Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edible Coating Popular Article
Edible Coating Popular Article
Uploaded by
PrakashCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Research HypothesisDocument6 pagesResearch HypothesisRati Gupta100% (1)
- Development of Edible Bioactive Coating Based On Modified Chitosan For Increasing PDFDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Edible Bioactive Coating Based On Modified Chitosan For Increasing PDFкатя калайдаNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and Methylcellulose-Based Edible Coatings On Storage Life and Quality of Horticultural Crops: ReviewDocument7 pagesEffect of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and Methylcellulose-Based Edible Coatings On Storage Life and Quality of Horticultural Crops: ReviewAsdNo ratings yet
- MS-AGS46F20 Bilal AminDocument2 pagesMS-AGS46F20 Bilal AminUsama HassanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666154323001308 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2666154323001308 MainSrinivas KasiNo ratings yet
- Int J of Food Sci Tech - 2021 - Duguma - Potential Applications and Limitations of Edible Coatings For Maintaining TomatoDocument14 pagesInt J of Food Sci Tech - 2021 - Duguma - Potential Applications and Limitations of Edible Coatings For Maintaining TomatophotosalampuragriculturalNo ratings yet
- 10.1016@B978 0 12 803581 8.11509 7Document14 pages10.1016@B978 0 12 803581 8.11509 7Nguyễn Trần Hòa HợpNo ratings yet
- Review - Effects of Edible Coating On Fresh-Cut FruitsDocument8 pagesReview - Effects of Edible Coating On Fresh-Cut FruitsdwisriretnowidowatiNo ratings yet
- Coatings: Non-Conventional Tools To Preserve and Prolong The Quality of Minimally-Processed Fruits and VegetablesDocument31 pagesCoatings: Non-Conventional Tools To Preserve and Prolong The Quality of Minimally-Processed Fruits and VegetablesMaria AspriNo ratings yet
- Hauzoukim Et Al 2020Document10 pagesHauzoukim Et Al 2020Salwa HaneefahNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in Gum Edible Coating Applications For Fruits and Vegetables Preservation - A ReviewDocument15 pagesRecent Developments in Gum Edible Coating Applications For Fruits and Vegetables Preservation - A ReviewNguyên Trân Nguyễn PhúcNo ratings yet
- Bioactive Coatings From Non-Conventional Loquat (Eriobotrya Japonica Lindl.) Seed Starch To Extend Strawberries Shelf-Life - An Antioxidant PackagingDocument13 pagesBioactive Coatings From Non-Conventional Loquat (Eriobotrya Japonica Lindl.) Seed Starch To Extend Strawberries Shelf-Life - An Antioxidant PackagingguxxtavobarbattoNo ratings yet
- PomegranateDocument10 pagesPomegranatevivek kumarNo ratings yet
- polymers-14-01341 (1)Document23 pagespolymers-14-01341 (1)Iqbal PratamaNo ratings yet
- Foods 12 03570Document18 pagesFoods 12 03570Felipe CabezasNo ratings yet
- EdibleCoatingofFruitsVegetables AReviewDocument18 pagesEdibleCoatingofFruitsVegetables AReviewmasayangadaNo ratings yet
- Foods 10 00116Document14 pagesFoods 10 00116YAYON PAMULA MUKTINo ratings yet
- FINAL 6 Good PDFDocument6 pagesFINAL 6 Good PDFTanakorn RachapilaNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S0023643817301354-Rajiv Dhital Strawberry Shelf Life 2017Document28 pages1-s2.0-S0023643817301354-Rajiv Dhital Strawberry Shelf Life 2017Andres FAGNo ratings yet
- Bio-Coatings For Preservation of Fresh Fruits andDocument34 pagesBio-Coatings For Preservation of Fresh Fruits andRedhaLavNo ratings yet
- Coatings: /Coatings-Performances and PerspectivesDocument46 pagesCoatings: /Coatings-Performances and Perspectivesfahrullah unhasNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Edible Coatings and Films, Herbal Films, Shelf Life, Food Preservation, NovelDocument30 pagesKeywords: Edible Coatings and Films, Herbal Films, Shelf Life, Food Preservation, NovelVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- The_Role_of_Packaging_Technology_in_The_Food_ProduDocument5 pagesThe_Role_of_Packaging_Technology_in_The_Food_ProduSouvia RahimahNo ratings yet
