Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How RBI Was Formed
How RBI Was Formed
Uploaded by
Vishal Deepak MusicCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Unit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDocument109 pagesUnit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDr. S. Nellima KPRCAS-CommerceNo ratings yet
- Project Role of RBI Word Doc.3Document66 pagesProject Role of RBI Word Doc.3nilesh dhivreNo ratings yet
- Careers CloudDocument35 pagesCareers Cloudaravind lagishettiNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument21 pagesReserve Bank of IndiaUttamveer Singh GhalotNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument21 pagesReserve Bank of IndiaAcchu BajajNo ratings yet
- Of RbiDocument16 pagesOf RbiMohit VinayakNo ratings yet
- Banking NotesDocument60 pagesBanking NotesarunimaNo ratings yet
- Banking Evolution - HistoryDocument40 pagesBanking Evolution - HistoryYuvnesh Kumar R.JNo ratings yet
- New Final ReportDocument33 pagesNew Final Reportvarshinivars2223No ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument4 pagesReserve Bank of Indiakingsonstj1001No ratings yet
- Comperative Study On Performance of Public & Private Sector BanksDocument96 pagesComperative Study On Performance of Public & Private Sector BanksJaimit Shah Raja100% (2)
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument10 pagesReserve Bank of IndiasardeepanwitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 History of Banking in IndiaDocument95 pagesChapter-1 History of Banking in IndiaJaimit Shah RajaNo ratings yet
- RESERVE BANK OF INDIA Its Origin, Structure and Function - ReportDocument11 pagesRESERVE BANK OF INDIA Its Origin, Structure and Function - ReportAnirban DebNo ratings yet
- History of Reserve Bank of India An OverviewDocument7 pagesHistory of Reserve Bank of India An Overviewanusaya1988No ratings yet
- Function # 1. Monopoly of Note IssueDocument6 pagesFunction # 1. Monopoly of Note IssueprincebanswarNo ratings yet
- Banking: History of Banking in IndiaDocument4 pagesBanking: History of Banking in IndiatsfabmNo ratings yet
- Banking System in IndiaDocument8 pagesBanking System in IndiaShikha ShuklaNo ratings yet
- History of Indian Banking IndustryDocument34 pagesHistory of Indian Banking IndustryRani AngelNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Topic: 1.1.1 Definition of BankDocument12 pages1.1 Introduction To Topic: 1.1.1 Definition of BankMegha JainNo ratings yet
- Bank Ops PPT+Word Docs Unit 1-10Document39 pagesBank Ops PPT+Word Docs Unit 1-10Anand PadhyeNo ratings yet
- Project It in Bank-2Document66 pagesProject It in Bank-2Rohan SoansNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument6 pagesBanking in Indiajasim ansariNo ratings yet
- Banking StudyDocument5 pagesBanking Studymav7788No ratings yet
- Introduction of Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument9 pagesIntroduction of Reserve Bank of IndiaAbeer Mansingh MahapatraNo ratings yet
- List of Public Sector Banks in India Is As FollowsDocument24 pagesList of Public Sector Banks in India Is As Followsjoy parimalaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis HDFCDocument24 pagesFinancial Analysis HDFCbunnyNo ratings yet
- History of Banking in IndiaDocument10 pagesHistory of Banking in IndiaandalibNo ratings yet
- History of Banking in IndiaDocument10 pagesHistory of Banking in IndiaWilliam JPNo ratings yet
- History of Banking in IndiaDocument10 pagesHistory of Banking in IndiaLolaNo ratings yet
- Mrunal Lecture 5 @ PDFDocument9 pagesMrunal Lecture 5 @ PDFZabi ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Banking Law: PrimerDocument21 pagesBanking Law: PrimerAnonymous XuOGlMiNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of India - WikipediaDocument22 pagesReserve Bank of India - WikipediaVishnuNo ratings yet
- Banking NotesDocument41 pagesBanking Notesmba departmentNo ratings yet
- Union BankDocument35 pagesUnion BankNarendra MuppasaniNo ratings yet
- Report FileDocument58 pagesReport FileDinesh ChahalNo ratings yet
- Banking & Financial InstitutionsDocument20 pagesBanking & Financial Institutionsjiya.jNo ratings yet
