Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Factors Affecting The Ionisation Energy
Factors Affecting The Ionisation Energy
Uploaded by
Ti Yee SanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryAyah FNo ratings yet
- Unless Otherwise Stated, All Images in This File Have Been Reproduced FromDocument18 pagesUnless Otherwise Stated, All Images in This File Have Been Reproduced FromAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- 5DP Ionisation EnergiesDocument17 pages5DP Ionisation EnergiesVaida MatulevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- Chem HL PeriodicityDocument5 pagesChem HL PeriodicityCsya Raynold NgNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HL (Atomic Structure HL)Document11 pagesUnit 2 HL (Atomic Structure HL)ellhamnasserNo ratings yet
- 4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument68 pages4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- 2 chapter 2 原子半径以及电离能Document33 pages2 chapter 2 原子半径以及电离能Pingping chenNo ratings yet
- AS Level Summary-Unit 1Document11 pagesAS Level Summary-Unit 1Filiz Kocayazgan ShanablehNo ratings yet
- A - Level Inorganic Chemistry 2-1Document171 pagesA - Level Inorganic Chemistry 2-1kitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- Ionization EnergyDocument8 pagesIonization EnergyHafiza Sikder AnishaNo ratings yet
- Unit Objectives: Periodic TrendsDocument9 pagesUnit Objectives: Periodic Trendsmartin mulengaNo ratings yet
- Size of The Nuclear ChargeDocument2 pagesSize of The Nuclear ChargeREZA FARDGHASSEMINo ratings yet
- A - Level Inorganic ChemistryDocument543 pagesA - Level Inorganic Chemistrystephenshada9No ratings yet
- Chap 1.1Document48 pagesChap 1.1Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- Periodicity Part 1Document1 pagePeriodicity Part 1Green SlimeNo ratings yet
- Ion EnergiesDocument4 pagesIon EnergiesNamratha NairNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3Md Al AminNo ratings yet
- Periodicity: Ionisation EnergyDocument3 pagesPeriodicity: Ionisation EnergyFouziaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties of ElementsDocument53 pagesPeriodic Properties of Elementschandro57No ratings yet
- Atomic Radii: Atomic Structure: Periodic TrendsDocument5 pagesAtomic Radii: Atomic Structure: Periodic TrendsRajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry NotesDocument105 pagesInorganic Chemistry NotesOdongo TonnyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Document9 pagesEngineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Nivetha ENo ratings yet
- Ionization EnergiesDocument16 pagesIonization EnergiesChloe C TanuNo ratings yet
- Document From Michi?Document55 pagesDocument From Michi?audrey abaasaNo ratings yet
- Ionisation EnergyDocument6 pagesIonisation EnergyAathifa ThowfeekNo ratings yet
- A039level Chemistry Inorganic NotesDocument108 pagesA039level Chemistry Inorganic NotesNasser SsennogaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument31 pagesAtomic StructureNurul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Electron Configurations-Transition, IonizationDocument33 pagesElectron Configurations-Transition, IonizationRayan BotanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic Structureleonide357No ratings yet
- 3.2 Periodicity PDFDocument86 pages3.2 Periodicity PDFnurulnadzirah_99100% (1)
- Che Chapter 3Document7 pagesChe Chapter 3lisaNo ratings yet
- 05 - CHEM 111 - Lecture 5 - Periodicity of The ElementsDocument50 pages05 - CHEM 111 - Lecture 5 - Periodicity of The ElementsBrian NkhomaNo ratings yet
- Periodicity: The Periodic Table and Physical PropertiesDocument25 pagesPeriodicity: The Periodic Table and Physical PropertiesJi Min LimNo ratings yet
- Patterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableDocument7 pagesPatterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableRugen RajNo ratings yet
- Btech Chem NIFFT Part 1 PDFDocument53 pagesBtech Chem NIFFT Part 1 PDFকৃ ষ্ণাNo ratings yet
- Ionisation and Energy LevelsDocument23 pagesIonisation and Energy LevelsAzuralianNo ratings yet
