Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
23 viewsPharmacology in Nursing
Pharmacology in Nursing
Uploaded by
Jessa Mae BarquillaThis document summarizes key concepts in pharmacology and nursing related to medication administration and drug effects. It defines terms like adverse effects, drug action phases, metabolism, toxicity, and tolerance. It provides examples of commonly used respiratory drugs including antihistamines, nasal decongestants, and intranasal glucocorticoids. It also covers medication orders, calculations involving weight and volume, and concepts like loading dose and half-life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CAD CAM Splints For The Functional and Esthetic Evaluation of Newly Defined Occlusal Dimensions PDFDocument12 pagesCAD CAM Splints For The Functional and Esthetic Evaluation of Newly Defined Occlusal Dimensions PDFEsme ValenciaNo ratings yet
- PDF Thors Power Program Load Calculator Microsoft Excelgsheet PDFDocument4 pagesPDF Thors Power Program Load Calculator Microsoft Excelgsheet PDFSxf KtmNo ratings yet
- 09 ITLS PretestDocument6 pages09 ITLS PretestArlanosaurus100% (2)
- Drug Study: Epinephrine: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Epinephrine: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- EpinephrineDocument4 pagesEpinephrinegovind_soni_15No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument2 pagesCholinergic AntagonistsAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORYDocument44 pagesRESPIRATORYJannele BernadasNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument3 pagesPharmaVinceNo ratings yet
- Pharm Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm Drugs ChartsTris100% (1)
- Morphine SulfateDocument1 pageMorphine SulfateyeshaellatapucayNo ratings yet
- All Other ClassificationsDocument6 pagesAll Other ClassificationsCorey100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraDocument15 pagesDRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraCharm Abyss la MorenaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Course TaskDocument7 pagesWeek 5 - Course TaskCher Allain BellosilloNo ratings yet
- FlupentixolDocument3 pagesFlupentixolshiplusNo ratings yet
- W9 PharmacologyDocument5 pagesW9 PharmacologyEh paano kung HindiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJhucyl Mae GalvezNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIAdrugstudyDocument5 pagesPSYCHIAdrugstudyJss Rosete-De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Atropine: RecommendedDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Atropine: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- J.H. Cerilles State CollegeDocument27 pagesJ.H. Cerilles State CollegeJonna JuntillaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Delos SantosDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY - Delos SantosJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document3 pagesModule 2Esmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Bronchospasm Child: PO 2-6 Y, 0.1-: 0.2 MG/KG T.I.D. (Max: 4 Mg/dose) 6-12 Y, 2 MG 3-4 Times/dDocument2 pagesBronchospasm Child: PO 2-6 Y, 0.1-: 0.2 MG/KG T.I.D. (Max: 4 Mg/dose) 6-12 Y, 2 MG 3-4 Times/dArnold De Guzman Jr.No ratings yet
- College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing Drug StudyJaye Aprile Adrianne KuizonNo ratings yet
- Drug study-FIRST TWO MEDICAL WARDDocument2 pagesDrug study-FIRST TWO MEDICAL WARDErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Adiel Joy P. Calsa Drug Study March 9, 2022Document5 pagesAdiel Joy P. Calsa Drug Study March 9, 2022Adiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeChenime Añana0% (1)
- Drug Study: EpinephrineDocument5 pagesDrug Study: EpinephrineOmyl-Khayr M. SulogNo ratings yet
- Ipratroprium Drug CardDocument3 pagesIpratroprium Drug CardXiaoDuckyNo ratings yet
- Tolleno Drug Study (Hemo Dialysis)Document5 pagesTolleno Drug Study (Hemo Dialysis)Hannah TollenoNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System Adrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesAdrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System Adrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument2 pagesAtropine SulfateMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyshiela marie cortezNo ratings yet
- Drugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyDocument5 pagesDrugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyMarjoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyMichelle TamorNo ratings yet
