Professional Documents
Culture Documents
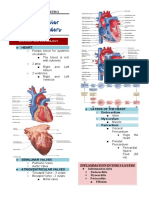
Theoretical Foundations of Nursing (TFN) Reviewer Part 1
Theoretical Foundations of Nursing (TFN) Reviewer Part 1
Uploaded by
Sofia Li0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views26 pagesThis document provides an overview of Katie Eriksson's theory of caritative caring. Some key points:
1) Caritative caring is based on the concepts of caritas (unconditional love) and caring communion. The goal is to alleviate suffering and serve life through establishing a caring relationship.
2) Caring involves concepts like faith, hope, love, dignity, and invitation. It aims to confirm patients in their suffering through establishing communion.
3) Nursing from this perspective is motivated by caritas and combines eros (passion) and agape (unconditional love). The core of nursing is caritative caring which emphasizes alleviating patient suffering and meeting desires through love and charity.
Original Description:
Board exam reviewer
Original Title
Theoretical Foundations of Nursing (Tfn) Reviewer Part 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of Katie Eriksson's theory of caritative caring. Some key points:
1) Caritative caring is based on the concepts of caritas (unconditional love) and caring communion. The goal is to alleviate suffering and serve life through establishing a caring relationship.
2) Caring involves concepts like faith, hope, love, dignity, and invitation. It aims to confirm patients in their suffering through establishing communion.
3) Nursing from this perspective is motivated by caritas and combines eros (passion) and agape (unconditional love). The core of nursing is caritative caring which emphasizes alleviating patient suffering and meeting desires through love and charity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views26 pagesTheoretical Foundations of Nursing (TFN) Reviewer Part 1
Theoretical Foundations of Nursing (TFN) Reviewer Part 1
Uploaded by
Sofia LiThis document provides an overview of Katie Eriksson's theory of caritative caring. Some key points:
1) Caritative caring is based on the concepts of caritas (unconditional love) and caring communion. The goal is to alleviate suffering and serve life through establishing a caring relationship.
2) Caring involves concepts like faith, hope, love, dignity, and invitation. It aims to confirm patients in their suffering through establishing communion.
3) Nursing from this perspective is motivated by caritas and combines eros (passion) and agape (unconditional love). The core of nursing is caritative caring which emphasizes alleviating patient suffering and meeting desires through love and charity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 26
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
CARING despite any regardless condition of patient, and
(Katie Eriksson) also honesty, tolerance.
Caring elements
Caritative caring - The act of caring contains: Faith, hope, love,
- means that we take “caritas” into use when caring tending, playing, and learning.
for the human being in health and suffering. - Involves the categories of infinity and eternity and
- a manifestation of the love that ‘just exist’, invites to deep communion.
- Caring communion or true caring - The art of caring is the art of making something
- occurs when the one caring in a spirit of very special out of something less special.
caritas alleviates the suffering of the patient. Caring ethics
- Caritas – an art of giving a nursing care that is - Comprises the ethics of caring, the core of which
unconditional love is determined by the caritas motive.
- Main goal of the nurse in this theory: - deals with the basic relation between the patient
- to alleviates the suffering and serve life and and the nurse – the way in which the nurse meets
health. the patient in an ethical sense.
- once you got involved in an alleviating the Dignity
suffering of the patient you are already - constitutes one of the basic concepts of caritative
rendering caritas caring ethics.
- and once you start rendering caritas, you are - Human dignity is partly absolute dignity, partly
involving your patient in the caring relative dignity.
communion. - A human being’s absolute dignity involves the
Katie Eriksson right to be confirmed as a unique human being.
- Finland-Swedish nurse - Absolute dignity – it was provided to us upon in
- born in Nov 18, 1943 in Jacobstad, Finland. our creation, created by our parents, and you
- 1965 graduate of the Heisinki Swedish School of were born, you have your unique identity.
Nursing. - Relative dignity - we could acquire this through
- In 1967, she completed her public health nursing our environment, the way people treat us, the way
specialty education at the same institution. people give importance to us. They should
- She currently works as a professor of health recognize your existence.
science at Abo Akademi University in Vaasa, Invitation
where she built a master’s degree program in - Refers to the act that occurs when the
health science and four-year postgraduate career/nurse welcomes the patient to the caring
studies program leading to a doctoral degree in communion.
health sciences. - Allowed to rest a place that breathes genuine
Major Concepts and Definitions hospitality, and where the patients appeal for
Caritas charity meets with a response.
- Means love and charity - Once you embrace the patient, you introduce
- Eros and agape are united yourself, you start asking the patient about his
- Eros – passion; agape – unconditional love condition and doing procedure for the patient
- By nature, unconditional love. using the caritas – that’s already invitation.
Caring Communion Suffering
- Constitutes the context of the meaning of caring - An ontological concept described as a human
and is the structure that determines caring reality. being’s struggle between good and evil in a state
- Characterized by intensity and vitality, and by of becoming.
warmth, closeness, rest, respect, honesty and - Implies in some sense dying away from
tolerance. something, and through reconciliation, the
- How would you say that you are providing the wholeness of body, soul and spirit is re-created,
caring communion - if the type of environment when the human being’s holiness and dignity
you are providing is warm, love and closeness. appear.
And providing rest to the patient physically,
mentally, emotionally. Respecting the patient
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- Reconciliation – nahold mo na un suffering mo, the human obligation of serving with love and
ikaw na nag cocontroll ng suffering mo. Nakapag existing for the sake of others.
recreate ka na ng bagong ikaw - Seen as in constant becoming; he is constantly
Forms of Suffering changing and therefore never in a state of full
Suffering related to illness completion.
- Experiences in connection with illness and - Engaged in a continued struggle and living in a
treatment. tension between being and non-being.
Suffering related to Care - The human being is fundamentally dependent on
- When the patient is exposed to suffering caused communion.
by care or absence of caring - Seeks a communion where he can give and
- Which is always a violation of the patient’s dignity. receive love, experience faith and hope, and be
Suffering related to Life aware that his existence here and now has
- In the situation of being a patient, the entire life of meaning.
a human being may be experienced as suffering Nursing
related to life. - Caritas as the basic motive of caring
Suffering human being - The 2 basic forms of love – eros and agape are
- The concept that Eriksson uses to describe the combined. The motive of caritas becomes visible
patient. in a special ethical attitude in caring, or what calls
- The patient refers to the concept of “patiens” a caritative outlook.
(Latin) – means “suffering” - Caritas constitutes the inner force that is
- The patient is a suffering human being, or a connected with the mission to care.
human being who suffers and patiently endures. Caritative caring
Reconciliation - The innermost core of nursing
- Drama of suffering - She distinguishes between caring nursing and
- A human being who suffers wants to be nursing care.
confirmed in his/her suffering and be given time - Nursing care is based on the nursing care
and space to suffer and reach reconciliation. process, and it represents good care only when it
- Hindi mo pwedeng pilitin na madiliin un patient na is based on the innermost core of caring.
mag adjust agad. Hanggat maaccept nya yun - Caring nursing represents a kind of caring
condition nya at magadjust/move on. without prejudice that emphasizes the patient and
- “suffering is not holding you; You are holding his/her suffering and desires.
suffering” - love – we will alleviate the pain of the patient;
Caring culture charity – we will provide the needs/desires of the
- The concept that Eriksson uses instead of patient.
environment. Environment
- It characterizes the total caring reality and is - Eriksson uses the concept of ethos
based on cultural elements such as traditions, - The ethos of caring science as well as that of
rituals and basic values. caring, consist of the idea of love and charity and
- Respect for the human being, his or her dignity respect and honor of the holiness and dignity of
and holiness, forms the goal of communion and the human being.
participation in a caring culture. - Ethos originally refers to home, or to the place
The Human Being where a human being feels at home
- The concept that Eriksson uses instead of Alleviating a human being’s suffering implies being a
person. co-actor in the drama and confirming his/her suffering.
- Based on the belief that the human being is an A human being who suffers wants to have the suffering
entity of body, soul and spirit, emphasizes that confirmed and be given time and space to become
the human being is fundamentally a religious reconciled to it.
being. The ultimate purpose of caring is to alleviate suffering.
- Fundamentally holy, and this belief is related to Health
the idea of human dignity, which means accepting - As soundness, freshness, and well-being.
- It implies being whole in body, soul and spirit.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- As a pure concept wholeness and holiness - Which serve as a blueprint for professional
- To be able to consider whole (wholeness), nursing practice.
balance between mind, body and spirit. (pwedeng - You could be able to provide human caring to a
sabihin na, okay ka sa physically pero mentally patient if the type of caring you provide involves
hindi, you are not considered as healthy); the 3 elements. - 10 carative factors,
holiness – religion and faith. transpersonal caring relationship and caring
- Both movement and integration. occasion/moment
- Movement – implies a change; a human being is - Theory of caring focuses on the interpersonal and
being formed or destroyed, but never completely. transpersonal relationship between nurse and
- Movement in time and space other (self, patient, family, society, universe)
- Movement – dependent on vital force and on - “Human Caring is the moral idea of nursing”
vitality of body, soul, and spirit; the direction of
this movement is determined by the human The core of the Theory of Caring
being’s needs and desires; the will to find - Humans cannot be treated as objects and that
meaning, life, and love, strives toward a humans cannot be separated from self, other,
realization of one’s potential nature, and the larger workforce.
- Health is conceived as a becoming, a movement - Watson views the carative factors as a guide fop
toward a deeper wholeness and holiness. the core of nursing
- As a human being’s inner health potential is - Carative means caring with love
touched, a movement occurs that becomes
visible in the different dimensions of health as Transpersonal Caring Relationship
doing, being, and becoming with a wholeness that - Transpersonal – describes an intersubjective,
is unique to human beings. human to human relationship that encompasses
In doing two individuals, both the nurse and the patient in
- The persons thoughts concerning health are a given moment.
focused on healthy life habits and avoiding illness. - Describes how the nurse goes beyond the object
In being assessment to show concern toward the person’s
- The person strives for balance and harmony. subjective/deeper meaning of their health care
- Balance of mind, body and spirit. situation.
In becoming - Involves mutuality between the two individuals
- The human being becomes whole on a deeper involved.
level of integration. - Objective data – ito un naoobservahan mo lng;
- Deeper level of wholeness and holiness. Subjective assessment – communicating or by
asking the patient about his/her condition
THEORY OF TRANSPERSONAL NUSRING
(JEAN WATSON) - Occurs during the ‘caring event’, central to
- Theory of human caring and nursing: human Watson’s view of nursing.
science and human care. - Calls the nurse to go beyond the objective,
- Caring is the essence of nursing. physical assessment with concern for the
- TLC – Tender Loving Care person’s deeper, subjective well-being.
Jean Watson - The nurse “seeks to connect with and embrace
- Born on June 10, 1940 in West Virgina the spirits or soul of the other, through the
- Received her BSN from the University of process of caring and healing and being in
Colorado in 1964 authentic relation, in the moment.” (Park, 2001)
- 2013 – she was awarded the American Academy - Goal is to protect, enhance and preserve the
of Nursing’s ‘Living Legend’ award, its highest person’s dignity, humanity, wholeness, inner
honor. harmony and overall wellbeing.
- Can be nurtured by movements, gestures, facial
The Theory of Human caring and 10 Caritas and bodily expressions, the sharing of information,
Processes touch, sound, etc.