- As 1 PerDocument4 pagesAs 1 PerzoeakatNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 1 2 PDFDocument73 pagesInorganic Chem 1 2 PDFYT ChongNo ratings yet
- Eng SciDocument1 pageEng SciAzaa anuarNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By:: Mrs. Rashmi Dhiman Laksh Arora 10 /A Roll No: 27Document52 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By:: Mrs. Rashmi Dhiman Laksh Arora 10 /A Roll No: 27Noorpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrons and HolesDocument14 pagesElectrons and HolesMaxi GarzonNo ratings yet
- Ionization Enthalpy - AmenDocument3 pagesIonization Enthalpy - AmenusmodaanoNo ratings yet
- Chem 111 Week Three Notes BDocument7 pagesChem 111 Week Three Notes BnyachiosirNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Document70 pagesEngineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Abdul Rauf ChNo ratings yet
- Ion EnergiesDocument39 pagesIon Energiesabashir7852No ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesCIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureMyraNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesCIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Periodicity in Elements NotesDocument7 pagesPeriodicity in Elements NotesjqgjwgnnwkNo ratings yet
- Electronic StructureDocument26 pagesElectronic StructureDavidson ChanNo ratings yet
- Classification of ElementsDocument74 pagesClassification of ElementsJimit Patel BankNo ratings yet
- CHM 111 Lecture Note FiveDocument5 pagesCHM 111 Lecture Note Fivealfreddanladi321No ratings yet
- Solids and Semiconductor DevicesDocument18 pagesSolids and Semiconductor DevicesKashyap PatelNo ratings yet
- Solids and Semiconductor Devices 1-1Document19 pagesSolids and Semiconductor Devices 1-1sabatsuhani74No ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument6 pagesSemiconductordksingh369No ratings yet
- 1.1 Group 2Document32 pages1.1 Group 2SN1-0622 Khairul Bariah Binti IzaniNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure andDocument19 pagesAtomic Structure andDonna BonielNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry 2020Document94 pagesInorganic Chemistry 2020Deejay Griffin256No ratings yet
- Solids and Semiconductor Devices PDFDocument68 pagesSolids and Semiconductor Devices PDFdhruviNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sk015Document19 pagesChemistry Sk015Ahmad Munawir Ahmad WardiNo ratings yet
- Nikola Tesla - Case FilesDocument13 pagesNikola Tesla - Case FilesAryan KohliNo ratings yet
- Et 316Document30 pagesEt 316Ali IhtshamNo ratings yet
- Tuesday, May 03, 2022Document34 pagesTuesday, May 03, 2022Le Cong LapNo ratings yet
- Smart-UPS SMC3000IDocument3 pagesSmart-UPS SMC3000IAry WinariasariNo ratings yet
- A Review of Literature On Various Techniques of COP Improvement in Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemDocument9 pagesA Review of Literature On Various Techniques of COP Improvement in Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Kitchens Catalogue 2021Document40 pagesKitchens Catalogue 2021Rai SahibNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Tcg2032 DeutzDocument3 pagesData Sheet Tcg2032 DeutzMaximiliano SanchezNo ratings yet
- Safestart 700-Series: InstallationDocument1 pageSafestart 700-Series: InstallationSergei BiryukovNo ratings yet
- 10-87-02 Spec For Ceramic Fibre Blanket InsulationDocument5 pages10-87-02 Spec For Ceramic Fibre Blanket InsulationlightsonsNo ratings yet
- Boq No. Particulars Unit BOQ QTY Basic Rate Basic AmountDocument18 pagesBoq No. Particulars Unit BOQ QTY Basic Rate Basic AmountmanojNo ratings yet
- CompletionDocument107 pagesCompletionAdel ALkhaligyNo ratings yet
- ယမ်းထုတ်လုပ်နည်းမျာ 1Document30 pagesယမ်းထုတ်လုပ်နည်းမျာ 1jo joNo ratings yet
- Lecture-8 HEN Part3Document15 pagesLecture-8 HEN Part3Imran UnarNo ratings yet
- Touran No. 204 / 1: Position of Relays and Fuses Electronics Box Low, From May 2005Document18 pagesTouran No. 204 / 1: Position of Relays and Fuses Electronics Box Low, From May 2005Dariaxa Sos CarsNo ratings yet