- History: Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934Document15 pagesHistory: Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934neha shaikhNo ratings yet
- J&K BANK Final Project AadilDocument48 pagesJ&K BANK Final Project AadilzargarNo ratings yet
- Nationalized Banks in IndiaDocument3 pagesNationalized Banks in IndiaShaquib HussainNo ratings yet
- Canara Organisation Study Report.Document31 pagesCanara Organisation Study Report.Subhash MsNo ratings yet
- Structure of Indian BankingDocument12 pagesStructure of Indian BankingYatin DhallNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument6 pagesEvolution of Reserve Bank of IndiamotherfuckermonsterNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument5 pagesBanking in Indiamanjuparkavi_rkNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 BFSDocument83 pagesUnit 1 BFSsyedmoin85No ratings yet
- ICICI Project ReportDocument53 pagesICICI Project ReportPawan MeenaNo ratings yet
- History of Indian BankingDocument23 pagesHistory of Indian BankingLaxman KambleNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument16 pagesBanking in IndiaChirag GogriNo ratings yet
- Time-Value of Money - IciciDocument27 pagesTime-Value of Money - IciciJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Classification Banks NBFCsDocument16 pagesClassification Banks NBFCsbhavyaNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument32 pagesReserve Bank of Indiachakri.iiitnNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank Research PaperDocument53 pagesAxis Bank Research PaperRuchika Rai0% (1)
- Banking and Insurance Law Notes Part-2Document48 pagesBanking and Insurance Law Notes Part-2Ridam GangwarNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of India: ChrschmurthyDocument31 pagesReserve Bank of India: ChrschmurthyManoj Kumar JoshiNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument6 pagesBanking in IndiaAmandeep KambojNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship ProjectDocument62 pagesSummer Internship ProjectNagma ParmarNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934Document5 pagesReserve Bank of India Act, 1934neha shaikhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To BankingDocument61 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Bankingceweli8890No ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934Document13 pagesChapter - 1 Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934arushiNo ratings yet
- Dpb2033 Business MathematicsDocument2 pagesDpb2033 Business MathematicsMuhdHilmanNo ratings yet
- 4 Hire Purchase Material9018311258494236503Document15 pages4 Hire Purchase Material9018311258494236503Prabin stha100% (2)
- Management of Non-Performing Assets and ImplicationsDocument43 pagesManagement of Non-Performing Assets and ImplicationsManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- SME Insight 2022 Special ReportDocument15 pagesSME Insight 2022 Special ReportАлександр ВинокуровNo ratings yet
- Maths Project On Home BudgetDocument10 pagesMaths Project On Home BudgetKatyayni KohliNo ratings yet
- What Is A Bank Identification Number (BIN), and HDocument1 pageWhat Is A Bank Identification Number (BIN), and HYogeshwaran.sNo ratings yet
- 07 Activity 1 (24) .DocsDocument2 pages07 Activity 1 (24) .DocsNICOOR YOWWNo ratings yet
- Smart InvestmentDocument8 pagesSmart InvestmentShrikant JeeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For 2nd Eval Auditing Theory Answer KeyDocument11 pagesReviewer For 2nd Eval Auditing Theory Answer KeyadssdasdsadNo ratings yet
- Answers From InterviewsDocument188 pagesAnswers From InterviewsΆγγελος ΖορμπάςNo ratings yet
- Edp Module 3Document55 pagesEdp Module 3Seena AnishNo ratings yet
- PakistanDocument120 pagesPakistanAli RazaNo ratings yet
- 0 EE IM Tutorial VDocument2 pages0 EE IM Tutorial VSivanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation Plan - Steel Corporation of The Philippines V Mapfre InsuranceDocument2 pagesRehabilitation Plan - Steel Corporation of The Philippines V Mapfre InsuranceKatch Roraldo100% (1)
- Proforma InvoiceDocument1 pageProforma Invoicecharananwar100% (1)