TEN CARATIVE FACTORS
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
1. The formation of a Humanistic-altruistic system of - Watsons divides into interdependent internal and
values external variables, manipulated by the nurse in
- Which begins at an early age with the values order to provide support and protection for the
shared by parents. patient’s mental and physical health.
- The system of values is mediated by the nurse’s 9. Assistance with satisfying human needs
life experiences, learning gained, and exposure to - based on a hierarchy of needs similar to Maslow's.
the humanities. Each need is equally important for quality nursing
care and the promotion of the patient's health.
2. The installation of Faith-hope - In addition, all needs deserve to be valued and
- Which is essential to the carative and curative attended to by the nurse and patient.
processes. 10. The allowance for existential-phenomenological
- When modern science has nothing else to offer a forces
patient, a nurse can continue to use faith-hope to - which helps the nurse to reconcile and mediate
provide a sense of well-being through a belief the incongruity of viewing the patient holistically
system meaningful to the individual. while at the same time attending to the
3. The Cultivation of sensitivity to one’s self and to hierarchical ordering of needs.
othersWhich explores the need of nurses to feel an Key components of Jean Watson’s Theory
emotion as it presents itself. - focuses on the ten caritas processes, these are
- The nurses promote health and higher-level processes Watson believes the nurse must
functioning only when they form person-to-person consider and exemplify in order to be an
relationships. effectively caring nurse (Alligood & Tomey, 2010)
4. The development of a helping-trust relationship - “caritas” comes from the Greek word meaning to
- Which includes congruence, empathy, and
warmth.
- The strongest tool a nurse has is his/her mode of
communication, which establishes a rapport with
the patient, as well as caring by the nurse.
- Once na nagsabi na un pasyente about sa
sensitive information nya, ibigsabihin
pinagkakatiwalaan ka na nya.
5. The promotion and acceptance of the expression
of both positive and negative feelings
- Which need to be considered and allowed for in a
caring relationship.
- The awareness of the feelings helps the nurse cherish, to appreciate, to give special attention; it
and patient understand the behavior it causes. connotes something very fine, that indeed is
6. The systematic use of the scientific method for precious. (Medscape Nurses, 2005)
problem-solving and decision-making - Watson’s theory calls upon nurses to go beyond
- Which allows for control and prediction and procedures and task, but instead focuses on the
permits self-correction. nurse-patient relationship resulting in therapeutic
- Scientific method – it involves a process outcome and transpersonal caring process
7. The promotion of interpersonal teaching-learning (Alligood et al., 2010)
- Since the nurse should focus on the learning Caring Occasion/ Caring Moment
process as much as the teaching process. - The moment (focal point in space and time) when
- Understanding the person’s perception of the the nurse and another person come together in
situation assists the nurse to prepare a cognitive such a way that an occasion for human caring is
plan. created.
8. The provision for a supportive, protective and/or - Both persons, with their unique phenomenal fields
corrective mental, physical, socio-cultural and have the possibility to come together in a human-
spiritual environment to-human transaction.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
Watson (1999) insists that the nurse, i.e., the caregiver, - “The nurse-patient relationship is not a uniform,
also needs to be aware of her own consciousness and professionalized blueprint but rather kaleidoscope
authentic presence of being in a caring moment with of intimacy and distance in some of the most
her patient. dramatic, poignant and mundane moments of
Both the one care for and the one caring can be life.”
influenced by the caring moment through the choices - She was born on August 31, 1942 in Hampton,
and actions decided within the relationship, thereby, Virginia
influencing and becoming part of their own life history. - BSN from Pasadena College in 1964
Watson’s Metaparadigm in Nursing - MSN in 1970 and PhD in 1982 at University of
Person California
- Watson defines the person as a being-in-the- - Retired professor of University of California
world who holds three spheres of being—mind, From Novice to Expert
body, and spirit—that are influenced by the - One of the most useful frameworks for assessing
concept of self and who is unique and free to nurses' needs at different stages of professional
make choices. growth.
Caring - Proposes that expert nurses develop skills and
- a transpersonal interactive process. The self and understanding of patient care over time through a
person as transpersonal “mind-body-spirit” proper educational background as well as a
oneness. multitude of experiences.
The Dreyfus Model
Nursing care - By Stuart Dreyfus and Hubert Dreyfus
- a “way of being” rather than doing. - They develop this model to explain the skill
Healing space and environment acquisition but in line of sports (chess)
- can expand the person’s “awareness and 1. Novice
consciousness” and promote mind-body-spirit - Needs recipes, monitoring and first success.
wholeness and healing 2. Advanced Beginner
- importance of making the patient’s room a - Needs simple, controlled simulations.
soothing, healing and sacred place. 3. Competent
Health - Needs real world exposure.
- Person’s health as a subjective experience. 4. Proficient
Health also corresponds to the person’s harmony, - Needs unhindered practice and "the big picture"
or balance, within the mind body spirit, related to 5. Expert
the degree of congruence between the self as - Needs to expand knowledge and experience.
perceived Benner's Stages of Clinical Competence
- Health is a process of adapting, coping, and Novice
growing throughout life - The person has no professional background
experience of the situation he/she is involved
Summary - There is difficulty discerning between relevant
- Watson’s present definition includes caring as a and irrelevant aspects of the situation.
special way of being-in-relation with one’s self, - Beginner to profession or nurse changing area of
with others, and the broader environment. practice (Frisch, 2009)
- Such relationship requires both an intention and a - Generally, this level applies to nursing students
commitment to care for the individual. – Caritas - Must function with a clinical instructor
- In other words, the nurse has to be conscious and Advanced Beginner
engaged to care in order to connect and establish - Can note recurrent meaningful situational
a relationship with the cared-for to promote components, but not prioritize between them
health/healing. - Develops when the person can demonstrate
THE PRIMACY CARING OF MODEL FROM NOVICE TO marginally acceptable performance having coped
EXPERT NURSING MODEL with enough real situations to have pointed out by
(Patricia Benner) a mentor
Patricia Benner
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- You need help of your nurse supervisor to help - Health is defined as what can be assessed
you explain/define situations, to set priorities, and whereas well-being is the human experience of
to integrate practical knowledge health or wholeness
- Nurses functioning at this level are guided by - Well-being and being ill are understood as distinct
rules and oriented by task completion. ways of being the world.
- Read books in order to explain situations Environment/Situation
Competent - Benner uses situation rather than environment
- Begins to understand actions in terms of long- because situation conveys a social environment
range goals with social definition
- After 2-3 years in the same area of nursing the - "To be situated implies that one has a past,
nurse moves into the Competent stage present, and future and that all of these aspects…
- Is the most pivotal in clinical learning because the influence the current situation." -Dr. Benner
learner must begin to recognize patterns and Nursing
determine which elements of the situation warrant - Described as caring relationship
attention and which can be ignored - "Caring is primary because caring sets up the
- Devises new rules and reasoning procedures for possibility of giving and receiving help."
a plan while applying learned rules for action - Nursing is viewed as a caring practice whose
Proficient science is guided by the moral art and ethics of
- Perceives situations as wholes (total pictures), care and responsibility
rather than in terms of aspects - Dr. Benner understands that nursing practice as
- "The nurse possesses deep understanding of the care and study of the lived experience of
situations as they occur, less conscious planning health, illness, and disease and the relationships
is necessary, critical thinking and decision-making among the three elements
skills have developed" (Frisch, 2009) - Dependent on the first 3 paradigms
- After 3-5 years the nurse moves into the Domains of Nursing Practice
Proficient Stage 1. The helping role
- Is a qualitative leap beyond the competent - Creating climate for and establishing a
- Demonstrate a new ability to see changing commitment to healing
relevance in a situation including the recognition - Providing comfort measures and preserving
and the implementation of skilled responses to personhood in the face of pain and extreme
the situation as it evolves breakdown
Expert - Presence (being w/ the patient)
- Has intuitive grasp of the situation and zeros in on - Maximizing the patient's participation and control
the accurate region of the problem in his or her own recovery
- This stage occurs after 5 years or greater in the - Interpreting kinds of pain and selecting
same area of nursing appropriate strategies for pain management and
- The expert performer no longer relies on an control
analytic principle (rule, guideline, maxim) to - Providing comfort and communication through
connect her or his understanding of the situation touch
to an appropriate action - Providing emotional and informational support to
- Operates from a deep understanding of the total patient's families
situation - Guiding a patient through emotional and
Four Domains of Nursing Paradigm developmental change
Client/Person 2. The teaching - coaching function
- "The person is a self-interpreting being, that is the - Capturing the patient's readiness to learn (timing)
person does not come into the world predefined - Assisting patients to integrate the implications of
but gets defined in the course of living a life." -Dr. illness and recovery into their lifestyles
Benner - Eliciting and understanding the patient's
Health interpretation of his/her illness
- Dr. Benner focuses on the lived experience of - Providing an interpretation of the patient's
being healthy and being ill condition and giving a rationale for procedures
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- Making culturally avoided aspects of an illness 1. Demonstrating a clinical grasp and resource-
approachable and understandable based practice
3. The diagnostic and patient-monitoring function 2. Possessing the embodied know-how
- Detecting and documenting significant changes in 3. Seeing the big picture
patient's condition 4. Seeing the unexpected
- Anticipating breakdown and deterioration prior to Shaping our Future Nurse Leaders
explicit confirming diagnostic signs New graduate nurses are the future employee
- Anticipating problems pool
- Understanding particular demands and Job satisfaction & retention are greatly influenced
experiences of an illness by the quality of orientation and support received
- Assessing the patient's potential for wellness and by the new graduate nurse
for responding for various treatment strategies A positive experience will encourage the now
4. Effective management of rapidly changing proficient nurse to mentor novice nurses
situations "The mediocre teacher tells. The good teacher
- Skilled performing in extreme life-threatening explains. The superior teacher demonstrates. The
emergencies great teacher inspires." -William Arthur
- Rapid matching of demands and resources in
emergency situations "The utility of the concept of skill acquisition lies in helping
- Identifying and managing a patient crisis until a the teacher understand how to assist the learner in
physician assistance is available advancing to the next level" (McClure, 2005)
5. Administering and monitoring therapeutic Summary
interventions and regimens - Each step builds on the previous one as abstract
- Starting and maintaining intravenous therapy with principle are refined and expanded by experience
minimal risks and complications and the learner gains clinical expertise.
- Administering medications accurately and safety, - This theory changed the profession's
including monitoring untoward effects, reactions, understanding of what it means to be an expert,
therapeutic responses, toxicity, and placing this designation not on the nurse with the
incompatibilities most highly paid or most prestigious position, but
- Combating hazards of immobility, including on the nurse, who provided the most exquisite
preventing and intervening with skin breakdown, nursing care.
ambulating, exercising patients to maximize -
mobility and rehabilitation, and preventing UNITARY HUMAN BEINGS THOERY
respiratory complications (Martha Rogers)
- Creating a wound management strategy that
fosters healing, comfort, and appropriate drainage - she describes this in 1961 which became
6. Monitoring and ensuring the quality of health care controversial and a topic of numerous debates.
practices - During that time, it was rare that anyone in a
- Providing a back-up system to ensure safe medical profession viewed human beings as
medical and nursing care anything other than the receiver of care from as
- Assessing what can safely be omitted from or nurses and doctors.
added to medical orders - During that time, health care providers focus on a
- Getting appropriate and timely responses from rendering treatment.
physicians - Rogers insisted that a person is a unitary energy
7. Organizational work-role system in continuous mutual interaction with the
- Coordinating, ordering, and meeting multiple universal energy system.
patients’ needs and request - in other words, - Her theory, dramatically influence nursing by
setting priorities encouraging nursing to consider each person as
- Building and maintaining a therapeutic team to a whole being when planning and delivering care.
provide optimal therapy Martha E. Rogers
- Coping w/ staff shortage - May 12, 1914 – March 13, 1994 (80 years old)
Key aspects of expert nurse's practice are as follows: - American Nurse, Researcher, Theorist
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- Her landmark book, “Introduction to the Human being is considered as whole which cannot be
Theoretical Basis of Nursing” viewed as subparts.
