Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Week 10) Epidemiology and Disease Transmission
(Week 10) Epidemiology and Disease Transmission
Uploaded by
Diana Leen Dela CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(Week 10) Epidemiology and Disease Transmission
(Week 10) Epidemiology and Disease Transmission
Uploaded by
Diana Leen Dela CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
MLSP111; WEEK 10: EPIMIOLOGY AND DISEASE TRANSMISSION
Report cases of communicable diseases to proper agencies
EPIDEMIOLOGY and DISEASE TRANSMISSION Public education
Factors that Contribute to the Spread of Disease Identification and elimination of reservoirs of infection
Virulence of pathogen Isolated disease person
Susceptibility of the population Participate in immunization program
Lack of immunization Help to treat sick person
Inadequate sanitation procedures
Mode of transmission of the pathogen
Reservoirs of Infections
any site where the pathogen can multiply or merely survive until
it is transferred to the host
- Human reservoir
- Animal reservoir
- Inanimate reservoir
HUMAN RESERVOIR
principal living reservoir of disease because many human
pathogens are specie-specific
carrier – harbors the pathogen but have no signs and symptoms
incubatory carrier – transmits the pathogen during the
incubation period
convalescent carrier – transmit pathogen during
convalescence or recovery period
active carriers – completely recovered from disease but
continue to harbor the pathogen indefinitely
passive carriers – carry the pathogen without ever having the
disease
ANIMAL RESERVOIR
zoonoses- infectious diseases that humans acquire from animal
sources
Routes:
Direct contact – with infected animal or with domestic pet waste
Inhalation – from contaminated hides, fur, feathers
Ingestion – contaminated food and water; consumption of
infected animal products
Injection of the pathogen – insect vector
Inanimate (non-living) reservoir - e.g. air, soil, food, milk, water,
and fomites
Fomites – contaminated materials
- e.g. clothing, bedding, urinals/bedpans, eating and drinking
utensils
Air – contaminated by dust, smoke, and respiratory
secretions of humans expelled into the air by breathing,
blowing, sneezing, and coughing
MODE OF TRANSMISSION
1. Contact Transmission - spread of an agent of disease by direct,
indirect or droplet transmission
Direct Contact Transmission
- person to person transmission of an agent by
- physical contact (source to susceptible host)
- no intermediate host involved i.e. touching,
- kissing, sexual intercourse
Indirect Contact Transmission
- from source to a non-living object to a susceptible host
Droplet Transmission
- Microbe spread in droplet nuclei that travels only a short
distance (<1 meter) i.e. coughing, sneezing.
- Laughing or talking
2. Vehicle Transmission - transmission of disease agent by a medium
(i.e. water, food, air, etc)
Waterborne Transmission - water contamination i.e. cholera,
Shigella
Foodborne Transmission - raw of poorly preserved or prepared
food
Airborne Transmission - spread of agents of infection by
droplet nuclei in dust that travel > 1 meter from the reservoir to
host
3. Vector Transmission - animals that carry pathogens from one host
to another
Control of Epidemic Disease
MLSP111
1
You might also like
- ICU-Acquired Infections in Immunocompromised PatientsDocument18 pagesICU-Acquired Infections in Immunocompromised Patientsdarkangelmx1No ratings yet
- Genentech Student Worksheet - ResultDocument10 pagesGenentech Student Worksheet - ResultArijit MajiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Introduction To Communicable DiseaseDocument32 pages5 - Introduction To Communicable DiseaseGetom Ngukir100% (1)
- Communicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5 PDFDocument461 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5 PDFJordz Placi100% (3)