- Mirroring A Different Image - Policy Options From The Norwegian Government Pension Fund Global Relevant To Philippine House Bill 6608 or The Maharlika Investment Fund ActDocument55 pagesMirroring A Different Image - Policy Options From The Norwegian Government Pension Fund Global Relevant To Philippine House Bill 6608 or The Maharlika Investment Fund ActCarl June NaraisoNo ratings yet
- Ebook Synthetics en HQDocument53 pagesEbook Synthetics en HQBrian MwangiNo ratings yet
- Own House or Rental - DecisionDocument2 pagesOwn House or Rental - DecisionDevaraj DhanakottiNo ratings yet
- Indicadores 2023 08Document21 pagesIndicadores 2023 08Maria Fernanda TrigoNo ratings yet
- PT Asuransi Simas Jiwa (Asj) : Press Release Kredit Rating IndonesiaDocument2 pagesPT Asuransi Simas Jiwa (Asj) : Press Release Kredit Rating IndonesiaTri Nanda Christo MarthinusNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument2 pagesBudgetMitch FelsmanNo ratings yet
- New Drone Ind AS 116Document13 pagesNew Drone Ind AS 116rajNo ratings yet
- Project FinanceDocument3 pagesProject FinanceHaris AliNo ratings yet
- Venture Capital Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument24 pagesVenture Capital Advantages and DisadvantagesRLC VenturesNo ratings yet
- JAVADOVDocument1 pageJAVADOVSadiq PenahovNo ratings yet
- Bhushan Steel CaseDocument4 pagesBhushan Steel CaseSneha SolankiNo ratings yet
- Problem 14-4 (IAA)Document8 pagesProblem 14-4 (IAA)NIMOTHI LASE0% (1)
- Ocean Carriers Case StudyDocument7 pagesOcean Carriers Case Studyaida100% (1)
- Fundamentals DeptalsDocument7 pagesFundamentals DeptalsSamantha Nicole BonitoNo ratings yet
- Week 2: Solutions To Homework Problems: BKM Chapter 3Document4 pagesWeek 2: Solutions To Homework Problems: BKM Chapter 3Dean PhamNo ratings yet
How RBI Was Formed
How RBI Was Formed
Uploaded by
Vishal Deepak MusicOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How RBI Was Formed
How RBI Was Formed
Uploaded by
Vishal Deepak MusicCopyright:
Available Formats
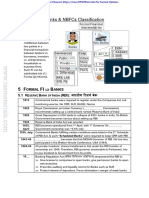
How RBI was formed
The Reserve Bank of India is India's central bank and regulatory body under the jurisdiction of
Ministry of Finance, Government of India. It is responsible for the issue and supply of the Indian
rupee and the regulation of the Indian banking system. Wikipedia
Headquarters: Mumbai
Founded: 1 April 1935, Kolkata.
The RBI was setup on the basis of the recommendation of the Hilton Young Commission.
What is Hilton Young Commission?
The Hilton Young Commission was a Commission of Inquiry appointed in 1926 to look into
the possible closer union of the British territories in East and Central Africa
Prior to the establishment of RBI the function of the central bank done by the
Imperial Bank of India.
Imperial Bank of India made by merging 3 presidencies bank of colonial India which was
BANK OF BANK OF BANK OF
MADRAS BOMBAY BENGAL
IMPERIAL
BANK OF
Until 1935 the Imperial Bank of India performed a number of function which are normally
carried out by a central banks.
RBI commenced its operation as Commercial Bank. ( means it had majority of shares
belonging to private shareholders). So it continued to operate as private owned till
independence.
1948 -RBI act of 1948 passed means All shares in the capital of the Bank were deemed
transferred to the Central Government on payment of a suitable compensation.
1949 – RBI was nationalized.
GOI passed Banking Regulation Act of 1949 Gave RBI the power
to regulate other banks.
(1) Prohibition of Trading
(2) Non-Banking Assets
(3) Management
(4) Minimum Capital and Reserves
(5) Capital Structure
(6) Payment of Commission, Brokerage etc.
(7) Reserve Fund/Statutory Reserve
(8) Cash Reserve
(9) Liquidity Norms
(10) Restrictions on Loans and Advances and
(11) Accounts and Audit .
1951 - Five year plan were introduced (the idea of five year plan was
adopted from Soviet union)
1955 – RBI acquired controlling interest in Imperial Bank of India.
Imperial Bank of India renamed as State Bank of India.
During 1951-1960 RBI was playing a special role in development in
agriculture sector in India.