- Drug study-THIRD TWO MEDICAL WARDDocument2 pagesDrug study-THIRD TWO MEDICAL WARDErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Generic NameDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Generic NameMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- General AnestheticDocument2 pagesGeneral AnestheticKirby AcobaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResposibilitiesDocument10 pagesDrug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResposibilitiesAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Drug Study-MW2-Case 1Document4 pagesDrug Study-MW2-Case 1Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IMDocument2 pagesDrug Study IMAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyLovelyNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Haloperidol)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Haloperidol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyZek Comidoy100% (1)
- Tramadol, Paracetamol, Calmoseptine, B12Document5 pagesTramadol, Paracetamol, Calmoseptine, B12Denise EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics Indication Origin Market Name Absorption Peak Plasma Level Half-Life Excretion DoseDocument4 pagesCharacteristics Indication Origin Market Name Absorption Peak Plasma Level Half-Life Excretion DoseShafiqah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Drug Studymarvinsanantonio0612No ratings yet
- PDF Drug Study Morphine SulfateDocument3 pagesPDF Drug Study Morphine SulfateCrishelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Student: - Zeena Rose S. Llanes Block: - 261 - BBB (Group G)Document2 pagesDrug Study: Student: - Zeena Rose S. Llanes Block: - 261 - BBB (Group G)hey judeNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY HndoutDocument12 pagesPSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY HndoutMhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Exam Ii NotesDocument24 pagesPharm Exam Ii Noteskatiana louisNo ratings yet
- Injection, OTC Nasal Solution:: Generic Name: Action: IndicationsDocument8 pagesInjection, OTC Nasal Solution:: Generic Name: Action: IndicationsRonald Anthony TobiasNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument11 pagesEmergency DrugsJade Hemmings100% (1)
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Breathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetDocument8 pagesBreathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument2 pagesPsychotherapeutic AgentsjustinahorroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For LM, NBS and FPDocument2 pagesReviewer For LM, NBS and FPJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Oxy and Fluids FinalsssssssDocument1 pageOxy and Fluids FinalsssssssJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oxy and Fluids MidtermsDocument3 pagesReviewer in Oxy and Fluids MidtermsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Skills LabDocument2 pagesSkills LabJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in TheoryDocument1 pageReviewer in TheoryJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesReviewer in Fluids and ElectrolytesJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CHN ReviewerDocument2 pagesChapter 8 CHN ReviewerJessa Mae Barquilla100% (1)
- CHN - Nursing ConceptsDocument5 pagesCHN - Nursing ConceptsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Care of Older AdultsDocument2 pagesCare of Older AdultsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- CHN - School Nursing and OccupationalDocument4 pagesCHN - School Nursing and OccupationalJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- CARE 0F OLDERS ADULTS MidtermsDocument2 pagesCARE 0F OLDERS ADULTS MidtermsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Ar 2014 PDFDocument234 pagesAr 2014 PDFDoni SusantoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology TortoraDocument33 pagesMicrobiology TortoraLaizaEuniceT.Monte100% (1)
- Historical Phases of CSRDocument12 pagesHistorical Phases of CSRHIMANSHU RAWATNo ratings yet
- Socrates 8dDocument8 pagesSocrates 8dcarolinaNo ratings yet
- Acidifiers and Antiseptics Lecture Notes-Dr - Jibachha Sah, Lecturer, M.V.SC (Pharmacology)Document29 pagesAcidifiers and Antiseptics Lecture Notes-Dr - Jibachha Sah, Lecturer, M.V.SC (Pharmacology)jibachha sahNo ratings yet
- ZA eCTD Module 1 Technical v1Document74 pagesZA eCTD Module 1 Technical v1vinayNo ratings yet
