Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Urine Analysis PDF
Urine Analysis PDF
Uploaded by
Manjul Rajput0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views65 pagesUrinalysis is commonly used for screening and monitoring treatment of renal diseases, urinary tract infections, and metabolic disorders like diabetes. A proper urine specimen requires minimum labeling with patient information and collection timing. Urine color can indicate various underlying conditions, while normal freshly voided urine has a clear appearance. Microalbuminuria is detected through urine albumin and creatinine ratio testing and can indicate early kidney disease. Hematuria is tested through microscopic examination of urine sediment and chemical tests that detect hemoglobin through its peroxidase activity.
Original Description:
Original Title
URINE ANALYSIS.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentUrinalysis is commonly used for screening and monitoring treatment of renal diseases, urinary tract infections, and metabolic disorders like diabetes. A proper urine specimen requires minimum labeling with patient information and collection timing. Urine color can indicate various underlying conditions, while normal freshly voided urine has a clear appearance. Microalbuminuria is detected through urine albumin and creatinine ratio testing and can indicate early kidney disease. Hematuria is tested through microscopic examination of urine sediment and chemical tests that detect hemoglobin through its peroxidase activity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views65 pagesUrine Analysis PDF
Urine Analysis PDF
Uploaded by
Manjul RajputUrinalysis is commonly used for screening and monitoring treatment of renal diseases, urinary tract infections, and metabolic disorders like diabetes. A proper urine specimen requires minimum labeling with patient information and collection timing. Urine color can indicate various underlying conditions, while normal freshly voided urine has a clear appearance. Microalbuminuria is detected through urine albumin and creatinine ratio testing and can indicate early kidney disease. Hematuria is tested through microscopic examination of urine sediment and chemical tests that detect hemoglobin through its peroxidase activity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 65
URINALYSIS-INTRODUCTION
Used most frequently-Screening test
Ø Can also be utilized –monitoring response to
treatment &
To note the progression of a disease.
Ø Suspected renal diseases like
glomerulonephritis,nephrotic syndrome,pyelonephritis
and renal failure.
Ø Detection of urinary tract infection.
Ø Detection & management of metabolic disorders like
Diabetes mellitus.
Ø Differential diagnosis of jaundice.
Ø Diagnosis of pregnancy.
Ø Hematuria (with or without proteinuria) on urine
dipstick test.
Preanalytical
Assessment
• Before proceeding for examination, specimen must be evaluated
in terms of its acceptability.
1. Minimum Labeling Requirements: Patient’s full name, Date
and Time of collection,Test ordered,Name of ordering clinician /
physician.
2. Intactness: There shouldn’t be any leakage, spillage and damage
to container.
3. Timing of collection: First voided morning urine is the best for
Routine analysis.
4. Preferences: If multiple investigations are to be done from a
single specimen, bacteriologic examination should be
performed first. Hence, volume of urine should be noted
properly.
2. COLOUR RED:BLOOD
porphyria
GREEN:
MEDICATION NORMAL
BLUE-green:PSEUDOMONAS
INFECTION
BLACK:MELANURIA
Alkaptonuria
BROWN:
HAEMOGLOBIN
myoglobin
DARK GREEN: COLOURLESS:
BILIVERDIN DILUTE URINE AMBER:
ORANGE:
BILIRUBIN
PYRIDIUM
BRIGHT YELLOW:
VITAMINS
APPEARANCE
Normal freshly voided urine is clear in
appearance.
Foamy urine occurs in the presence of excess
proteins or bilirubin.
Detection of microalbuminuria
Can not be detected by routine test for
proteinuria.
Methods are :
1. Measurement of albumin-creatinine ratio in
a random urine sample.
2. Measurement of albumin in an early
morning or random urine sample.
3. Measurement of albumin in 24hr sample.
4. Test strips.
5. Exact quantitation by radioimmunoassay or
enzyme linked immunosorbent assay.
Test for detection
1-Microscopic examination of urinary sadiment
2-Chemical test:
These test detect both intracellular and extracellular hem
( intact and lysed red cell) as well as myoglobin.