- CHITOSAN WITH Citrus Bergamia (BERGAMOT) OIL AS A PROTECTIVE COATING IN PRESERVING QUALITY AND PROLONGING SHELF LIFE OF Raphanus Sativus (RADISH)Document39 pagesCHITOSAN WITH Citrus Bergamia (BERGAMOT) OIL AS A PROTECTIVE COATING IN PRESERVING QUALITY AND PROLONGING SHELF LIFE OF Raphanus Sativus (RADISH)Shaina AustriaNo ratings yet
- Polysaccharide, Protein, Lipid-Based Coatings and Their Impact On Fruit Crops: ReviewDocument9 pagesPolysaccharide, Protein, Lipid-Based Coatings and Their Impact On Fruit Crops: ReviewHimanshu RohillaNo ratings yet
- CucumberDocument25 pagesCucumberPuja BarmanNo ratings yet
- Foods 10 02088 v3Document22 pagesFoods 10 02088 v3Bronil, John Angelo J.No ratings yet
- Application of Edible Coatings On Fruits and VegetablesDocument14 pagesApplication of Edible Coatings On Fruits and VegetablesbhagwatNo ratings yet
- Agroindustria 4Document23 pagesAgroindustria 4Camilo MartínezNo ratings yet
- Bioactive Edible Films Based On Arrowroot Starch IDocument12 pagesBioactive Edible Films Based On Arrowroot Starch ITairine PimentelNo ratings yet
- Fruits and Vegetables With A Coating That Is Edible A ReviewDocument9 pagesFruits and Vegetables With A Coating That Is Edible A ReviewKarhol MartinezNo ratings yet
- Natural Gums of Plant Origin As Edible Coatings For Food Industry ApplicationsDocument16 pagesNatural Gums of Plant Origin As Edible Coatings For Food Industry ApplicationslunosicaNo ratings yet
- IFRJDocument16 pagesIFRJpaolaNo ratings yet
- LWT - Food Science and Technology: I.M. Brasil, C. Gomes, A. Puerta-Gomez, M.E. Castell-Perez, R.G. MoreiraDocument7 pagesLWT - Food Science and Technology: I.M. Brasil, C. Gomes, A. Puerta-Gomez, M.E. Castell-Perez, R.G. MoreiraAndriati NingrumNo ratings yet
- Avance Reciente en El Recubrimiento Comestible y Su Efecto en La Calidad de Las Frutas Frescas - Recién CortadasDocument15 pagesAvance Reciente en El Recubrimiento Comestible y Su Efecto en La Calidad de Las Frutas Frescas - Recién CortadasJHON FABER FORERO BARCONo ratings yet
- New Insights in The Production of Fruit Leather: Sparsh Kashyap and Dr. Neha SharmaDocument12 pagesNew Insights in The Production of Fruit Leather: Sparsh Kashyap and Dr. Neha Sharmakb12192127No ratings yet
- FB01 Chapter1Document7 pagesFB01 Chapter1Reymundo Pantonial Tugbong JrNo ratings yet
- Edible Coating of Fruits and Vegetables: Prince Kumar Singh (16112045), Premprakash Bairwa (16112044)Document1 pageEdible Coating of Fruits and Vegetables: Prince Kumar Singh (16112045), Premprakash Bairwa (16112044)prince singhNo ratings yet
- Edible Coating and Edible Film As Food Packaging Material: A ReviewDocument10 pagesEdible Coating and Edible Film As Food Packaging Material: A Reviewcaseco4756No ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of Related LiteratureDaisyrie Joy DesabilleNo ratings yet
- Acknowledge NTDocument20 pagesAcknowledge NTRehan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Coatings FruitDocument17 pagesCoatings FruitbbhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Chitosan and Guava Leaf Extract As Preservative To Extend The Shelf-Life of FruitsDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Chitosan and Guava Leaf Extract As Preservative To Extend The Shelf-Life of FruitsclitcheNo ratings yet
- Edible Films and Coatings Classification, Preparation, PDFDocument10 pagesEdible Films and Coatings Classification, Preparation, PDFmaryamNo ratings yet
- InnotacionDocument16 pagesInnotacioncamilaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesDocument9 pagesReview of Related Literature and StudiesJay-Ar S. SungaNo ratings yet
- Edible Film Based On Candelilla Wax Improve The Shelf Life and Quality of Avocado Saucedo-Pompa 2009 FRIDocument5 pagesEdible Film Based On Candelilla Wax Improve The Shelf Life and Quality of Avocado Saucedo-Pompa 2009 FRIXochitl Ruelas ChaconNo ratings yet
- Edible Coatings To Incorparate Active IngredientsDocument10 pagesEdible Coatings To Incorparate Active Ingredientscarranclan077No ratings yet
- Nthimole Et Al. (2022)Document18 pagesNthimole Et Al. (2022)Santiago DangerNo ratings yet