- Organic Strawberries: Production Guide ForDocument60 pagesOrganic Strawberries: Production Guide ForJosé A. MCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1Melaku WalelgneNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Clinical PsychologyFINISHED AllanDocument33 pagesResearch Methods in Clinical PsychologyFINISHED AllanAllan DiversonNo ratings yet
- Airfit-N20 Disinfection-Sterilization-Guide Amer Eng PDFDocument3 pagesAirfit-N20 Disinfection-Sterilization-Guide Amer Eng PDFhorse888No ratings yet
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Food BioscienceDocument39 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Food BiosciencerenNo ratings yet
- Boerick Compendium of Materia MedicaDocument180 pagesBoerick Compendium of Materia Medicadbsmanian100% (9)
- Daikin AP Catalogue Digital1Document32 pagesDaikin AP Catalogue Digital1Sowham ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Contingency Plan FormatDocument2 pagesContingency Plan FormatNagarajanNo ratings yet
- CS2 Booklet 7 (Mortality Projection) 2019 FINALDocument38 pagesCS2 Booklet 7 (Mortality Projection) 2019 FINALAnsh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Tikus Sparague DawleyDocument7 pagesTikus Sparague DawleyardeajauhansyahNo ratings yet
- Induction Program ScriptDocument2 pagesInduction Program ScriptAl-var A AtibingNo ratings yet
- Arteritis TemporalisDocument5 pagesArteritis TemporalisbagasNo ratings yet
- Home Remedies Using Mustard Seeds Prophet666Document2 pagesHome Remedies Using Mustard Seeds Prophet666Hussainz AliNo ratings yet
- VR TherapyDocument5 pagesVR TherapyHec ChavezNo ratings yet
- South Carolina In-Patient Drug & Alcohol Treatment ProgramsDocument2 pagesSouth Carolina In-Patient Drug & Alcohol Treatment ProgramsABC News 4100% (1)
- Aldridge A Short Introduction To CounsellingDocument22 pagesAldridge A Short Introduction To Counsellingbyron chieNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Care Di DenmarkDocument6 pagesPharmaceutical Care Di DenmarkBaiq KartikasariNo ratings yet
- BiographyDocument7 pagesBiographyapi-348852766No ratings yet
- Health 7 LAS Quarter 3 1 1Document62 pagesHealth 7 LAS Quarter 3 1 1raymart zalunNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System of IVRCL LIMITEDDocument70 pagesQuality Management System of IVRCL LIMITEDSagar Paul'g100% (1)
- Physical Inactivity TestDocument66 pagesPhysical Inactivity TestNHEMSTERS xoxoNo ratings yet
Pharmacology in Nursing
Pharmacology in Nursing
Uploaded by
Jessa Mae Barquilla100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
23 views1 pageThis document summarizes key concepts in pharmacology and nursing related to medication administration and drug effects. It defines terms like adverse effects, drug action phases, metabolism, toxicity, and tolerance. It provides examples of commonly used respiratory drugs including antihistamines, nasal decongestants, and intranasal glucocorticoids. It also covers medication orders, calculations involving weight and volume, and concepts like loading dose and half-life.
Original Description:
Original Title
PHARMACOLOGY IN NURSING
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key concepts in pharmacology and nursing related to medication administration and drug effects. It defines terms like adverse effects, drug action phases, metabolism, toxicity, and tolerance. It provides examples of commonly used respiratory drugs including antihistamines, nasal decongestants, and intranasal glucocorticoids. It also covers medication orders, calculations involving weight and volume, and concepts like loading dose and half-life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
23 views1 pagePharmacology in Nursing
Pharmacology in Nursing
Uploaded by
Jessa Mae BarquillaThis document summarizes key concepts in pharmacology and nursing related to medication administration and drug effects. It defines terms like adverse effects, drug action phases, metabolism, toxicity, and tolerance. It provides examples of commonly used respiratory drugs including antihistamines, nasal decongestants, and intranasal glucocorticoids. It also covers medication orders, calculations involving weight and volume, and concepts like loading dose and half-life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
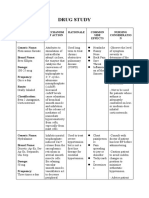
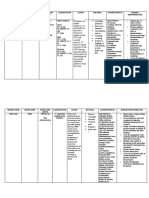
PHARMACOLOGY IN NURSING Adverse Effects – unexpected, sever life
DRUG – chemical agent threatening effects First-generation antihistamine