- She began her college education to studying The life process of human is irreparable and one way
science at the University of Tennessee i.e. from birth to death.
- Receiving her nursing diploma from Knoxville Health and illness are the continuous expression of
General Hospital School of Nursing in 1936. the life process.
- She obtain her Bachelor’s degree from George The energy flows freely between the individual and
Peabody College in Nashville, Tennessee, then environment.
she pursued her various Master’s and Doctoral Human being possesses the ability to think, imagine,
degrees. sense, feel, and can use language for expression.
- She was appointed professor and Head of the Human beings have the ability to adapt according to
division of Nursing at New York University, right the new changes in the environment.
after graduating from John Hopkins School of Concepts:
Public Health were, she serves 21 years until the - abstract ideas that occur in the mind, in speech or
time that she retired in 1975. thoughts; fundamental of building blocks of
- Following her retirement, she continued to teach thoughts and beliefs; it contains 2 dimensions
at New York University and was a frequent All the human being is viewed as an integral part of
presenter at scientific conferences throughout the universe. (integral part - there is continuous mutual or
world. simultaneous interaction between human and the
- She was also actively involved in professional environmental fields)
nursing organizations and associations
Human beings and the environment have energy field,
concerned with an educations and scholarship.
nursing action is directed towards patterning and
- 1979, she became professor Emerita and
maintaining these energy fields.
continued to have active role in the development
Energy fields
of a nursing and the science of Unitary Human
- It is the inevitable part of life. Human and
beings.
environment both have energy field which is open
- In 1970, Rogers conceptual model of nursing
i.e. energy can freely flow between human and
rested on 5 basic assumptions that describes the
environment.
life process in human beings.
- It’s the fundamental unit of both the living and
- In her 1993 paradigm, Rogers postulated 4
non-living things.
building blocks for her model: Energy Fields,
- It provides a way to view people and environment
Universe of Openness, Pattern and
as irreducible wholes.
Pandimensionality.
- Continuously vary in intensity, density and extent.
- Rogers consistently updated this conceptual
Openness
model through revision of the homeodynamics
- There is no boundary or barrier that can inhibit
principle. It was that time, also that she decided to
the flow of energy between human and
change the wordings.
environment which leads to the continuous
- Originally her theory called “Science of Unitary
movement or matter of energy.
Man”, she removed the word Man and change it
- It refers to the fact that human and environmental
to Human Beings because she wanted to remove
fields are constantly exchanging their energies.
the concept of gender.
- In nursing, anything and everything can affect our
- She was the first to promote gender equality.
clients’ condition.
- She emphasizes that our care for clients should
Pattern
be Humanistic and Humanitarian in nature.
- The distinguishing character of the energy fields.
Nursing should be directed towards the unitary
- Single wave, it is an abstraction and gives identity
human and its concerned with the nature and
to field.
direction of the human development.
- The nature of the pattern changes continuously
Assumptions:
and innovatively, and these changes give identity
- beliefs and values that use to describe the
to energy field. Each human field pattern is
foundation of nursing theory.
unique.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- There have pragmatic and imaginative patients. Rogers’ Metaparadigm in Nursing
Pragmatic – realistic patients; Imaginative – they Person
think out of the box - A unitary human being is open system which
Pandimensional continuously interact with environment
- Undeviating field which is not constricted by - A person cannot be viewed as parts, it should be
space or time, it is and infinite domain without considered as a whole.
boundary. Environment
- Spaceless and timeless reality. - It includes the entire energy field other than a
- Parameters that human used in language to person.
describe events are arbitrary and the present are - These energy fields are irreducible, not limited by
relatives. There is no temporal ordering of lives. space and time, identified by it pattern and
Principle of Homeodynamics organization.
- The balance between the dynamic life process - It is interconnected with everything that happens
and environment. to us.
- These principles help to view human as unitary Health
human being - It is determined by the interaction between energy
- The three separate principles are integrality, fields i.e. human and environment.
resonancy and heliecy. - Bad interaction or misplacing of the energy leads
to illness.
Principles of Integrality - As an expression of life process, it is the
- Energy fields are dynamic and constantly interact characteristics and behaviors coming from the
with the human and environment, which affects mutual simultaneous interaction of the human and
our environment and vice versa. environment.
- Which meditation and humor works to produce a Nursing
positive environment. - Both science and art.
- In this model, the role of the nurse is to serve - It constantly maintains the energy fields which is
people. conducive for patient.
- Rogers also proposes noninvasive modalities for - Nursing actions directs the interaction of person
nursing. Such as Therapeutic touch. Being a and environment to maximize health potential.
nurse doesn’t mean that we just need to carry out Clinical Practice:
doctors’ order, we have our own treatment Nursing action is always focused on unitary human
modalities and those are noninvasive. being and change the energy field between human
Principle of Resonancy and environment.
- an ordered arrangement of rhythm characterizing Nursing interventions include all the noninvasive
both human field and environmental field. actions such as guided imaginary, humor, therapeutic
- Constant change in the way or pattern of the touch, music etc. which are used to increase the
energy field from a lower to higher frequency. potential of human being.
- This movement of energy can be made by human Nursing Education:
touch, guided imagery activities, drawing, Emphasis should be given on the understanding of
storytelling and other active use of imagination. the patient and self, energy field and environment.
Principle of Heliecy Training should lay more focus on teaching non-
- Any minute change in the environment which invasive modalities such as therapeutic touch,
leads to ripple effect i.e. results in a larger change meditation, humor, regular in-service education
in other field. programmer etc.
- This change is constant, unpredictable and there Nursing process to according to SUBH:
are many factors which mutually interact and 1. Pattern appraisal
cause the change. - It is an inclusive assessment of human and
- The human environment field is dynamic, its an environment energy fields, its organization of
open system in which change continuous due to energy field, and identification of areas of
the constant interchange between the human and dissonance.
environment.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- Nurses validate the entire appraisal along with the where she receives her diploma of nursing in the
client. early 1930s.
2. Mutual patterning - She receives her BS in Nursing Education from
- It is the proper patterning of the energy fields the Catholic University of America in 1939. And
between the human and environment. her Masters of science in nursing from the same
- It is the mutual interaction between the client and university in 1946.
nurse. - She earned several Honorary Doctorate degrees.
- Patterning can be done by suggesting the various She was given Honorary Doctorates of Science
alternatives, educating, empowering, encouraging from both Georgetown University in 1976 and
etc. depending on the client’s condition and Incarnate Word College in 1980. She was given
needs. an Honorary Doctorate of Humane Letters from
3. Evaluation Illinois Wesleyan University in 1988, and a
- Done by repeating the pattern appraisal after the Doctorate Honoris Causae from the University of
mutual patterning to determine the extents of Missouri in Columbia in 1998.
dissonance and harmony. Assumptions:
Generality: People should be self-reliant, and responsible for their
- the uses on non-invasive modalities are very care, as well as others in their family who need care.
useful and important to nursing even today. People are distinct individuals.
- SUBH is the foundation of many theories and it Nursing is a form of action. It is an interaction
can be applied in a variety of setting and all between two or more people.
sphere of life. Successfully meeting universal and development self-
Summary: care requisites is an important component of primary
- In this model, the role of the nurse is to serve care prevention and ill health.
people. A person’s knowledge of potential health problems is
- Rogers also proposes noninvasive modalities for needed for promoting self-care behaviors.
nursing, such as therapeutic touch, humor, music, Self-care and dependent care are behaviors learned
meditation and guided imagery, and even the use within a socio-cultural context.
of color. Central Theme: nursing and self-care activities
- The interventions of nurses are meant to Orem’s Metaparadigm in Nursing
coordinate the rhythm between the human and Person
environmental fields, help the patient in the - Humans with physical, psychological,
process of change, and to help patients move interpersonal and social components, meeting
toward better health. self-care needs through learned behavior.
- The practice of nursing, according to Rogers, Man as an integrated Whole
should be focused on pain management, and - She further describes man as a logical organism
supportive psychotherapy for rehabilitation. with rational powers.
- As a biological organism, man exists and
SELF-CARE DEFICIT THEORY responds both as organism and object in an
(Dorothea Orem) environment with physical and biological
- Orem theory define nursing as the act of assisting components.
others in the provision and management of self- Environment
care to maintain or improve human functioning at - The modern society’s values and expectations.
home level of effectiveness. - Encompasses elements external to man.
Dorothea Elizabeth Orem - She considered man and environment as an
- July 15, 1914 – June 22, 2007 (92 years old) integrated system. Environment conditions
- From Baltimore, Maryland. conductive to development include:
- She was considered as one of the American 1. Opportunities to be helped by being with
foremost nursing theorists who developed of the other persons or groups where care is
self-care deficit nursing theory. offered.
- She began her nursing career at Providence 2. Available opportunities for solitude and
Hospital School of Nursing in Washington, D.C. companionship.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
3. Provision of help for personal and group Dorothy E. Johnson
concerns without limiting individual - was one of the greatest nursing theorists who
decisions and personal pursuits. developed the “Behavioral System Model.”
4. Shared respect, belief, and trust. - Johnson has noted that her theory evolved from
5. Recognition and fostering of philosophical ideas, theory and research, her
developmental potential. clinical background, and many years of thought,
Health discussions, and writing.
- Wellness is the integrity of the individual, illness - Johnson’s Behavioral System Model (JBSM) was
results in the person’s inability to maintain self- heavily influenced by Florence Nightingale’s book,
care. “Notes on Nursing”
- A state of wholeness or integrity of the individual Education:
human being, his parts and his modes of 1942, graduated BSN from Vanderbilt University
functioning. School of Nursing, Nashville, Tennessee
- The responsibility of a total society and all its - Top student in her class
members. - Received the Prestigious Vanderbilt Founder’s
Nursing Medal
- a service, an art and a technology. 1948, graduated master’s degree in public health
- The giving of direct assistance to persons who from Harvard University in Boston
are unable to meet their own self-care needs, Career and Appointments:
developed through nursing education and 1943-1944
experiences. - Staff nurse at the Chatham- Savannah Health
- As a community service: nursing is a service of Council
deliberately selected and performed actions to - Instructor and an assistant professor in
assists individuals or groups to maintain self-care, pediatric nursing at Vanderbilt University School
including structural integrity, functioning and of Nursing.
development. 1949- 1978
- As an interpersonal process: since it requires the - Assistant professor of pediatric nursing, an
social interaction of a nurse with a patient and associate professor of nursing, and a professor
involves transaction between them. of nursing at the University of California, Los
Theory of Nursing system: Angeles.
