Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GED0001 Activity
GED0001 Activity
Uploaded by
Waffle Jr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesOriginal Title
GED0001_Activity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesGED0001 Activity
GED0001 Activity
Uploaded by
Waffle JrCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
GED 0001 ACTIVITY
Buela, Charles Bill
Magdaluyo, Jotham Rey
Riego, Patricia Anne
Saliba, Mark Ian Julius
Santos, Gerard Joshua
Source:
Kishore, N., Marqués, D., Mahmud, A., Kiang, M. V., Rodriguez, I., Fuller, A., Ebner, P.,
Sorensen, C., Racy, F., Lemery, J., Maas, L., Leaning, J., Irizarry, R. A., Balsari,
S., & Buckee, C. O. (2018). Mortality in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria. In
New England Journal of Medicine (Vol. 379, Issue 2, pp. 162–170).
Massachusetts Medical Society. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmsa1803972
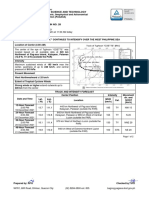
Location in the Text
Features of a
Examples from the Selection (paragraph and page
Scientific/Technical Text
number)
According to the Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention, deaths can be
directly attributed to a tropical cyclone
if they are caused by forces related to
Multiple-clause sentences the event, such as flying debris, or if Introduction, par.2
they are caused by unsafe or
unhealthy conditions resulting in injury,
illness, or loss of necessary medical
services.
The timely estimation of the death toll
after a natural disaster is critical to
defining the scale and severity of the
crisis and to targeting interventions
for recovery. The
Passive Voice disaster-relatedness of deaths has Discussion par. 4
additional importance for families
because it provides emotional
closure, qualifies them for
disaster-related aid, and promotes
resiliency.
In our survey, interruption of medical
Subject-verb interruption care was the primary cause of Discussion par. 3
sustained high mortality rates in the
months after the hurricane, a finding
consistent with the widely reported
disruption of health systems.37 Health
care disruption is now a growing
contributor to both morbidity and
mortality in natural disasters.15,38,39
In the United States, this phenomenon
has been observed in the aftermaths
of Hurricane Katrina, Superstorm
Sandy, and more recently Hurricanes
Harvey and Irma, in which nursing
home residents and those dependent
on life-sustaining equipment were
disproportionately affected.40
Consent for participation was
acquired before administration of the
survey. This study was granted a
Nominalization
human subjects research exemption Methods, par.3
(45CFR46) by the institutional review
board of the Harvard T.H. Chan School
of Public Health.
Significant population displacement
was found in the survey, which the
respondents attributed to Hurricane
Maria (Figure 2). There were reports
of 268 people (2.8% of the studied
population) leaving their homes as a
result of the hurricane. The median
age of individuals who left the home
and did not return, or who went
missing, was 25, whereas the median
age of those who remained or passed
Visual Content Results, par. 2
away at the home was 50. The
majority (52%) of persons who
evacuated due of the hurricane moved
somewhere in Puerto Rico, although
many (41%) went to various locations
on the US mainland. The hurricane is
said to have caused a total of 521
people (5.5% of the sampled
population) to move into the surveyed
households. the proportion of
households unable to other issue.
