Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsOxy and Fluids Finalsssssss
Oxy and Fluids Finalsssssss
Uploaded by
Jessa Mae BarquillaThis document discusses cardiac output and heart failure. It defines cardiac output as the volume of blood pumped by the heart with each contraction and lists factors that can affect it like peripheral vascular tone and neuropulmonary factors. Heart failure is when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, and symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling. Risk factors for heart failure include medical history, weight, age, hypertension, infection, and genetic diseases. The document also discusses signs and symptoms of right ventricular heart failure and treatments for conditions like myocardial infarction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Heart Failure by IvsDocument66 pagesHeart Failure by IvsArianne LasamNo ratings yet
- MEDICAL PATHOLOGIES - CardiovascularDocument6 pagesMEDICAL PATHOLOGIES - Cardiovascularngachangong victorineNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Occur TogetherDocument5 pagesHeart Failure: Occur TogetherPrince Ahmed100% (1)
- HY Internal MedicineDocument449 pagesHY Internal MedicineMohamed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular HO Final GROUP2Document72 pagesCardiovascular HO Final GROUP2Siraj ShiferawNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure in ChildrenDocument47 pagesHeart Failure in ChildrenDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- HY SurgeryDocument283 pagesHY SurgerytejNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument16 pagesHeart FailureRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: Elias S. (MD+) March 2015 DBUDocument35 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: Elias S. (MD+) March 2015 DBUkikiNo ratings yet
- Left Sided HFDocument5 pagesLeft Sided HFGwendolyn Talahiban LusaraNo ratings yet
- HY Family MedicineDocument314 pagesHY Family MedicinetejNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument9 pagesCongestive Heart FailureAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument31 pagesHeart Failuretravis efraimNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC FAILURE NewDocument60 pagesCARDIAC FAILURE NewJake MillerNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease in PregnancyDocument15 pagesHeart Disease in PregnancyAnkur YadavNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diseases Management Amp Nursing CareDocument76 pagesCardiovascular Diseases Management Amp Nursing CareAlberto MeroNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Heart FailureDocument31 pagesPediatric Heart Failureanwar jabariNo ratings yet
- CHF Left SidedDocument21 pagesCHF Left SidedSandie Daniel GabalunosNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Diseases During PregnancyDocument10 pagesCardiac Diseases During PregnancySandyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument38 pagesCardiovascular Disordersmark100% (4)
- PP CardiacDocument62 pagesPP CardiacMarie Queenly Pagaran100% (1)
- Heart FailureDocument40 pagesHeart FailureRebira WorkinehNo ratings yet
- Patho 1Document153 pagesPatho 1ademabdellaaleNo ratings yet
- The Heart-1Document30 pagesThe Heart-1Ebuka AniNo ratings yet
- By: Darryl Jamison Nremt-P Macon County EMS Training CoordinatorDocument52 pagesBy: Darryl Jamison Nremt-P Macon County EMS Training CoordinatordafaferNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument11 pagesCardiovascular SystemMihraban OmerNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure & Circulatory ShockDocument34 pagesHeart Failure & Circulatory ShockMuskaan ZaharaNo ratings yet
- (311 - Rakshita) (312 - Aashish Bharti) - There Are Six Principal Mechanisms of Cardiovascular DysfunctionDocument15 pages(311 - Rakshita) (312 - Aashish Bharti) - There Are Six Principal Mechanisms of Cardiovascular DysfunctionAyshwarya LalNo ratings yet
- Cardio and Hema - DR PueyoDocument161 pagesCardio and Hema - DR Pueyoapi-3735995100% (2)
- CHFDocument3 pagesCHFROSE COLLINSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermDocument11 pagesChapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermJœnríčk AzueloNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument10 pagesCongestive Heart FailureGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Pulmo HPNDocument36 pagesPulmo HPNAlexander Santiago ParelNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument6 pagesCongenital Heart Diseasestheglobalnursing100% (2)
- HY CardioDocument73 pagesHY Cardio190004No ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument55 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasesRajaNo ratings yet
