 2 - History of ComputersDocument46 pagesGE ELECTIVE 2 - History of ComputersVincent BlancoNo ratings yet
- CAO Assignment 1 - SIMBAJONDocument5 pagesCAO Assignment 1 - SIMBAJONShaun Wesley SimbajonNo ratings yet
- Ict1 Lec 1Document13 pagesIct1 Lec 1mevam22No ratings yet
- Asma Computer AssignmentDocument4 pagesAsma Computer AssignmentUmaima NoorNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1 - Introdution To ComputerDocument72 pagesPresentation 1 - Introdution To ComputerRyan NguyaNo ratings yet
- Oliveboard Computer PDFDocument33 pagesOliveboard Computer PDFrrphysicsinstituteNo ratings yet
- Generation of ComputersDocument4 pagesGeneration of ComputersanshifhaarNo ratings yet