- Briggs and Stratton Log Splitter 1264320036E1Document29 pagesBriggs and Stratton Log Splitter 1264320036E1AndrewNo ratings yet
- Case Note: Greenpeace Nordic and Nature and Youth v. Ministry of Energy, January 2024Document6 pagesCase Note: Greenpeace Nordic and Nature and Youth v. Ministry of Energy, January 2024octavientNo ratings yet
- 111 - White Paper - Fire-Safety-In-Electric-Vehicle-Parking-GaragesDocument23 pages111 - White Paper - Fire-Safety-In-Electric-Vehicle-Parking-GaragesDmitryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Module 2Document4 pagesChapter 7 Module 2Sarmiento, Jovenal B.No ratings yet
- 1a UthmDocument9 pages1a UthmMohamad Muslihuddin RazaliNo ratings yet
- Science2 - Chapterwise Practice Papers + PYQDocument37 pagesScience2 - Chapterwise Practice Papers + PYQ12 XB Atharva kharatNo ratings yet
- Call For Papers ICEFSI 27 PDFDocument2 pagesCall For Papers ICEFSI 27 PDFSeif eddine Ben hammoudaNo ratings yet
- FilterDocument4 pagesFilterjaimhakal100% (1)
- Life Cycle of A Star - WorksheetDocument4 pagesLife Cycle of A Star - WorksheetLNo ratings yet
- Boric Acid CorrosionDocument47 pagesBoric Acid CorrosionFedak MarosNo ratings yet
- D2 (D2EU) : User ManualDocument2 pagesD2 (D2EU) : User ManualAlper GümüştekinNo ratings yet
- Depletion and Decline Curve Analysis in Crude Oil ProductionDocument112 pagesDepletion and Decline Curve Analysis in Crude Oil ProductionaliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Calculations - Midterm ExamDocument12 pagesChemical Engineering Calculations - Midterm ExamJohnNo ratings yet
- Weda50 2954531000-3 ENDocument20 pagesWeda50 2954531000-3 ENMikael TuokkolaNo ratings yet
- Group 02Document22 pagesGroup 02WSMengine WSMengineNo ratings yet
- List of Parts For Tractors ApplicationDocument9 pagesList of Parts For Tractors ApplicationSanjay Kumar BansalNo ratings yet
Factors Affecting The Ionisation Energy
Factors Affecting The Ionisation Energy
Uploaded by
Ti Yee SanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Factors Affecting The Ionisation Energy
Factors Affecting The Ionisation Energy
Uploaded by
Ti Yee SanCopyright:
Available Formats
Factors Affecting the Ionisation Energy
1) Atomic radius
The valence electrons of an atom with a larger radius experience a less attraction
towards nucleus,hence possesses a low ionization energy.
2) Effective nuclear charge,Zeff
The higher the nuclear charge, the stronger the attraction between the nucleus and
electrons.This causes the ionization energy to increase.
3) Shielding effect (screening effect)
The shielding effect of the electrons in the inner orbitals causes the outer electrons to
be less attracted to the nucleus and thus decrease the magnitude of ionization energy.
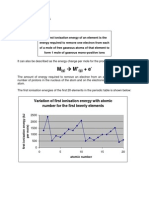
Variation in the 1st IE when:
(1) Moving across a period
When moving across a period,the element become less metallic or non-metallic
The effective nuclear change,Zeff increases and the atomic size decreases.
Valence electrons are closer to the nucleus.
The force of attraction between the nucleus and the valence e becomes stronger.
More difficult to remove an electron from the atom.
More energy is needed to remove the outermost electrons.
Thus,the ionisation energy increases.
-Anomalous Cases
Increase of IE with proton number is not uniform.
In period 2,
Between group 2(Be) and 13(B).Ionization energy of BE>B.
Completely filled orbital is more stable than partially filled orbital
1)Be:1s2 2s2 2)B:1s22s22p1
In Be,removing an e from a fully In B,removing an electron in 2p
filled 2s orbital the atom less orbital makes the atom more
stable stable
Hard to remove the valence Easy to remove the valence
electrons electron
More energy is needed to remove Shielding effect increase
the valence electron in 2s Attraction between the nucleus
Zeff will be higher and 2p electron is weak
Attraction between nucleus and Less energy is needed to remove
valence electrons in 2s is the electron
stronger Therefore ionization energy of B
Therefore ionization energy of is lower than Be
Be is higher than B
Between group 15(N) and 16(O).Ionization energy of N>O.