Principle:
Haem proteins in hemoglobin act as peroxidase,which
reduces hydrogen peroxide to water.
This process needs a hydrogen
donor(benzidine,orthotoluidine,or guaiac).
Oxidation of hydrogen donor leads to development of
color.
Intensity of color development is proportional to
amount of hemoglobin present.
You might also like
- CPH Lab Manual NewDocument12 pagesCPH Lab Manual NewPhoebe TuyogonNo ratings yet
- Activity 12 UrineDocument52 pagesActivity 12 UrineNoraine Princess TabangcoraNo ratings yet
- Normal Daily Urine Output: 600-2000mL (With Night Urine 400mL) Average Urine Output: 1200-1500mL (1% of The Filtered Plasma Volume)Document8 pagesNormal Daily Urine Output: 600-2000mL (With Night Urine 400mL) Average Urine Output: 1200-1500mL (1% of The Filtered Plasma Volume)Chrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument7 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineChie HisuganNo ratings yet
- Heme Metabolism: - Heme Biosynthesis and Porphyrias - Heme Degradation: JaundiceDocument19 pagesHeme Metabolism: - Heme Biosynthesis and Porphyrias - Heme Degradation: JaundiceMithilesh RautNo ratings yet
- Urine ExaminationDocument8 pagesUrine ExaminationAnban SureshNo ratings yet
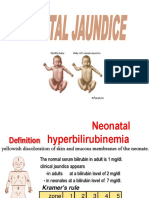
- Neo JaundiceDocument67 pagesNeo Jaundicemanisha thakur100% (1)
- UrinaryDocument3 pagesUrinaryIYA LABAO100% (1)
- Aubf - Chapter 4Document6 pagesAubf - Chapter 4Kristin SoquilloNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin Group2Document53 pagesBilirubin Group2ChiNo ratings yet
- AUBF LEC - Physical ExaminationDocument3 pagesAUBF LEC - Physical Examinationcherrycayari13No ratings yet
- Urochrome Yellow: Uroerythrin PinkDocument6 pagesUrochrome Yellow: Uroerythrin Pink3CBSMLSBRILLO Ma. Therese CabantingNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics of UrineDocument2 pagesPhysical Characteristics of UrineClair TugnaNo ratings yet
- Correlation of Urine ColorDocument1 pageCorrelation of Urine Colorzeverino castilloNo ratings yet
- Clinical Microscopy: Definition and Volume Disease and Cause PolyuriaDocument5 pagesClinical Microscopy: Definition and Volume Disease and Cause PolyuriaJovanni andesNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Bilirubin: - Biosintesis Heme Dan Porphyrias - Metabolisme Bilirubin: Ikterus: JaundiceDocument32 pagesMetabolisme Bilirubin: - Biosintesis Heme Dan Porphyrias - Metabolisme Bilirubin: Ikterus: JaundiceTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UrinalysisDocument5 pagesIntroduction To UrinalysisseanleeqtNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin: Clinical SignificanceDocument14 pagesBilirubin: Clinical SignificanceLyka PapaNo ratings yet
- Liver EnzymesDocument6 pagesLiver EnzymesWande AyodeleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Physical Examination PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Physical Examination PDFJulie Anne Soro ValdezNo ratings yet
- Physical Analysis: Analysis of Urine and Body FluidsDocument8 pagesPhysical Analysis: Analysis of Urine and Body FluidsChristin SchlittNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology SEMIS TransDocument5 pagesBacteriology SEMIS TransRachelle May DumapayNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Other Body FluidsDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Other Body FluidsBEVERLY JANE LLUVERASNo ratings yet
- BilirubinDocument6 pagesBilirubinwandebesNo ratings yet
- LFT Interpretation - 122355Document26 pagesLFT Interpretation - 122355Hitesh TanwarNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument34 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineLawrence Genelago GamboaNo ratings yet
- Identification and Examination of Dangerous DrugsDocument3 pagesIdentification and Examination of Dangerous DrugsCreedNo ratings yet