- Biodegradable Films and Composite Coatings: Past, Present and FutureDocument8 pagesBiodegradable Films and Composite Coatings: Past, Present and FutureIzabele RamosNo ratings yet
- Plants 11 00351Document24 pagesPlants 11 00351Abi Irfan Habibi LubisNo ratings yet
- Shelf Life Study of Fruit BarDocument8 pagesShelf Life Study of Fruit BarAmna SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Oregel Zamudio2017Document7 pagesOregel Zamudio2017REETU PALTHANIANo ratings yet
- Foods 11 02641Document17 pagesFoods 11 02641Kajal MIshraNo ratings yet
- Value-Added Crackers Enriched With Red Onion Skin AnthocyaninsDocument19 pagesValue-Added Crackers Enriched With Red Onion Skin AnthocyaninsMonica Adina BaneaNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument8 pagesRRLkyrograpixNo ratings yet
- Foto Pengawetan ApelDocument8 pagesFoto Pengawetan ApelheraNo ratings yet
- Journal of Food Science - 2024 - Antonino - Effect of Edible Coatings and Films Enriched With Plant Extracts and EssentialDocument25 pagesJournal of Food Science - 2024 - Antonino - Effect of Edible Coatings and Films Enriched With Plant Extracts and EssentialStefanus Prima NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Exploring the Future of Food : Organic Farming and GeneticsFrom EverandExploring the Future of Food : Organic Farming and GeneticsNo ratings yet
- From Seedling to Sanctuary : The Whole Farm Guide to Sustainable SuccessFrom EverandFrom Seedling to Sanctuary : The Whole Farm Guide to Sustainable SuccessNo ratings yet
Edible Coating Popular Article
Edible Coating Popular Article
Uploaded by
PrakashOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Edible Coating Popular Article
Edible Coating Popular Article
Uploaded by
PrakashCopyright:
Available Formats
Application of Edible Coating on Fruits and Vegetables
Article ID: 37634
P Babu1, A Prakash1
1Subject Matter Specialist (Agril. Engg), KVK, Kondempudi, Anakapalle, Teaching Associate, Dept of
Agril. Engg, SKCAS, ANGRAU.
Summary
Now-a-days, there is a great demand in the market for fruits and vegetables due its high nutritional
composition. As we know that fruits and vegetables are perishable in nature and having short shelf life.
About 25-30% of fruits and vegetables are majorly affected by insects, microorganisms, transportation and
storage. Preservation and storage of fruits is the major problem facing by the farmers all over the world.
To overcome the problem, Edible gum coating is applied to the fruit and vegetable. Edible gum coating is
an effective method for prolonging the shelf life of fruits and vegetables and also allows preserving of fresh
and processed food, maintaining quality, preventing microbial contamination and/or oxidation reactions.
Edible coatings are of different types such as hydrocolloids, lipids and plasticisers. Natural and synthetic
edible gum coatings were used for fruits and vegetables. These have good barrier properties to oxygen,
carbon dioxide, moisture and water vapour. In this paper, author discussed about the importance of
application of edible coating on fruits and vegetables.
Introduction
In India, the recent years population was increased and also there is a great demand for fruits and
vegetables which are having essential constituents of daily diet. Fruits and vegetables had good source of
vitamins, essential minerals, antioxidants, bio-flavonoids, dietary fibres and flavour compounds. As we
know that fruits and vegetables are highly perishable in the nature and the estimated high postharvest
losses was 15-30 % (Raghav P. K et al., 2016).
The estimated losses were mainly due to microbes, insects, respiration and transpiration. For acceptability
of fruits and vegetables in the market, the fresh produce has to maintain texture, colour, appearance,
flavour and nutritional value. Now-a-days there is a serious problem in postharvest losses of fruits and
vegetables and mainly deteriorates them during handling, transport and storage. Edible coating with
natural gums is one of the oldest and promising technologies for reducing the postharvest losses. Edible
coating over fruits and vegetables are used to improve their quality and enhance the shelf life.