1) N:1s22s22p3 2) O:1s22s22p4
Completely filled orbital is more stable than partially filled orbital
In N,removing an e from the half In O,removing an electron in the
filled 2p orbital makes the atom 2p orbital makes the atom more
less stable stable.
Hard to remove the valence Easy to remove the valence
electrons electrons
More energy is needed to Shielding effect increase
remove the valence electron Attraction between the nucleus
Zeff will be higher and 2p electron is weak
Attraction between nucleus and Less energy is needed to remove
valence electrons in 2p is the electron
stronger Therefore ionization energy of
Therefore ionization energy of Oxygen is lower than Nitrogen.
Nitrogen is higher than Oxygen.
In Period 3,
Between Group 2(Mg) and 13(Al)
Completely filled orbital is more stable than partially filled orbital
1)Mg:1s22s22p63s2 2)Al:1s22s22p63s23p1
In Mg,removing an e from a In Al,removing an electron in the
fully filled 3s orbital makes the 3p orbital makes the atom more
atom less stable stable.
Hard to remove the valence e Easy to remove the valence
More energy is needed to electron
remove the valence e in 3s Shielding effect increase
Zeff will be higher Attraction between the nucleus
Attraction between nucleus and and 3p electron is weak
valence electrons in 3s is Less energy is needed to remove
stronger the electron
Therefore ionization energy of Therefore ionization energy of
Mg is higher than Al Ai is lower than Mg
Between group 15(P) and 16(S).Ionization energy P>S
Completely filled orbital is more stable than partially filled orbital
1) P:1s22s22p63s23p3 2) S:1s22s22p43s23p4
In P, removing an e from the half In Al,removing an electron in the
filled 3p orbital makes the atom 3p orbital makes the atom more
less stable stable
Hard to remove the valence Easy to remove the valence
electrons electrons
More energy is needed to Shielding effect increase
remove the valence electron Attraction between the nucleus
Zeff will be higher and 3p electron is weak
Attraction between nucleus and Less energy is needed to remove
valence electron in 3p is stronger the electron
Therefore ionization energy of P Therefore ionization energy of S
is higher than S is lower than P.
(ii)Going down the group
On descending a group …
The atomic radius increases as more electrons are added to next energy levels.(no. of
shell, n increases)
This causes the screening effect to increase
Valence electrons are further away from the nucleus
The force of attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons becomes weaker
It is easier to remove an electron from each atom
Therefore,less energy is needed to remove the first electron
Therefore, ionization energy decreases
You might also like
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryAyah FNo ratings yet
- Unless Otherwise Stated, All Images in This File Have Been Reproduced FromDocument18 pagesUnless Otherwise Stated, All Images in This File Have Been Reproduced FromAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- 5DP Ionisation EnergiesDocument17 pages5DP Ionisation EnergiesVaida MatulevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- Chem HL PeriodicityDocument5 pagesChem HL PeriodicityCsya Raynold NgNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HL (Atomic Structure HL)Document11 pagesUnit 2 HL (Atomic Structure HL)ellhamnasserNo ratings yet
- 4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument68 pages4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- 2 chapter 2 原子半径以及电离能Document33 pages2 chapter 2 原子半径以及电离能Pingping chenNo ratings yet
- AS Level Summary-Unit 1Document11 pagesAS Level Summary-Unit 1Filiz Kocayazgan ShanablehNo ratings yet
- A - Level Inorganic Chemistry 2-1Document171 pagesA - Level Inorganic Chemistry 2-1kitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- Ionization EnergyDocument8 pagesIonization EnergyHafiza Sikder AnishaNo ratings yet
- Unit Objectives: Periodic TrendsDocument9 pagesUnit Objectives: Periodic Trendsmartin mulengaNo ratings yet
- Size of The Nuclear ChargeDocument2 pagesSize of The Nuclear ChargeREZA FARDGHASSEMINo ratings yet
- A - Level Inorganic ChemistryDocument543 pagesA - Level Inorganic Chemistrystephenshada9No ratings yet
