Professional Documents
Culture Documents
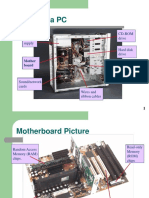
Topic 2d Parts of A Motherboard PDF
Topic 2d Parts of A Motherboard PDF
Uploaded by
Theo NdedaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2d Parts of A Motherboard PDF
Topic 2d Parts of A Motherboard PDF
Uploaded by
Theo NdedaCopyright:
Available Formats
Course Code :
BISF 1104
Course Description:
Installation and Customization
Lesson 2d : Parts of a Motherboard
Lecturer Name: Eric G Kariuki
Email: ekariuki@kcau.ac.ke
Tel: 0721487915
06/22/16
I/O Cables/Connectors – Floppy Cable
Lecture 5 • The motherboard should come with one
"standard" 34-pin floppy disk cables. This
is the unusual-looking cable with 5
I N S TA L L AT I O N connectors on it (one plus two pairs), with
& a half-twist in 7 of the wires in the middle
of the cable
C U S TO M IZ ATIO N
06/22/16 BIT 2223 1 06/22/16 BIT 2223 4
Lecture Outline IDE/ATA Interface Cable
• I/O Cables or Connectors • A motherboard normally comes with one
• Motherboard integrated components standard 40-pin IDE (ATA) hard disk / CD-
– Printed Circuit Board ROM cable. It should have 3 connectors on it,
– Processor Sockets/Slots but sometimes will only have 2. If you want
– Memory sockets to use two IDE channels (which is preferred
– I/O Bus Slots in most cases for performance reasons), you
– Power connectors will usually have to purchase an additional
– Ports and headers interface cable.
• Motherboard snapshot
06/22/16 BIT 2223 2 06/22/16 BIT 2223 5
I/O Cables or Connectors Motherboard Integrated Components
• If your motherboard uses the ATX, LPX or NLX form – These refer to components that have
factors, it has integrated serial and parallel port
connectors. If it is AT or Baby AT style, then you
been mounted or firmly attached to the
normally should get three ribbon cables with the main board. They could be fixed or
motherboard to connect the serial and parallel soldered on the board such that they
connectors to the motherboard. The serial cables
normally have 9 wires each (even if they go to 25-pin become part of the board.
connectors) and the parallel cable has 25. These
connectors normally come pre-mounted into metal
inserts intended to be installed into the case where
expansion cards go.
06/22/16 BIT 2223 3 06/22/16 BIT 2223 6
06/22/16
Memory Sockets
• Most motherboards today come with between 2 and 8
sockets for the insertion of memory. These are usually
either SIMMs (single inline memory modules) or DIMMs
(dual inline memory modules). These can come in different
sizes
• The motherboard usually labels these sockets "SIMM0"
through "SIMM7" or "DIMM1" through "DIMM3", etc.
The sockets are almost always filled starting with the
lowest numbered socket first. Most Pentium class or higher
motherboards require SIMMs to be inserted in pairs, but
DIMMs may be inserted individually.
– Note: The maximum number of memory modules on a motherboard is
dictated by the design of the motherboard's chipset.
06/22/16 BIT 2223 7 06/22/16 BIT 2223 10
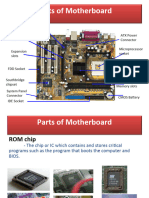
Printed Circuit Board I/O Bus Slots
• All motherboards have one or more system I/O
– Motherboards are multiple layer printed buses, that are used to expand the computer's
circuit boards, also sometimes called PCBs. capabilities. The slots in the back of the machine are
The physical board that you see is actually a where expansion cards are placed (like your video
sandwich of several thinner layers, each card, sound card, network card, etc.). These slots
containing some of the circuitry required to allow you to expand the capabilities of your machine
connect the various components on the board. in many different ways, and the proliferation of both
At one time this was expensive, difficult-to- general purpose and very specific expansion cards is
manufacture technology, but time and part of the success story of the PC platform.
automation has reduced this complexity to the • Three types of I/O Bus slots exist namely ISA (Industry
point where the board itself is a minor Standard Architecture), PCI (Peripheral Component
component of overall cost. Interconnect) and AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port –
specifically for Monitors.