These can also be safely eaten as part of the product and do not add unfavourable properties to the foodstuff.
Edible coatings have high potential to control browning, discolour activity, off flavour, microbial activity of
fruits and vegetables. In present years, new edible films and coatings have been developed with the addition
of natural and edible herbs, antimicrobial compounds to store the fresh fruits and vegetables. It helps in
controlling the maturation, development and respiratory rate.
Edible Coating
Edible coatings are defined application of edible gum as the thin layer of material which can be consumed
and provide a barrier to microbes of external source, oxygen, moisture and solute movement for food. Edible
coating acts as a semi permeable barrier which was provided and aimed to increase the shelf life by
decreasing moisture and solute migration, gas exchange, oxidative reaction rates and respiration as well
as to reduce physiological disorders on fresh cut fruits. These properties of the edible coating films were
(Hongbo et al., 2019): Edible coatings have good barrier properties to water, moisture, O2, CO2, and
ethylene. It improves appearance and colour and maintain structure. Edible coating contains active
components such as antioxidants, vitamins etc., they enhance nutritional composition without affecting its
quality. These coatings provide a protective covering on fruits and vegetables and enhance their shelf life.
The main advantages of edible coating are its edibility, non-toxic nature and cost effective as compared to
other synthetic coating.
Volume 04 - Issue 07 - July 2022 410 | P a g e
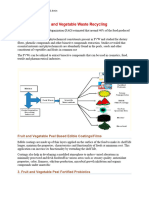
Classification of Edible Coatings (Sushmitha Reddy and Jatinder Singh, 2020)
Edible coatings are having hydrophobic (lipid-based or waxes) and hydrocolloids (polysaccharides-based,
protein based) or combination of both groups to improve function of edible coating. Edible Coatings are
natural, not chemically synthesised and generally used for good appearance and preservation of fruits and
vegetables. Edible coating materials are generally made up of polysaccharides, proteins and lipids. The
edible coatings are mainly divided into three classes:
1. Hydrocolloids: Polysaccharides, proteins and alginate.
2. Lipids: Fatty acids, acryl glycerides and waxes.
3. Composites: e.g., Protein/protein, polysaccharides/protein, lipid/polysaccharides.
Polysaccharides Derived Edible Coatings
Hydrocolloids: Generally, hydrocolloids are originated from vegetables, animals, microbial or synthetic.
Examples of hydrocolloids: Alginate, Carrageenan, Pectin, Carboxy Methyl Cellulose (CMC), Xanthan gum
and Gum Arabic. All hydrocolloids are partially or completely dissolved in water, act as an emulsifier due
to this stabilising effect. The hydrocolloids are divided into two classes :1. Polysaccharide-based, 2. Protein
based.
Cellulose Derivative: Cellulose is easily found in nature. Cellulose derivative coatings and films have
poor gas and water barrier properties. Polysaccharides derivatives are hydrophilic in nature that’s why
they have poor mechanical properties. Examples of cellulose derivatives : Methyl cellulose, Hydroxypropyl
cellulose (HPC), Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC), Methyl ethyl Cellulose (MEC), Carboxy Methyl
Cellulose (CMC).
Starch Derivatives: Starch is the most common polysaccharide and obtained from cereal grains belong
to poaceae family viz., wheat, maize, rice etc., The good source of starch were Potato, tapioca, legumes and
other tuber crops.
Chitosan: Chitosan is derived from chitin mainly available in animal shells. Chitosan is the most common
non-toxic and natural product after cellulose for formation of edible coating. chitosan has maximum
viscosity than other natural gums. Mostly all gums are polysaccharides it consists of sugars. Gums are
used for preparation of edible coating on fruits and vegetables because of its texture capability. Generally,
gums are divided into three parts- a.Extractive gums (e.g., guar gum) b. Exudate gums (e.g., gum Arabic)
c. Microbial fermentation gums (e.g., xanthan gum).
Alginate: Alginate is mostly found in brown seaweed, and has unique colloidal property. It contains
excellent barrier for moisture and water vapour. It acts as a stabilising and thickening agent.
Pectin: Pectin which is derived from plants and belongs to the polysaccharides group. It is naturally found
in fruits and vegetables and is good for low moisture fruits and vegetables.
