Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Negotiable Instrument
Negotiable Instrument
Uploaded by
Janna Francine BorlagdanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Negotiable Instrument
Negotiable Instrument
Uploaded by
Janna Francine BorlagdanCopyright:
Available Formats
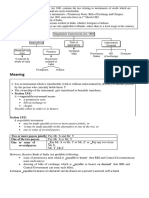
Negotiable Instrument- Written contracts for the payment of money; by its form, intended as a substitute for money and
• That kind of money that the law compels a creditor to accept payment of a debt when tendered by the debtor in the
intended to pass from hand to hand, to give the holder in due course the right to hold the same and collect the sum due. right amount
• That which a debtor may compel a creditor to accept
Requisites of negotiability:
1. It must be in writing and signed by the maker and drawer (it could be any paper or substitute for paper and is NOT LEGAL TENDER—ONLY PHILIPPINE NOTES AND COINS ISSUED BY THE BANGKO SENTRAL NG PILIPINAS ARE LEGAL
inked) TENDER.
2. It must be unconditional order/promise to pay a sum certain in money (like for example bawal ang I promise to COINS – LEGAL TENDER ONLY UP TO P20.00 for P0.10 ; and up to P50.00 for P0.25 and above
neg. instruments were
pay rea 1m if she graduated cum laude) (“hope” “authorize” do not connote command “please” “kindly” does
not affect negotiability)
3. It must be payable on demand at a fixed or determinable future time
4. Payable to order/bearer
5. BOE – where it is addressed to a drawee, he must be named therein or otherwise indicated with reasonable
certainty( governed by Arts. 439-566 of
the Code of
Factors to determine the negotiability of the instrument:
Words that appear on the face of negotiable instrument
Requirements enumerated in Section 1 of NIL
Commerce. Implied repeal
Intention of the parties by considering the whole of the instruments
Negotiation-is the process of transferring negotiable instruments from one person to another with the parameters said by
law.
An instrument is negotiated when it is transferred from one person to another in such manner as to constitute the
transferee the holder thereof. If payable to bearer, it is negotiated by delivery; if payable to order, it is negotiated by the
indorsement of the holder and completed by delivery.
only hence provisions not
Governing Law
Code of Commerce. — Negotiable instruments were governed by Arts. 439-566 of Code of Commerce. Implied repeal only
inconsistent with the NIL
LAW still in
hence provisions not consistent with the NIL law still in force such as provisions on crossed checked since there is o
provision in the NIL that deals with the crossed checks.
NEW CIVIL CODE , ACT. 386 HAS SUPPLETORY EFFECT IN CASE OF DEFICIENCY IN THE PROVISIONS OF THE NIL. – in one
case the SC applied suppletorily the provisions of Article 1216of the New Civil code which provides that “ the creditor may
proceed against any one of the solidary debtors or some or all of them simultaneously” and that “ demand made against
one of them shall not be an obstacle to those which may subsequently be directed against the others, so long as the debt
force such as provisions on
crossed check since there is no
has not been fully collected.
Functions of Negotiable Instruments
1. Substitute for money
provision in the NIL that deals
2. Medium of exchange
3. Credit instrument which increases credit circulation
4. Increase purchasing medium in circulation
5. Evidence of transaction
What is Legal Tender? with
crossed check neg. instruments were
neg. instruments were governed by Arts. 439-566 of
governed by Arts. 439-566 of the Code of
the Code of Commerce. Implied repeal
Commerce. Implied repeal only hence provisions not
only hence provisions not inconsistent with the NIL
inconsistent with the NIL LAW still in
LAW still in force such as provisions on
force such as provisions on crossed check since there is no
crossed check since there is no provision in the NIL that deals
provision in the NIL that deals with
with crossed check
crossed check Two Important features of negotiable instruments:
Negotiability — This is that quality or attribute of a bill or note whereby it may pass from hand to hand similar to money, Foreign Bill of Exchange- is a bill which is, or on its face purports to be, drawn or payable outside the Philippine Islands.
so as to give the holder in due course the right to hold the instrument and collect the sum payable for himself free from
any infirmity. a. to be drawn in the Philippines but payable outside thereof; or
b. to be payable in the Philippines but drawn outside thereof.