Nursing system
- the approaches nurses use to assist patient with Behavioral System Model
deficits in self-care due to a condition of health. - a model of nursing care that advocates the fostering
Wholly compensatory system of efficient and effective behavioral functioning in
- The patient has no active role in the performance the patient to prevent illness.
of his care. The nurse acts for the patient. - The patient is identified as a behavioral system
Partly compensatory system composed of seven behavioral subsystems:
- Both nurse and patient perform care measures affiliative, dependency, ingestive, eliminative,
requiring manipulative tasks or ambulation. sexual, aggressive, and achievement.
Supportive- educative system The subsystem of Behavior
- The patient is able to perform, or can learn to - parts of the behavioral system.
perform, required measures of therapeutic self- - It carries out specialized task/function needed to
care but cannot do so without assistance. maintain the integrity of the whole system
Moving towards… - It has a set of behavioral responses that are
Quality developed through motivation, experience and
Safe learning
Nursing 7 Subsystems of the Behavior System Model:
Care 1. Attachment or affiliative subsystem
2. Dependency subsystem
BEHAVIORAL SYSTEM MODEL 3. Ingestive subsystem
(Dorothy Johnson) 4. Eliminative subsystem
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
5. Sexual subsystem - Balance or steady state in maintaining balance
6. Aggressive- protective subsystem within an acceptable range.
7. Achievement subsystem 8. Stressor
Johnson’s Metaparadigm in Nursing - A stimulus from the internal or external world that
Person results in stress or instability
- Defined as behavioral system that strives to make 9. Structure
continual adjustments to achieve, maintain, or - The parts of the system that make up the whole
regain balance to the steady state that is adaptation. 10. System
Environment - That which functions as a whole by virtue of
- is not directly defined, but it is implied to include all organized independent interaction of its parts
elements of the surroundings of the human system 11. Subsystem
and includes interior stressors. - A minisystem maintained in relationship to the
Health entire system when it or the environment is not
- is seen as the opposite of illness, and Johnson disturbed.
defines it as “some degree of regularity and 12. Tension
constancy in behavior, the behavioral system - The system’s adjustment to demands, change or
reflects adjustments and adaptations that are growth, or to actual disruptions
successful in some way and to some degree… 13. Variables
adaptation is functionally efficient and effective. - Factors outside the system that influence the
Nursing system’s behavior, but which the system lacks
- is seen as “an external regulatory force which acts power to change
to preserve the organization and integration of the ADAPTIVE MODEL OF NURSING
patient’s behavior at an optimal level under those (Sr. Callista Roy)
conditions in which the behavior constitutes a threat Sister Callista L. Roy
to physical or social health, or in which illness is - Born October 14, 1939
found.” - She is known for her groundbreaking work in
Three functional requirements of Human: creating the Adaptation Model of Nursing.
1. To be protected from noxious influences with which - belongs to the Sisters of St. Joseph of Carondelet.
the person cannot cope Education:
2. To be nurtured though the input of supplies from the 1963, Graduated Bachelor of Arts Major in Nursing
environment from Mount Saint Mary’s College in Los Angeles
3. To be stimulated to enhance growth and prevent 1966, graduated Master’s degree in nursing from
stagnation. the University of California
Concepts in Behavioral System Theory: 1973, Earned her master’s degree in sociology,
1. Behavioral system University of California
- Man is a system that indicates the state of the 1977, Received her doctorate degree in sociology,
system through behaviors University of California
2. Boundaries Career:
- The point that differentiates the interior of the Worked as a Pediatric nurse
system from the exterior. Associate professor and chairperson of the
3. Function Department of Nursing at Mount Saint Mary’s
- Consequences or purposes of actions College until 1982
4. Functional requirements Professor, Mount Saint Mary’s College and the
- Input that the system must receive to survive and University of Portland in 1983
develop
Clinical Nurse Scholar in Neuroscience, she was a
5. Homeostasis
Robert Wood Johnson postdoctoral fellow at the
- Process of maintaining stability
University of California, San Francisco from 1983 to
6. Instability
1985
- State in which the system output of energy depletes
Resident Nurse Theorist, at Boston College School
the energy needed to maintain stability.
of Nursing 1987- present
7. Stability
Adaptation Model of Nursing
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- The RAM focuses on the inter relatedness of four 3. Residual Stimuli
adaptive systems - Factors that may be affecting behavior but whose
- It focuses on persons coping(adaptative)abilities in efforts are not validated.
response to constantly to changing environment
(Lopes, Pagliuca, Araujo,2006) Roy’s metaparadigm in nursing
- Nursing can promote effective coping by asking” Person
How can I modify this patient’s environment to - Human systems have thinking and feeling
facilitate his adaptation (Chitty & Black, 2011) capacities, rooted in consciousness and meaning,
4 Adaptive Modes: by which they adjust effectively to changes in the
1. Psychological Mechanism environment and, in turn, affect the environment.
- Physical and chemical process involved in the Environment
function and activities of living organism. - The conditions, circumstances and influences
- The basic need of this mode is composed of the surrounding and affecting the development and
needs associated with oxygenation, nutrition, behavior of persons or groups, with particular
elimination, activity and rest, and protection. consideration of mutuality of person and health
- The complex processes of this mode are resources that includes focal, contextual and
associated with the senses, fluid and electrolytes, residual stimuli.
neurologic function, and endocrine function. Health
2. Self-concept - Health is not freedom from the inevitability of
- The goal of coping is to have a sense of unity, death, disease, unhappiness and stress but the
meaning the purposefulness in the universe, as ability to cope with them in a competent way.
well as a sense of identity integrity Nursing
- This includes body image and self-ides. - The goal of nursing is the promotion of adaptation
3. Role-function mode for individuals and groups in each of the four
- Focuses on the primary, secondary and tertiary adaptive modes, thus contributing to health,
roles that a person occupies in society, and quality of life, and dying with dignity.
knowing where he or she stands as a member of
society. NEUMAN SYSTEMS MODEL
4. Interdependence mode (Betty Neuman)
- Focuses on attaining relational integrity through Betty Neuman
the giving the receiving of love, respect and value. - 1924 – present
- This is achieved with effective communication - 1947, she received her RN Diploma from Peoples
and relations Hospital school of Nursing, Akron Ohio.
Subsystem (internal process) - Hospital nurse and head nurse at Los Angeles
Regulator County General Hospital, school nurse, industrial
- a basic type of adaptive process that responds nurse, and clinical instructor at the University of
automatically through neural, chemical, and Southern California Medical Center, Los Angeles.
endocrine coping channels. - 1957, she received a baccalaureate degree in
Cognator public health and psychology with honors. Amidst
- a major coping process involving four cognitive her hectic life as a nurse, she also managed to work
motive channels: perceptual and information as a fashion model and learned to fly a plane.
processing, learning, judgment, and emotion. - 1966, earned master’s degree in mental health,
Types of Stimuli public health consultation in 1966 from the
1. Focal Stimulus University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA)
- The degree of change or stimulus more Neuman’s systems model
immediately confronting the person and the one - Views the client as an open system that responds to
to which the person must make adaptive stressors in the environment.
response. - The client variables are physiological, sociocultural,
2. Contextual Stimuli developmental, and spiritual. The client system
- Present to contribute to the behavior caused or consists of a basic or core structure that is
precipitated by the focal stimuli. protected by lines of resistance.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- The usual level of health is identified as the normal - A system in which there is a continuous flow of
line of defense that is protected by a flexible line of input and process, output and feedback. It is a
defense. system of organized complexity, where all elements
are in interaction.
Basic structure and Energy Resources
- The basic structure, or central core, is made up of
Major concepts of Neuman Systems Model: those basic survival factors common to the species.
Person - These factors include the system variables, genetic
- Human being is viewed as an open system that features, and strengths and weaknesses of the
interacts with both internal and external system parts.
environment forces or stressors. Client Variables:
- The human is in constant change, moving toward a Physiological variable
dynamic state of system stability or toward illness of - refers to the structure and functions of the body.
varying degrees. Psychological variable
Environment - refers to mental processes and relationships.
- a vital arena that is germane to the system and its Sociocultural variable
function. - refers to system functions that relate to social and
- The environment may be viewed as all factors that cultural expectations and activities.
affect and are affected by the system. Developmental variable
- In Neuman Systems Model identifies three relevant - refers to those processes related to development
environments: (1) internal, (2) external, and (3) over the lifespan.
created. Spiritual variable
a) The internal environment exists within the client - refers to the influence of spiritual beliefs.
system. All forces and interactive influences that Core
are solely within boundaries of the client system - The heart of the client system
make up this environment. - Is the survival factor, source of energy
b) The external environment exists outside the client - Survival factors
system. 1. Flexible Line of Defense
c) The created environment is unconsciously - A protective accordion-like mechanism that
developed and is used by the client to support surrounds and protects the normal line of defense
protective coping. from invasion by stressors.
Health 2. Normal Line of Defense
- defined as the condition or degree of system - An adaptational level of health developed over
stability and is viewed as a continuum from time and considered normal for a particular
wellness to illness. individual client or system
- When system needs are met, optimal wellness - it becomes a standard for wellness-deviance
exists. When needs are not satisfied, illness exists. determination.
When the energy needed to support life is not 3. Lines of Defense
available, death occurs. - Protection factors activated when stressors have
Nursing penetrated the normal line of defense, causing a
- define the appropriate action in situations that are reaction symptomatology.
stress-related or in relation to possible reactions of Stressor
the client or client system to stressors. - any phenomenon that might penetrate both the
- Nursing interventions are aimed at helping the flexible and normal lines of defense, resulting in
system adapt or adjust and to retain, restore, or either a positive or negative outcome.
maintain some degree of stability between and a) Intrapersonal stressors are those that occur within
among the client system variables and the client system boundary and correlate with the
environmental stressors with a focus on conserving internal environment.
energy. b) Interpersonal stressors occur outside the client
Open system system boundary, are proximal to the system, and
have an impact on the system.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
c) Extrapersonal stressors also occur outside the - She focused on spousal communication and
client system boundaries but are at a greater interaction in effective or ineffective number of
distance from the system that are interpersonal children in families.
stressors. An example is social policy. - Focused on people who do not make healthy
Concepts of levels of prevention transitions and the discovery of interventions to
1. Primary prevention facilitate healthy transitions.
- It includes health promotion and maintenance of Transition Theory
wellness. - “to help people go through healthy transitions,
2. Secondary prevention including mastery of behaviors, sentiments, cues,
- Focuses on strengthening the internal lines of and symbols associated with new roles and
resistance and, thus, protects the basic structure identities and non-problematic processes, to
through appropriate treatment of symptoms. enhance healthy outcomes”
3. Tertiary prevention - leads to development of nursing therapeutics that
- To maintain wellness or protect the client system are congruent with the unique experience of
reconstitution through supporting existing clients and their families in transition, thus
strengths and continuing to preserve energy. promoting healthy responses in transition.
Nursing Process
1. Assess the stressor and patient’s response to the
stressor.
2. Identify nursing diagnosis
3. Plan patient centered care
4. Implement interventions
5. Evaluate the patient’s response Nature of Transition
6. Determine if the stressor is resolved. Types Patterns Properties
4 goals of Nursing Developmental Single Awareness
To assist the patient:
Situational Multiple Engagement
- Whose behavior is proportional to social demands.
Health/ illness Sequential Change and
- Who is able to modify his behavior in ways that it
difference
supports biological imperatives.