Immediately after independence India was running low on capital.
Since it was the first five year plan, there were many projects, but
there were very less money, so Government of India need funds to
promote the economy.
For that Govt. Of India restructure and nationalize many
small and big banks and asked RBI to maintain and control the structure.
1960- Govt. Of India introduced Deposit Insurance Policy. During 1950s bank failures
were common phenomena. DIP seem as a measure to protect the depositors from the
loss of the savings by bank failures.
1967- 14 largest banks were merged and nationalized.
1969 1985
Between 1969-1985 92% of banks were nationalized.
RBI introduce intervention policies, (IR, CRR, SLR)
1962- Indo-China war
1965-Nationwide Drought, Indo-Pak War
1973- Global oil crisis.
1971- Indo-Pak War
1975- Emergency in India
All these above events substantially lowered the GDP growth.
1985 – India started facing BoP(Balance of payment)
problem.
Means India was importing more than that
exporting. And import debt was rising which went
till 1991.
The condition was bad that India had no money that could even
support 3 weeks’ worth of imports.
RBI had refuge any new credit.
Foreign exchange was all time low.
India was almost at the verge of bankruptcy
Then it is a GOLD which saved us.
So, to meet BoP crisis the option of selling of gold was
considered.
So, by selling the gold India could increase its foreign
reserves and pay for imports.
20 Metric tonnes of gold from Govt.
Of India account was airlifted then
sold to UBS.
After a few months gold was
repurchase and it was brought by
SBI and returned to Govt. Of India.
Manmohan Singh was the Finance Minister at that time.
He introduced reforms that liberalised Indian
Economy.
He converted this crisis to the opportunity.
Before 1991 the role of RBI was to regulate the
banking sector.
But after 1991 financial reform introduced.
1. The main purpose of these reform were to reduce the role of
RBI from a regulator to facilitator.
2. Basically now RBI started working towards creating roadmap
in the ‘interest of the banks’.
3. This meant the finance sector was allowed to take decision on
its own, without having consult to the RBI.
Then private sector as well as foreign banks starts
arriving India.
The banks were given to open branches without
taking appearance from RBI.
Exchange rates became a
1993 market determined.
1994 Nationalized bank were
allowed to tap the capital
1995 Banks were allowed to fix
their own interest rates.
1999
RBI came up with the idea of
the Debit card and Smart card.
NEFT was introduced (online
2005 transfer) RBI’s idea.
You might also like
- Unit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDocument109 pagesUnit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDr. S. Nellima KPRCAS-CommerceNo ratings yet
- Project Role of RBI Word Doc.3Document66 pagesProject Role of RBI Word Doc.3nilesh dhivreNo ratings yet
- Careers CloudDocument35 pagesCareers Cloudaravind lagishettiNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument21 pagesReserve Bank of IndiaUttamveer Singh GhalotNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument21 pagesReserve Bank of IndiaAcchu BajajNo ratings yet
- Of RbiDocument16 pagesOf RbiMohit VinayakNo ratings yet
- Banking NotesDocument60 pagesBanking NotesarunimaNo ratings yet
- Banking Evolution - HistoryDocument40 pagesBanking Evolution - HistoryYuvnesh Kumar R.JNo ratings yet
- New Final ReportDocument33 pagesNew Final Reportvarshinivars2223No ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument4 pagesReserve Bank of Indiakingsonstj1001No ratings yet
- Comperative Study On Performance of Public & Private Sector BanksDocument96 pagesComperative Study On Performance of Public & Private Sector BanksJaimit Shah Raja100% (2)
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument10 pagesReserve Bank of IndiasardeepanwitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 History of Banking in IndiaDocument95 pagesChapter-1 History of Banking in IndiaJaimit Shah RajaNo ratings yet
- RESERVE BANK OF INDIA Its Origin, Structure and Function - ReportDocument11 pagesRESERVE BANK OF INDIA Its Origin, Structure and Function - ReportAnirban DebNo ratings yet