Protein-Based Edible Coating: Protein based edible coatings are mostly found from plants and animal.
The plant-based protein edible coating material: milk protein casein, soy protein whey protein, zein, gluten,
etc. The animal-based protein is egg albumen, collagen etc. Protein based edible coating consist excellent
barrier properties for oxygen, aroma, and oil and it gives strength but it is not effective for moisture barrier.
Lipid Based Edible Coating: These edible coatings are used for preservation of perishable products.
They provide glossy appearance, colour and shiny to food. Most common lipid-based coating materials: bees
wax, carnauba wax, paraffin wax. Lipids are having good water barrier capacity. Wax coatings contain very
good moisture barrier properties as compare to other lipid based coating and non-lipid coating.
Disadvantages
Thick coating can prohibit oxygen exchange, causes off- flavour development. Edible coatings have good
gas barrier properties which causes anaerobic respiration due to this normal ripening process is disturbed
in fruits and vegetables. Some edible coatings are hygroscopic in nature, which helps to increase microbial
growth.
Conclusion
Now-a-days, edible coating technology is highly popularized for storage of fruits and vegetables in the food
industry. Different type of edible gum coating materials is used such as hydrocolloids, waxes, protein.
Volume 04 - Issue 07 - July 2022 411 | P a g e
Edible coatings were environment friendly and safely eaten with fruits and Vegetables. According to this
article, edible coatings help in extending of shelf life, reduce the moisture content, delayed ripening process
and also prevent microbial growth. For preservation of fruits and vegetables, application of edible coating
is the best solution for reducing postharvest losses.
References
1. Raghav P.K., Agarwal N. and Saini M., (2016). Edible coating of fruits and vegetables: A review. Int. J. Scientific Res.1(1):
188-204.
2. Hongbo, C., J. Wang, Y. Cheng, C. Wang, H. Liu, H. Bian, Y. Pan, J. Sun and W.n Han., (2019). Application of Protein-Based
Films and Coatings for Food Packaging: A Review, Polymers. 11: 2039.
3. Susmitha Reddy, K. and Jatinder Singh. 2020. Edible Coatings in Fruits - A Review. Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci. 9(11): 2953-
2969.
Volume 04 - Issue 07 - July 2022 412 | P a g e
You might also like
- Research HypothesisDocument6 pagesResearch HypothesisRati Gupta100% (1)
- Development of Edible Bioactive Coating Based On Modified Chitosan For Increasing PDFDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Edible Bioactive Coating Based On Modified Chitosan For Increasing PDFкатя калайдаNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and Methylcellulose-Based Edible Coatings On Storage Life and Quality of Horticultural Crops: ReviewDocument7 pagesEffect of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and Methylcellulose-Based Edible Coatings On Storage Life and Quality of Horticultural Crops: ReviewAsdNo ratings yet
- MS-AGS46F20 Bilal AminDocument2 pagesMS-AGS46F20 Bilal AminUsama HassanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2666154323001308 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2666154323001308 MainSrinivas KasiNo ratings yet
- Int J of Food Sci Tech - 2021 - Duguma - Potential Applications and Limitations of Edible Coatings For Maintaining TomatoDocument14 pagesInt J of Food Sci Tech - 2021 - Duguma - Potential Applications and Limitations of Edible Coatings For Maintaining TomatophotosalampuragriculturalNo ratings yet
- 10.1016@B978 0 12 803581 8.11509 7Document14 pages10.1016@B978 0 12 803581 8.11509 7Nguyễn Trần Hòa HợpNo ratings yet
- Review - Effects of Edible Coating On Fresh-Cut FruitsDocument8 pagesReview - Effects of Edible Coating On Fresh-Cut FruitsdwisriretnowidowatiNo ratings yet
