Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Historical Foundation L4-7
Historical Foundation L4-7
Uploaded by
Jhonny Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument47 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationDomric Panunciar100% (6)
- Revlon Case Report - Big BossDocument32 pagesRevlon Case Report - Big BossMohd EizraNo ratings yet
- EDUC 60 Presentation2Document34 pagesEDUC 60 Presentation2Erica Jare Laborte0% (1)
- Foundations of EducationDocument84 pagesFoundations of Educationsawsaw85% (20)
- ASTM D 1075 Effect of Water On Strength of Compacted BitumenDocument2 pagesASTM D 1075 Effect of Water On Strength of Compacted BitumenRajesh Kumar100% (3)
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument35 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationJoy MartinezNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of Education PandanDocument40 pagesHistorical Foundations of Education Pandanpaulinmae888No ratings yet
- ED-7 (Book 1)Document23 pagesED-7 (Book 1)RialynNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument56 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationJenelyn EnjambreNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of EducationDocument4 pagesHistorical Foundations of EducationAthena Kiesha TornoNo ratings yet
- The Nature of EducationDocument67 pagesThe Nature of EducationKimmy OniotNo ratings yet
- Prof EdDocument24 pagesProf EdDhain LheeNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of Education by DRDocument5 pagesHistorical Foundations of Education by DRTotep Reyes50% (2)
- Thomas Aquinas (1255-1274) Helped Change byDocument2 pagesThomas Aquinas (1255-1274) Helped Change byLouie Jane EleccionNo ratings yet
- Oup 2. Profed5Document17 pagesOup 2. Profed5Reven RangasaNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of Education Presentation Transcript PDFDocument9 pagesHistorical Foundations of Education Presentation Transcript PDFDominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation7Document80 pagesHistorical Foundation7Eugene Jamandron100% (1)
- Presenter: Darlene D. DavidDocument27 pagesPresenter: Darlene D. DavidDarlene Dacanay DavidNo ratings yet
- LET-Historical Foundation7-ShorterDocument83 pagesLET-Historical Foundation7-ShorterMatt Bernal Jr.No ratings yet
- Teaching Profession Hand-Outs PDFDocument26 pagesTeaching Profession Hand-Outs PDFAye YayenNo ratings yet
- Profed Handout 6 (Ta)Document10 pagesProfed Handout 6 (Ta)Generose JeremiasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Historical Foundations of EducationDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Historical Foundations of EducationghileemeliaNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Education Presentation Transcript PDFDocument5 pagesHistorical Development of Education Presentation Transcript PDFDominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation On EducationDocument56 pagesHistorical Foundation On EducationAldwin Paul Parac100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 The Teacher and The CommunityDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 2 The Teacher and The CommunityGalutera, Rachel Ann B.No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PROFED3Document35 pagesChapter 2 PROFED3Mae Jeah Cloma BungarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Historical Foundations of EducationDocument16 pagesChapter 2 - Historical Foundations of EducationKym Dacudao86% (7)
- Inbound 931481636696559112Document10 pagesInbound 931481636696559112Roselle Luzano GalugaNo ratings yet
- 2 Edu 32 Unit 1 Topic 2Document15 pages2 Edu 32 Unit 1 Topic 2MaroLynn Natalia RominaNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out The Ancient Greek, SummarianDocument5 pagesHand-Out The Ancient Greek, Summarianaira justinianoNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument42 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationBENEDICT JAMES ARADANo ratings yet
- EDUC302 Chapter2Document100 pagesEDUC302 Chapter2rai moNo ratings yet
- Foundations Lecture 1Document5 pagesFoundations Lecture 1Dwain DoctanaNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument33 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationMia AstilloNo ratings yet
