Professional Documents
Culture Documents
13 - DNA Recombination (Babas)
13 - DNA Recombination (Babas)
Uploaded by
Joy ValentinoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
13 - DNA Recombination (Babas)
13 - DNA Recombination (Babas)
Uploaded by
Joy ValentinoCopyright:
Available Formats
DNA Recombination Technology
Jeffrey Babas
Nowadays, human lives are very much dependent on three things: food, health and
environment in which we can see that it is now more common than before. With increasing
population and depleting resources we cannot assure if the food we have is enough to feed the
growing numbers. We can also notice the vast amount of waste we produced as we process
raw materials and even the impacts of environment on the agriculture sector. Some people
suffers from illness and face inevitable death early. Rapid increase in industrialization has
soared up the environmental pollution and industrial wastes are directly allowed to mix with
water, which has affected aquatic marines and, indirectly, human-beings. Therefore, these
issues urge to be addressed through modern technologies.
Although traditional techniques are used to aid these problems about health,
agriculture, environmental issues by using traditional or alternative medicines, traditional
farming and reducing and recycling waste respectively, genetic engineering use modern tools
and approaches DNA cloning and the like, in which consume less time and produce more
effective and quality products.
DNA recombination technology is playing an important role on improving human’s live
with regards on health, lifestyle and techniques as it provides vital things such as vaccines,
medicines for various diseases, modern generation of more quality and effective products such
as vegetables, fruits and meat which greatly improves our way of living.
KEY TERMS
Microinjection- is the process of transferring genetic materials into a living cell using glass
micropipettes or metal microinjection needles. Glass micropipettes can be of various sizes with
tip diameters ranging from 0.1 to 10 µm. DNA or RNA is injected directly into the cell's nucleus.
Electroporation- is a physical transfection method that uses an electrical pulse to create
temporary pores in cell membranes through which substances like nucleic acids can pass into
cells.
Vector- is used as a vehicle to carry a particular DNA segment into a host cell as part of a
cloning or recombinant DNA technique.
Plasmid- A plasmid is a small circular DNA molecule found in bacteria and some other
microscopic organisms. Plasmids are physically separate from chromosomal DNA and replicate
independently.
Genetic library- It is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism.
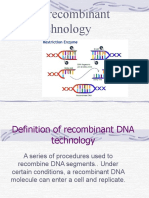
What is Recombinant DNA technology?
DNA Recombination Technology
Jeffrey Babas
It is the alteration of genetic material outside an organism to obtain enhanced and
desired characteristics in living organisms or as their products. This technology involves the
insertion of DNA fragments from a variety of sources, having a desirable gene sequence via
appropriate vector.
What is the most widely used vectors?
Today, the E. coli λ bacteriophage is one of the most widely used vectors used to carry
recombinant DNA into bacterial cells. This virus makes an excellent vector because about one-
third of its genome is considered nonessential, meaning that it can be removed and replaced by
foreign DNA.
Why is this important?
DNA Recombination technology is used on many aspects such as medicine, agriculture
and industry. This is important because It enables the creation of multiple copies of genes and
to manipulate the genes in order to achieve new or desirable trait.
How DNA recombination works?
There is a process on achieving DNA Recombination:
i. Isolation of gene of interest to be cloned
On the first step of genetic recombination, we need to first obtain our gene of
interest in order to isolate it and put it into our vector later on. We can find these genes
on a genetic Library in which It is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single
organism.
ii. Insertion of isolated gene into suitable vector (carrier)
After we isolate our gene of interest we will now proceed on getting our vector which
refers to the carrier “vehicle” of our gene of interest. After that, the vector which is
commonly from bacteria with circular structure is called plasmid, will now appear as
cleaved due to restriction enzymes in order to the gene of interest combine with the
vector. The structure now is called DNA recombinant
iii. Introduction of vector to a host (transformation)
After the unification between vector and gene is done, the DNA recombinant is
now introduced on the host cell, commonly bacteria with a process of either physical
like electroporation (using electric pulses to have a permeable cell membrane) or micro
injecting or chemical based like Calcium chloride mediated.