MEDICATION – drug that promotes a Rifampicin - to treat tuberculosis (TB) in Traditional
therapeutic effect many different parts of the body. - Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
Phases of Drug Action SE: Red Orange dc of secretion - Chlorphenamine
Pharmacokinetics AE: Hepatoxicity (jaundice) - Hydroxyzine
A – Absorption TOXICITY – damage to certain organs of Side effects:
D – Distribution the body - Drowsiness
M – Metabolism TACHYPLAXIS/TOLERANCE – decrease - Anticholinergic symptoms (blurred
E – Excretion response to the usual dose of drug vision, dry throat, urinary retention,
Without meals Resistance means not effective and constipation)
Metabolism – Cells DEPENDENCE – appearance of withdrawal SNS – Epinephrine,
Digestion – Digestive System symptoms when the drug is withheld Norepinephrine>Catecholine
Liver – primary organ for metabolism Alcohol-dependent PNS – Acetylcholine
Kidney – primary organ for excretion S&S: Tremors and sweating Second-generation antihistamine
Pharmacodynamics MEDICATION ORDERS Loratadine
Stimulation or depression Standing – may be carried out Cetirizine
independently Consideration: Safety
Replacement
PRN – as needed - Avoidance of other
Inhibition or killing of organism
Single – Once at a specified time drugs/substances
Irritation STAT – immediately and only once - Activity modification
Hyperthyroidism Epinephrine – cardiac arrest 2. Nasal-decongestants
Thin MEDICATION CALCULATION - Action: SNS Stimulation
Long hair Weight Nasal vasoconstriction
Tapazole - It works by stopping the 1kg =1,000g - Local (Spray, drops) – avoid
thyroid gland from making too much 1kg = 2.2 lbs. prolonged use
thyroid hormone. 1g = 1000 mg Rebound congestion
Insulin – Type 1 - Systemic (tab, cap, syrup)
1mg = 1000mcg
Both Type 1 and Type 2 - phenylephrine, pseudoephedrine,
1 grain = 60 mg
Dulcolax – irritates the new endings phenylpropandamine
Volume
Used to treat constipation Length - Caution: HTN, Cardiac
BASIC CONCEPTS FORMULA: D X Q 3. Intranasal glucocorticoids
Loading Dose S Steroids – anti-inflammatory
Initial dose which is larger than the RESPIRATORY DRUGS (URTI) Suffix: - sone
maintenance dose Rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis - Beclomethasone
Half-life 1. Antihistamines: H1 Blockers - Dexamethasone
Duration it takes for half of the drug Decrease Nasopharyngeal - Flulocasone
to be removed from the body. production - Budosmide
DRUG EFFECTS Delayed onset
Not indicated anaphylaxis –
Side Effects – secondary, expected and Risk for infection
epinephrine
unintended effects.
Bronchoconstriction – DOP
Vasodilation (massive) – low BP
You might also like
- CAD CAM Splints For The Functional and Esthetic Evaluation of Newly Defined Occlusal Dimensions PDFDocument12 pagesCAD CAM Splints For The Functional and Esthetic Evaluation of Newly Defined Occlusal Dimensions PDFEsme ValenciaNo ratings yet
- PDF Thors Power Program Load Calculator Microsoft Excelgsheet PDFDocument4 pagesPDF Thors Power Program Load Calculator Microsoft Excelgsheet PDFSxf KtmNo ratings yet
- 09 ITLS PretestDocument6 pages09 ITLS PretestArlanosaurus100% (2)
- Drug Study: Epinephrine: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Epinephrine: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- EpinephrineDocument4 pagesEpinephrinegovind_soni_15No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument2 pagesCholinergic AntagonistsAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORYDocument44 pagesRESPIRATORYJannele BernadasNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument3 pagesPharmaVinceNo ratings yet
- Pharm Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm Drugs ChartsTris100% (1)
- Morphine SulfateDocument1 pageMorphine SulfateyeshaellatapucayNo ratings yet
- All Other ClassificationsDocument6 pagesAll Other ClassificationsCorey100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraDocument15 pagesDRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraCharm Abyss la MorenaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Course TaskDocument7 pagesWeek 5 - Course TaskCher Allain BellosilloNo ratings yet
- FlupentixolDocument3 pagesFlupentixolshiplusNo ratings yet