- Chap 1.1Document48 pagesChap 1.1Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- Periodicity Part 1Document1 pagePeriodicity Part 1Green SlimeNo ratings yet
- Ion EnergiesDocument4 pagesIon EnergiesNamratha NairNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3Md Al AminNo ratings yet
- Periodicity: Ionisation EnergyDocument3 pagesPeriodicity: Ionisation EnergyFouziaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties of ElementsDocument53 pagesPeriodic Properties of Elementschandro57No ratings yet
- Atomic Radii: Atomic Structure: Periodic TrendsDocument5 pagesAtomic Radii: Atomic Structure: Periodic TrendsRajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry NotesDocument105 pagesInorganic Chemistry NotesOdongo TonnyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Document9 pagesEngineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Nivetha ENo ratings yet
- Ionization EnergiesDocument16 pagesIonization EnergiesChloe C TanuNo ratings yet
- Document From Michi?Document55 pagesDocument From Michi?audrey abaasaNo ratings yet
- Ionisation EnergyDocument6 pagesIonisation EnergyAathifa ThowfeekNo ratings yet
- A039level Chemistry Inorganic NotesDocument108 pagesA039level Chemistry Inorganic NotesNasser SsennogaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument31 pagesAtomic StructureNurul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Electron Configurations-Transition, IonizationDocument33 pagesElectron Configurations-Transition, IonizationRayan BotanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic Structureleonide357No ratings yet
- 3.2 Periodicity PDFDocument86 pages3.2 Periodicity PDFnurulnadzirah_99100% (1)
- Che Chapter 3Document7 pagesChe Chapter 3lisaNo ratings yet
- 05 - CHEM 111 - Lecture 5 - Periodicity of The ElementsDocument50 pages05 - CHEM 111 - Lecture 5 - Periodicity of The ElementsBrian NkhomaNo ratings yet
- Periodicity: The Periodic Table and Physical PropertiesDocument25 pagesPeriodicity: The Periodic Table and Physical PropertiesJi Min LimNo ratings yet
- Patterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableDocument7 pagesPatterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableRugen RajNo ratings yet
- Btech Chem NIFFT Part 1 PDFDocument53 pagesBtech Chem NIFFT Part 1 PDFকৃ ষ্ণাNo ratings yet
- Ionisation and Energy LevelsDocument23 pagesIonisation and Energy LevelsAzuralianNo ratings yet
- As 1 PerDocument4 pagesAs 1 PerzoeakatNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 1 2 PDFDocument73 pagesInorganic Chem 1 2 PDFYT ChongNo ratings yet
- Eng SciDocument1 pageEng SciAzaa anuarNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By:: Mrs. Rashmi Dhiman Laksh Arora 10 /A Roll No: 27Document52 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By:: Mrs. Rashmi Dhiman Laksh Arora 10 /A Roll No: 27Noorpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrons and HolesDocument14 pagesElectrons and HolesMaxi GarzonNo ratings yet
- Ionization Enthalpy - AmenDocument3 pagesIonization Enthalpy - AmenusmodaanoNo ratings yet
- Chem 111 Week Three Notes BDocument7 pagesChem 111 Week Three Notes BnyachiosirNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Document70 pagesEngineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Abdul Rauf ChNo ratings yet
- Ion EnergiesDocument39 pagesIon Energiesabashir7852No ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesCIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureMyraNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesCIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Periodicity in Elements NotesDocument7 pagesPeriodicity in Elements NotesjqgjwgnnwkNo ratings yet
- Electronic StructureDocument26 pagesElectronic StructureDavidson ChanNo ratings yet
- Classification of ElementsDocument74 pagesClassification of ElementsJimit Patel BankNo ratings yet
- CHM 111 Lecture Note FiveDocument5 pagesCHM 111 Lecture Note Fivealfreddanladi321No ratings yet
- Solids and Semiconductor DevicesDocument18 pagesSolids and Semiconductor DevicesKashyap PatelNo ratings yet