- EpidemiologyDocument1 pageEpidemiologyevan vidanesNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease 2Document12 pagesCommunicable Disease 2Bianca CordovaNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine - Dynamic of Disease TransmissionDocument41 pagesCommunity Medicine - Dynamic of Disease Transmissionbashar0901052795No ratings yet
- 3) Communicable DiseasesDocument27 pages3) Communicable DiseasesessaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument25 pagesCommunicable DiseasesMaria Jubel Maceda Cabahug100% (1)
- IV-Infectious Diseases: Epidemiology, Reservoirs of Infection, Mode of Transmission of Infection, Specificity of Infectious AgentsDocument7 pagesIV-Infectious Diseases: Epidemiology, Reservoirs of Infection, Mode of Transmission of Infection, Specificity of Infectious Agentsjabea lyongaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Process: "All Contagious Diseases Are Communicable But Not All Communicable Diseases Are Contagious"Document8 pagesInfectious Process: "All Contagious Diseases Are Communicable But Not All Communicable Diseases Are Contagious"Micah TuringanNo ratings yet
- LONG Communicable Disease NursingDocument33 pagesLONG Communicable Disease NursingSK PatacboNo ratings yet
- The Patient From Becoming Re-Infected and The Infection From Spreading To Other PersonsDocument13 pagesThe Patient From Becoming Re-Infected and The Infection From Spreading To Other PersonshahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Yobe State College OF Agriculture, Gujba Public Health DepartmentDocument13 pagesYobe State College OF Agriculture, Gujba Public Health DepartmentYakubu Adamu JajereNo ratings yet
- 4 Communicable Disease NursingDocument44 pages4 Communicable Disease NursingDaryl Emmanuel ChuaNo ratings yet
- Prefinals MPDocument7 pagesPrefinals MPJireh Joy TangaraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Epidemiology of Infection Diseases PDFDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Epidemiology of Infection Diseases PDFRovaidKhanNo ratings yet
- Terminologies:: Asepsis and Infection ControlDocument7 pagesTerminologies:: Asepsis and Infection ControlDaniella TupasNo ratings yet
- Key Points: NUR 100 Week 6 Sherpath Lesson - Spread of InfectionDocument5 pagesKey Points: NUR 100 Week 6 Sherpath Lesson - Spread of Infectioncaloy2345caloyNo ratings yet
- P 3 InfectiousDocument39 pagesP 3 InfectiousHIMANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- Control of Communicable DiseaseDocument4 pagesControl of Communicable DiseaseBianca CordovaNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION (AutoRecovered)Document8 pagesMIDTERM EXAMINATION (AutoRecovered)Mae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Skills Asepsis and Infection Control Final3Document33 pagesNCM 106 Skills Asepsis and Infection Control Final3StudentnurseMjNo ratings yet
- Conceptualize Infection and ImmunityDocument5 pagesConceptualize Infection and Immunityالمثنى العمريNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases: Catapang, Shaira Mae D. Oňa, Charles Adriane BDocument64 pagesCommunicable Diseases: Catapang, Shaira Mae D. Oňa, Charles Adriane BAldinNo ratings yet
- Stages of Pathogenesis Lec 4Document2 pagesStages of Pathogenesis Lec 4markmuiruri581No ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Infectious (Communicable) DiseasesDocument27 pagesEpidemiology of Infectious (Communicable) Diseasesramadhani mangapiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Communicable Disease ControlDocument26 pagesLecture 7 - Communicable Disease ControlBianca AnguloNo ratings yet
- Bacteria and Disease Part 1Document19 pagesBacteria and Disease Part 1Gaspar SantosNo ratings yet
- CD NursingDocument43 pagesCD NursingCharlayne AnneNo ratings yet
- Vector and Zoonoses Control 2019. Health Care LectureDocument60 pagesVector and Zoonoses Control 2019. Health Care LectureGwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tropical MedicineDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Tropical MedicineisaacturyabikirizaNo ratings yet