- Physiological Problems: HyperbilirubinemiaDocument21 pagesPhysiological Problems: HyperbilirubinemiaTina Ann JohnNo ratings yet
- Final Jaundice1Document43 pagesFinal Jaundice1ahmad solehinNo ratings yet
- JAUNDICE Internal Medicine PresentationDocument34 pagesJAUNDICE Internal Medicine PresentationShitanjni WatiNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice: ObjectivesDocument12 pagesNeonatal Jaundice: ObjectivesMadx VNo ratings yet
- Referat Hiperbil ZDocument26 pagesReferat Hiperbil ZAzando Rizki PutraNo ratings yet
- Urine Examination - PhysicalDocument12 pagesUrine Examination - PhysicalAbheet NagarNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestDocument50 pagesLiver Function TestJhannNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin2021 TheoryDocument8 pagesBilirubin2021 TheoryPawanNo ratings yet
- Hyper Bilirubin Emi ADocument36 pagesHyper Bilirubin Emi ASai Krishna MaddiralaNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination AubfDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination AubfHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Laboratory Correlation of Urine ColorDocument2 pagesLaboratory Correlation of Urine ColorKyle PicocNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument27 pagesJaundice: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacherryann_calinogNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin EstimationDocument18 pagesBilirubin EstimationDeepthiNo ratings yet
- Silpa Jose REVIEW 4Document26 pagesSilpa Jose REVIEW 4silpa joseNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument4 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineIceNo ratings yet
- NEONATAL - JAUNDICE - Al SabbahDocument61 pagesNEONATAL - JAUNDICE - Al SabbahGidu SaidNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Bilirubin DeterminationDocument9 pages2.6 Bilirubin Determinationiridescent brightwinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Microscopy - MTDocument200 pagesClinical Microscopy - MTJihrus Mendoza100% (1)
- 04 NNJDocument39 pages04 NNJKiramatNo ratings yet
- Examination of Body Fluids (Urinalysis)Document109 pagesExamination of Body Fluids (Urinalysis)kiedd_04100% (9)
- Iii. Medical Management A. Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDocument11 pagesIii. Medical Management A. Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresNickaela CalalangNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument58 pagesMetabolismZ ZernsNo ratings yet
- Urine Examination & Analysis: Assigned By: DR - Javeria Khan Presented By: DR - Noor-ul-Ain SarwarDocument123 pagesUrine Examination & Analysis: Assigned By: DR - Javeria Khan Presented By: DR - Noor-ul-Ain SarwarErenjaeger TitanNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: Seminar Under The Guidance Of-Dr. Shiva NarangDocument47 pagesJaundice: Seminar Under The Guidance Of-Dr. Shiva NarangMiguel MansillaNo ratings yet
- Disturbance of Pigment MetabolismDocument37 pagesDisturbance of Pigment MetabolismKaushik BhuvaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Body FluidsDocument14 pagesExamination of Body Fluidskiedd_04100% (11)
- Bilirubin: Conjugated UnconjugatedDocument2 pagesBilirubin: Conjugated UnconjugatedOrhan AsdfghjklNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lec Week#4 Physical Examination of UrineDocument19 pagesAUBF Lec Week#4 Physical Examination of UrineLexaNatalieConcepcionJuntadoNo ratings yet
- Bile Pigment Bile SaltsDocument15 pagesBile Pigment Bile SaltsGunner StonerNo ratings yet
- 4 Protein NotesDocument4 pages4 Protein NotesChitogeNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument11 pagesNeonatal JaundiceImAlien OrGodNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument13 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineJannen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Medication Safety Alerts: David UDocument3 pagesMedication Safety Alerts: David UVina RulinaNo ratings yet