You might also like
- Public Health Nursing and The Disaster Management CycleDocument25 pagesPublic Health Nursing and The Disaster Management CycleLeadisti ArianiNo ratings yet
- Disaster Nursing - SeminarDocument41 pagesDisaster Nursing - SeminarVjesh V Mohan100% (12)
- Science 8 Summative Test Mod 2 Unit 2Document2 pagesScience 8 Summative Test Mod 2 Unit 2Jboy Mnl85% (75)
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesJoyce Anne GarduqueNo ratings yet
- Natural Disaster Scavenger HuntDocument4 pagesNatural Disaster Scavenger Huntapi-279520270No ratings yet
- Yoa70049 1427 1434Document8 pagesYoa70049 1427 1434a.iranpour1378No ratings yet
- Jacob 2008 People During EmergencyDocument13 pagesJacob 2008 People During EmergencyPilar AufrastoNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Hurricane-Related Stressors and Mental Illness After Hurricane KatrinaDocument8 pagesExposure To Hurricane-Related Stressors and Mental Illness After Hurricane KatrinaIcha YulianiNo ratings yet
- Vaishali, Zoonoses Post Disaster (Bagus)Document6 pagesVaishali, Zoonoses Post Disaster (Bagus)JeumpaNo ratings yet
- DRM Fact Sheet Mass Casualty ManagementDocument2 pagesDRM Fact Sheet Mass Casualty ManagementRahat KhanNo ratings yet
- El NiñoDocument2 pagesEl Niñojdpq47qx8tNo ratings yet
- Dampak Bencana PD LansiaDocument8 pagesDampak Bencana PD Lansiaistianna nurhidayatiNo ratings yet
- Listening To and Learning From Older Adult Hurricane Katrina SurvivorsDocument10 pagesListening To and Learning From Older Adult Hurricane Katrina SurvivorsMaulida NurapipahNo ratings yet
- Does This Patient Have: Influenza?Document34 pagesDoes This Patient Have: Influenza?SamuelQuindeNo ratings yet
- Maniscript-20-04 PediatricDocument8 pagesManiscript-20-04 PediatricAntonella CavallaroNo ratings yet
- Mxi 004Document11 pagesMxi 004hajar daoudiNo ratings yet
- Disaster Resilience in A Hakka Community in TaiwanDocument11 pagesDisaster Resilience in A Hakka Community in TaiwansittaNo ratings yet
- Welton 2019Document8 pagesWelton 2019Mahanani Edy PutriNo ratings yet
- Q3 Lesson 3 Effect of Disasters On Ones LifeDocument2 pagesQ3 Lesson 3 Effect of Disasters On Ones LifeShanayaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Nursing SeminarDocument41 pagesDisaster Nursing Seminartanmai nooluNo ratings yet
- Psychological Sequelae of Pet Loss Following Hurricane KatrinaDocument14 pagesPsychological Sequelae of Pet Loss Following Hurricane KatrinaAmari SolisNo ratings yet
- Cyclones, Tsunamis, and Human HealthDocument10 pagesCyclones, Tsunamis, and Human HealthRUCOOLNo ratings yet
- The Imprtance of End of Life Care in Nursing Home Settings Is Not Diminished by A DisasterDocument14 pagesThe Imprtance of End of Life Care in Nursing Home Settings Is Not Diminished by A DisasterIrfan FauziNo ratings yet
- Types of DisasterDocument6 pagesTypes of DisasterShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Heat Index JournalDocument13 pagesHeat Index Journalgeneva faithNo ratings yet
- Natural Disaster - Gabisa Di HighlightDocument26 pagesNatural Disaster - Gabisa Di HighlightJeumpaNo ratings yet
- Wxad 043Document5 pagesWxad 043thinh_41No ratings yet
- Pediatric Care in Disasters 2013Document6 pagesPediatric Care in Disasters 2013Cris TobalNo ratings yet
- Q3 Disaster Readiness & Risk Reduction: DAY 1 & 2 What Is The Meaning of Disaster?Document5 pagesQ3 Disaster Readiness & Risk Reduction: DAY 1 & 2 What Is The Meaning of Disaster?Kinect Nueva EcijaNo ratings yet
- Pubs - Kovats.Wilkinson CAMBIO CLIMATICO EN ESPAÑADocument11 pagesPubs - Kovats.Wilkinson CAMBIO CLIMATICO EN ESPAÑAGregorio ChavezNo ratings yet
- Milbank Memorial Fund, Wiley The Milbank QuarterlyDocument44 pagesMilbank Memorial Fund, Wiley The Milbank Quarterlyapi-395576671No ratings yet
- Disasterand Nurses RoleDocument5 pagesDisasterand Nurses RoleSandeepa WeerawarnaNo ratings yet
- Fussell and LoweDocument8 pagesFussell and LoweSUVAM BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Disasters and Public HealthDocument7 pagesDisasters and Public HealthShelbi WatsonNo ratings yet
- Warsini+28 36Document9 pagesWarsini+28 36Amalia eka PutriNo ratings yet