Accumulation of secondary contracts – instrument is negotiated from person to another person
Kinds of promissory note
Kins of Negotiable Instruments CERTIFICATE OF DEPOSIT – a form of promissory note which is a written acknowledgment of a bank or its receipt of a
Bill of Exchange- Unconditional order in writing addressed by one person to another, signed by the person giving it, certain sum with a promise to pay the same
requiring the person to whom it is addressed to pay on demand or at a fixed or determinable future time a sum certain in . • BONDS – a certificate or evidence of a debt on which the issuing company or governmental body promises to pay the
money to order or to bearer. bondholders a specified amount of interest for a specified length of time and to repay the loan on the expiration date.
• DEBENTURE – a promissory note or bond backed by the general credit of a corporation and usually not secured by a
Promissory Note- An unconditional promise in writing made by one person to another, signed by the maker, engaging to mortgage or lien on any specific property.
pay on demand, or at a fixed or determinable future time, a sum certain in money to order or to bearer.
When can a Bill of exchange be treated as promissory note?
Kins of Bill of Exchange Where the sum payable is expressed in words and also in figures and there is a discrepancy between the two, the
Draft – a common term for all bills of exchange and they are used synonymous sum denoted by the words is the sum payable; but if the words are ambiguous or uncertain, reference may be
had to the figures to fix the amount;
Trade Acceptance – a bill of exchange payable to order and at a certain maturity, drawn by a seller against the purchaser of Where the instrument provides for the payment of interest, without specifying the date from which interest is to
goods as drawee, for a fixed sum of money, showing on its face the acceptance of the purchaser of the goods and that it run, the interest runs from the date of the instrument, and if the instrument is undated, from the issue thereof;
has arisen out of a purchase by goods by the acceptor. Where the instrument is not dated, it will be considered to be dated as of the time it was issued;
Where there is a conflict between the written and printed provisions of the instrument, the written provisions
Banker’s Acceptance – a draft or a bill of exchange of which the acceptor is a bank or banker engaged generally in the prevail;
business of granting banker’s acceptance credit. It is similar to a trade acceptance, the fundamental difference being that
Where the instrument is so ambiguous that there is doubt whether it is a bill or note, the holder may treat it as
the banker’s acceptance is drawn against a bank instead of the buyer.
either at his election;
Trust Receipt – the written or printed document signed by the entrustee in favor of the entruster containing terms and Where a signature is so placed upon the instrument that it is not clear in what capacity the person making the
conditions substantially complying with the provisions of PD 115 (Trust Receipt Law, which took effect on January 21, same intended to sign, he is to be deemed an endorser;
1973). No further formality of execution or authentication shall be necessary to the validity of the trust receipt. Where an instrument containing the word "I promise to pay" is signed by two or more persons, they are deemed
to be jointly and severally liable thereon.
Treasury Warrants – a “treasury warrant” bearing on its face the words “payable from the appropriation for food
administration” is actually an order for payment out of a particular fund and is NOT UNCONDITIONAL, and does not fulfill Negotiable Promissory Note vs. Negotiable Bill of Exchange
the one of the essential requirements of a negotiable instrument. (Abubakar v. Auditor General)
Money Order – a species of draft drawn by the post-office upon another for an amount of money deposited at the first
post office by the person purchasing the money order and payable at the second office to a payee named in the order.
Clean and Documentary Bills of Exchange – “Clean bill of exchange” is one to which are not attached to documents of title
to be delivered to the person against whom the bill is drawn when he either accepts or pays the bill.
D/A and D/P Bills of Exchange - “Documents Against Payment Bill” – “D/P Bill” is a sight or time bill to which are attached
documents to be delivered and surrendered to the drawee when he has paid the corresponding bill.
“Sight bills” are bills which are payable upon presentation or at sight or on demand. 10. “Time or usance bills” – are bills
which are payable at a fixed future time or at a determinable future time.
Inland Bill of Exchange – is a bill which is or on its face purports to be BOTH drawn and payable within the Philippine
Islands.