Organizational Simultaneous Transition time
- Who is able to benefit to the fullest extent during
span
illness from the physician’s knowledge and skill.
Related Critical points
- Whose behavior does not give evidence of
and events
unnecessary trauma as a consequence of illness
Unrelated
Grand and Middle-ranged Theories Meleis’ Metaparadigm in Nursing
NURSING
TRANSITION THEORY - Nurses are primary caregivers of clients and their
(Afaf Ibrahim Meleis) families who are undergoing transitions.
Afaf Ibrahim Meleis - Transition both result in change and are the result
- born in Alexandria, Egypt. of change.
- University of Alexandria in Egypt – BSN PERSON
- University of California – MS in Nursing, PhD - Transition involve a process of movement and
- a prominent nurse sociologist, a sought-after changes in fundamental life patterns.
theorist, researcher and speaker. - Transition cause changes in identities, roles,
- her research focused on people who do not make relationships, abilities and patterns of behavior.
healthy transitions and the discovery of HEALTH
interventions to facilitate healthy transitions. - Transitions are complex and multidimensional.
- Her theory was the result of her masters and PhD Patterns of multiplicity and complexity.
research on the topics phenomena of planning - All transitions are characterized by flow and
pregnancy and mastering parenting roles. movement over time.
- mastery, ability to assume new roles.
ENVIRONMENT
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
- Vulnerability is related to transition experiences, help people of a particular culture to retain and/or
interactions, and environmental conditions that preserve relevant care values so that they can
expose individuals to potential damage, maintain their well-being, recover from illness, or
problematic or extended recovery or delayed or
face handicaps and/or death.
unhealthy coping.
- CULTURAL CARE ACCOMMODATION
TRANSCULTURAL NURSING THEORY also known as NEGOTIATION, includes those
(Madeleine M. Leininger) assistive, supportive, facilitative, or enabling
Madeleine M. Leininger creative professional actions and decisions that
- founder of transcultural nursing and leader in help people of a designated culture to adapt to or
transcultural nursing and human care theory. negotiate with others for a beneficial or satisfying
- the first professional nurse with graduate
health outcome with professional care providers.
preparation in nursing to hold a doctorate in
cultural and social anthropology. - CULTURE CARE REPATTERNING OR
- St. Anthony School of Nursing – bachelor’s RESTRUCTURING includes those assistive,
degree supporting, facilitative, or enabling professional
- Catholic University in America – master’s degree actions and decisions that help a clients reorder,
in psychiatric nursing change, or greatly modify their lifeways for new,
- University of Washington – doctoral study on different, and beneficial health care pattern while
cultural, social, and psychological anthropology.
respecting the clients cultural values and beliefs
Transcultural Nursing theory (Culture Care Theory)
- Through her observations while working as a and still providing a beneficial or healthier
nurse, Madeleine Leininger identified a lack of lifeway than before the changes were
cultural and care knowledge as the missing coestablished with the clients. (Leininger, 1991
component to a nurse’s understanding of the - MAJOR CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS
many variations required in patient care to - HUMAN CARE AND CARING- refers to
support compliance, healing, and wellness.
the abstract and manifest phenomena with
Main Focus: for the nursing care to fit with or have
beneficial meaning and health outcomes for people of expressions of assistive, supportive, enabling,
different or similar cultural backgrounds and facilitating ways to help self or others with
The Sunrise Enabler: comprehensively guide and to evident or anticipated needs to improve health, a
make culturally congruent care, decisions and actions. human condition, or lifeways, or to face
Major Assumptions: disabilities or dying.
Universality of care - CULTURE- refers to patterned life ways,
- reflects the common nature of human beings and
values, beliefs, norms, symbols, and practices of
humanity
Diversity of care individuals, groups, or institutions that are learned,
- reflects the discovered variability and unique shared, and usually transmitted from one
features of human beings. generation to another.
Care - CULTURE CARE- refers to the
- essence and the central dominant, distinct and synthesized and culturally constituted assistive,
unifying focus of nursing. No curing without caring. supportive, enabling, or facilitative caring acts
Transcultural nursing
toward self or others focused on evident or
- is a discipline with a body of knowledge and
practices to attain and maintain the goal of anticipated needs for the client’s health or well-
culturally congruent care for health and well-being. being, or to face disabilities, death, or other
THREE MODES OF NURSING CARE AND DECISION human conditions.
- CULTURAL CARE PRESERVATION is - CULTURE CARE DIVERSITY refers to
also known as MAINTENANCE and includes cultural variability or differences in care beliefs,
those assistive, supporting, facilitative, or meanings, patterns, values, symbols, and
enabling professional actions and decisions that
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
lifeways within and between cultures and human The goal of nursing care is to provide care
beings. congruent with cultural values, beliefs, and
- CULTURECARE UNIVERSALITY refers practices.
to commonalities or similar culturally based care Nurses can actually observe on how a patient’s
cultural background is related to his or her health,
meanings (“truths”), patterns, values, symbols,
and use that knowledge to create a nursing plan
and lifeways reflecting care as a universal that will help the patient get healthy quickly while
humanity. still being sensitive to his or her cultural
- EMIC- refers to local, indigenous, or the background.
insider’s views and values about a phenomenon
- ETIC - refers to the outsider’s or more HEALTH AS EXPANDING CONSCIOUSNESS
universal views and values about a phenomenon. (Margaret A. Newman)
Margaret A. Newman
- TRANSCULTURAL NURSING- refers to
- born October 10, 1933 in Memphis, Tennessee.
a formal area of humanistic and scientific - She presented her theory of health in 1978 –
knowledge and practices focused on holistic researching the relationship of movement, time
Culture Care (caring) phenomena and and consciousness and development of her
competencies to assist individuals or groups to theory of health as expanding consciousness.
maintain or regain their health (or wellbeing) and - illness reflected the life patterns of the person and
to deal with disabilities, dying, or other human that what was needed was the recognition of that
pattern and acceptance of it for what it meant to
conditions in culturally congruent and beneficial that person.
ways. - Theory of Development in Nursing, Health as
- CULTURE CARE PRESERVATION Expanding Consciousness”
OR MAINTENANCE- refers to those assistive, - “Transforming Presence: The Difference that
supportive, facilitative, or enabling professional Makes Nursing Science Quarterly”
actions and decisions that help people of a Consciousness
- is both the informational capacity of the system &
particular culture to retain or maintain meaningful
the ability of the systems & the ability of the
care values and lifeways for their well-being, to system to interact with its environment.
recover from illness, or to deal with handicaps or Three patterns and manifestation of a whole:
dying. 1. Time
- CULTURALLY COMPETENT 2. Movement
NURSING CARE - refers to the explicit use of 3. Space
culturally based care and health knowledge in Newman’s Metaparadigm in Nursing
Nursing
sensitive, creative, and meaningful ways to fit the
- The focus of nursing is the primacy of relationship
general lifeways and needs of individuals or both nurse-client relationship & relationships
groups for beneficial and meaningful health and within client’s lives.
well-being, or to face illness, disabilities, or death. Person
- CROSS-CULTURAL NURSING - refers - client, individual, patient, human-being
to nurses using applied or medical - Clients are viewed as participants in the process.
anthropological concepts - Individuals are identified by their individual
patterns of consciousness.
- ETHNONURSING- Is a study of nursing Environment
care beliefs, values and practices as cognitively - A larger whole which contains the consciousness
perceived and known by a designated culture of the individual.
through their direct experience, beliefs and value - Client & environment are viewed as a unitary
system evolving pattern.
Health
Summary: - The pattern of the whole.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
Summary: - Configuring rhythmical patterns is the revealing-
- The theory asserts that every person in every concealing and enabling-limiting of connecting-
situation, no matter how disordered and hopeless it separating
may seem, is part of the universal process of - Cotranscending with possible is the powering and
expanding consciousness – a process of becoming originating of transforming
more of oneself, of finding greater meaning in life, Transcendence is:
and of reaching new dimensions of connectedness - About change and positivity
with other people and the world. - To believe one thing or another
- To go in one direction or another
Parse’s Metaparadigm in Nursing
THEORY OF HUMANBECOMING Nursing
(Rosemarie Rizzo Parse) - Nursing as a discipline will enjoy the recognition
Rosemarie Rizzo Parse of having a unique knowledge base & the
- a founder & editor of Nursing Science Quarterly & profession will be distinct from Medicine.
the President of Discovery International. - People / client will actually seek nurses for
- The assumptions & principles of human becoming nursing care, not medical diagnosis.
are: Environment, Person, Health
Incarnate a deep concern for the delicate - viewed as Humanuniverse, Humanbecoming and
sentiments of being human. Living Quality
Shows a profound recognition of human Summary:
freedom. - Parse’s Theory of Humanbecoming is a vital way
Shows a profound recognition of human to develop an effective relationship with your
dignity. patient especially given the short period of time
Awards: you are with them. The humanbecoming theory
- The Martha E. Rogers Golden Slinky Award develops trust and mutual understanding of care;
- New York Times Nurse Educator of the Year relieves stress and facilities healing all of which
Award are the foundation holistic care and nursing.
- 2012 Medal of Honor at the University of Lisbon Margaret A. Newman The Theory of Expanding
in Portugal Consciousness
Principle 1: Structing meaning is the imaging and valuing Newman (October 10, 1933 - December 18, 2018)
of language. was an American nurse, university professor and
Principle 2: configuring rhythmical patterns is the nursing theorist. She authored the theory of health as
revealing-concealing and enabling limiting of connecting expanding consciousness, which was influenced by
separating. earlier theoretical work by Martha E. Rogers, one of
Principle 3: cotranscending with possible is the powering her mentors from graduate school.
and originating of transforming. Description of the Theory
Squares: powering emerges with the revealing-concealing The theory of health as expanding consciousness
of imaging. stems from Rogers' theory of unitary human
Ovals: originating emerges with the enabling-limiting of beings. The theory of health as expanding
valuing. consciousness was stimulated by concern for
Triangles: transforming emerges with the languaging of those for whom health as the absence of disease
connecting-separating. or disability is not possible, (Newman, 2010).
“The theory of health as expanding
Humanbecoming Theory consciousness (HEC) was stimulated by concern
Three principles/ major assumptions for those for whom health as the absence of
- Structuring meaning is the imaging and valuing of disease or disability is not possible.
languaging The theory has progressed to include the health
- Meaning is borne in the messages that person of all persons regardless of the presence or
give & take with others in Speaking, Moving, absence of disease
Silence, & Stillness. The theory asserts that every person in every
situation, no matter how disordered and hopeless
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
it may seem, is part of the universal process of ■ Hildegard E. Peplau has been described as the
expanding consciousness mother of psychiatric nursing because her
Humans are open to the whole energy system of theoretical and clinical work led to the
the universe and constantly interacting with the development of the distinct specialty field of
energy. psychiatric nursing
Newman also redefines nursing according to her MAJOR CONCEPTS
nursing is the process of recognizing the ■ The theory explains the purpose of nursing to
individual in relation to environment and it is the help others identify there difficulties
process of understanding of consciousness ■ Nurses should apply principles of human relations
Humans are constantly changing through time to their problem that arise at all level of
and space and it shows unique pattern of reality experience
MAJOR ASSUMPTIONS ■ Nursing itself is therapeutic, and that healing is an
Health encompasses condition, described art, assisting an individual who is sick
as illness or pathology ■ It explain the phases of Interpersonal Process.