- Lome-Hurtado Et Al 2021 - Impact of Natural HazardsDocument6 pagesLome-Hurtado Et Al 2021 - Impact of Natural HazardsAlejandro Lome HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument47 pagesDisaster ManagementSùjâl PätídàrNo ratings yet
- China y Covid 2Document3 pagesChina y Covid 2MariaNo ratings yet
- 1096-8644 (2000) 43 31+ 3 Aid-Ajpa2 3.0.co 2-ZDocument29 pages1096-8644 (2000) 43 31+ 3 Aid-Ajpa2 3.0.co 2-ZMaïga YoussouphNo ratings yet
- 7bioterrorism Noah 2012Document4 pages7bioterrorism Noah 2012Aaron SolatorioNo ratings yet
- Management 20 of 20 DeadDocument10 pagesManagement 20 of 20 DeadKIRTI GARGNo ratings yet
- American Journal of Emergency Medicine: Brit Long, Stephen Y. Liang, Michael GottliebDocument8 pagesAmerican Journal of Emergency Medicine: Brit Long, Stephen Y. Liang, Michael GottliebEster DuwitNo ratings yet
- BiomedicalizationDocument35 pagesBiomedicalizationDto de Epidemiologia Hosp J R VidalNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument6 pagesClimate ChangeJennifer SamsonNo ratings yet
- Nihms 69926Document18 pagesNihms 69926a.iranpour1378No ratings yet
- Revisi Literatur Cadaveres MorganDocument6 pagesRevisi Literatur Cadaveres MorganBorja Domenech RieraNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Abrahams (2001) - Disaster Management in Australia The National Emergency Management System.Document9 pagesJonathan Abrahams (2001) - Disaster Management in Australia The National Emergency Management System.Budi WidiyantoNo ratings yet
- Aviles SantaDocument23 pagesAviles Santasaad nNo ratings yet
- Supports Public Health Practice and Research With Information TechnologyDocument21 pagesSupports Public Health Practice and Research With Information TechnologymisanthropicgodsNo ratings yet
- Orengo Aguayo Implementation of InterventionDocument43 pagesOrengo Aguayo Implementation of Interventionbqncdc.tacNo ratings yet
- Epidemics After Natural Disasters PDFDocument5 pagesEpidemics After Natural Disasters PDFRafael CastilloNo ratings yet
- Disasterand Nurses RoleDocument5 pagesDisasterand Nurses RoleMilcah NuylesNo ratings yet
- CHN 4 RCDocument11 pagesCHN 4 RCMarga AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Emerging and Reemerging Infectious DiseasesDocument13 pagesEmerging and Reemerging Infectious DiseasesSayu100% (1)
- Disaster Preparedness Among Older Japanese Adults With Longterm Care Needs and Their Family CaregiversDocument8 pagesDisaster Preparedness Among Older Japanese Adults With Longterm Care Needs and Their Family Caregiversistianna nurhidayatiNo ratings yet
- Postmortem Inquiries andDocument16 pagesPostmortem Inquiries andBianca NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Nature Manuscript 2024Document9 pagesNature Manuscript 2024japu.associationNo ratings yet
- The Lancet Commissions: Executive SummaryDocument48 pagesThe Lancet Commissions: Executive SummaryMónica GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Douglas11 3finalDocument9 pagesDouglas11 3finalFrench Sarah NeraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Disaster and Its EffectsDocument18 pagesLesson 3 - Disaster and Its Effectsjhondee lagramaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5. CHAp. 1 Disaster NursingDocument67 pagesTopic 5. CHAp. 1 Disaster Nursingwinner lovemeloveme100% (1)
- Bioterrorism: Implications For The Clinical Microbiologist: Linical Icrobiology EviewsDocument18 pagesBioterrorism: Implications For The Clinical Microbiologist: Linical Icrobiology EviewsMajedalNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 PDFDocument2 pagesActivity 1 PDFWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- The Era of Fake Video Begins PDFDocument5 pagesThe Era of Fake Video Begins PDFWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- WW#1Document4 pagesWW#1Waffle JrNo ratings yet
- (M1S1-POWERPOINT) Historical Antecedents of S&T in The World PDFDocument55 pages(M1S1-POWERPOINT) Historical Antecedents of S&T in The World PDFWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- (M3-GUIDE) Reading The TextDocument6 pages(M3-GUIDE) Reading The TextWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- M1S1 Meaning and Relevance of History PDFDocument28 pagesM1S1 Meaning and Relevance of History PDFWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- What Would You Ask...Document1 pageWhat Would You Ask...Waffle JrNo ratings yet