DNA Recombination Technology
Jeffrey Babas
iv. Identifying host with the recombinant DNA created
This process is not done to a single host only, there are multiple hosts in order to
make sure that there is a chance of having the cell they are looking for. Sometimes,
there are instances that the host is not be compatible with the introduced DNA
recombinant giving us a 3 possible result;
Non-transformed cell
This is the cell with no traces of any DNA recombinant
Transformed cell with unchanged vector
This has the vector, but not the substrate
Transformed cell with Recombinant DNA
This has the DNA recombinant and the one we are looking for;
subject for replication.
v. Multiplication of the introduced gene from the host
At this time, the cell will now replicate and the gene of interest will have two works: to
clone more genes or to use the gene in order to create protein.
DNA recombination Uses
Therapeutic products
Therapeutics products including vaccines, growth hormone, and insulin are results of
genetic engineering as there are disease–causing microorganisms can be treated using specific
protein, there is a gene that is responsible on growth, and there’s also a gene that is
responsible on producing insulin which are used for person with diabetes.
Genetically modified products
Plant genes are modified in order to yield more and produce quality products, for
instance they genetically modified a certain type of rice to have beta- carotene which our body
converts into vitamin A.
Energy production
It is used to produce clean fuel such as biohydrogen which is from photosynthetic
bacteria and non-photosynthetic bacteria from combustion of water. They are genetically
engineered to have more capacity to produce efficiently.
You might also like
- Summary & Study Guide - A Crack in Creation: Gene Editing and the Unthinkable Power to Control EvolutionFrom EverandSummary & Study Guide - A Crack in Creation: Gene Editing and the Unthinkable Power to Control EvolutionNo ratings yet
- BioInformatics Quiz1 Week6Document6 pagesBioInformatics Quiz1 Week6chahoubNo ratings yet
- Dna Recombinant Technology BiotechnologyDocument172 pagesDna Recombinant Technology BiotechnologytasniyanNo ratings yet
- What Is Recombinant DNA Technology?Document9 pagesWhat Is Recombinant DNA Technology?Usha DeviNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 NotesDocument5 pagesGenbio2 NotesalliyahmuanaNo ratings yet
- Micro BiotechDocument28 pagesMicro Biotechreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument29 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologysannsannNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TECHNOLOGYDocument29 pagesRecombinant DNA TECHNOLOGYsannsannNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TECHNOLOGYDocument29 pagesRecombinant DNA TECHNOLOGYsannsannNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology (Principles & Processes) I PDFDocument53 pagesBiotechnology (Principles & Processes) I PDFMahesh lenkaNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Lecture Notes - AP BioDocument10 pagesRecombinant DNA Lecture Notes - AP Bioshiva121294No ratings yet
- Module Biotech Week 2 QTR 3Document6 pagesModule Biotech Week 2 QTR 3Julia SanhiNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument30 pagesLECTURE 4 Recombinant DNA Technologyzari_pak2010No ratings yet
- Handout Week 1Document8 pagesHandout Week 1Vien Lovelle Macanip Cabug-osNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 1489485680Document52 pagesLecture 1 1489485680Dato TevzadzeNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology - Definition, Steps, ApplicationsDocument7 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology - Definition, Steps, ApplicationsVikas PatreyNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: 1-Bio-Based Sustainable Production of Chemicals, Energy, Fuels and MaterialsDocument20 pagesBiotechnology: 1-Bio-Based Sustainable Production of Chemicals, Energy, Fuels and MaterialsHizbullah RiazNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument3 pagesRecombinant DNABenedick CruzNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology Notes Ch11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument9 pages12 Biology Notes Ch11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- GB2 Lesson 1 and 2Document109 pagesGB2 Lesson 1 and 2mitch anne c desquitadoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document63 pagesGeneral Biology 1kenneth mendozaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and Processes NotesDocument9 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processes NotessameemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Genetics and BiotechnologyDocument43 pagesChapter 13 Genetics and BiotechnologyMUHAMMAD SAALIM100% (2)