- W9 PharmacologyDocument5 pagesW9 PharmacologyEh paano kung HindiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJhucyl Mae GalvezNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIAdrugstudyDocument5 pagesPSYCHIAdrugstudyJss Rosete-De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Atropine: RecommendedDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Atropine: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- J.H. Cerilles State CollegeDocument27 pagesJ.H. Cerilles State CollegeJonna JuntillaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Delos SantosDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY - Delos SantosJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document3 pagesModule 2Esmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Bronchospasm Child: PO 2-6 Y, 0.1-: 0.2 MG/KG T.I.D. (Max: 4 Mg/dose) 6-12 Y, 2 MG 3-4 Times/dDocument2 pagesBronchospasm Child: PO 2-6 Y, 0.1-: 0.2 MG/KG T.I.D. (Max: 4 Mg/dose) 6-12 Y, 2 MG 3-4 Times/dArnold De Guzman Jr.No ratings yet
- College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing Drug StudyJaye Aprile Adrianne KuizonNo ratings yet
- Drug study-FIRST TWO MEDICAL WARDDocument2 pagesDrug study-FIRST TWO MEDICAL WARDErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Adiel Joy P. Calsa Drug Study March 9, 2022Document5 pagesAdiel Joy P. Calsa Drug Study March 9, 2022Adiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeChenime Añana0% (1)
- Drug Study: EpinephrineDocument5 pagesDrug Study: EpinephrineOmyl-Khayr M. SulogNo ratings yet
- Ipratroprium Drug CardDocument3 pagesIpratroprium Drug CardXiaoDuckyNo ratings yet
- Tolleno Drug Study (Hemo Dialysis)Document5 pagesTolleno Drug Study (Hemo Dialysis)Hannah TollenoNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System Adrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesAdrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System Adrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument2 pagesAtropine SulfateMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyshiela marie cortezNo ratings yet
- Drugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyDocument5 pagesDrugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyMarjoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyMichelle TamorNo ratings yet
- Drug study-THIRD TWO MEDICAL WARDDocument2 pagesDrug study-THIRD TWO MEDICAL WARDErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Generic NameDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Generic NameMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- General AnestheticDocument2 pagesGeneral AnestheticKirby AcobaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResposibilitiesDocument10 pagesDrug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResposibilitiesAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Drug Study-MW2-Case 1Document4 pagesDrug Study-MW2-Case 1Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IMDocument2 pagesDrug Study IMAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyLovelyNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Haloperidol)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Haloperidol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyZek Comidoy100% (1)
- Tramadol, Paracetamol, Calmoseptine, B12Document5 pagesTramadol, Paracetamol, Calmoseptine, B12Denise EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics Indication Origin Market Name Absorption Peak Plasma Level Half-Life Excretion DoseDocument4 pagesCharacteristics Indication Origin Market Name Absorption Peak Plasma Level Half-Life Excretion DoseShafiqah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Drug Studymarvinsanantonio0612No ratings yet
- PDF Drug Study Morphine SulfateDocument3 pagesPDF Drug Study Morphine SulfateCrishelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Student: - Zeena Rose S. Llanes Block: - 261 - BBB (Group G)Document2 pagesDrug Study: Student: - Zeena Rose S. Llanes Block: - 261 - BBB (Group G)hey judeNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY HndoutDocument12 pagesPSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY HndoutMhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Exam Ii NotesDocument24 pagesPharm Exam Ii Noteskatiana louisNo ratings yet
- Injection, OTC Nasal Solution:: Generic Name: Action: IndicationsDocument8 pagesInjection, OTC Nasal Solution:: Generic Name: Action: IndicationsRonald Anthony TobiasNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument11 pagesEmergency DrugsJade Hemmings100% (1)