- History of EducationDocument3 pagesHistory of EducationecnivasuntionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Historical Foundation of EducationDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Historical Foundation of EducationSydsyd DawiliNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of Education: Unit 2Document13 pagesHistorical Foundation of Education: Unit 2Marilyn BersolaNo ratings yet
- History of Premitive-Phil. Educational SystemDocument6 pagesHistory of Premitive-Phil. Educational SystemEBUENGA, Raymarc Brian R.No ratings yet
- Module II: Historical Foundation of Education: Unit I: Educational FoundationDocument9 pagesModule II: Historical Foundation of Education: Unit I: Educational FoundationSc JuanicoNo ratings yet
- REPORTccDocument39 pagesREPORTccVKTNNo ratings yet
- Preof Ed 4 (Prelim Reviewer)Document10 pagesPreof Ed 4 (Prelim Reviewer)arabelarazal0605No ratings yet
- History of Education Topic 2 and 4Document33 pagesHistory of Education Topic 2 and 4Mejah GeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument38 pagesHistorical Foundation of Educationfernandez ararNo ratings yet
- Formal Education in The Middle AgesDocument64 pagesFormal Education in The Middle AgesAnjenethAldaveNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Dimensions of Education TaDocument14 pagesPhilosophical Dimensions of Education Taelza.apostolNo ratings yet
- Samuel Guillero WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesSamuel Guillero WPS OfficeKen Lloyd PiedadNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of Education TimelineDocument1 pageHistorical Foundation of Education TimelineRonald Sol Salen JordasNo ratings yet
- Preof Ed 4 (Prelim Reviewer)Document15 pagesPreof Ed 4 (Prelim Reviewer)arabelarazal0605No ratings yet
- The Teacher and The Community... Reading MaterialDocument10 pagesThe Teacher and The Community... Reading Materialgriffinymana86No ratings yet
- 2-4 AssignDocument9 pages2-4 AssignMay Ann IgguaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Historical Foundation of EducationDocument13 pagesLesson 2 Historical Foundation of EducationWenna100% (2)
- Week 3Document7 pagesWeek 3kidowapoNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of EducationDocument64 pagesHistorical Foundations of EducationMa Zhaira Grace CastroNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - Periods in Phil EducationDocument4 pagesSession 3 - Periods in Phil EducationSumague, Princess Cristine R.No ratings yet
- Summary: Theoretical Views On EducationDocument11 pagesSummary: Theoretical Views On EducationClaire MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument55 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationDaniel Moraleda AsaulaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 2 Chapter 2Document7 pagesProf Ed 2 Chapter 2John Paul Guim GalillagaNo ratings yet
- Reformation (Ad 1500 - Ad 1600)Document13 pagesReformation (Ad 1500 - Ad 1600)Trixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 2009 Let-Prof Ed.Document83 pages2009 Let-Prof Ed.Jealyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - Periods in Phil EducationDocument4 pagesSession 3 - Periods in Phil Educationjane,laica brutasNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Education: New Directions in Theory and PracticeFrom EverandIndigenous Education: New Directions in Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- EDUC-313C AssessmentDocument2 pagesEDUC-313C AssessmentJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument14 pagesLectureJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Theories Related To The LearnerDocument7 pagesTheories Related To The LearnerJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Rizal ScienceDocument6 pagesRizal ScienceJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Science Lecture 2Document2 pagesScience Lecture 2Jhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Rizal 203 BeedDocument14 pagesRizal 203 BeedJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Celestion Guitar Loudspeakers Brochure PDFDocument20 pagesCelestion Guitar Loudspeakers Brochure PDFAndrei ZamfirNo ratings yet