- Genetic Engineering ProcessDocument23 pagesGenetic Engineering ProcessBLACKPINK LOVERNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Sahib Dino 28575 (Bs Physics 5th Semester)Document18 pagesBiotechnology: Sahib Dino 28575 (Bs Physics 5th Semester)shams ul haqNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument5 pagesGenetic EngineeringDe Juan, Angela Marie G.No ratings yet
- Micropara Assignment 2Document2 pagesMicropara Assignment 2Fruit FlyNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument5 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyMonika KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Notes - BiologyDocument41 pagesNotes - BiologyJamie Rose FontanillaNo ratings yet
- AppliDocument35 pagesApplipranjal09999No ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering: By: Faiza Rashid Lecturer City University of Science and Information Technology, Peshawar, PakistanDocument19 pagesGenetic Engineering: By: Faiza Rashid Lecturer City University of Science and Information Technology, Peshawar, PakistanFaiza RashidNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument19 pagesRecombinant DNAAbhash0% (1)
- BIOLOGY Chapter 7 - Aspects of Genetic EngineeringDocument7 pagesBIOLOGY Chapter 7 - Aspects of Genetic Engineeringchelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- 06-Genomics, Proteomics, and Genetic EngineeringDocument4 pages06-Genomics, Proteomics, and Genetic EngineeringBen AbellaNo ratings yet
- GENECLONINGDocument10 pagesGENECLONINGsafira permata dewiNo ratings yet
- CloningDocument14 pagesCloningvitalie rusuNo ratings yet
- Scope and Application of Genetic Engineering RS Maam HWDocument29 pagesScope and Application of Genetic Engineering RS Maam HWRani SapkotaNo ratings yet
- The Simple Addition, Deletion, or Manipulation of A Single Trait in An Organism To Create A Desired ChangeDocument23 pagesThe Simple Addition, Deletion, or Manipulation of A Single Trait in An Organism To Create A Desired ChangeBobby100% (1)
- RT-week10-Lecture10-April 6 2023Document24 pagesRT-week10-Lecture10-April 6 2023amirkhan091018No ratings yet
- Research Paper - Biotechnology q3Document3 pagesResearch Paper - Biotechnology q3Ma Lizha RafaelNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Recombinant Dna DRFTDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Recombinant Dna DRFTGaspel Joy OrgasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Bio2 Genetic EngineeringDocument42 pagesModule 1 Bio2 Genetic Engineeringjaydie domalaonNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NewDocument21 pagesBiotechnology NewANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- 1 Updated BiotechnologyModuleDocument24 pages1 Updated BiotechnologyModuleDevilNo ratings yet
- Wsedrftghdfghx FGDFGHWJK FGHXCVBDocument2 pagesWsedrftghdfghx FGDFGHWJK FGHXCVBJay PeeNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleDocument26 pagesStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleEsther SparksNo ratings yet
- GeneTransfer and Recombinant DNADocument5 pagesGeneTransfer and Recombinant DNAKIPNGETICH FREDRICKNo ratings yet
- C. Genetic Modification ObjectivesDocument9 pagesC. Genetic Modification ObjectivesFengyiNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectSubhiksha100% (1)
- General Biology 2 Q3 - SLK - W1 - Recombinant DNADocument26 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Q3 - SLK - W1 - Recombinant DNANikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- A Seminar ON Genetic Engineering and Gene Cloning BY Ayinde Samson MATRIC NUMBER: 168859049 Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Ekiti State University. JUNE, 2021Document12 pagesA Seminar ON Genetic Engineering and Gene Cloning BY Ayinde Samson MATRIC NUMBER: 168859049 Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Ekiti State University. JUNE, 2021SamsonNo ratings yet
- 1 - Recombinant DNADocument26 pages1 - Recombinant DNALiam Alexander VasquezNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering & TechniquesDocument11 pagesGenetic Engineering & TechniqueszunairyasinNo ratings yet
- Genetic TechnologyDocument36 pagesGenetic TechnologyAnggraeni Kusuma Wardani100% (1)
- Biotechnology: Presented by M QasimDocument15 pagesBiotechnology: Presented by M QasimFaiza RashidNo ratings yet
- Bai Giang Nhap Mon CNSH-bai 1-1.2024Document192 pagesBai Giang Nhap Mon CNSH-bai 1-1.2024nguyentrucquynh2t66No ratings yet