- Heart Valve Problems and Homeopathy - (50 PP)Document50 pagesHeart Valve Problems and Homeopathy - (50 PP)Marcelo Guerra100% (1)
- OXY-Cardio Care ManagementDocument114 pagesOXY-Cardio Care Managementlalaine22daleNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Heart FailureDocument25 pagesLec 3 Heart FailureDelete AccountNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Slides 2024Document43 pagesHeart Failure Slides 2024b9p6vmfnc4No ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease - SeminarDocument35 pagesCongenital Heart Disease - SeminarAsha jilu100% (2)
- HHFFDocument56 pagesHHFFNesru Ahmed AkkichuNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Failure 1Document83 pagesCardiac Failure 1Unathi MbamboNo ratings yet
- 42 Kelainanpatologi Cardiovasc Dr. DianDocument126 pages42 Kelainanpatologi Cardiovasc Dr. DianSurya ArhNo ratings yet
- Cardiac II Study GuideDocument6 pagesCardiac II Study GuiderunnermnNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure and ShockDocument34 pagesHeart Failure and Shockfrenee aradanasNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy With Internal Medical Diseases: Department of Gynaecology and ObstetricsDocument84 pagesPregnancy With Internal Medical Diseases: Department of Gynaecology and ObstetricssanjivdasNo ratings yet
- 18 Heartpart1 Basiccongestiveheartfailure 110919083613 Phpapp01Document43 pages18 Heartpart1 Basiccongestiveheartfailure 110919083613 Phpapp01Atikah PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- 1cardiovascular System DisordersDocument13 pages1cardiovascular System DisordersArvin MalondrasNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument35 pagesCHFMarione GimenezNo ratings yet
- 8 CardiovascularDocument18 pages8 Cardiovascularfiji drNo ratings yet
- Cardiac (Heart) FailureDocument27 pagesCardiac (Heart) FailureSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary HypertensionDocument9 pagesPulmonary HypertensionPricob ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument7 pagesHeart FailureBea Marie A. ValdezNo ratings yet
- Decompensatio Cordis: Disusun Oleh: Andi Rizky Fatir 2010730122 Pembimbing: Dr. Toton Suryotono Sp. PDDocument17 pagesDecompensatio Cordis: Disusun Oleh: Andi Rizky Fatir 2010730122 Pembimbing: Dr. Toton Suryotono Sp. PDHuda KamalNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesDisorders of The Circulatory Systemistep100% (1)
- Mengapa VSR Lebih Sering Terjadi Pada PerempuanDocument2 pagesMengapa VSR Lebih Sering Terjadi Pada PerempuanIde Yudis TiyoNo ratings yet
- الباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فوراDocument163 pagesالباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فورانادين مطر0% (1)
- Reviewer For LM, NBS and FPDocument2 pagesReviewer For LM, NBS and FPJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology in NursingDocument1 pagePharmacology in NursingJessa Mae Barquilla100% (1)
- Reviewer in Oxy and Fluids MidtermsDocument3 pagesReviewer in Oxy and Fluids MidtermsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Skills LabDocument2 pagesSkills LabJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in TheoryDocument1 pageReviewer in TheoryJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesReviewer in Fluids and ElectrolytesJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Care of Older AdultsDocument2 pagesCare of Older AdultsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- CHN - Nursing ConceptsDocument5 pagesCHN - Nursing ConceptsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CHN ReviewerDocument2 pagesChapter 8 CHN ReviewerJessa Mae Barquilla100% (1)
- CHN - School Nursing and OccupationalDocument4 pagesCHN - School Nursing and OccupationalJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- CARE 0F OLDERS ADULTS MidtermsDocument2 pagesCARE 0F OLDERS ADULTS MidtermsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
Oxy and Fluids Finalsssssss
Oxy and Fluids Finalsssssss
Uploaded by
Jessa Mae Barquilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document discusses cardiac output and heart failure. It defines cardiac output as the volume of blood pumped by the heart with each contraction and lists factors that can affect it like peripheral vascular tone and neuropulmonary factors. Heart failure is when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, and symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling. Risk factors for heart failure include medical history, weight, age, hypertension, infection, and genetic diseases. The document also discusses signs and symptoms of right ventricular heart failure and treatments for conditions like myocardial infarction.