- Epidimiology Lect 3Document12 pagesEpidimiology Lect 3abumaweriNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument19 pagesCommunicable DiseaseRwapembe StephenNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease 2Document82 pagesCommunicable Disease 2pauline mangadaNo ratings yet
- Module3lec ReviewerDocument8 pagesModule3lec ReviewermikaNo ratings yet
- Infection PreventionDocument38 pagesInfection PreventionAmanda ScarletNo ratings yet
- Saint Mary's University School of Health and Natural Science Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDocument5 pagesSaint Mary's University School of Health and Natural Science Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentAubrey NideaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Preventive Pharmacy 1Document44 pagesUnit 2 Preventive Pharmacy 1tshradha2003No ratings yet
- Epicdc Handout 1Document16 pagesEpicdc Handout 1api-3858544No ratings yet
- Communicable and Non-Communicable DiseaseDocument44 pagesCommunicable and Non-Communicable DiseaseSajida Bibi NoonariNo ratings yet
- CD Respiratory 1Document8 pagesCD Respiratory 1gwen manalonNo ratings yet
- L - 2 PH SS - CDCDocument21 pagesL - 2 PH SS - CDCKhizer HumayunNo ratings yet
- 2ND SEM Spread of Infection 4RTHDocument12 pages2ND SEM Spread of Infection 4RTHbilal ahmedNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases 2Document8 pagesCommunicable Diseases 2martinaNo ratings yet
- CD2 NDDocument51 pagesCD2 NDNhelia Santos BañagaNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Epidemic ProcessDocument8 pagesThe Concept of Epidemic Processalfaz lakhaniNo ratings yet
- PMLS FinalsDocument20 pagesPMLS FinalsPhilipp LibasoraNo ratings yet
- Reservoirs of Infection From Human, Animal & Non LivingDocument15 pagesReservoirs of Infection From Human, Animal & Non LivingAdibah AdawiyahNo ratings yet
- Transmission of Food ContaminationDocument3 pagesTransmission of Food ContaminationShaista MahvishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document32 pagesChapter 13Kat KatNo ratings yet
- Sources and ReservoirDocument25 pagesSources and ReservoirNagendrappa MalipatilNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Document461 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- (Week10) Epidemiologic MethodsDocument1 page(Week10) Epidemiologic MethodsDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MLSP111 TransesDocument9 pagesMLSP111 Transesrd timolaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases EpidemiologyDocument28 pagesInfectious Diseases EpidemiologySarad Chand YadavNo ratings yet
- 15 Communicable Disease - Health Risk and PreventionDocument81 pages15 Communicable Disease - Health Risk and PreventionsyakirohNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3, Comminicable DiseaseDocument47 pagesCHAPTER 3, Comminicable Diseasetechsam605No ratings yet
- COMMUNICABLE AND NCDsDocument147 pagesCOMMUNICABLE AND NCDschristine gisembaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases EpidemiologyDocument44 pagesCommunicable Diseases EpidemiologyIrum QureshiNo ratings yet
- Zoonoses TerminologiesDocument10 pagesZoonoses TerminologiesBirhanu AyeleNo ratings yet
- (Week 11) Technical Standards & Min Req, MT EducDocument4 pages(Week 11) Technical Standards & Min Req, MT EducDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- (Week10) Epidemiologic MethodsDocument1 page(Week10) Epidemiologic MethodsDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
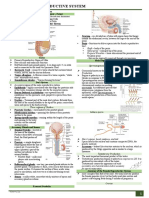
- (Week 17) Reproductive SystemDocument3 pages(Week 17) Reproductive SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
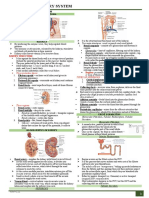
- (Week 16) Urinary SystemDocument3 pages(Week 16) Urinary SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