These pathological conditions maybe ■ Hildegard Peplau’s theory emphasized the nurse-
considered a total pattern of the individual client relationship as the foundation of nursing
The pattern of the individual manifest practice.
itself as pathology is primary and exist ■ She form an interpersonal model emphasizing the
prior to structural or functional changes need for a partnership between nurse and client
Removal of the pathology will not change as passively receiving treatment and the nurse
the pattern of the individual passively acting out doctor’s orders.
Removal of the pathology will not change PHASE IN NURSE PATIENT INTERACTION
the pattern of the individual ■ Orientation Phase.
If becoming ill is the only way the ■ Identification Phase
individual’s pattern can manifest, then ■ Exploitation Phase.
that is the health for that person ■ Resolution Phase.
Health is an expansion of consciousness PEPLAU METAPARADIGM
Nursing Paradigm ■ Person, which is a developing organism that tries
Nursing. to reduce anxiety caused by needs
The focus of nursing is the primacy of relationship ■ Environment, which consists of existing forces
both nurse-client relationship & relationships within client’s outside of the person, and put in the context of
lives. culture
Person. ■ Health, which is a word symbol that implies
Client, individual, patient, human-being, Clients forward movement of personality
are viewed as participants in the process. Individuals are ■ Nursing, which is a significant therapeutic
identified by their individual patterns of consciousness. interpersonal process that functions cooperatively
Environment. with other human process that make health
A larger whole which contains the consciousness possible for individuals in communities.
of the individual. Client & environment are viewed as a APPLICATION OF THEORY IN NURSING PRACTICE,
unitary evolving pattern. Person & environment are not RESEARCH
key process. NURSING PRACTICE RESEARCH
Health • Focuses on the • It is used to develop
is the pattern of the whole. interpersonal and test a nursing
Processes and intervention
THEORY OF INTERPERSONAL RELATIONS therapeutic framework for
relationship working with
■ Hildegard Peplau was born on September 1, • It requires the anxious patients.
1909. She was raised in Pennsylvania by her nurse to attend to Students develops
parents of German descent, Gustav and Otyllie interpersonal competency at the
Peplau processes that beginning of
occurs between the interpersonal
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
nurse and client relationship set mutual goal act to achieve these goals it is the
• Interpersonal basic assumption of Nursing Process
process is the ■ Each human being perceives the world as a total
maturing force for person in making transaction with individual and
personality things in the environment
IMOGENE KING – GOAL ATTAINMENT THEORY NURSE PATIENT TRANSACTION MODEL
■ Imogene King Conceptual Framework emphasizes ■ Action is a means of behavior or activities that are
the importance of interaction between the nurse towards the accomplishments of certain act. It is
and patients both physical and mental.
■ Interaction is an open system which is in constant ■ Reaction is a form of reacting or a response to a
interaction with the environmental factors certain stimuli.
■ The 3 systems are Personal, Interpersonal, Social ■ Interaction is any situation wherein the nurse relates
Systems and deals with a clientele or patient.
KINGS OPEN SYSTEM FRAMEWORK ■ Transaction is a unique observable in which human
■ Nursing Focus is the care of human being being communicate with the environment
■ Nursing Goal is the health of the individual and METAPARADIGM
health care for the group ■ Person existing in an open system who makes
■ Human Beings are open system in constant choices and select alternative action
interaction with the environment ■ Health as continuous adjustment to stress in the
INTERACTING SYSTEMS IN THE THEORY OF GOAL internal and external environment
ATTAINMENT ■ Environment as the process of balance involving
■ Personal System internal ad external interactions inside the social
– Perception system
– Self ■ Nursing is an observable behavior found in the
– Growth and Development health care systems in society”. The goal of
– Body Image nursing “is to help individuals maintain their health
– Time so they can function in their roles”
– Space SIGNIFICANCE IN NURSING PRACTICE, EDUCATION
■ Interpersonal system AND RESEARCH
– How the nurse interrelates with a co- Nursing Practice Education Research
worker or patient, particularly in a nurse- Individualize It is used in It is
patient relationship d the plans curriculum design
■ Interaction of care while design in and
■ Communication encouraging nursing conduct
■ Transaction active programs ed to
■ Role participation It provides a impleme
■ Stress from clients systematic nt this
■ Social system The means of system
– An organized system of social role, profession viewing in
behavior and practices of nursing nursing as hospital,
■ Organization function profession, ambulat
■ Authority through an organize ory,
■ Power individuals body of commun
■ Status and groups knowledge ity and
■ Decision Making within the and home
INTERACTING SYSTEMS IN THE THEORY OF GOAL environment clarifying care
ATTAINMENT nursing as nursing
ASSUMPTIONS discipline
■ Basic Assumptions of goal attainment theory is that
the nurse and patient communicate information,
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
THE THEORY OF NURSING AS CARING: A MODEL – The nature of relationship is transformed
FOR TRANSFORMING PRACTICE through caring.
■ Background of the Theorist ■ NURSING
■ Anne Boykin – Kaukauna, Wisconsin – Six: Nursing is Both a Discipline and a
– Alverno College in Milwaukee, Wisconsin Profession
in 1966 (Nursing) – Nursing is an exquisitely interwoven unity
– Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia of aspects of the discipline and
(Masters) profession of nursing.
– Vanderbilt University in Nashville,
Tennesee (Doctorate) NOLA PENDER: HEALTH PROMOTION MODEL
– currently the Director of Nursing at
Florida Atlantic University. ■ Nola Pender was born on August 16, 1941, in
■ Savina O. Schoenhoffer Lansing, Michigan to parents who advocated
– Wichita State University – (Nursing, education for women.
Masters) ■ Her first encounter with the nursing profession was
– Kansas State University – PhD when she was 7 years old and witnessed the care
– 1990 – cofounded – Nightingale Songs – given to her hospitalized aunt by nurses.
beauty of nursing in poetry and prose. ■ This situation led her to the desire to care for other
– co authored with Boykin people and her goal was to help people care for
– serves as Professor of Nursing and themselves.
Ethics Advisory Committee at the ■ The Health Promotion Model was designed to be a
University of Mississippi Medical Center. “complementary counterpart to models of health
DANCE OF A CARING PERSON protection.”
a visual representation of the theoretical assertion ■ It develops to incorporate behaviors for improving
that lived caring between the nurse and the nursed health and applies across the life span.
expresses underlying relationships. ■ The purpose is to assist nurses in knowing and
understanding the major determinants of health
SIX MAJOR ASSUMPTIONS behaviors as a foundation for behavioral
PERSON counseling to promote well-being and healthy
One: Persons Are Caring by Virtue of Their lifestyles.
Humanness CONCEPT HEALTH PROMOTION MODEL
- sets forth the ontological and ethical bases on ■ Health promotion
which the theory is grounded. Person – each ■ Health protection
person throughout his life grows in the capacity to ■ Individual characteristics and experiences
express caring. ■ Behavior-specific cognitions and affect
Two: Person Are Whole and Complete in the Moment ■ Behavioral outcomes
- being complete in the moment signifies that there SUB CONCEPT OF THE HEALTH PROMOTION
is no insufficiency, no brokenness, and no MODEL
absence of something. ■ Personal Factors (biological, psychological, and
Three: Person Live Caring, Moment to Moment socio-cultural)
- caring is a lifetime process that is lived moment to ■ Perceived benefit of action
moment and is constantly unfolding. ■ Perceived barrier to action
HEALTH ■ Perceived self efficacy
Four: Personhood is Living Life Grounded In Caring. ■ Activity related Affect
– The fullness of being human is expressed ■ Interpersonal Influence
in living-caring uniquely day to day. ■ Situational Influences
■ HEALTH BEHAVIORAL OUTCOME
– Five: Personhood Is Enhanced Through ■ Commitment to plan of action
Participating In Nurturing Relationships ■ Positive Competing demands
With Caring Others. ■ A health promoting behavior
MAJOR ASSUMPTIONS
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
PERSON Peplau went on to form an interpersonal model
- seek to create conditions of living through which emphasizing the need for a partnership between nurse
they express their unique human health potential. and client as opposed to the client passively receiving
- have the capacity for reflective self awareness treatment and the nurse passively acting out doctor’s
- value growth in directions viewed as positive and orders.
attempt to achieve a personally acceptable PHASES IN THE NURSE PATIENT RELATIONSHIP
balance between change and stability ORIENTATION PHASE
HEALTH The orientation phase is directed by the nurse
- health professionals constitute a part of the and involves engaging the client in treatment, providing
interpersonal environment, which exerts influence explanations and information, and answering questions.
on persons throughout their life spans. IDENTIFICATION PHASE.
ENVIRONMENT The identification phase begins when the client
- individuals in all their biophysical complexity interact works interdependently with the nurse, expresses feelings,
with the environment, progressively transforming and begins to feel stronger.
the environment and being transformed over time. EXPLOITATION PHASE.
In the exploitation phase, the client makes full use
of the services offered.
RESOLUTION PHASE.
In the resolution phase, the client no longer needs
professional services and gives up dependent behavior.
The relationship ends.
THE 4 COMPONENTS OF THE THEORY
Person, which is a developing organism that tries
HILDEGARD PEPLAU THEORY OF INTERPERSONAL to reduce anxiety caused by needs
RELATIONS Environment, which consists of existing forces
Hildegard Peplau was born on September 1, outside of the person, and put in the context of
1909. She was raised in Reading, Pennsylvania by her culture
parents of German descent, Gustav and Otyllie Peplau. Health, which is a word symbol that implies
Hildegard E. Peplau has been described as the forward movement of personality
mother of psychiatric nursing because her Nursing, which is a significant therapeutic
theoretical and clinical work led to the interpersonal process that functions cooperatively with
development of the distinct specialty field of psychiatric other human process that make health possible for
nursing. Her scope of influence in nursing includes her individuals in communities.
contributions as a psychiatric nursing expert, educator,
author, and nursing leader and theorist. IMOGENE KING THEORY OF GOAL ATTAINMENT
According to Peplau (1952/1988), nursing is Imogene M. King was born on January 30, 1923,
therapeutic because it is a healing art, assisting an in West Point, Iowa. She died December 24, 2007, in
individual who is sick or in need of health care. Nursing St. Petersburg, Florida,
can be viewed as an interpersonal process because it She was one of the pioneers and most sought
involves interaction between two or more individuals with nursing theorists for her Theory of Goal
a common goal. In nursing, this common goal provides Attainment which was developed in the early
the incentive for the therapeutic process in which the 1960s. Her work is being taught to thousands of nursing
nurse and patient respect each other as individuals, both students from all over the world and is implemented in a
of them learning and growing as a result of the interaction. variety of service settings as well.