- Performance #1 Basic Movement PatternsDocument4 pagesPerformance #1 Basic Movement PatternsWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- (M2S2-POWERPOINT) Meso-American, Asian, Middle Eastern, and AfricanDocument53 pages(M2S2-POWERPOINT) Meso-American, Asian, Middle Eastern, and AfricanWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- MTPPT3 - Science and Technology For Nation-BuildingDocument17 pagesMTPPT3 - Science and Technology For Nation-BuildingWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- M2S3 Declaration of Philippine IndependenceDocument6 pagesM2S3 Declaration of Philippine IndependenceWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- (M4-MAIN) Post-Reading The TextDocument77 pages(M4-MAIN) Post-Reading The TextWaffle JrNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 January 6Document2 pagesActivity 1 January 6Waffle JrNo ratings yet
- Performance #1Document5 pagesPerformance #1Waffle JrNo ratings yet
- Individual Activity 1Document5 pagesIndividual Activity 1Waffle JrNo ratings yet
- Revised Radar Form 1 2 TemplateDocument2 pagesRevised Radar Form 1 2 TemplateCorrine RosaNo ratings yet
- Flood in ThoothukudiDocument3 pagesFlood in Thoothukudichandru0% (1)
- Comparing ResourcesDocument4 pagesComparing Resourcesapi-335617097No ratings yet
- PAGASA 24-Hour Public Weather Forecast and Extended Weather OutlookDocument1 pagePAGASA 24-Hour Public Weather Forecast and Extended Weather OutlookCoolbuster.NetNo ratings yet
- Function Notation Real World Application Problems 2017-2018Document12 pagesFunction Notation Real World Application Problems 2017-2018api-366582437No ratings yet
- West Bengal Cyclone Amphan-Page 5.5Document4 pagesWest Bengal Cyclone Amphan-Page 5.5Rajib LoharNo ratings yet
- CSU ForecastDocument41 pagesCSU ForecastFOX8No ratings yet
- Situation Report StormDocument2 pagesSituation Report StormTaylor EllisNo ratings yet
- Tata Power-DDL Presentation Template Final UpdatedDocument25 pagesTata Power-DDL Presentation Template Final UpdatedTanuj RanaNo ratings yet
- Beaufort Wind ScaleDocument2 pagesBeaufort Wind ScaleBatak LegendsNo ratings yet
- Natural-Disasters Pre Exam 2nd Grade PDFDocument2 pagesNatural-Disasters Pre Exam 2nd Grade PDFjoshuabaezNo ratings yet
- Cyclone Prone Areas in Tamil Nadu State A Geospatial Approach IJERTV4IS020623Document4 pagesCyclone Prone Areas in Tamil Nadu State A Geospatial Approach IJERTV4IS020623Madhu SubbuNo ratings yet
- Parts of A TyphoonDocument19 pagesParts of A TyphoonAlfred NitorNo ratings yet
- SYNOPTIC CHARTS ExerciseDocument4 pagesSYNOPTIC CHARTS Exercises5132No ratings yet
- Performance Task in Science 8 - Pix OnlyDocument12 pagesPerformance Task in Science 8 - Pix OnlyCrisanto Tesado Garzon100% (1)
- Climate of PakistanDocument4 pagesClimate of Pakistanfatima JumaniNo ratings yet
- Rainfall Map For Hurricane Harvey: Axis TitleDocument7 pagesRainfall Map For Hurricane Harvey: Axis TitleHemant ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP English 3Document5 pagesDetailed LP English 3Adrienne MartinezNo ratings yet
- Cot 3 PPT Science 5Document17 pagesCot 3 PPT Science 5GOLDIE TRONGCONo ratings yet
- Sample FeatureDocument2 pagesSample FeatureManisha DeenaNo ratings yet
- Actividad 3Document3 pagesActividad 3zujeyNo ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument35 pagesHydrometeorological HazardsEmie Lou Cordero - Anfone100% (2)
- Local Weather Forecast (PM) - Northern Luzon PAGASA Regional Services Division (18 September 21, Saturday)Document5 pagesLocal Weather Forecast (PM) - Northern Luzon PAGASA Regional Services Division (18 September 21, Saturday)acelaerdenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Hydrometeorological HazardsEthanYTNo ratings yet
- Toefl TestDocument4 pagesToefl TestNoely Hernández0% (1)
- Grade 8 - Science - Q2 - Wk6 - GLAKDocument20 pagesGrade 8 - Science - Q2 - Wk6 - GLAKANGEL MANGLICMOTNo ratings yet
- Uttar Pradesh MausamDocument11 pagesUttar Pradesh MausamAmrish TrivediNo ratings yet