Bill of Exchange vs. Check
You might also like
- Negotiable Instruments LawDocument41 pagesNegotiable Instruments LawMiguel Ancheta95% (19)
- Negotiable Instruments Reviewer (Agbayani Villanueva Sundiang Aquino)Document88 pagesNegotiable Instruments Reviewer (Agbayani Villanueva Sundiang Aquino)Lee Anne Yabut100% (3)
- Reviewer in NegoDocument7 pagesReviewer in NegoJoan BartolomeNo ratings yet
- NegoDocument2 pagesNegoYasser AureadaNo ratings yet
- RELEBUS - Negotiable Instrument (Part 1)Document10 pagesRELEBUS - Negotiable Instrument (Part 1)Abby Gail TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Nego Reviewer KweenDocument38 pagesNego Reviewer KweenRIZELLE BERNADINE MALANGENNo ratings yet
- Nego Case DoctrinesDocument4 pagesNego Case DoctrinesFlorence RoseteNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Law MT Reviewer (BCT)Document28 pagesNegotiable Instruments Law MT Reviewer (BCT)Mary BoaquiñaNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Law - Philippine Law ReviewersDocument49 pagesNegotiable Instruments Law - Philippine Law ReviewersRenalyn DarioNo ratings yet
- Rfbt3 Negoin Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesRfbt3 Negoin Lecture NotesWilmar Abriol100% (1)
- Negotiable Instruments LawDocument50 pagesNegotiable Instruments LawAbigail Faye Roxas100% (1)
- RFBT Reviewer Nego FreeDocument5 pagesRFBT Reviewer Nego FreeANNE GRACE MOSQUEDANo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Law (Act No. 2031)Document5 pagesNegotiable Instruments Law (Act No. 2031)Laila Ismael SalisaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in NegoDocument9 pagesReviewer in NegoMhayBinuyaJuanzonNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments ReviewerDocument9 pagesNegotiable Instruments ReviewerAlyssa MabalotNo ratings yet
- NI ACT NotesDocument15 pagesNI ACT NotesGarima SambarwalNo ratings yet
- Commercial Law, Professors Sundiang and Aquino) : Promissory Note Bill of ExchangeDocument10 pagesCommercial Law, Professors Sundiang and Aquino) : Promissory Note Bill of Exchangeroa yusonNo ratings yet
- Zarah Notes NegoDocument28 pagesZarah Notes NegoHarvey Leo RomanoNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Negotiable Instruments: Section 126Document17 pagesKinds of Negotiable Instruments: Section 126Seventeen 17No ratings yet
- Negotiable Inctruments LawDocument15 pagesNegotiable Inctruments LawAr Di SagamlaNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Law: ACT NO. 2031Document43 pagesNegotiable Instruments Law: ACT NO. 2031Majorie ArimadoNo ratings yet
- Atty. D Old Topics in RFBTDocument51 pagesAtty. D Old Topics in RFBTKathleen MirallesNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments ReviewerDocument67 pagesNegotiable Instruments ReviewercamilhamjaNo ratings yet
- Nego-Bar Rev Memo Aid 2019 PDFDocument15 pagesNego-Bar Rev Memo Aid 2019 PDFSofia DavidNo ratings yet
- LAw Course OutlineDocument24 pagesLAw Course OutlineJhanelle MarquezNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentsDocument7 pagesNegotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentsCyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Negotiable-Instruments NOTESDocument19 pagesNegotiable-Instruments NOTESkikoNo ratings yet
- Mercantile Reviewer UP 2016 NEGO PDFDocument48 pagesMercantile Reviewer UP 2016 NEGO PDFAnonymousNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTDocument12 pagesASSIGNMENTMindalyn FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Law Reviewer PDFDocument51 pagesNegotiable Instruments Law Reviewer PDFKarla Mae RicardeNo ratings yet
- Commercial LawDocument29 pagesCommercial LawTeofel John Alvizo PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Zarah Notes NegoDocument28 pagesZarah Notes NegoJoshua ParilNo ratings yet