An individual learns when she or he selects stimuli in the Imogene King contributed to the advancement of
environment and then reacts to these stimuli. nursing knowledge through the development of her
Hildegard Peplau’s Interpersonal Relations conceptual system and middle-range Theory of
Theory emphasized the nurse-client relationship as Goal Attainment. By focusing on the attainment of
the foundation of nursing practice. It gave goals, or outcomes, by nurse-patient partnerships, King
emphasis on the give-and-take of nurse-client provided a conceptual system and middle-range theory
relationships that was seen by many as revolutionary. that has demonstrated its usefulness to nurses. Nurses
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
working in a variety of settings with patients from around unique and holistic, of intrinsic worth, and capable of
the world continue to use King’s work to improve the rational thinking and decision making in most situations.
quality of patient care Individuals differ in their needs, wants, and goals
According to King, the patient is a social being Health is a dynamic state in the life cycle, while
who has three fundamental needs: the need for health illness interferes with that process. Health “implies
information, the need for care that seeks to prevent illness, continuous adjustment to stress in the internal and
and the need for care when the patient is unable to help external environment through the optimum use of one’s
him or herself. She explains health as involving life resources to achieve the maximum potential for daily
experiences of the patient, which includes adjusting to living.
stressors in the internal and external environment by Environment is “an understanding of the ways
using resources available. The environment is the that human beings interact with their environment to
background for human interaction. It involves the internal maintain health was essential for nurses”. Open systems
environment, which transforms energy to enable people to imply that interactions occur constantly between the
adjust to external environmental changes, and it involves system and the system’s environment., “adjustments to
the external environment, which Is formal and informal life and health are influenced by an individual’s interaction
organizations. A nurse is considered part of the patient’s with environment. Each human being perceives the world
environment. as a total person in making transactions with individuals
There are three interacting systems in the and things in the environment”
Theory of Goal Attainment according to King.
Personal system as a patient or a nurse. King’s middle-range Theory of Goal
specified the concepts of body image, Attainment focused on all aspects of the nursing process:
growth assessment, planning, implementation, and
and development, perception, self, space, evaluation. The body of literature clearly establishes
and time in order to comprehend human beings as King’s work as important for knowledge building in the
persons. discipline of nursing. Individuals are unique and holistic, of
Interpersonal system form when two or intrinsic worth, and capable of rational thinking and
more individuals interact, forming dyads decision making in most situations. Individuals differ
(two people) or triads (three people). The in their needs, wants, and goals.
dyad of a nurse and a patient is one type Assessment the nurse collects data
of interpersonal system. Families, when regarding the patient including his or her
acting as small groups, also can be growth and development, the perception
considered interpersonal systems. of self, and current health status.
Understanding the interpersonal system Perception is the base for the collection
requires the concepts of communication, and interpretation of data.
interaction, role, stress, and transaction. Communication is required to verify the
Social system A more comprehensive accuracy of the perception, as well as for
interacting system consists of groups that interaction and translation.
make up society, Religious, educational, Nursing Diagnosis is developed using the
and health care systems are examples of data collected in the assessment. In the
social systems Within a social system, process of attaining goals, the nurse
the concepts of authority, decision identifies problems, concerns, and
making, organization, power, and status disturbances about which the patient is
guide system understanding. seeking help
Major Assumptions of Imogene King Create a care plan of interventions to
Nursing is an observable behavior found in the solve the problems identified. The
health care systems in society”. The goal of nursing planning is represented by setting goals
“is to help individuals maintain their health so they can and making decisions about the means to
function in their roles” achieve those goals
Individuals are spiritual beings and have the Implementation phase of the nursing
ability through their language and other symbols to record process is the actual activities done to
their history and preserve their culture. . Individuals are achieve the goals. In this model of
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
nursing, it is the continuation of that each act of a person be caring, but it does require the
transaction. acceptance that “fundamentally, potentially, and actually,
Evaluation involves determining whether each person is caring.
or not goals were achieved. The Persons are whole or complete in the moment.
explanation of evaluation in King’s theory Respect for the person is communicated by the notion of
addresses meeting goals and the person as whole or complete in the moment there is no
effectiveness of nursing care. insufficiency, no brokenness, and no absence of
something. Wholeness, or the fullness of being, is forever
ANNE BOYKIN AND SAVINA O. SCHOENHOFER present.
THE THEORY OF NURSING AS CARING Persons live caring, moment to moment.
Caring is a lifetime process that is lived moment to
The theory of Nursing As Caring is a general or moment and is constantly unfolding. In the rhythm of life
grand nursing theory that can be used as a framework experiences, we continually develop expressions
to guide nursing practice. The theory is grounded in of ourselves as caring persons.
several key assumptions: persons are caring by Health. Personhood is a process of living
virtue of their humanness. grounded in caring. Personhood acknowledges the
Anne Boykin grew up in Kaukauna, Wisconsin, potential for unfolding caring possibilities moment to
the eldest of six children. She began her career in moment. From the perspective of Nursing as Caring,
nursing in 1966, graduating from Alverno College in personhood is the universal human call. This implies that
Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Boykin has a longstanding the fullness of being human is expressed in living caring
commitment to the advancement of knowledge in the uniquely day to day and is enhanced through participation
discipline, especially regarding the phenomenon of caring. in caring relationships
Savina O. Schoenhofer, Ph.D, is a professor of Environment. Personhood is enhanced
Graduate Nursing at Alcorn State University in Natchez, through participating in nurturing relationships with
Mississippi. She is the co-founder of the nursing caring others. Personhood acknowledges the potential
aesthetics publication, Ninghtingale songs. Her of persons to live caring and is enhanced through
publication are in the areas of everyday caring, outcomes participation in nurturing relationships with caring others.
in nursing, nursing values, nursing home management, Nursing. Nursing is both a discipline and
and affectional touch. profession. Nursing is an “exquisitely interwoven” unity of
aspects of the discipline and profession of nursing. As a
The Theory of Nursing as Caring: A Model for discipline,nursing is a way of knowing, being, valuing, and
Transforming Practice living in the world, and is envisaged as a unity of
Nursing is an “exquisitely interwoven” unity of knowledge within a larger unity.
aspects of the discipline and profession of
nursing. DANCE OF CARING PERSONS.
The focus and aim of nursing as a discipline of
knowledge and a professional service is Dancers enter the nursing situation, visualized as
“nurturing persons living caring and growing in a circle of caring that provides organizing purpose and
caring.” integrated functioning (Boykin,Schoenhofer, Smith, et
Caring in nursing is “an altruistic, active al.,2003).
expression of love, and is the intentional and Dancers move freely; some dancers
embodied recognition of value and touch, some dance alone, but all dance in
connectedness.” relation to each other and to the circle.
Assumptions Each dancer brings special gifts as the
The belief that persons are caring by virtue of nursing situation evolves.
their humanness sets forth the ontological and ethical Some dancers may hear different notes
bases on which the theory is grounded. Being a person and a different rhythm, but all harmonize
means living caring, through which being and possibilities in the unity of the dance and the oneness
are known to the fullest. Each person throughout his or of the circle.
her life grows in the capacity to express caring. The Personal knowing of self and other is
assumption that all persons are caring does not require integral to the connectedness of persons
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
in the dance, in which the nature of benefits of action, perceived barriers to
relating in the circle is grounded in action, perceived self-efficacy, activity-
valuing and respecting person (Boykin & related affect, interpersonal influences,
Schoenhofer, 2001a). and situational influences).
All in the nursing situation, including the Behavioral outcomes (commitment to a
nurse and the nursed, sustain the dance, plan of action, immediate competing
being energized and resonating with the demands and preferences, and health-
music of caring. promoting behavior).
NOLA PENDER HEALTH PROMOTION MODEL SUB CONCEPT OF THE HEALTH PROMOTION
MODEL
Nola Pender was born on August 16, 1941, in Personal Factors
Lansing, Michigan to parents who advocated education
for women. Her first encounter with the nursing profession o Biological factors include variables
was when she was 7 years old and witnessed the care such as age gender body mass index
given to her hospitalized aunt by nurses. This situation pubertal status, aerobic capacity, strength,
led her to the desire to care for other people and agility, or balance.
her goal was to help people care for themselves. o psychological factors. Include variables
The Health Promotion Model was designed to be such as self-esteem, self-motivation,
a “complementary counterpart to models of health personal competence, perceived health
protection.” status, and definition of health.
It develops to incorporate behaviors for o socio-cultural factors. Include variables
improving health and applies across the such as race, ethnicity, acculturation,
life span. education, and socioeconomic status.
The purpose is to assist nurses in Perceived benefit of action they are anticipated
knowing and understanding the major positive outcomes that will occur from health behavior.
determinants of health behaviors as a Perceived barrier to action is an anticipated,
foundation for behavioral counseling to imagined or real blocks and personal costs of
promote well-being and healthy lifestyles. understanding a given behavior.
Perceived Self-Efficacy is a judgment of
Pender’s health promotion model defines health personal capability to organize and execute a health-
as “a positive dynamic state not merely the absence promoting behavior
of disease.” It is directed at increasing a client’s level of Activity-Related Affect is subjective positive or
well-being. It describes the multi-dimensional nature negative feeling that occurs before, during and
of persons as they interact within the environment following behavior based on the stimulus properties of the
to pursue health. behavior itself.
Interpersonal Influence include norms
Concept Health Promotion Model (expectations of significant others), social support
(instrumental and emotional encouragement), and
Health promotion is defined as behavior modeling (vicarious learning through observing others
motivated by the desire to increase well-
engaged in a particular behavior). Primary sources of
being and actualize human health
interpersonal influences are families, peers,
potential
and health care providers.
Health protection or illness prevention is Situational influences are personal perceptions
described as behavior motivated desire to and cognitions of any given situation or context that can
actively avoid illness, detect it early, or facilitate or impede behavior. They include
maintain functioning within the constraints perceptions of available options, demand
of illness. characteristics, and aesthetic features of the environment
Individual characteristics and in which given health-promoting behavior is proposed to
experiences (prior related behavior and take place. Situational influences may have direct or
personal factors). indirect influences on health behavior.
Behavior-specific
cognitions and affect (perceived
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF NURSING BLAST REVIEWER
The following are immediate antecedents of
behavior or behavioral outcomes.
Commitment to plan of action. It describes the
concept of intention and identification of a planned
strategy that leads to implementation of health behavior.
Immediate competing demands are alternative
behaviors over which individuals have low control,
because there are environmental contingencies such as
work or family care responsibilities..Competing
preferences are alternative behaviors over which
individuals exert relatively high control, such as choice of
ice cream or an apple for a snack.
A health-promoting behavior is an end point or
action outcome that is directed toward attaining positive
health outcomes such as optimal well-being, personal
fulfillment, and productive living. Examples of health-
promoting behavior are eating a healthy diet, exercising
regularly, managing stress, gaining adequate rest
and spiritual growth, and buildingpositive
relationships.