06/22/16 BIT 2223 8 06/22/16 BIT 2223 11
Processor(s) Sockets/Slots Power Connectors
– The motherboard has one or more sockets or slots to • The motherboard has a socket to attach the power
hold the processor(s). Single-processor motherboards cables coming from the power supply. ATX form
are by far the most common, but dual processor and factor motherboards and power supplies use a
even quad processor boards are not hard to find. (Quad
boards often use special, proprietary designs employing
single, keyed 20-wire motherboard power cable.
riser cards.) The type of socket or slot used dictates the All others use a pair of 6-wire cables. The cables
type of processor (and in some cases the speed) that can are connected to the motherboard so that the black
be used by the motherboard. Most older Intel wires (grounds) are together in the middle.
processors, up to the Pentium Pro, use a square-shaped
• This connector is usually found near the back
socket for the processor. The newest processors from
Intel, starting with the Pentium II, are mounted on a right-hand side of the motherboard, near the
daughterboard, which plugs into an SEC ("single-edge power supply.
connector") slot to connect to the motherboard.
06/22/16 BIT 2223 9 06/22/16 BIT 2223 12
06/22/16
Ports and Headers Types of Ports and Headers – Cont’d
• Ports are connectors used to connect external cables • Primary and Secondary IDE/ATA Hard Disk
and devices to the motherboard. In addition to the Interface: Most newer motherboards have
keyboard and PS/2 mouse connectors, some types of integrated headers for two IDE channels. Each
motherboards (such as the ATX) have on the back has 40 pins.
edge of the motherboard integrated serial and • Floppy Disk Interface: Most newer
parallel ports. motherboards provide a 34-pin header for the
• Motherboards that don't use integrated ports, use floppy disk cable.
headers on the motherboard instead. Headers are
• SCSI: Some motherboards have integrated SCSI
groups of pins used to connect devices or ports to
ports or headers, though they are uncommon.
the motherboard. A cable runs from the port and is
plugged into the header on the board.
They are either 50 or 68 pins in size, depending
on the flavour of SCSI implemented.
06/22/16 BIT 2223 13 06/22/16 BIT 2223 16
Types of Ports and Headers
• Serial Ports: As mentioned, there are usually
two serial port headers. Each has 9 or 10 pins
(only the first 9 are used, however).
• Parallel Port: This header is used for the
external parallel port and has 26 pins (25 are
actually used).
• PS/2 Mouse Port: Some good motherboards
provide a header for a PS/2 mouse port when this
port is not already on the board. This lets you
add a PS/2 port yourself so you can enjoy its
advantages. The PS/2 mouse header has 5 pins.
06/22/16 BIT 2223 14 06/22/16 BIT 2223 17
Types of Ports and Headers – Cont’d
• USB (Universal Serial Bus): A new technology,
USB is proposed to be the new standard for
connecting devices such as keyboards, mice and
external modems to the PC.
• IR (Infrared) Port: Some motherboards have a
header to allow you to run a connection for an
infrared communications port, typically used for
wireless communication to printers and similar
devices. Infrared ports are far more common on
laptop computers than desktop machines.
06/22/16 BIT 2223 15
You might also like
- Module 6: Etherchannel: Instructor MaterialsDocument35 pagesModule 6: Etherchannel: Instructor MaterialsJohn100% (1)
- Mboard TshootingDocument29 pagesMboard TshootingDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument31 pagesMotherboardGabbriel Emmanuel Y. CabagnotNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - IcsDocument70 pagesCHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - Icsruzanna abu bakarNo ratings yet
- Topic 2a MotherboardsDocument37 pagesTopic 2a MotherboardsTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- MOTHERBOARDDocument70 pagesMOTHERBOARDCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Basics ICD2ODocument8 pagesMotherboard Basics ICD2Oziadabdelgayed1No ratings yet
- Components of A MotherboardDocument114 pagesComponents of A Motherboarddeejhay14100% (1)
- Motherboard SlidesDocument21 pagesMotherboard Slidesmubiru moses100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Motherboard Components (Notes)Document73 pagesChapter 2 - Motherboard Components (Notes)Nr AimaNo ratings yet
- 3 - MotherboardDocument41 pages3 - MotherboardMe RylleNo ratings yet
- Motherboardppt41 160905161959Document39 pagesMotherboardppt41 160905161959Adrian Yan Yan DelaraNo ratings yet
- Mother BoardDocument15 pagesMother BoardSyd SiasonNo ratings yet
- The MotherboardDocument39 pagesThe MotherboardGenevev Reyes100% (1)
- IEEE 1394 PortDocument4 pagesIEEE 1394 PortPRincess ScarLetNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument2 pagesMotherboardGrace BravoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard ConnectorsDocument5 pagesMotherboard Connectorsmohitpar128No ratings yet
- CHS Set2 W4-6Document136 pagesCHS Set2 W4-6Omar Sharif CuyuganNo ratings yet
- Motherboard PresentationDocument20 pagesMotherboard PresentationAMIT SINGH100% (1)