- History of Reserve Bank of India An OverviewDocument7 pagesHistory of Reserve Bank of India An Overviewanusaya1988No ratings yet
- Function # 1. Monopoly of Note IssueDocument6 pagesFunction # 1. Monopoly of Note IssueprincebanswarNo ratings yet
- Banking: History of Banking in IndiaDocument4 pagesBanking: History of Banking in IndiatsfabmNo ratings yet
- Banking System in IndiaDocument8 pagesBanking System in IndiaShikha ShuklaNo ratings yet
- History of Indian Banking IndustryDocument34 pagesHistory of Indian Banking IndustryRani AngelNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Topic: 1.1.1 Definition of BankDocument12 pages1.1 Introduction To Topic: 1.1.1 Definition of BankMegha JainNo ratings yet
- Bank Ops PPT+Word Docs Unit 1-10Document39 pagesBank Ops PPT+Word Docs Unit 1-10Anand PadhyeNo ratings yet
- Project It in Bank-2Document66 pagesProject It in Bank-2Rohan SoansNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument6 pagesBanking in Indiajasim ansariNo ratings yet
- Banking StudyDocument5 pagesBanking Studymav7788No ratings yet
- Introduction of Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument9 pagesIntroduction of Reserve Bank of IndiaAbeer Mansingh MahapatraNo ratings yet
- List of Public Sector Banks in India Is As FollowsDocument24 pagesList of Public Sector Banks in India Is As Followsjoy parimalaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis HDFCDocument24 pagesFinancial Analysis HDFCbunnyNo ratings yet
- History of Banking in IndiaDocument10 pagesHistory of Banking in IndiaandalibNo ratings yet
- History of Banking in IndiaDocument10 pagesHistory of Banking in IndiaWilliam JPNo ratings yet
- History of Banking in IndiaDocument10 pagesHistory of Banking in IndiaLolaNo ratings yet
- Mrunal Lecture 5 @ PDFDocument9 pagesMrunal Lecture 5 @ PDFZabi ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Banking Law: PrimerDocument21 pagesBanking Law: PrimerAnonymous XuOGlMiNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of India - WikipediaDocument22 pagesReserve Bank of India - WikipediaVishnuNo ratings yet
- Banking NotesDocument41 pagesBanking Notesmba departmentNo ratings yet
- Union BankDocument35 pagesUnion BankNarendra MuppasaniNo ratings yet
- Report FileDocument58 pagesReport FileDinesh ChahalNo ratings yet
- Banking & Financial InstitutionsDocument20 pagesBanking & Financial Institutionsjiya.jNo ratings yet
- History: Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934Document15 pagesHistory: Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934neha shaikhNo ratings yet
- J&K BANK Final Project AadilDocument48 pagesJ&K BANK Final Project AadilzargarNo ratings yet
- Nationalized Banks in IndiaDocument3 pagesNationalized Banks in IndiaShaquib HussainNo ratings yet
- Canara Organisation Study Report.Document31 pagesCanara Organisation Study Report.Subhash MsNo ratings yet
- Structure of Indian BankingDocument12 pagesStructure of Indian BankingYatin DhallNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument6 pagesEvolution of Reserve Bank of IndiamotherfuckermonsterNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument5 pagesBanking in Indiamanjuparkavi_rkNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 BFSDocument83 pagesUnit 1 BFSsyedmoin85No ratings yet
- ICICI Project ReportDocument53 pagesICICI Project ReportPawan MeenaNo ratings yet
- History of Indian BankingDocument23 pagesHistory of Indian BankingLaxman KambleNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument16 pagesBanking in IndiaChirag GogriNo ratings yet
- Time-Value of Money - IciciDocument27 pagesTime-Value of Money - IciciJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Classification Banks NBFCsDocument16 pagesClassification Banks NBFCsbhavyaNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument32 pagesReserve Bank of Indiachakri.iiitnNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank Research PaperDocument53 pagesAxis Bank Research PaperRuchika Rai0% (1)