- Assignment III: Microbiology (Lecture)Document22 pagesAssignment III: Microbiology (Lecture)Alain SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Animal CloningDocument5 pagesAnimal CloningSirat ShaikhNo ratings yet
- DNA Recombinant TechnologyDocument16 pagesDNA Recombinant TechnologyIRON SQUADNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna Technology & It's ApplicationDocument20 pagesRecombinant Dna Technology & It's Applicationiamcold866No ratings yet
- rDNA TechDocument4 pagesrDNA TechTrisha SenNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Science II ExamDocument4 pagesSecond Quarter Science II ExamJoy ValentinoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter TOS Science8Document2 pages3rd Quarter TOS Science8Joy ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration ActivityDocument11 pagesElectron Configuration ActivityJoy ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Midterm CORE 10 TOSDocument1 pageMidterm CORE 10 TOSJoy ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Mutagenesis IntroDocument11 pagesMutagenesis IntrokrishnamruthatsureshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Transgenic AnimalsDocument34 pagesChapter 12 - Transgenic AnimalsDr-Paras PorwalNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Q3 - Week 4 - MutationDocument48 pagesG10 Science Q3 - Week 4 - Mutationmaclarrisse.biacoNo ratings yet
- R-DNA TechDocument2 pagesR-DNA TechgopimicroNo ratings yet
- BVA Masters 2022 VýsledkyDocument102 pagesBVA Masters 2022 VýsledkyJan PotůčekNo ratings yet
- Gene Mutation: Presentated By: - Abida Khan - Shumaila Gull - Mehwish RahmanDocument15 pagesGene Mutation: Presentated By: - Abida Khan - Shumaila Gull - Mehwish RahmanMehwish RahmanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 Dna ReplicationDocument16 pagesSheet 1 Dna Replicationsharmaekta1801No ratings yet
- List of Mutant Genes in Genus Agapornis: Mutation Wild-Type MutantDocument2 pagesList of Mutant Genes in Genus Agapornis: Mutation Wild-Type MutantKhurramNo ratings yet
- Yac Bac and Shuttle VectorsDocument53 pagesYac Bac and Shuttle VectorsBhavya ThakuriaNo ratings yet
- The FEBS Journal - 2014 - Ma - Genome Modification by CRISPR Cas9Document8 pagesThe FEBS Journal - 2014 - Ma - Genome Modification by CRISPR Cas9Alberto Luis Lizcano GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Site Directed MutagenesisDocument22 pagesSite Directed MutagenesisARUN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Tools of Recombinant Dna TechnologyDocument3 pagesTools of Recombinant Dna Technologyamora eliNo ratings yet
- Ferrières Et Al. - 2010 - Silent Mischief Bacteriophage Mu Insertions ContaDocument10 pagesFerrières Et Al. - 2010 - Silent Mischief Bacteriophage Mu Insertions ContaEtienne OssonaNo ratings yet
- Presentation PCRDocument14 pagesPresentation PCRcyrilcastillo123No ratings yet
- Genetics Laboratory Activity6Document3 pagesGenetics Laboratory Activity6Norsaidin TungkagNo ratings yet
- 4 Basic Steps of Genetic Recombination EngineeringDocument1 page4 Basic Steps of Genetic Recombination Engineeringshainemary niones100% (1)
- Mutation and Its TypesDocument21 pagesMutation and Its TypesDr.Noman AsgharNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach by SandersDocument14 pagesTest Bank For Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach by SandersAnthonyJacksonciysn100% (36)
- Transformation, Transduction, ConjugationDocument35 pagesTransformation, Transduction, ConjugationMaham ChNo ratings yet
- Transgenic AnimalsDocument4 pagesTransgenic AnimalsRiza Joy PalomarNo ratings yet
- A2 Meghoneel 21326040Document4 pagesA2 Meghoneel 21326040T. MEGHONEEL AMINNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Sabrina KilleDocument8 pagesDissertation Sabrina KilleHelpWritingCollegePapersUK100% (1)
- 2017-Nat Biotechnology-Increasing The Efficiency of Precise Genome Editing With CRISPR-Cas9 by Inhibition of Nonhomologous End JoiningDocument9 pages2017-Nat Biotechnology-Increasing The Efficiency of Precise Genome Editing With CRISPR-Cas9 by Inhibition of Nonhomologous End Joining小熊JoeNo ratings yet
- Replication ErrorsDocument16 pagesReplication Errorsilkay turanNo ratings yet
- Manuscript Introduction - Plain TextDocument2 pagesManuscript Introduction - Plain Textد. محمد قاسمNo ratings yet
- BIOL4411: Plant & Food BiotechnologyDocument68 pagesBIOL4411: Plant & Food BiotechnologyTing Yan LeeNo ratings yet
- Cosmid Vectors Mcba P7 TDocument8 pagesCosmid Vectors Mcba P7 Tsister girlfriendNo ratings yet
- ზიგოტის გაყოფა, ბლასტულაციაDocument14 pagesზიგოტის გაყოფა, ბლასტულაციაAna BeridzeNo ratings yet
- GMO InfographicDocument1 pageGMO InfographicPrimal GroudonNo ratings yet