- Coatings: Non-Conventional Tools To Preserve and Prolong The Quality of Minimally-Processed Fruits and VegetablesDocument31 pagesCoatings: Non-Conventional Tools To Preserve and Prolong The Quality of Minimally-Processed Fruits and VegetablesMaria AspriNo ratings yet
- Hauzoukim Et Al 2020Document10 pagesHauzoukim Et Al 2020Salwa HaneefahNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in Gum Edible Coating Applications For Fruits and Vegetables Preservation - A ReviewDocument15 pagesRecent Developments in Gum Edible Coating Applications For Fruits and Vegetables Preservation - A ReviewNguyên Trân Nguyễn PhúcNo ratings yet
- Bioactive Coatings From Non-Conventional Loquat (Eriobotrya Japonica Lindl.) Seed Starch To Extend Strawberries Shelf-Life - An Antioxidant PackagingDocument13 pagesBioactive Coatings From Non-Conventional Loquat (Eriobotrya Japonica Lindl.) Seed Starch To Extend Strawberries Shelf-Life - An Antioxidant PackagingguxxtavobarbattoNo ratings yet
- PomegranateDocument10 pagesPomegranatevivek kumarNo ratings yet
- polymers-14-01341 (1)Document23 pagespolymers-14-01341 (1)Iqbal PratamaNo ratings yet
- Foods 12 03570Document18 pagesFoods 12 03570Felipe CabezasNo ratings yet
- EdibleCoatingofFruitsVegetables AReviewDocument18 pagesEdibleCoatingofFruitsVegetables AReviewmasayangadaNo ratings yet
- Foods 10 00116Document14 pagesFoods 10 00116YAYON PAMULA MUKTINo ratings yet
- FINAL 6 Good PDFDocument6 pagesFINAL 6 Good PDFTanakorn RachapilaNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S0023643817301354-Rajiv Dhital Strawberry Shelf Life 2017Document28 pages1-s2.0-S0023643817301354-Rajiv Dhital Strawberry Shelf Life 2017Andres FAGNo ratings yet
- Bio-Coatings For Preservation of Fresh Fruits andDocument34 pagesBio-Coatings For Preservation of Fresh Fruits andRedhaLavNo ratings yet
- Coatings: /Coatings-Performances and PerspectivesDocument46 pagesCoatings: /Coatings-Performances and Perspectivesfahrullah unhasNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Edible Coatings and Films, Herbal Films, Shelf Life, Food Preservation, NovelDocument30 pagesKeywords: Edible Coatings and Films, Herbal Films, Shelf Life, Food Preservation, NovelVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- The_Role_of_Packaging_Technology_in_The_Food_ProduDocument5 pagesThe_Role_of_Packaging_Technology_in_The_Food_ProduSouvia RahimahNo ratings yet
- CHITOSAN WITH Citrus Bergamia (BERGAMOT) OIL AS A PROTECTIVE COATING IN PRESERVING QUALITY AND PROLONGING SHELF LIFE OF Raphanus Sativus (RADISH)Document39 pagesCHITOSAN WITH Citrus Bergamia (BERGAMOT) OIL AS A PROTECTIVE COATING IN PRESERVING QUALITY AND PROLONGING SHELF LIFE OF Raphanus Sativus (RADISH)Shaina AustriaNo ratings yet
- Polysaccharide, Protein, Lipid-Based Coatings and Their Impact On Fruit Crops: ReviewDocument9 pagesPolysaccharide, Protein, Lipid-Based Coatings and Their Impact On Fruit Crops: ReviewHimanshu RohillaNo ratings yet
- CucumberDocument25 pagesCucumberPuja BarmanNo ratings yet
- Foods 10 02088 v3Document22 pagesFoods 10 02088 v3Bronil, John Angelo J.No ratings yet
- Application of Edible Coatings On Fruits and VegetablesDocument14 pagesApplication of Edible Coatings On Fruits and VegetablesbhagwatNo ratings yet
- Agroindustria 4Document23 pagesAgroindustria 4Camilo MartínezNo ratings yet
- Bioactive Edible Films Based On Arrowroot Starch IDocument12 pagesBioactive Edible Films Based On Arrowroot Starch ITairine PimentelNo ratings yet
- Fruits and Vegetables With A Coating That Is Edible A ReviewDocument9 pagesFruits and Vegetables With A Coating That Is Edible A ReviewKarhol MartinezNo ratings yet
- Natural Gums of Plant Origin As Edible Coatings For Food Industry ApplicationsDocument16 pagesNatural Gums of Plant Origin As Edible Coatings For Food Industry ApplicationslunosicaNo ratings yet
- IFRJDocument16 pagesIFRJpaolaNo ratings yet
- LWT - Food Science and Technology: I.M. Brasil, C. Gomes, A. Puerta-Gomez, M.E. Castell-Perez, R.G. MoreiraDocument7 pagesLWT - Food Science and Technology: I.M. Brasil, C. Gomes, A. Puerta-Gomez, M.E. Castell-Perez, R.G. MoreiraAndriati NingrumNo ratings yet