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument14 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- Motherboard OverviewDocument4 pagesMotherboard OverviewMC ICT LabNo ratings yet
- Motherboard PPT Bhupen GargDocument20 pagesMotherboard PPT Bhupen GargBhupen GargNo ratings yet
- Parts of Motherboard: Reporters: Ebajo, Bonete, and SatorinasDocument11 pagesParts of Motherboard: Reporters: Ebajo, Bonete, and SatorinasHirai MomoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts of A MotherboardPamieDyNo ratings yet
- Baby at Form FactorDocument35 pagesBaby at Form FactorLouie RazalasNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Name - Sachin Roll No - 20156 Branch - CseDocument39 pagesMotherboard: Name - Sachin Roll No - 20156 Branch - CseSachin DhamiNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: - Chip SetDocument19 pagesMotherboard: - Chip SetAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 - Firewire HeaderDocument4 pages1 - Firewire HeaderVishnu TejaNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument8 pagesMotherboardSudarsan JaganathanNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocument28 pagesMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan50% (2)
- Hardware Notes New Ports and Slots PDFDocument8 pagesHardware Notes New Ports and Slots PDFKrish NeupaneNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument21 pagesMotherboardYash KumarNo ratings yet
- 3.assignment ITCDocument3 pages3.assignment ITCHuman FreedomNo ratings yet
- How Motherboards WorkDocument5 pagesHow Motherboards Workapi-19737301No ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument9 pagesTable of ContentsSoumyadip SardarNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Document4 pagesParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNo ratings yet
- Motherboard TerminologyDocument8 pagesMotherboard TerminologyshockkrewNo ratings yet
- Parts of Mother BoardDocument17 pagesParts of Mother BoardJeza Estaura Cuizon50% (2)
- Computer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardDocument5 pagesComputer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardErickson JavonitallaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorDocument12 pages1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorTuesept Anne Vargas UrgenteNo ratings yet
- MOTHERBOARDDocument13 pagesMOTHERBOARDUday HrudaiNo ratings yet
- Parts of Mother BoardDocument17 pagesParts of Mother BoardHans De la CruzNo ratings yet
- System Unit PDFDocument49 pagesSystem Unit PDFFrinzcharls Dajao DavocolNo ratings yet
- Course ContentsDocument147 pagesCourse ContentsPralhad Thorat100% (1)
- Hard Ware Note BookDocument22 pagesHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- How Motherboards WorkDocument61 pagesHow Motherboards WorkLorena TeofiloNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument27 pagesMotherboardமகான் சிறோன்No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Motherboards UpdateDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Motherboards Updatelodelyn caguilloNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument8 pagesReportapi-3734554100% (1)
- A+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationDocument40 pagesA+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationLindasharon AwourNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument9 pagesMotherboardAhmed AbuNasserNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Wilmar Jennie V. Motea, MitDocument83 pagesMotherboard: Wilmar Jennie V. Motea, MitGretchen Sarmiento Cabarles AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Common Laptop Problem1Document41 pagesTroubleshooting Common Laptop Problem1Teddy Worku100% (2)
- ITE7 Chp1Document35 pagesITE7 Chp1abbasgass48No ratings yet
- Motherboard Components: By:-Aryan Panchal Roll No: - 1881026Document10 pagesMotherboard Components: By:-Aryan Panchal Roll No: - 1881026Aryan PanchalNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Mother BoardDocument28 pagesParts of A Mother BoardReilina KylaNo ratings yet
- Master System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15From EverandMaster System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Neo Geo Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #23From EverandNeo Geo Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #23No ratings yet
- Game Boy Advance Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #7From EverandGame Boy Advance Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #7No ratings yet
- NES Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #1From EverandNES Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3From EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3No ratings yet
