Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.3 Eukayotic and Prokaryotic Cells - Odp
1.3 Eukayotic and Prokaryotic Cells - Odp
Uploaded by
Zaynab ShaikhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.3 Eukayotic and Prokaryotic Cells - Odp
1.3 Eukayotic and Prokaryotic Cells - Odp
Uploaded by
Zaynab ShaikhCopyright:
Available Formats
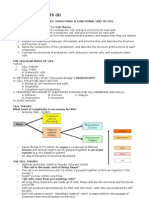
1.
3
EUKARYOTIC & PROKARYOTIC
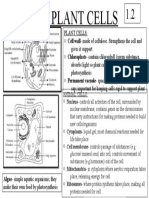
PROKARYOTIC CELLS
CELLS
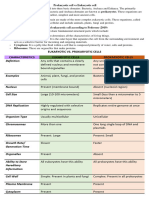
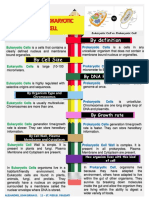
Eukaryotic cells
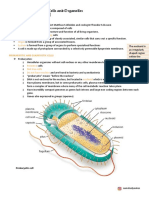
o They all have a cell membrane, o Prokaryotic cells consist of cytoplasm and a cell membrane
surrounded by a cell wall (does not contain cellulose)
cytoplasm, and genetic material
o The genetic material is not in a distinct nucleus- it forms a
enclosed in a nucleus
single DNA loop (bacterial chromosome, found free in
o The genetic material is a chemical
cytoplasm)
called DNA- this forms structures o Prokaryotes may contain 1 or more extra small rings of DNA
(chromosomes) that are contained (plasmids)
within the nucleus. o Plasmids code for very specific features such as antibiotic
o All animals (including humans), plants, resistance
fungi and Protista are eukaryotes o Bacteria (single celled living organisms) are all prokaryotes.
Some types of bacteria have:
100m Giant redwood - Protective slime capsule around outside of cell wall
10m Minke whale - Have at least one flagellum- long protein strand that lashes
Human eye
1m
Human about (uses it to move themselves around)
10cm Apple o Many bacteria have little or no effect on other organisms, many
Light microscope
1cm Wasp are very useful
1mm Ant o Some bacteria are harmful, bacteria can cause diseases in
100μm
Electron microscope
Eukaryotic cells humans, animals and plants. They can also decompose and
10μm
destroy stored food
1μm Prokaryotic cells
Relative sizes: Bigger number / smaller number is:
100nm Viruses o Less than 10- same order of magnitude
10nm DNA o Around 10- (10*1) an order of magnitude
1nm A small molecule o Around 100- (10*2) two order of magnitude
You might also like
- Zoology 100 Notes 2Document27 pagesZoology 100 Notes 2Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroNo ratings yet
- Campbell and Reece Chapter 1Document7 pagesCampbell and Reece Chapter 1ninado92No ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- B1 - Cell Structure and TransportDocument11 pagesB1 - Cell Structure and TransportSahasra BhongirwarNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument23 pagesCell Structure and FunctionMoosa KhanNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Cells A ReviewDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - Cells A ReviewalanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1Pratik PawarNo ratings yet
- EUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Document2 pagesEUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Alea AicoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - Unit - 1Document19 pagesCell Biology - Unit - 1shivangipurohitNo ratings yet
- Biomedical 01Document26 pagesBiomedical 01api-3706483No ratings yet
- Cell - Study NotesDocument16 pagesCell - Study NotesrockyajeetNo ratings yet
- The Cell 1: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityDocument84 pagesThe Cell 1: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityLinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Prokaryotes and EukaryotesRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction To The CellDocument18 pagesLecture 1-Introduction To The CellThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- G.Bio. AL-Saeeda (18 - 41)Document24 pagesG.Bio. AL-Saeeda (18 - 41)naaaa7733770No ratings yet
- 01) B - Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument17 pages01) B - Cell - The Unit of Lifepriybratshukla1No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles LectureDocument54 pagesCell Organelles LectureAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Name: Marie Char C. Agustines Course: Bsed-Science 22 BiochemistryDocument6 pagesName: Marie Char C. Agustines Course: Bsed-Science 22 BiochemistryAgustines, Marie Char C.No ratings yet
- CeluarDocument7 pagesCeluarJef PerezNo ratings yet