- Commercial Law Review: Maria Zarah Villanueva - CastroDocument28 pagesCommercial Law Review: Maria Zarah Villanueva - CastroMia VinuyaNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentsDocument31 pagesNegotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentsMychie Lynne MayugaNo ratings yet
- Business Law ReviewerDocument30 pagesBusiness Law ReviewerBea EchiverriNo ratings yet
- Commercial Law - Negotiable Instruments LawDocument9 pagesCommercial Law - Negotiable Instruments LawMunchie MichieNo ratings yet
- Nego Reviewer!!Document7 pagesNego Reviewer!!amaliamirasol21No ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Law (Sec1-23)Document11 pagesNegotiable Instruments Law (Sec1-23)Julienne GayondatoNo ratings yet
- Negotiable InstrumentDocument23 pagesNegotiable InstrumentFerluenz SahagunNo ratings yet
- NIL WK 1 2Document123 pagesNIL WK 1 2Jeanette Formentera100% (1)
- Act 2031, 03 February 1911 Sec. 60, New Central Bank Act, R.A. 7653 Art. 1249, CCDocument57 pagesAct 2031, 03 February 1911 Sec. 60, New Central Bank Act, R.A. 7653 Art. 1249, CCrdNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Law (Nil) : (Act No. 2031, Effective June 2, 1911Document24 pagesNegotiable Instruments Law (Nil) : (Act No. 2031, Effective June 2, 1911David MesaNo ratings yet
- Law On Negotiable InstrumentsDocument7 pagesLaw On Negotiable InstrumentsHannah Loren ComendadorNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentsDocument34 pagesNegotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentslopoNo ratings yet
- RFBT - Negotiable InstrumentsDocument3 pagesRFBT - Negotiable InstrumentsMarilyn Cercado FernandezNo ratings yet
- Commercial Law - Negotiable Instruments LawDocument32 pagesCommercial Law - Negotiable Instruments LawGlenda PambagoNo ratings yet
- Nego Ins SummaryDocument31 pagesNego Ins SummaryRay John Arandia DorigNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instrument 1: Negotiability - Right of Transferee To Hold The Instrument and Collect The Sum DueDocument4 pagesNegotiable Instrument 1: Negotiability - Right of Transferee To Hold The Instrument and Collect The Sum DuetrebororNo ratings yet
- Nego Memo AidDocument49 pagesNego Memo AidGigiRuizTicarNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentsDocument41 pagesNegotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentsPrincess Aiza MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Negotional Instrument Law 2Document9 pagesNegotional Instrument Law 2Kristiana Montenegro GelingNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instrument LawDocument16 pagesNegotiable Instrument LawVel June100% (1)
- Negotin ReviewerDocument11 pagesNegotin ReviewerDanaNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentsDocument18 pagesNegotiable Instruments Non-Negotiable InstrumentsRichard DuranNo ratings yet
- Nego Slides Part 1Document184 pagesNego Slides Part 1Ryan A. SuaverdezNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsFrom EverandA Simple Guide for Drafting of Conveyances in India : Forms of Conveyances and Instruments executed in the Indian sub-continent along with Notes and TipsNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsFrom EverandIntroduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Revealed From A Top Realtor: The Fastest Way To Sell Properties Like Crazy In Real Estate - Even If You Are A Complete NewbieFrom EverandRevealed From A Top Realtor: The Fastest Way To Sell Properties Like Crazy In Real Estate - Even If You Are A Complete NewbieNo ratings yet