- Billable Elements PDFDocument9 pagesBillable Elements PDFheidel anneNo ratings yet
- Handbag Hype Replica - Spy MC Replica Sunglasses BuyDocument1 pageHandbag Hype Replica - Spy MC Replica Sunglasses BuyHg1dHADopNo ratings yet
- DR - Ajay Wahi 2019Document3 pagesDR - Ajay Wahi 2019vidya jyotiNo ratings yet
- Antibacerials PharmacolgyDocument53 pagesAntibacerials PharmacolgyHamid AryanNo ratings yet
- Univ Que 3rd mbbs-1990-2016 PDFDocument19 pagesUniv Que 3rd mbbs-1990-2016 PDFSamyuktha NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Teen DepressionDocument8 pagesTeen Depressionsirthana697547No ratings yet
- Dear Emma Plank LaveryDocument3 pagesDear Emma Plank Laveryapi-517962430No ratings yet
- MCQ Nelson 20Document588 pagesMCQ Nelson 20della mouradNo ratings yet
- Abstract - Big Data Analytics and Evaluation For Cancer Prognosis and Diagnosis - Abdullahi Kabiru - PHD (IT)Document2 pagesAbstract - Big Data Analytics and Evaluation For Cancer Prognosis and Diagnosis - Abdullahi Kabiru - PHD (IT)abunishanNo ratings yet
- PIIS0953620519303413Document7 pagesPIIS0953620519303413romyNo ratings yet
- SIGN 155 - Pharmacological Management of Migraine: A National Clinical Guideline February 2018Document52 pagesSIGN 155 - Pharmacological Management of Migraine: A National Clinical Guideline February 2018Yahya RizkiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan of IonDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan of IonvhentesixNo ratings yet
- Rashtrasant Tukadoji Maharaj Nagpur University: B. Sc. (Home-Science) Semester-Vi Examination of Summer, 2020Document1 pageRashtrasant Tukadoji Maharaj Nagpur University: B. Sc. (Home-Science) Semester-Vi Examination of Summer, 2020Akash RautNo ratings yet
- Health Strategy: PTI's Health VisionDocument67 pagesHealth Strategy: PTI's Health VisionPTI Official100% (14)
- CV April 1Document2 pagesCV April 1api-281813422No ratings yet
- Navigating Powerchart For Ed Ob orDocument2 pagesNavigating Powerchart For Ed Ob orapi-224958119No ratings yet
- Types of Medication OrdersDocument4 pagesTypes of Medication Ordersjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- List of Medical DiagnosticsDocument6 pagesList of Medical Diagnosticschris pansoyNo ratings yet
- Hashmani CV June 2020Document6 pagesHashmani CV June 2020api-519870640No ratings yet
- Project On Hospital Training: Diploma in Hemodialysis TechnicianDocument47 pagesProject On Hospital Training: Diploma in Hemodialysis TechnicianS V ENTERPRISESNo ratings yet
- Evening Clinic Doctors at Banner Ghat A Road, BangaloreDocument4 pagesEvening Clinic Doctors at Banner Ghat A Road, BangaloreSumit100% (1)
- Evaluación Clínica de La Eficacia Aguda de Un Preparado de Valeriana y Lúpulo en La Mejora Del SueñoDocument7 pagesEvaluación Clínica de La Eficacia Aguda de Un Preparado de Valeriana y Lúpulo en La Mejora Del SueñoGianny PastorNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 Care of Clients With Problems in Oxygenation Part 1Document185 pagesLec 7 Care of Clients With Problems in Oxygenation Part 1Chucky VergaraNo ratings yet
- 1 Brochure WJH Program FinalDocument16 pages1 Brochure WJH Program FinalsusyqarmonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Epilepsy in PregnancyDocument18 pagesLesson Plan On Epilepsy in PregnancyRajaNo ratings yet
- 1.15AYUSH Final DraftDocument60 pages1.15AYUSH Final Draftshubham kumarNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Notes For StudentsDocument5 pagesBlood Transfusion Notes For StudentsMegan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis Genu: Gutama Arya Pringga, DRDocument21 pagesOsteoarthritis Genu: Gutama Arya Pringga, DRvirginiaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Science and Medicine 2017 PDFDocument112 pagesJournal of Science and Medicine 2017 PDFtadruidNo ratings yet