- 3.0 The Nature of CellsDocument1 page3.0 The Nature of CellsBorger Prays MelktiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument26 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsKirito HatakuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 pagesUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document4 pagesCell (Biology)Marella SatorreNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesFundamental Unit of LifeAdil KhanNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Sem 1 NotesDocument12 pagesGen Bio Sem 1 NotesFrances Chynna KhoNo ratings yet
- (M1) The CellDocument14 pages(M1) The CellBSN 1-1No ratings yet
- Prokalytic Vs EurokalyticDocument1 pageProkalytic Vs EurokalyticJessielyn DangananNo ratings yet
- ORGANISASI SELULER - Struktur Dan Fungsi-2017 PDFDocument58 pagesORGANISASI SELULER - Struktur Dan Fungsi-2017 PDFMantanindah 0206No ratings yet
- Week 3 - Bacteriology LectureDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Bacteriology LectureReangg SerranoNo ratings yet
- Botany InformationDocument19 pagesBotany InformationJana Mohamed Mohamed Asaad Ibrahim AwadNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- 01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFDocument6 pages01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- The Cell: An OverviewDocument31 pagesThe Cell: An OverviewTracy IlaganNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts & Functions PRSNTTN 20Document136 pagesCell Parts & Functions PRSNTTN 20Scar ShadowNo ratings yet
- Prokariotik Dan Eukariotik 2Document22 pagesProkariotik Dan Eukariotik 2hanumNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- 2300 Module 3 Infection and MicrobiologyDocument33 pages2300 Module 3 Infection and Microbiologymegan.abbinkNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesdaddysharkNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-Notes - SampleDocument2 pages8 Cell - The Unit of Life-Notes - SampleManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Biology Study NotesDocument40 pagesBiology Study NotesnishNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Chimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 ReviewerDocument15 pagesGenbio1 ReviewerMichelle VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- 01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFDocument5 pages01 Bio IX ICSE Cell PDFsonali voraNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 SImilarities and Differences Between Generalised Plant, Animal and Bacterial CellsDocument7 pagesTopic 1 SImilarities and Differences Between Generalised Plant, Animal and Bacterial CellsHol UpNo ratings yet
- 2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1Document24 pages2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1saidatulNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 BioDocument39 pagesTopic 3 BioTsukiNo ratings yet
- Chem113lec Week 3.2Document5 pagesChem113lec Week 3.2Darryl orcaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organization and Structure (Option C)Document4 pagesCell Organization and Structure (Option C)-Sabiraaa -No ratings yet
- تخدير المحاضرة الاولىDocument7 pagesتخدير المحاضرة الاولىXcv FfgNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Navigation SearchDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : Navigation Searchsamz95100% (1)
- Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic CellDocument3 pagesCells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cellgafir1230No ratings yet
- CELLDocument15 pagesCELLbithiinnNo ratings yet
- As Chapter 1Document20 pagesAs Chapter 1vt_greedhareeNo ratings yet
- Cytology 2023Document18 pagesCytology 2023emakelvin040No ratings yet
- 1.2 - Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes - EA-1Document26 pages1.2 - Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes - EA-1sophiewayman07No ratings yet
- Micropara ReviewerDocument6 pagesMicropara ReviewerlovelyNo ratings yet