- Borlagdan BSBAFM3B VAWGDocument1 pageBorlagdan BSBAFM3B VAWGJanna Francine BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- CreditDocument1 pageCreditJanna Francine BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- NarrativeReport JuniorCouncilors2023Document2 pagesNarrativeReport JuniorCouncilors2023Janna Francine BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesQuestionnaireJanna Francine BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- Able of Ontents: (Batch: Pcb1) Mrunal'S Economy Pillar#3-Bop & Intl - Trade Page 347Document32 pagesAble of Ontents: (Batch: Pcb1) Mrunal'S Economy Pillar#3-Bop & Intl - Trade Page 347Ritesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Various Cases in ConflictsDocument221 pagesVarious Cases in ConflictsHollyhock MmgrzhfmNo ratings yet
- Pre - Employment Orientation Seminar: Lapera, Eula Dioneto May 02, 2022Document1 pagePre - Employment Orientation Seminar: Lapera, Eula Dioneto May 02, 2022chromatech worksNo ratings yet
- Veneration Key PtsDocument16 pagesVeneration Key PtsCHRIS ARWIEL PENALESNo ratings yet
- Sterling Johnson JR., Prosecutor Turned U.S. Judge in Brooklyn, DiesDocument1 pageSterling Johnson JR., Prosecutor Turned U.S. Judge in Brooklyn, Diesedwinbramosmac.comNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Rental Agreement 1RMXV6Document2 pagesEnterprise Rental Agreement 1RMXV6ronaldomessias7No ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument10 pagesThe French RevolutionAarav GuliaNo ratings yet
- 5 County Letter To Speaker and Pro Tem Opposing Excess ERAF Legislation 6.10.20Document2 pages5 County Letter To Speaker and Pro Tem Opposing Excess ERAF Legislation 6.10.20Joe EskenaziNo ratings yet
- U Sai Aung Tun - The Tai Ethnic MigrationDocument15 pagesU Sai Aung Tun - The Tai Ethnic MigrationDuran ThiyamNo ratings yet
- Pinellas County Sheriff's Amicus Brief in Mary's Law CaseDocument6 pagesPinellas County Sheriff's Amicus Brief in Mary's Law CaseWCTV Digital TeamNo ratings yet
- Central Government SchemesDocument5 pagesCentral Government SchemesKoruprolu SatishNo ratings yet
- UK Visas & Immigration: Personal InformationDocument11 pagesUK Visas & Immigration: Personal InformationwmxtmqfsvxNo ratings yet
- Flipkart Labels 22 Feb 2022-11-32Document4 pagesFlipkart Labels 22 Feb 2022-11-32vaibhav dhakaNo ratings yet
- Jailhouse Lawyer by Margolin PhillipDocument9 pagesJailhouse Lawyer by Margolin PhillipGoodangs idNo ratings yet
- Ethical DilemmaDocument4 pagesEthical DilemmaPrashant Rampuria33% (3)
- Three Documentary IdeasDocument5 pagesThree Documentary Ideasngoth678No ratings yet
- 1990 Bantala Rape Case - WikipediaDocument1 page1990 Bantala Rape Case - Wikipediabaponcsarkar2004No ratings yet
- Toyota Shaw DigestDocument3 pagesToyota Shaw DigestAtty. R. PerezNo ratings yet
- Radiowealth Vs PalileoDocument4 pagesRadiowealth Vs PalileoKaren Daryl BritoNo ratings yet
- Elite Theories of Pa Reto, Mosca and Michels: March 2018Document14 pagesElite Theories of Pa Reto, Mosca and Michels: March 2018Gyan kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Taxation 1 Atty. Arnel A. Dela Rosa, CPA, REB, READocument31 pagesLecture Notes Taxation 1 Atty. Arnel A. Dela Rosa, CPA, REB, REAweewoouwu100% (1)
- Dole D.o.19-93Document23 pagesDole D.o.19-93Kyrell John A OperarioNo ratings yet
- Horizon Supplier's Registration Form Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesHorizon Supplier's Registration Form Page 1 of 5aman3327No ratings yet
- PT Vloowless Kosmetik Indonesia PayslipDocument1 pagePT Vloowless Kosmetik Indonesia PayslipZyka OediNo ratings yet
- IssueDocument8 pagesIssueBùi Long Việt100% (1)
- Pt. Saka Wahana Utama: Client Information Sheet - CisDocument3 pagesPt. Saka Wahana Utama: Client Information Sheet - Cis2km presentNo ratings yet
- MOA and AOA MSDocument2 pagesMOA and AOA MSMALAVIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Employment AgreementDocument2 pagesEmployment AgreementLexico InternationalNo ratings yet
- Invoice DocumentDocument1 pageInvoice DocumentALL IN ONENo ratings yet
- Nantsune Engineering Proposal Overall Flow: Proposal Matters From Our SalesDocument1 pageNantsune Engineering Proposal Overall Flow: Proposal Matters From Our SalesgNo ratings yet