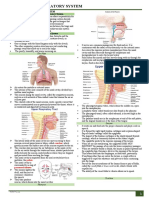
- (Week 14) Respiratory SystemDocument3 pages(Week 14) Respiratory SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
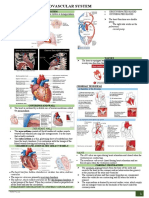
- (Week 13) Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pages(Week 13) Cardiovascular SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Stewardship in OrthopedicsDocument17 pagesAntibiotic Stewardship in Orthopedicsjomari dvNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To First AidDocument31 pages1 Intro To First AidRayban AriñoNo ratings yet
- Child AbuseDocument19 pagesChild AbuseGOUTAM DESHWALINo ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbation of AsthmaDocument28 pagesAcute Exacerbation of AsthmaMike singhNo ratings yet
- Pretend Play Printables I'm A Zoo Keeper - 123 Homeschool 4 MeDocument22 pagesPretend Play Printables I'm A Zoo Keeper - 123 Homeschool 4 Mekantor perencanaan2022No ratings yet
- Overview of Global HIVDocument27 pagesOverview of Global HIVAhmed AdemNo ratings yet
- Guia Australiana de Manejo de Pie Diabetico - 2022Document32 pagesGuia Australiana de Manejo de Pie Diabetico - 2022Martina HuamánNo ratings yet
- RoPE Score CalculatorDocument1 pageRoPE Score CalculatorEliza PopaNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics Solved OspeDocument24 pagesPaediatrics Solved OspeSalim KhaleelNo ratings yet
- The Physiologically Difficult Airway An Emerging ConceptDocument7 pagesThe Physiologically Difficult Airway An Emerging ConceptKarla HernandezNo ratings yet
- Breast Tumours: Introductory NotesDocument8 pagesBreast Tumours: Introductory Notesdiego fernando lobo moncadaNo ratings yet
- Extra-Intestinal NematodesDocument4 pagesExtra-Intestinal NematodesRichell VillacarlosNo ratings yet
- Cow Milk AllergyDocument17 pagesCow Milk AllergyVahni SamarooNo ratings yet
- Mw2 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMw2 Drug Studyc.cagas.529054No ratings yet
- Anemia and The Risk of ProgressionDocument8 pagesAnemia and The Risk of ProgressionArriza MaulanaNo ratings yet
- NUR 4717CCalendarMoUsethis (9) OutlineDocument17 pagesNUR 4717CCalendarMoUsethis (9) OutlineSomie Jr. SanchezNo ratings yet
- 1TM Cancer Pain - Introduction & Principles 2012 (Trainer's Guide)Document39 pages1TM Cancer Pain - Introduction & Principles 2012 (Trainer's Guide)khairulfatinNo ratings yet
- Interna Derangements NyangwidaDocument18 pagesInterna Derangements NyangwidaSerowe MangaidaNo ratings yet
- 7.denora Valdire - Case NoteDocument3 pages7.denora Valdire - Case NoteONT OETONLINE100% (1)
- Lymphomas and Leukemias (MedLive by DR Priyanka)Document471 pagesLymphomas and Leukemias (MedLive by DR Priyanka)Akshay RajNo ratings yet
- Capital Punishment Portfolio VersionDocument4 pagesCapital Punishment Portfolio Versionapi-286225082No ratings yet
- Qafe Green Coffee-Power Point Presentation-FinalDocument11 pagesQafe Green Coffee-Power Point Presentation-FinalPrem MathewNo ratings yet
- AnaplasmaDocument22 pagesAnaplasmaSomesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Day 3 Starting From Fall Scenarios To D16 NOTES Samson Academy 15sep2022 PDFDocument390 pagesDay 3 Starting From Fall Scenarios To D16 NOTES Samson Academy 15sep2022 PDFkhakNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Pulmonary EmbolismDocument17 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Pulmonary EmbolismHGZ1 RESIDENTESNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument4 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseViktoria Leeahna LehNo ratings yet
- First Announcement PIN IKABDI Medan 2024Document11 pagesFirst Announcement PIN IKABDI Medan 2024pinikabdimedan2024100% (1)
- Trastuzumab Deruxtecan Versus Trastuzumab Emtansine For Breast CancerDocument12 pagesTrastuzumab Deruxtecan Versus Trastuzumab Emtansine For Breast CancergabrielaNo ratings yet