- G3X GarminDocument450 pagesG3X GarmincrguanapolloNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Accounting June 2023Document9 pagesForm 3 Accounting June 2023Bonolo RamofoloNo ratings yet
- 12 Phrases That Will Defuse Any ArgumentDocument4 pages12 Phrases That Will Defuse Any ArgumentSidajayNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University: Assignment No: 1Document11 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University: Assignment No: 1Akhtar AliNo ratings yet
- Triple Bottomline - ClassDocument11 pagesTriple Bottomline - ClassM ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Dragos PetrescuDocument34 pagesDragos PetrescuClaudiu-Mihai DumitrescuNo ratings yet
- Account TitlesDocument28 pagesAccount TitlesTom FernandoNo ratings yet
- Aeroplane - Issue 582 - October 2021Document132 pagesAeroplane - Issue 582 - October 2021Tomasz Ginter100% (1)
- Research in Education HandoutsDocument4 pagesResearch in Education HandoutsJessa Quiño EscarpeNo ratings yet
- GT Writing Task 1Document41 pagesGT Writing Task 1mahmudshaownNo ratings yet
- Social and Ethical ValuesDocument55 pagesSocial and Ethical ValuesPavan Kumar MakasiNo ratings yet
- Ivylorainepenriquez: Page1of4 248brgymaahas 0 9 1 9 - 2 8 2 5 - 1 7 Lagunalosbanos 4 0 3 0Document4 pagesIvylorainepenriquez: Page1of4 248brgymaahas 0 9 1 9 - 2 8 2 5 - 1 7 Lagunalosbanos 4 0 3 0ivy loraine enriquezNo ratings yet
- Booking Report 6-11-2021Document3 pagesBooking Report 6-11-2021WCTV Digital TeamNo ratings yet
- Story 2Document2 pagesStory 2TESL3-0618 Humaira Husna Binti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Sushil - Poudel - Resume SampleDocument1 pageSushil - Poudel - Resume SampleSushil PaudelNo ratings yet
- Pe ReviewerDocument3 pagesPe Reviewerig: vrlcmNo ratings yet
- The Global Impact of COVIDDocument4 pagesThe Global Impact of COVIDmuddasirNo ratings yet
- Decoding A Term SheetDocument1 pageDecoding A Term Sheetsantosh kumar pandaNo ratings yet
- India Water Crisis and Its SolDocument2 pagesIndia Water Crisis and Its SolKanishk KatareNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 223844Document7 pagesG.R. No. 223844Faux LexieNo ratings yet
- Sample Corporate ResumeDocument2 pagesSample Corporate ResumeshairaNo ratings yet
- 14&21-Realubit v. Jaso G.R. No. 178782 September 21, 2011Document5 pages14&21-Realubit v. Jaso G.R. No. 178782 September 21, 2011Jopan SJNo ratings yet
- Ubud Tour Bali - Cheap Price Day TourDocument9 pagesUbud Tour Bali - Cheap Price Day TourTri RanggaNo ratings yet
- MUH 2512 Exam 2 Study GuideDocument14 pagesMUH 2512 Exam 2 Study GuideAlan DeVall100% (1)
- MDU Fiber WhitePaperDocument6 pagesMDU Fiber WhitePaperbuicongluyenNo ratings yet
- Adani Under Attack: Q&A With Finance Minister ON BUDGET 2023-24Document104 pagesAdani Under Attack: Q&A With Finance Minister ON BUDGET 2023-24Jorge Antonio PichardoNo ratings yet
- Condominium Act (To Read)Document2 pagesCondominium Act (To Read)John PaulNo ratings yet
Historical Foundation L4-7
Historical Foundation L4-7
Uploaded by
Jhonny Dela CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Historical Foundation L4-7
Historical Foundation L4-7
Uploaded by
Jhonny Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
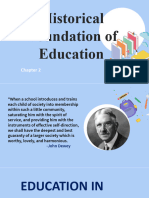
HISTORICAL FOUNDATIONS OF EDUCATION wonderful
Military education -only for the sons of the nobles
PRIMITIVE EDUCATION/PRIMITIVE SOCIETIES (7000 B.C.- Education for public administration- for those who
5000 B.C.) aspired for positions in the government because the
pharaoh needed many assistants to implement his
• Educational Goals desires.
–To teach group the survival skills--- protection from the Methods of Instruction
destructive forces of nature, both human and divine -Apprenticeship
–to cultivate group cohesiveness/ social security –Observation
•Curriculum –Imitation
–Practical skills of hunting, fishing, food gathering •Agents
–Theoretical through stories, myths, songs, poems, –Family
dances –Temples- centers of advanced learning
•Agents •Influences on Western Education
–Family/Parents –Importance of Apprenticeship
–Tribal Elders –Education on Different Disciplines
–Priests/ Leaders of Worshippers
•Influences on Western Education HINDU EDUCATION (3000 B.C.)