- Solids and Semiconductor Devices 1-1Document19 pagesSolids and Semiconductor Devices 1-1sabatsuhani74No ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument6 pagesSemiconductordksingh369No ratings yet
- 1.1 Group 2Document32 pages1.1 Group 2SN1-0622 Khairul Bariah Binti IzaniNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure andDocument19 pagesAtomic Structure andDonna BonielNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry 2020Document94 pagesInorganic Chemistry 2020Deejay Griffin256No ratings yet
- Solids and Semiconductor Devices PDFDocument68 pagesSolids and Semiconductor Devices PDFdhruviNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sk015Document19 pagesChemistry Sk015Ahmad Munawir Ahmad WardiNo ratings yet
- Nikola Tesla - Case FilesDocument13 pagesNikola Tesla - Case FilesAryan KohliNo ratings yet
- Et 316Document30 pagesEt 316Ali IhtshamNo ratings yet
- Tuesday, May 03, 2022Document34 pagesTuesday, May 03, 2022Le Cong LapNo ratings yet
- Smart-UPS SMC3000IDocument3 pagesSmart-UPS SMC3000IAry WinariasariNo ratings yet
- A Review of Literature On Various Techniques of COP Improvement in Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemDocument9 pagesA Review of Literature On Various Techniques of COP Improvement in Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Kitchens Catalogue 2021Document40 pagesKitchens Catalogue 2021Rai SahibNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Tcg2032 DeutzDocument3 pagesData Sheet Tcg2032 DeutzMaximiliano SanchezNo ratings yet
- Safestart 700-Series: InstallationDocument1 pageSafestart 700-Series: InstallationSergei BiryukovNo ratings yet
- 10-87-02 Spec For Ceramic Fibre Blanket InsulationDocument5 pages10-87-02 Spec For Ceramic Fibre Blanket InsulationlightsonsNo ratings yet
- Boq No. Particulars Unit BOQ QTY Basic Rate Basic AmountDocument18 pagesBoq No. Particulars Unit BOQ QTY Basic Rate Basic AmountmanojNo ratings yet
- CompletionDocument107 pagesCompletionAdel ALkhaligyNo ratings yet
- ယမ်းထုတ်လုပ်နည်းမျာ 1Document30 pagesယမ်းထုတ်လုပ်နည်းမျာ 1jo joNo ratings yet
- Lecture-8 HEN Part3Document15 pagesLecture-8 HEN Part3Imran UnarNo ratings yet
- Touran No. 204 / 1: Position of Relays and Fuses Electronics Box Low, From May 2005Document18 pagesTouran No. 204 / 1: Position of Relays and Fuses Electronics Box Low, From May 2005Dariaxa Sos CarsNo ratings yet
- Briggs and Stratton Log Splitter 1264320036E1Document29 pagesBriggs and Stratton Log Splitter 1264320036E1AndrewNo ratings yet
- Case Note: Greenpeace Nordic and Nature and Youth v. Ministry of Energy, January 2024Document6 pagesCase Note: Greenpeace Nordic and Nature and Youth v. Ministry of Energy, January 2024octavientNo ratings yet
- 111 - White Paper - Fire-Safety-In-Electric-Vehicle-Parking-GaragesDocument23 pages111 - White Paper - Fire-Safety-In-Electric-Vehicle-Parking-GaragesDmitryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Module 2Document4 pagesChapter 7 Module 2Sarmiento, Jovenal B.No ratings yet
- 1a UthmDocument9 pages1a UthmMohamad Muslihuddin RazaliNo ratings yet
- Science2 - Chapterwise Practice Papers + PYQDocument37 pagesScience2 - Chapterwise Practice Papers + PYQ12 XB Atharva kharatNo ratings yet
- Call For Papers ICEFSI 27 PDFDocument2 pagesCall For Papers ICEFSI 27 PDFSeif eddine Ben hammoudaNo ratings yet
- FilterDocument4 pagesFilterjaimhakal100% (1)
- Life Cycle of A Star - WorksheetDocument4 pagesLife Cycle of A Star - WorksheetLNo ratings yet
- Boric Acid CorrosionDocument47 pagesBoric Acid CorrosionFedak MarosNo ratings yet
- D2 (D2EU) : User ManualDocument2 pagesD2 (D2EU) : User ManualAlper GümüştekinNo ratings yet
- Depletion and Decline Curve Analysis in Crude Oil ProductionDocument112 pagesDepletion and Decline Curve Analysis in Crude Oil ProductionaliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Calculations - Midterm ExamDocument12 pagesChemical Engineering Calculations - Midterm ExamJohnNo ratings yet
- Weda50 2954531000-3 ENDocument20 pagesWeda50 2954531000-3 ENMikael TuokkolaNo ratings yet
- Group 02Document22 pagesGroup 02WSMengine WSMengineNo ratings yet
- List of Parts For Tractors ApplicationDocument9 pagesList of Parts For Tractors ApplicationSanjay Kumar BansalNo ratings yet