- Avance Reciente en El Recubrimiento Comestible y Su Efecto en La Calidad de Las Frutas Frescas - Recién CortadasDocument15 pagesAvance Reciente en El Recubrimiento Comestible y Su Efecto en La Calidad de Las Frutas Frescas - Recién CortadasJHON FABER FORERO BARCONo ratings yet
- New Insights in The Production of Fruit Leather: Sparsh Kashyap and Dr. Neha SharmaDocument12 pagesNew Insights in The Production of Fruit Leather: Sparsh Kashyap and Dr. Neha Sharmakb12192127No ratings yet
- FB01 Chapter1Document7 pagesFB01 Chapter1Reymundo Pantonial Tugbong JrNo ratings yet
- Edible Coating of Fruits and Vegetables: Prince Kumar Singh (16112045), Premprakash Bairwa (16112044)Document1 pageEdible Coating of Fruits and Vegetables: Prince Kumar Singh (16112045), Premprakash Bairwa (16112044)prince singhNo ratings yet
- Edible Coating and Edible Film As Food Packaging Material: A ReviewDocument10 pagesEdible Coating and Edible Film As Food Packaging Material: A Reviewcaseco4756No ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of Related LiteratureDaisyrie Joy DesabilleNo ratings yet
- Acknowledge NTDocument20 pagesAcknowledge NTRehan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Coatings FruitDocument17 pagesCoatings FruitbbhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Chitosan and Guava Leaf Extract As Preservative To Extend The Shelf-Life of FruitsDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Chitosan and Guava Leaf Extract As Preservative To Extend The Shelf-Life of FruitsclitcheNo ratings yet
- Edible Films and Coatings Classification, Preparation, PDFDocument10 pagesEdible Films and Coatings Classification, Preparation, PDFmaryamNo ratings yet
- InnotacionDocument16 pagesInnotacioncamilaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesDocument9 pagesReview of Related Literature and StudiesJay-Ar S. SungaNo ratings yet
- Edible Film Based On Candelilla Wax Improve The Shelf Life and Quality of Avocado Saucedo-Pompa 2009 FRIDocument5 pagesEdible Film Based On Candelilla Wax Improve The Shelf Life and Quality of Avocado Saucedo-Pompa 2009 FRIXochitl Ruelas ChaconNo ratings yet
- Edible Coatings To Incorparate Active IngredientsDocument10 pagesEdible Coatings To Incorparate Active Ingredientscarranclan077No ratings yet
- Nthimole Et Al. (2022)Document18 pagesNthimole Et Al. (2022)Santiago DangerNo ratings yet
- Biodegradable Films and Composite Coatings: Past, Present and FutureDocument8 pagesBiodegradable Films and Composite Coatings: Past, Present and FutureIzabele RamosNo ratings yet
- Plants 11 00351Document24 pagesPlants 11 00351Abi Irfan Habibi LubisNo ratings yet
- Shelf Life Study of Fruit BarDocument8 pagesShelf Life Study of Fruit BarAmna SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Oregel Zamudio2017Document7 pagesOregel Zamudio2017REETU PALTHANIANo ratings yet
- Foods 11 02641Document17 pagesFoods 11 02641Kajal MIshraNo ratings yet
- Value-Added Crackers Enriched With Red Onion Skin AnthocyaninsDocument19 pagesValue-Added Crackers Enriched With Red Onion Skin AnthocyaninsMonica Adina BaneaNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument8 pagesRRLkyrograpixNo ratings yet
- Foto Pengawetan ApelDocument8 pagesFoto Pengawetan ApelheraNo ratings yet
- Journal of Food Science - 2024 - Antonino - Effect of Edible Coatings and Films Enriched With Plant Extracts and EssentialDocument25 pagesJournal of Food Science - 2024 - Antonino - Effect of Edible Coatings and Films Enriched With Plant Extracts and EssentialStefanus Prima NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Exploring the Future of Food : Organic Farming and GeneticsFrom EverandExploring the Future of Food : Organic Farming and GeneticsNo ratings yet
- From Seedling to Sanctuary : The Whole Farm Guide to Sustainable SuccessFrom EverandFrom Seedling to Sanctuary : The Whole Farm Guide to Sustainable SuccessNo ratings yet