–Emphasis on role of informal education in transmission •Educational Goals
of skills and values –Intellectual
–Religious
SUMERIAN EDUCATION (5000 B.C.-4000 B.C.) –Cultural
“He whose eyes are not open enters it, •CURRICULUM
He whose eyes are wide open comes out of it” Religious, Vocational, Literature, Law, History, Medicine,
•Educational Goals Mathematics and Military education
–Train the learners to be good •Agents
•Curriculum –Home
–Reading, Writing, Arithmetic, Vocational, –Monasteries
Professional and Art Education, Law •Gurukula System
•Agents •Outstanding Contribution in Education
–Home –Decimal System in Arithmetical Notation
–Temples (Edduba) Teacher (Ummia)
•Methods of Instruction CHINESE EDUCATION
Imitation and copying the students just imitated copying Educational Goals
what the teacher had written. Followed by minimal –Ideological and Moral Learning
explanation –Cultural Development
Preparation of tablets dealt with their lessons –Civil Services and Military
Flogging the penalty of the pupil who failed to prepare •Curriculum
his tables –Maxims and Doctrines, Civic and Military Education
•Outstanding Contribution to Education Agents
–Cuneiform Writing –Home, Schools, Teachers of rich pupils
-Sexagesimal (base 60) is a numeral system with sixty as •Methods
its base. –Confucian Method, Memorization
•Outstanding Contribution to Education
EGYPTIAN EDUCATION (3000 B.C.-300 B.C.) –Civil Service Administration
•Educational Goals
–Cultural--To preserve their culture GREEK EDUCATION
–Utilitarianwriting and account keeping Educational Goals
•Curriculum –To cultivate civic responsibility and identity with city-
–Domestic Training state
–Religious and Vocational-Professional *In Athens
Types of Education –To develop a well rounded person
Religious education – predominant as the priests wanted -Reading, writing, arithmetic, drama, music, physical
to inculcate in the mind of the learners proper respect for education, literature, poetry
the gods, moral conduct, and a preparation for life after Agents
death Private Teachers and schools, Sophists/philosophers
Vocational-professional education also predominant Influences to Western Civilization
because they wanted perpetuate the artistic skills that •The concept of well-rounded, liberally educated person
embellished their temples and other buildings and their
–Christian Education
* in Sparta –Monasticism
-To develop soldiers and military leaders Curriculum –Scholasticism
•Drill, military songs and tactics •Christian Education
Agents –Educational Aim
•Military Teachers, Drill Sergeants •Moral regeneration of the individual
Influences to Western Civilization Content
–The concept of military state –Basic Elements of Church Doctrines, Church Rituals and
morals virtues taught by Christ
ROMAN EDUCATION •Agents
• Educational Goals –Church, Cathechumenal Schools/ CatecheticalSchools
–To develop sense of civic responsibility for republic and Monasticism
then empire –School of Monks
–To develop administrative and military skills •Aim- salvation of human souls, moral and physical
–To develop the “vir bonus”- the good citizen, the good discipline
soldier and the good worker Monasticism
• Curriculum Content
–Reading, Writing & Arithmetic, Laws of Twelve Tables, –4Rs, Trivium (Grammar, Rhetoric and Dialectic)
Law and Philosophy, Roman History –Quadrivium (Arithmetic, Geometry, Astronomy and
•Agents Music)
–Family, elementary teacher (ludi magister), grammar •Scholasticism
teacher (gramaticus), in the school of rhetorics, teachers Aim- Doctrines of the Church by rational judgment
were called the rhetors MEDIEVAL EDUCATION
Two of the most influential teachers and thinkers in Rome •SCHOLASTICISM
were Cicero and Quintilian. –Rise of Medieval Universities in Europe Guild Approach
Cicero- The Orator to Education
–He exposed the wide practical experience on the art of The Crusaders brought the Rise of Social Class
leadership Rise of Appenticeship
Quintilian-Institutes of Oratory Two Types of Guilds
–He suggested competition and awards as a basis for –Merchant guild and Craft Guild
motivation in place of corporal punishment. Influences to Western Education
• Influences on Western Civilization –Organization of the University
–Emphasis on the ability to use education for practical –Institutionalization and preservation of Knowledge
administrative skills; relating education to civic
responsibility. Renaissance Education
–Romans were the first to study foreign languages to put Aim
women in schools. –To cultivate humanist who was expert in the classics-
–Regulation of the school was under the support of the Greek and Latin
state. –To prepare courtiers for service to dynastic leaders
•Curriculum
ARABIC EDUCATION –Latin, Greek, classical Literature , poetry and art Agents
Educational Goals –Court Schools- for the nobility
–To cultivate religious commitment to Islamic beliefs –Classical secondary Schools
–To develop expertise in Mathematics, medicine and –Gymnasium
science. Influences to Western Education
Curriculum –Emphasis on literary knowledge, excellence and style
–Reading, Writing, –Two track system of schools
Mathematics, Religious Literature, Scientific studies.