- Topic 5c MS DOS PDFDocument8 pagesTopic 5c MS DOS PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Linux Operating SystemDocument7 pagesLinux Operating SystemTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5a Application Software PDFDocument7 pagesTopic 5a Application Software PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4c - Mass Storage Devices PDFDocument3 pagesTopic 4c - Mass Storage Devices PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3a Computer Disassembly and Reassembly Upgrading A Computer PDFDocument42 pagesTopic 3a Computer Disassembly and Reassembly Upgrading A Computer PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6b Network Devices PDFDocument24 pagesTopic 6b Network Devices PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4b - Computer Memory PDFDocument4 pagesTopic 4b - Computer Memory PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7a Computer Security PDFDocument44 pagesTopic 7a Computer Security PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6a Computer Networks PDFDocument66 pagesTopic 6a Computer Networks PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2b Motherboard Form FactorsDocument5 pagesTopic 2b Motherboard Form FactorsTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3b Computer Hardware PDFDocument9 pagesTopic 3b Computer Hardware PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Printers PDFDocument4 pagesTopic 9 Printers PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Computer Softwares Applications PDFDocument1 pageTopic 4 Computer Softwares Applications PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Software Installation and CustomizationDocument88 pagesComputer Hardware Software Installation and CustomizationTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4a Parts of A Hard Drive PDFDocument4 pagesTopic 4a Parts of A Hard Drive PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2c Motherboards Technical Analysis PDFDocument10 pagesTopic 2c Motherboards Technical Analysis PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2a MotherboardsDocument37 pagesTopic 2a MotherboardsTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Dasasloki PDFDocument2 pagesDasasloki PDFPhanimadhiraNo ratings yet
- Sri Ramakrishna Prabha Telugu Monthly Magazine Subscription - RK MathDocument2 pagesSri Ramakrishna Prabha Telugu Monthly Magazine Subscription - RK Mathroyalrans100% (1)
- C Modeling and Prediction Using Seasonal ARIMA: Wireless Tra ModelsDocument8 pagesC Modeling and Prediction Using Seasonal ARIMA: Wireless Tra ModelsMalik harisNo ratings yet
- A Tutorial On The Aitken Convergence AcceleratorDocument13 pagesA Tutorial On The Aitken Convergence AcceleratorPablo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CS204 - Operating Systems (S) Dec 2019 - Ktu QbankDocument3 pagesCS204 - Operating Systems (S) Dec 2019 - Ktu QbankJessel CherianNo ratings yet
- Lead Generation Roadmap FINAL PDFDocument27 pagesLead Generation Roadmap FINAL PDFYaj BusawonNo ratings yet
- Building Insurance 101Document3 pagesBuilding Insurance 101Desiree C. BaricuatroNo ratings yet
- The Brown Bauhaus STUDIO ARCHITECTURE: Fundamental Course - Comprehensive Ale Review + Preparation ProgramDocument10 pagesThe Brown Bauhaus STUDIO ARCHITECTURE: Fundamental Course - Comprehensive Ale Review + Preparation ProgramClaro III TabuzoNo ratings yet
- 1 - PERT-CPM (Part 1)Document9 pages1 - PERT-CPM (Part 1)JiroNo ratings yet
- Claims Officer Cover LetterDocument6 pagesClaims Officer Cover Letterbcrbcw6a100% (2)
- C#Document2 pagesC#Gunturu LavanyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 E10 KeyDocument7 pagesUnit 8 E10 KeyThảo Nguyên-32-9350% (4)
- FFFFDocument1 pageFFFFYanetNo ratings yet
- Lte 2100M SSV - Bad2m7109 - 12 - 08 - 2016Document51 pagesLte 2100M SSV - Bad2m7109 - 12 - 08 - 2016dinzo ccsiNo ratings yet
- Digital Ic TesterDocument28 pagesDigital Ic TesterChris ManojNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Notes.Document8 pagesBlockchain Notes.Hussein IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Application SoftwareDocument33 pagesApplication SoftwareJowel VistaNo ratings yet
- Regional Online Training On Geographic Information System For Hydrology - v3Document5 pagesRegional Online Training On Geographic Information System For Hydrology - v3YosephNo ratings yet
- OS Assignment 1: Introduction: Student NameDocument2 pagesOS Assignment 1: Introduction: Student NameKiko Doragon Inoue TsubasaNo ratings yet
- Movies at 50 in 2021Document12 pagesMovies at 50 in 2021SilviuSerbanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Internet ProtocolsDocument37 pagesLesson 3 Internet ProtocolsReign Jay FerrerNo ratings yet
- PWC Internet Cookies FinalDocument91 pagesPWC Internet Cookies FinalshabiumerNo ratings yet
- Tracker Sensor CombustibleDocument16 pagesTracker Sensor CombustibleAngie BrownNo ratings yet
- Zero Trust Maturity AssessmentDocument132 pagesZero Trust Maturity AssessmentrodrigoNo ratings yet
- Java - Introduction To Programming: String BuilderDocument3 pagesJava - Introduction To Programming: String BuilderAndaNo ratings yet
- Approved TALQ Specification Version 2.3.0Document52 pagesApproved TALQ Specification Version 2.3.0Firas KACHROUDINo ratings yet
- Online Grocery Store SynopsisDocument4 pagesOnline Grocery Store SynopsisFarhan SjNo ratings yet
- 302 002 576 Troubleshooting ChecklistDocument18 pages302 002 576 Troubleshooting ChecklistMahmood SafariNo ratings yet
- ZXM10 EISU TrainingDocument28 pagesZXM10 EISU TrainingelmoustaphaelNo ratings yet