- Animal Farm Chapter 1Document1 pageAnimal Farm Chapter 1Zaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Specialisation in Plant Cells - OdpDocument1 page1.5 Specialisation in Plant Cells - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Specialisation in Animal Cells - OdpDocument1 page1.4 Specialisation in Animal Cells - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Chemical Equations - OdpDocument1 page1.2 Chemical Equations - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1.5 History of An Atom - OdpDocument1 page1.5 History of An Atom - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Animal and Plant Cells - OdpDocument1 page1.2 Animal and Plant Cells - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The World of The Microscope - OdpDocument1 page1.1 The World of The Microscope - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Fractional Distillation and Paper Chromatography - OdpDocument1 page1.4 Fractional Distillation and Paper Chromatography - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Separating Mixtures - OdpDocument2 pages1.3 Separating Mixtures - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atoms - OdpDocument1 page1.1 Atoms - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureIrvin Jacob AquinoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - NCERT BasedDocument4 pagesWorksheet 1 - NCERT BasedSonia GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bacteria - Definition, Shapes, Characteristics, Types & ExamplesDocument2 pagesBacteria - Definition, Shapes, Characteristics, Types & ExamplesBaikuntha SabarNo ratings yet
- Looking Inside Cells: Introduction To Plant & Animal Cells Chapter 10 Lesson 3Document21 pagesLooking Inside Cells: Introduction To Plant & Animal Cells Chapter 10 Lesson 3Maricel BautistaNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter ExaminationDocument3 pagesSecond Quarter ExaminationHenry Canon LumangtadNo ratings yet
- 1St Quarterly Test in Science 7Document4 pages1St Quarterly Test in Science 7Joanne GodezanoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells and MicroorganismsDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cells and MicroorganismsClarisse TanNo ratings yet
- Exercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsDocument16 pagesExercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsHidayatul ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Organisms Can Be Classified Based On Physical Similarities.: Key ConceptDocument52 pagesOrganisms Can Be Classified Based On Physical Similarities.: Key ConceptCarylle Keona IlanoNo ratings yet
- Bacte Lec Mod.1 TranscriptDocument10 pagesBacte Lec Mod.1 TranscriptWinslet Kaye SuerteNo ratings yet
- Cls 8 Rev SheetDocument11 pagesCls 8 Rev SheetAashi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biological Evolution (Table of Contents)Document10 pagesIntroduction To Biological Evolution (Table of Contents)Mitch Forbes100% (1)
- Orientation 3Document2 pagesOrientation 3andoithinkerNo ratings yet
- chapter-3-CELL STRUCTURE TAXONOMYDocument54 pageschapter-3-CELL STRUCTURE TAXONOMYCza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Virtual Laboratory Exercise 2Document4 pagesVirtual Laboratory Exercise 2Jung Somin100% (1)
- EuglenaDocument5 pagesEuglenaAngel García MNo ratings yet
- RAT Science 7Document8 pagesRAT Science 7Ann Geddies Lotino100% (1)
- Bio CH 2 (Cell - The Unit of Life) Book Exercise AnswersDocument15 pagesBio CH 2 (Cell - The Unit of Life) Book Exercise AnswersKeshav Agrawal100% (1)
- Laboratory Manual in BiochemistryDocument37 pagesLaboratory Manual in BiochemistrySOPHIA MARGARETTE NOVELONo ratings yet
- Topical Past PapersDocument208 pagesTopical Past PapersShafaq RamzanNo ratings yet
- Cell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaDocument10 pagesCell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Science 7Document5 pagesWeek 9 Science 7Jerline Jane AntioquiaNo ratings yet
- ACT BIOLOGY HighlightsDocument157 pagesACT BIOLOGY HighlightsOmar SedkeyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and Taxonomyporkypig100% (11)
- Ch25-Life The Science of Biology 12th Ed 2020Document21 pagesCh25-Life The Science of Biology 12th Ed 2020slatorrem14No ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument19 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryoteapi-296074239No ratings yet
- Lesson1 2Document4 pagesLesson1 2Cheradee AnimNo ratings yet
- Zoology 100 NotesDocument12 pagesZoology 100 Notesangel_witchie619No ratings yet
- Domain Eukarya-YR10 - PART2 - TUTE2Document7 pagesDomain Eukarya-YR10 - PART2 - TUTE2Sandalu Romeshika PereraNo ratings yet