•Agents REFORMATION EDUCATION
Mosques, Court Schools Educational Goal
Influences on Western Civilization –To cultivate a sense of commitment to a particular
–Arabic Numerals and Computation religious denomination
–Classical Materials on Science and Medicine Educational –To cultivate general literacy
Goals Curriculum
–4r’s, catechism, Latin and Greek Theology
Medieval Education Agents Vernacular elementary schools for the masses
–To develop religious commitments knowledge, and ritual Classical schools for the Upper class
–To reestablish social order • Influences to Western Education
–To prepare persons for appropriate roles Components –Commitment of universal literacy to the masses
–Origins of schools systems -National support for elementary education
-Compulsory education enrolled in grade 1
-Adoption of one teacher one class
HISTORY OF THE PHILIPPINE EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM HISTORY OF THE PHILIPPINE EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM
EDUCATION DURING THE PRE-COLONIAL PERIOD JAPANESE OCCUPATION
•Education was unstructured, decentralized. -Make the people understand the East Asian Co-
•Informal education Prosperity Sphere
•Children were provided vocational training but lesser -Eradication of the idea of reliance upon Western States
academics. particularly the US and Great Britain
•Tribal tutors (Babaylan or katalonan) -Fostering a new Filipino culture based on the
Education during the Spanish Era consciousness of the people as Orientals
*Education was formal and organized. -Elevating the moral of the young people giving up over-
*Authoritarian emphasis on materialism
*Parochial Schools -Diffusion of the elementary education and promotion of
*Instruction was religious centered vocation education
*Christian doctrines, sacred songs and prayers -Striving for the diffusion of the Japanese language in the
*Ilustrados were accommodated in the schools Philippines and the termination of the use of English in
The Educational Decree of1863 schools.
*This law gave the Filipinos a complete system of -Developing in people the love of labor
education from elementary to the collegiate level. Post-Colonial Philippines
*Establishment of elementary schools in all -Education aimed at the full of realization of the
municipalities. Curriculum was focused on 3 r’s, Christian democratic ideals and way of life.
doctrine, Spanish language. -The Civil Service Eligibility of teachers was made
*Attendance in school was compulsory between the ages permanent Pursuant to R.A. 1079 in June 15, 1954
of 7-12 -A daily flag ceremony was made compulsory in all
Education During the American Regime (1898-1946) schools including the singing of National Anthem pursuant
*The Americans promoted democratic ideals and the to R.A. 1265 approved on June 11, 1955.
democratic way of life. -Curricular in all schools about the life of Jose Rizal
*A system of free and compulsory education was -Elementary education was nationalized and
established by the Malolos Constitution matriculation fees were abolished.