- Banking and Insurance Law Notes Part-2Document48 pagesBanking and Insurance Law Notes Part-2Ridam GangwarNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of India: ChrschmurthyDocument31 pagesReserve Bank of India: ChrschmurthyManoj Kumar JoshiNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument6 pagesBanking in IndiaAmandeep KambojNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship ProjectDocument62 pagesSummer Internship ProjectNagma ParmarNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934Document5 pagesReserve Bank of India Act, 1934neha shaikhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To BankingDocument61 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Bankingceweli8890No ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934Document13 pagesChapter - 1 Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934arushiNo ratings yet
- Dpb2033 Business MathematicsDocument2 pagesDpb2033 Business MathematicsMuhdHilmanNo ratings yet
- 4 Hire Purchase Material9018311258494236503Document15 pages4 Hire Purchase Material9018311258494236503Prabin stha100% (2)
- Management of Non-Performing Assets and ImplicationsDocument43 pagesManagement of Non-Performing Assets and ImplicationsManisha SinghNo ratings yet
- SME Insight 2022 Special ReportDocument15 pagesSME Insight 2022 Special ReportАлександр ВинокуровNo ratings yet
- Maths Project On Home BudgetDocument10 pagesMaths Project On Home BudgetKatyayni KohliNo ratings yet
- What Is A Bank Identification Number (BIN), and HDocument1 pageWhat Is A Bank Identification Number (BIN), and HYogeshwaran.sNo ratings yet
- 07 Activity 1 (24) .DocsDocument2 pages07 Activity 1 (24) .DocsNICOOR YOWWNo ratings yet
- Smart InvestmentDocument8 pagesSmart InvestmentShrikant JeeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For 2nd Eval Auditing Theory Answer KeyDocument11 pagesReviewer For 2nd Eval Auditing Theory Answer KeyadssdasdsadNo ratings yet
- Answers From InterviewsDocument188 pagesAnswers From InterviewsΆγγελος ΖορμπάςNo ratings yet
- Edp Module 3Document55 pagesEdp Module 3Seena AnishNo ratings yet
- PakistanDocument120 pagesPakistanAli RazaNo ratings yet
- 0 EE IM Tutorial VDocument2 pages0 EE IM Tutorial VSivanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation Plan - Steel Corporation of The Philippines V Mapfre InsuranceDocument2 pagesRehabilitation Plan - Steel Corporation of The Philippines V Mapfre InsuranceKatch Roraldo100% (1)
- Proforma InvoiceDocument1 pageProforma Invoicecharananwar100% (1)
- Mirroring A Different Image - Policy Options From The Norwegian Government Pension Fund Global Relevant To Philippine House Bill 6608 or The Maharlika Investment Fund ActDocument55 pagesMirroring A Different Image - Policy Options From The Norwegian Government Pension Fund Global Relevant To Philippine House Bill 6608 or The Maharlika Investment Fund ActCarl June NaraisoNo ratings yet
- Ebook Synthetics en HQDocument53 pagesEbook Synthetics en HQBrian MwangiNo ratings yet
- Own House or Rental - DecisionDocument2 pagesOwn House or Rental - DecisionDevaraj DhanakottiNo ratings yet
- Indicadores 2023 08Document21 pagesIndicadores 2023 08Maria Fernanda TrigoNo ratings yet
- PT Asuransi Simas Jiwa (Asj) : Press Release Kredit Rating IndonesiaDocument2 pagesPT Asuransi Simas Jiwa (Asj) : Press Release Kredit Rating IndonesiaTri Nanda Christo MarthinusNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument2 pagesBudgetMitch FelsmanNo ratings yet
- New Drone Ind AS 116Document13 pagesNew Drone Ind AS 116rajNo ratings yet
- Project FinanceDocument3 pagesProject FinanceHaris AliNo ratings yet
- Venture Capital Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument24 pagesVenture Capital Advantages and DisadvantagesRLC VenturesNo ratings yet
- JAVADOVDocument1 pageJAVADOVSadiq PenahovNo ratings yet
- Bhushan Steel CaseDocument4 pagesBhushan Steel CaseSneha SolankiNo ratings yet
- Problem 14-4 (IAA)Document8 pagesProblem 14-4 (IAA)NIMOTHI LASE0% (1)
- Ocean Carriers Case StudyDocument7 pagesOcean Carriers Case Studyaida100% (1)
- Fundamentals DeptalsDocument7 pagesFundamentals DeptalsSamantha Nicole BonitoNo ratings yet
- Week 2: Solutions To Homework Problems: BKM Chapter 3Document4 pagesWeek 2: Solutions To Homework Problems: BKM Chapter 3Dean PhamNo ratings yet