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Breathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetDocument8 pagesBreathing Problems Drowsiness, Dizziness Constipation, Nausea Vomiting Sweating Numbness, Tingling, or Cold Feeling in Your Hands and FeetGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument2 pagesPsychotherapeutic AgentsjustinahorroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For LM, NBS and FPDocument2 pagesReviewer For LM, NBS and FPJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Oxy and Fluids FinalsssssssDocument1 pageOxy and Fluids FinalsssssssJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oxy and Fluids MidtermsDocument3 pagesReviewer in Oxy and Fluids MidtermsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Skills LabDocument2 pagesSkills LabJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in TheoryDocument1 pageReviewer in TheoryJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesReviewer in Fluids and ElectrolytesJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CHN ReviewerDocument2 pagesChapter 8 CHN ReviewerJessa Mae Barquilla100% (1)
- CHN - Nursing ConceptsDocument5 pagesCHN - Nursing ConceptsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Care of Older AdultsDocument2 pagesCare of Older AdultsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- CHN - School Nursing and OccupationalDocument4 pagesCHN - School Nursing and OccupationalJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- CARE 0F OLDERS ADULTS MidtermsDocument2 pagesCARE 0F OLDERS ADULTS MidtermsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Ar 2014 PDFDocument234 pagesAr 2014 PDFDoni SusantoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology TortoraDocument33 pagesMicrobiology TortoraLaizaEuniceT.Monte100% (1)
- Historical Phases of CSRDocument12 pagesHistorical Phases of CSRHIMANSHU RAWATNo ratings yet
- Socrates 8dDocument8 pagesSocrates 8dcarolinaNo ratings yet
- Acidifiers and Antiseptics Lecture Notes-Dr - Jibachha Sah, Lecturer, M.V.SC (Pharmacology)Document29 pagesAcidifiers and Antiseptics Lecture Notes-Dr - Jibachha Sah, Lecturer, M.V.SC (Pharmacology)jibachha sahNo ratings yet
- ZA eCTD Module 1 Technical v1Document74 pagesZA eCTD Module 1 Technical v1vinayNo ratings yet
- Organic Strawberries: Production Guide ForDocument60 pagesOrganic Strawberries: Production Guide ForJosé A. MCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1Melaku WalelgneNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Clinical PsychologyFINISHED AllanDocument33 pagesResearch Methods in Clinical PsychologyFINISHED AllanAllan DiversonNo ratings yet
- Airfit-N20 Disinfection-Sterilization-Guide Amer Eng PDFDocument3 pagesAirfit-N20 Disinfection-Sterilization-Guide Amer Eng PDFhorse888No ratings yet
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Food BioscienceDocument39 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Food BiosciencerenNo ratings yet
- Boerick Compendium of Materia MedicaDocument180 pagesBoerick Compendium of Materia Medicadbsmanian100% (9)
- Daikin AP Catalogue Digital1Document32 pagesDaikin AP Catalogue Digital1Sowham ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Contingency Plan FormatDocument2 pagesContingency Plan FormatNagarajanNo ratings yet
- CS2 Booklet 7 (Mortality Projection) 2019 FINALDocument38 pagesCS2 Booklet 7 (Mortality Projection) 2019 FINALAnsh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Tikus Sparague DawleyDocument7 pagesTikus Sparague DawleyardeajauhansyahNo ratings yet
- Induction Program ScriptDocument2 pagesInduction Program ScriptAl-var A AtibingNo ratings yet
- Arteritis TemporalisDocument5 pagesArteritis TemporalisbagasNo ratings yet
- Home Remedies Using Mustard Seeds Prophet666Document2 pagesHome Remedies Using Mustard Seeds Prophet666Hussainz AliNo ratings yet
- VR TherapyDocument5 pagesVR TherapyHec ChavezNo ratings yet
- South Carolina In-Patient Drug & Alcohol Treatment ProgramsDocument2 pagesSouth Carolina In-Patient Drug & Alcohol Treatment ProgramsABC News 4100% (1)
- Aldridge A Short Introduction To CounsellingDocument22 pagesAldridge A Short Introduction To Counsellingbyron chieNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Care Di DenmarkDocument6 pagesPharmaceutical Care Di DenmarkBaiq KartikasariNo ratings yet
- BiographyDocument7 pagesBiographyapi-348852766No ratings yet
- Health 7 LAS Quarter 3 1 1Document62 pagesHealth 7 LAS Quarter 3 1 1raymart zalunNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System of IVRCL LIMITEDDocument70 pagesQuality Management System of IVRCL LIMITEDSagar Paul'g100% (1)
- Physical Inactivity TestDocument66 pagesPhysical Inactivity TestNHEMSTERS xoxoNo ratings yet