*Training was done through the schools both public and -Magna Carta for Teachers was passed into law by virtue
secular manned by Chaplains and Military Officers of the of R.A.4670
US Army Other Developments
*Thomasites arrived in the Philippines on August 23, -Integration of values in all areas
1901. The University of the Philippines was founded in -Mandates the use of English and Filipino separately as
1908. It was the first state school of university status. media of instruction
The Department of Public Instruction Education Act of 1982- created the Ministry of Education,
–1st level (4 year primary, 3 year intermediate or seven Culture and Sports
year curriculum) NCEE- National College Entrance
–2nd level (4 year junior college) -Examination introduced Executive Order No. 117-
–3rd level (4 year degree program President Corazon Aquino
Commonwealth Period (1935-1942) -Creation of the Board for Professional Teachers
*Free education in public schools -Replacement of PBET to LET
*Vocational education -Transfer of authority in administering LET CSC and DECS
*Education also emphasized nationalism to the Board of
*Goods manners and discipline Professional Teachers under PRC
*Establishment of private education -Trifocalization of Education System
*Formal adult education was also given CHED is responsible for higher education. R.A. 7722-
• Executive Order No. 134 of 1936–Designating Tagalog Higher Education Act of 1994
as the National Language R.A. 9155- transforming DECS to DepEd
Executive Order No. 217- Quezon Code of Ethics was -Values education is offered as a separate education NESC
taught in the schools R.A. 10157- Kindergartern Act
Commonwealth Period R.A.10533- K-12 program
Executive Order No. 263- teaching of Filipino was
encourage
Education Act of 1940- reduction of 7 year elementary
course to 6 years
-Fixing school entrance at the age of 7
You might also like
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument47 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationDomric Panunciar100% (6)
- Revlon Case Report - Big BossDocument32 pagesRevlon Case Report - Big BossMohd EizraNo ratings yet
- EDUC 60 Presentation2Document34 pagesEDUC 60 Presentation2Erica Jare Laborte0% (1)
- Foundations of EducationDocument84 pagesFoundations of Educationsawsaw85% (20)
- ASTM D 1075 Effect of Water On Strength of Compacted BitumenDocument2 pagesASTM D 1075 Effect of Water On Strength of Compacted BitumenRajesh Kumar100% (3)
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument35 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationJoy MartinezNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of Education PandanDocument40 pagesHistorical Foundations of Education Pandanpaulinmae888No ratings yet
- ED-7 (Book 1)Document23 pagesED-7 (Book 1)RialynNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument56 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationJenelyn EnjambreNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of EducationDocument4 pagesHistorical Foundations of EducationAthena Kiesha TornoNo ratings yet
- The Nature of EducationDocument67 pagesThe Nature of EducationKimmy OniotNo ratings yet
- Prof EdDocument24 pagesProf EdDhain LheeNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of Education by DRDocument5 pagesHistorical Foundations of Education by DRTotep Reyes50% (2)
- Thomas Aquinas (1255-1274) Helped Change byDocument2 pagesThomas Aquinas (1255-1274) Helped Change byLouie Jane EleccionNo ratings yet
- Oup 2. Profed5Document17 pagesOup 2. Profed5Reven RangasaNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of Education Presentation Transcript PDFDocument9 pagesHistorical Foundations of Education Presentation Transcript PDFDominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation7Document80 pagesHistorical Foundation7Eugene Jamandron100% (1)
- Presenter: Darlene D. DavidDocument27 pagesPresenter: Darlene D. DavidDarlene Dacanay DavidNo ratings yet
- LET-Historical Foundation7-ShorterDocument83 pagesLET-Historical Foundation7-ShorterMatt Bernal Jr.No ratings yet
- Teaching Profession Hand-Outs PDFDocument26 pagesTeaching Profession Hand-Outs PDFAye YayenNo ratings yet