You might also like
- Full Chapter The Astonishing Adolescent Upheaval in Psychoanalysis 1St Edition Roosevelt Cassorla PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter The Astonishing Adolescent Upheaval in Psychoanalysis 1St Edition Roosevelt Cassorla PDFrandy.andrade807100% (4)
- TFN Katie Erickson 8Document26 pagesTFN Katie Erickson 8Yeng Bernabe67% (3)
- Middle-Range Theory of Spiritual Well-Being in IllnessDocument4 pagesMiddle-Range Theory of Spiritual Well-Being in IllnessMarimiel PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Biography and Career of Katie Eriksso1Document3 pagesBiography and Career of Katie Eriksso1candy perez100% (1)
- Nursing As Caring: A Model For Transforming Practice: Anne Boykin, PHD, RN Savina O. Schoenhofer, PHD, RNDocument20 pagesNursing As Caring: A Model For Transforming Practice: Anne Boykin, PHD, RN Savina O. Schoenhofer, PHD, RNAlvaro Galindo PuentesNo ratings yet
- The Galvanic CurrentDocument31 pagesThe Galvanic CurrentSameeha Abbass43% (7)
- Manual - Facoemulsificador Los DosDocument36 pagesManual - Facoemulsificador Los DosSoporte Técnico ElectronitechNo ratings yet
- NCMA110: 1. Eriksson, Watson and Benner 2. Rogers and Orem 3. Johnson, Roy and NeumanDocument31 pagesNCMA110: 1. Eriksson, Watson and Benner 2. Rogers and Orem 3. Johnson, Roy and NeumanMarian TorresNo ratings yet
- Theoretical 2Document31 pagesTheoretical 2Shane OseñaNo ratings yet
- KoeDocument14 pagesKoeKash Jamasali50% (2)
- Katie ErikssonDocument14 pagesKatie Erikssonsamantha tanoNo ratings yet
- Katie ErikssonDocument14 pagesKatie ErikssonJan Oliver Yares100% (3)
- Katie ErikssonDocument13 pagesKatie ErikssonGladys YaresNo ratings yet
- Katie ErikssonDocument14 pagesKatie ErikssonJan Oliver Yares67% (3)
- ErickssonDocument3 pagesErickssonAl Cris BarroNo ratings yet
- Biography and Career of Katie Eriksso1Document4 pagesBiography and Career of Katie Eriksso1candy perezNo ratings yet
- TFN Reviewer 1Document12 pagesTFN Reviewer 1Eugene FernandezNo ratings yet
- TFN Midterms ReviewerDocument11 pagesTFN Midterms ReviewerRomeo SabilaoNo ratings yet
- Eriksson's Caritative Caring Theory: Major ConceptsDocument3 pagesEriksson's Caritative Caring Theory: Major ConceptsRUIZ JAKE CANCILLER. VELARDENo ratings yet
- Margaret Jean Harman WatsonDocument3 pagesMargaret Jean Harman WatsonRachelle D. DEQUIÑANo ratings yet
- Katie ErikssonDocument3 pagesKatie ErikssonMarian M.BaloNo ratings yet
- Katie ErikssonDocument23 pagesKatie ErikssonJennylyn Unsil LumangkaNo ratings yet
- Katie ErikssonDocument4 pagesKatie Erikssondumbwaste528No ratings yet
- TFN03-Nursing Theories and ModelsDocument26 pagesTFN03-Nursing Theories and ModelsLyn YmiNo ratings yet
- ErikssonDocument3 pagesErikssonRoshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Katie Ericksson (Theory of Caritative Caring)Document2 pagesKatie Ericksson (Theory of Caritative Caring)brylleNo ratings yet
- Katie Erikson Carative CaringDocument3 pagesKatie Erikson Carative CaringBSN 1-YA-22 ELITIONG, MARY JEAN A.No ratings yet
- Joyce TravelbeeDocument3 pagesJoyce TravelbeeDionne BajasNo ratings yet
- TFN WatsonDocument39 pagesTFN WatsonCarl LazaroNo ratings yet
- Watsons Theory of Caring0806 PDFDocument12 pagesWatsons Theory of Caring0806 PDFWAHYU ROCHDIATNo ratings yet
- 4 Nursing Theories TFNDocument5 pages4 Nursing Theories TFNAeri OT9No ratings yet
- Lecture in Gec e 1Document8 pagesLecture in Gec e 1Marie Yllana DulhaoNo ratings yet
- Katie ErikssonDocument20 pagesKatie ErikssonAltheia Fei EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Eriksson's Caritative Caring Theory (1) .PPTX (Autosaved)Document38 pagesEriksson's Caritative Caring Theory (1) .PPTX (Autosaved)Gillian Mae CasipitNo ratings yet
- Erickson, Rogers, Orem, KingDocument14 pagesErickson, Rogers, Orem, KingaltheaNo ratings yet
- Katie Eriksson Contribution To Nursing TheoryDocument14 pagesKatie Eriksson Contribution To Nursing TheoryRona Camila MatibagNo ratings yet
- Erikssons 1Document32 pagesErikssons 1Narena BoniteNo ratings yet
- Notes in TFNDocument6 pagesNotes in TFNNickawaiiNo ratings yet
- TFN MIDTERMS HighlightDocument12 pagesTFN MIDTERMS HighlightphoebeNo ratings yet
- The Philosophy and Science of Caring Jean Watson: St. Luke'S College of Nursing Trinity University of AsiaDocument28 pagesThe Philosophy and Science of Caring Jean Watson: St. Luke'S College of Nursing Trinity University of AsiaAisha MagarangNo ratings yet
- Katie Eriksson ReviewrDocument5 pagesKatie Eriksson ReviewrcranchosanchezNo ratings yet
- SPIRITUALITYDocument4 pagesSPIRITUALITYAnne Arboleda100% (1)
- Theorists and Their WorksDocument25 pagesTheorists and Their WorksAthena OcampoNo ratings yet
- Jean WatsonDocument4 pagesJean Watsoncharles culanagNo ratings yet
- TFN Jean WatsonsDocument27 pagesTFN Jean Watsonschryss advinculaNo ratings yet
- TFN AssignmentDocument5 pagesTFN Assignmentrovic敗.No ratings yet
- Funda LecDocument20 pagesFunda LecJamie Annmari AmboyNo ratings yet
- Joyce TravelbeeDocument3 pagesJoyce TravelbeeLucilyn Mae CubilloNo ratings yet
- Jean WatsonDocument4 pagesJean WatsonbrylleNo ratings yet
- Theories and Principles of EthicsDocument4 pagesTheories and Principles of EthicsPatricia RamosNo ratings yet
- Theory ofDocument15 pagesTheory ofriche.arnaizNo ratings yet
- TFN NotesDocument23 pagesTFN Notessuezanne gabonNo ratings yet
- Jean Watson's Philosophy and Science of CaringDocument21 pagesJean Watson's Philosophy and Science of CaringJaylord AchanzarNo ratings yet
- Joyce TravelbeeDocument15 pagesJoyce TravelbeeGiorgette100% (1)
- Margaret Jean WatsonDocument3 pagesMargaret Jean WatsonApril Mae Agomo-oNo ratings yet
- TdfhihDocument3 pagesTdfhihAlec TanNo ratings yet
- Joyce TravelbeeDocument9 pagesJoyce TravelbeeCj ScarletNo ratings yet
- Nightingale Watson Benner ErikssonDocument68 pagesNightingale Watson Benner ErikssonRisha PedrosoNo ratings yet
- MODULE WEEK 5bDocument14 pagesMODULE WEEK 5bjessicamaeagujaNo ratings yet
- Watsons Theory of Human Caring Core Concepts and Evolution To Caritas Processes Handout 1Document7 pagesWatsons Theory of Human Caring Core Concepts and Evolution To Caritas Processes Handout 1Rachel JamagoNo ratings yet
- The Role of the Spiritual Caregiver to the Terminally Ill PatientsFrom EverandThe Role of the Spiritual Caregiver to the Terminally Ill PatientsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Body Deva: Working with the Spiritual Consciousness of the BodyFrom EverandThe Body Deva: Working with the Spiritual Consciousness of the BodyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Psychiatric NursingDocument31 pagesPsychiatric NursingSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Summary of SystemsDocument26 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Summary of SystemsSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing - Cardiovascular System DisordersDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - Cardiovascular System DisordersSofia LiNo ratings yet
- NCMB 314 - GERIATRICS (CARE OF THE OLDER ADULT) - Physical and Physiological Changes of AgingDocument3 pagesNCMB 314 - GERIATRICS (CARE OF THE OLDER ADULT) - Physical and Physiological Changes of AgingSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in OxygenationDocument20 pagesDisturbances in OxygenationSofia LiNo ratings yet
- NCMB 314 - GERIATRICS (CARE OF THE OLDER ADULT) - Concept, Principles, History, and Theories in The Care of Older AdultsDocument6 pagesNCMB 314 - GERIATRICS (CARE OF THE OLDER ADULT) - Concept, Principles, History, and Theories in The Care of Older AdultsSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Review and Check 11&12Document5 pagesReview and Check 11&12david04castillo2003No ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Muhammad Arif Khan Department of Surgery, Rcvets, LahoreDocument13 pagesProf. Dr. Muhammad Arif Khan Department of Surgery, Rcvets, LahoreMuhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- From Start To Phase 1 in 30 Months - Insilico MedicineDocument9 pagesFrom Start To Phase 1 in 30 Months - Insilico MedicinejeanNo ratings yet
- Refutation Paragraph (Abortion)Document2 pagesRefutation Paragraph (Abortion)Kyla JotojotNo ratings yet
- HLTWHS002 AE1 Scenarios V1.0Document10 pagesHLTWHS002 AE1 Scenarios V1.0writer topNo ratings yet
- PDF FactsDocument4 pagesPDF FactsSoham NaikNo ratings yet
- AslotDocument4 pagesAslotDrAlaa ZidanNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Development of SopsDocument5 pagesObjectives of Development of SopsGloria RamosNo ratings yet
- Blues CluesDocument24 pagesBlues CluesShy TolentinoNo ratings yet
- FELINE-Dental Radio Graphic Technique in CatsDocument7 pagesFELINE-Dental Radio Graphic Technique in Catstaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Shawn Achor Ted Talk ActivityDocument8 pagesShawn Achor Ted Talk ActivityLuciane MendesNo ratings yet
- A56 Artic Dumper HandoutDocument10 pagesA56 Artic Dumper HandoutRafal SiejkaNo ratings yet
- En - Avol Oxy White - 10Document9 pagesEn - Avol Oxy White - 10Twaha M&SNo ratings yet
- Textbook Health Care Information Systems A Practical Approach For Health Care Management 4Th Edition Karen A Wager Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument54 pagesTextbook Health Care Information Systems A Practical Approach For Health Care Management 4Th Edition Karen A Wager Ebook All Chapter PDFelton.kruger265100% (12)
- Price List Reguler Oktober 2021 PT. LikuidDocument1 pagePrice List Reguler Oktober 2021 PT. Likuidwahyudi pangestuNo ratings yet
- RP Manual TemplateDocument9 pagesRP Manual TemplateJay VeeNo ratings yet
- Funda NotesDocument9 pagesFunda Noteszyrenejoy.motita.mnlNo ratings yet
- Backyard Rabbit Farming: February 2009Document17 pagesBackyard Rabbit Farming: February 2009Nishant JeeNo ratings yet
- 2018-089. NASKAH PUBLIKASI Elsi Nursyahdin MayaranaDocument12 pages2018-089. NASKAH PUBLIKASI Elsi Nursyahdin MayaranaElsi NursyahdinNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Surgical ScissorsDocument5 pagesThe Different Types of Surgical ScissorsSerena FrommeNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Teledentistry 1Document7 pagesJurnal Teledentistry 1Dio Nella ArlinggaNo ratings yet
- 22-The Story of The Colombo PlanDocument61 pages22-The Story of The Colombo PlanDidik ApriantoNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS)Document2 pagesBachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS)Rohit GhuseNo ratings yet
- Service Learning Package Edu 280Document3 pagesService Learning Package Edu 280api-549461032No ratings yet
- Focus3 2E End of Year Test WritingDocument2 pagesFocus3 2E End of Year Test WritingLjhhggNo ratings yet
- UOG 2014 PG Programs AnnouncementDocument10 pagesUOG 2014 PG Programs Announcementsamuel mechNo ratings yet
- Sistem Terpadu Akademik Reguler UMSDocument1 pageSistem Terpadu Akademik Reguler UMSChoirida AilaniNo ratings yet