- Profed Handout 6 (Ta)Document10 pagesProfed Handout 6 (Ta)Generose JeremiasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Historical Foundations of EducationDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Historical Foundations of EducationghileemeliaNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Education Presentation Transcript PDFDocument5 pagesHistorical Development of Education Presentation Transcript PDFDominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation On EducationDocument56 pagesHistorical Foundation On EducationAldwin Paul Parac100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 The Teacher and The CommunityDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 2 The Teacher and The CommunityGalutera, Rachel Ann B.No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PROFED3Document35 pagesChapter 2 PROFED3Mae Jeah Cloma BungarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Historical Foundations of EducationDocument16 pagesChapter 2 - Historical Foundations of EducationKym Dacudao86% (7)
- Inbound 931481636696559112Document10 pagesInbound 931481636696559112Roselle Luzano GalugaNo ratings yet
- 2 Edu 32 Unit 1 Topic 2Document15 pages2 Edu 32 Unit 1 Topic 2MaroLynn Natalia RominaNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out The Ancient Greek, SummarianDocument5 pagesHand-Out The Ancient Greek, Summarianaira justinianoNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument42 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationBENEDICT JAMES ARADANo ratings yet
- EDUC302 Chapter2Document100 pagesEDUC302 Chapter2rai moNo ratings yet
- Foundations Lecture 1Document5 pagesFoundations Lecture 1Dwain DoctanaNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument33 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationMia AstilloNo ratings yet
- History of EducationDocument3 pagesHistory of EducationecnivasuntionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Historical Foundation of EducationDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Historical Foundation of EducationSydsyd DawiliNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of Education: Unit 2Document13 pagesHistorical Foundation of Education: Unit 2Marilyn BersolaNo ratings yet
- History of Premitive-Phil. Educational SystemDocument6 pagesHistory of Premitive-Phil. Educational SystemEBUENGA, Raymarc Brian R.No ratings yet
- Module II: Historical Foundation of Education: Unit I: Educational FoundationDocument9 pagesModule II: Historical Foundation of Education: Unit I: Educational FoundationSc JuanicoNo ratings yet
- REPORTccDocument39 pagesREPORTccVKTNNo ratings yet
- Preof Ed 4 (Prelim Reviewer)Document10 pagesPreof Ed 4 (Prelim Reviewer)arabelarazal0605No ratings yet
- History of Education Topic 2 and 4Document33 pagesHistory of Education Topic 2 and 4Mejah GeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument38 pagesHistorical Foundation of Educationfernandez ararNo ratings yet
- Formal Education in The Middle AgesDocument64 pagesFormal Education in The Middle AgesAnjenethAldaveNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Dimensions of Education TaDocument14 pagesPhilosophical Dimensions of Education Taelza.apostolNo ratings yet
- Samuel Guillero WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesSamuel Guillero WPS OfficeKen Lloyd PiedadNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of Education TimelineDocument1 pageHistorical Foundation of Education TimelineRonald Sol Salen JordasNo ratings yet
- Preof Ed 4 (Prelim Reviewer)Document15 pagesPreof Ed 4 (Prelim Reviewer)arabelarazal0605No ratings yet
- The Teacher and The Community... Reading MaterialDocument10 pagesThe Teacher and The Community... Reading Materialgriffinymana86No ratings yet
- 2-4 AssignDocument9 pages2-4 AssignMay Ann IgguaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Historical Foundation of EducationDocument13 pagesLesson 2 Historical Foundation of EducationWenna100% (2)
- Week 3Document7 pagesWeek 3kidowapoNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of EducationDocument64 pagesHistorical Foundations of EducationMa Zhaira Grace CastroNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - Periods in Phil EducationDocument4 pagesSession 3 - Periods in Phil EducationSumague, Princess Cristine R.No ratings yet
- Summary: Theoretical Views On EducationDocument11 pagesSummary: Theoretical Views On EducationClaire MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument55 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationDaniel Moraleda AsaulaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 2 Chapter 2Document7 pagesProf Ed 2 Chapter 2John Paul Guim GalillagaNo ratings yet
- Reformation (Ad 1500 - Ad 1600)Document13 pagesReformation (Ad 1500 - Ad 1600)Trixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 2009 Let-Prof Ed.Document83 pages2009 Let-Prof Ed.Jealyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - Periods in Phil EducationDocument4 pagesSession 3 - Periods in Phil Educationjane,laica brutasNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Education: New Directions in Theory and PracticeFrom EverandIndigenous Education: New Directions in Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- EDUC-313C AssessmentDocument2 pagesEDUC-313C AssessmentJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument14 pagesLectureJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Theories Related To The LearnerDocument7 pagesTheories Related To The LearnerJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Rizal ScienceDocument6 pagesRizal ScienceJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Science Lecture 2Document2 pagesScience Lecture 2Jhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Rizal 203 BeedDocument14 pagesRizal 203 BeedJhonny Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Celestion Guitar Loudspeakers Brochure PDFDocument20 pagesCelestion Guitar Loudspeakers Brochure PDFAndrei ZamfirNo ratings yet
- G3X GarminDocument450 pagesG3X GarmincrguanapolloNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Accounting June 2023Document9 pagesForm 3 Accounting June 2023Bonolo RamofoloNo ratings yet
- 12 Phrases That Will Defuse Any ArgumentDocument4 pages12 Phrases That Will Defuse Any ArgumentSidajayNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University: Assignment No: 1Document11 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University: Assignment No: 1Akhtar AliNo ratings yet
- Triple Bottomline - ClassDocument11 pagesTriple Bottomline - ClassM ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Dragos PetrescuDocument34 pagesDragos PetrescuClaudiu-Mihai DumitrescuNo ratings yet
- Account TitlesDocument28 pagesAccount TitlesTom FernandoNo ratings yet
- Aeroplane - Issue 582 - October 2021Document132 pagesAeroplane - Issue 582 - October 2021Tomasz Ginter100% (1)
- Research in Education HandoutsDocument4 pagesResearch in Education HandoutsJessa Quiño EscarpeNo ratings yet
- GT Writing Task 1Document41 pagesGT Writing Task 1mahmudshaownNo ratings yet
- Social and Ethical ValuesDocument55 pagesSocial and Ethical ValuesPavan Kumar MakasiNo ratings yet
- Ivylorainepenriquez: Page1of4 248brgymaahas 0 9 1 9 - 2 8 2 5 - 1 7 Lagunalosbanos 4 0 3 0Document4 pagesIvylorainepenriquez: Page1of4 248brgymaahas 0 9 1 9 - 2 8 2 5 - 1 7 Lagunalosbanos 4 0 3 0ivy loraine enriquezNo ratings yet
- Booking Report 6-11-2021Document3 pagesBooking Report 6-11-2021WCTV Digital TeamNo ratings yet
- Story 2Document2 pagesStory 2TESL3-0618 Humaira Husna Binti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Sushil - Poudel - Resume SampleDocument1 pageSushil - Poudel - Resume SampleSushil PaudelNo ratings yet
- Pe ReviewerDocument3 pagesPe Reviewerig: vrlcmNo ratings yet
- The Global Impact of COVIDDocument4 pagesThe Global Impact of COVIDmuddasirNo ratings yet
- Decoding A Term SheetDocument1 pageDecoding A Term Sheetsantosh kumar pandaNo ratings yet
- India Water Crisis and Its SolDocument2 pagesIndia Water Crisis and Its SolKanishk KatareNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 223844Document7 pagesG.R. No. 223844Faux LexieNo ratings yet
- Sample Corporate ResumeDocument2 pagesSample Corporate ResumeshairaNo ratings yet
- 14&21-Realubit v. Jaso G.R. No. 178782 September 21, 2011Document5 pages14&21-Realubit v. Jaso G.R. No. 178782 September 21, 2011Jopan SJNo ratings yet
- Ubud Tour Bali - Cheap Price Day TourDocument9 pagesUbud Tour Bali - Cheap Price Day TourTri RanggaNo ratings yet
- MUH 2512 Exam 2 Study GuideDocument14 pagesMUH 2512 Exam 2 Study GuideAlan DeVall100% (1)
- MDU Fiber WhitePaperDocument6 pagesMDU Fiber WhitePaperbuicongluyenNo ratings yet
- Adani Under Attack: Q&A With Finance Minister ON BUDGET 2023-24Document104 pagesAdani Under Attack: Q&A With Finance Minister ON BUDGET 2023-24Jorge Antonio PichardoNo ratings yet
- Condominium Act (To Read)Document2 pagesCondominium Act (To Read)John PaulNo ratings yet