Original Description:
Original Title
OXY AND FLUIDS FINALSSSSSSS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses cardiac output and heart failure. It defines cardiac output as the volume of blood pumped by the heart with each contraction and lists factors that can affect it like peripheral vascular tone and neuropulmonary factors. Heart failure is when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, and symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling. Risk factors for heart failure include medical history, weight, age, hypertension, infection, and genetic diseases. The document also discusses signs and symptoms of right ventricular heart failure and treatments for conditions like myocardial infarction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageOxy and Fluids Finalsssssss
Oxy and Fluids Finalsssssss
Uploaded by
Jessa Mae BarquillaThis document discusses cardiac output and heart failure. It defines cardiac output as the volume of blood pumped by the heart with each contraction and lists factors that can affect it like peripheral vascular tone and neuropulmonary factors. Heart failure is when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, and symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling. Risk factors for heart failure include medical history, weight, age, hypertension, infection, and genetic diseases. The document also discusses signs and symptoms of right ventricular heart failure and treatments for conditions like myocardial infarction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
1.
Cardiac output Is the blood volume with systolic
cardiac contraction.
2. What affects cardiac output.
- Peripheral vascular tone
- Neuropulmonary factors
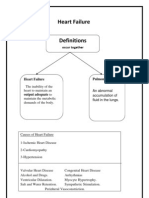
3. Heart failure – cannot pump enough blood to meet
the body’s needs.
4. and symptoms of heart failure
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling
- All of the above
5. If a patient can have heart failure without being
aware of it. – True
6. Risk factors of Heart Failure
- Medical history of disease, weight and age
7. Sudden onset of severe shortness of breathing and
coughing is called
- Orthopnea or Paroxysmal dyspnea
8. Increased respiratory muscle is due to
- Interstitial pulmonary edema
- Vessel enlargement
- Both
9. Mechanism Congestive Heart Failure
- To reduce afterload (pressure in the aorta)
10. Right sided or right ventricular failure result to left
sided heart failure. – True
11. Cause of Cardiomyopathy – Hypertension, infection
and diseases
12. Genetics is a disposing factor
- Duchemme muscular dystrophy
- Muscular atrophy
13. Not a result of activation – hyperplasia
14. Signs and Symptoms of Right VHF
- Accumulation of fluids
- Hepatomegaly
- Edema, anxiety, lethargy, agitation
15. Supine position reveals extended jugular veins –
Increase central venous pressure (10-12 normal)
16. A 55 years old – Heart Failure
17. Alter cardiac output – sleeping
18. ECG – T Waves – Ventricular Tachycardia
19. Blood Pressure and Peripheral Perfusion – frequent
immature ventricular contraction
20. Why caring sustained MI – notify the physician
21. Emergency lab, chest pain, physician, myoglobin –
myocardial infarction
22. A nurse, conduction of the heart
23. Inadequate blood volume - fluids
You might also like
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Heart Failure by IvsDocument66 pagesHeart Failure by IvsArianne LasamNo ratings yet
- MEDICAL PATHOLOGIES - CardiovascularDocument6 pagesMEDICAL PATHOLOGIES - Cardiovascularngachangong victorineNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Occur TogetherDocument5 pagesHeart Failure: Occur TogetherPrince Ahmed100% (1)
- HY Internal MedicineDocument449 pagesHY Internal MedicineMohamed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular HO Final GROUP2Document72 pagesCardiovascular HO Final GROUP2Siraj ShiferawNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure in ChildrenDocument47 pagesHeart Failure in ChildrenDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- HY SurgeryDocument283 pagesHY SurgerytejNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument16 pagesHeart FailureRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: Elias S. (MD+) March 2015 DBUDocument35 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: Elias S. (MD+) March 2015 DBUkikiNo ratings yet
- Left Sided HFDocument5 pagesLeft Sided HFGwendolyn Talahiban LusaraNo ratings yet
- HY Family MedicineDocument314 pagesHY Family MedicinetejNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument9 pagesCongestive Heart FailureAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument31 pagesHeart Failuretravis efraimNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC FAILURE NewDocument60 pagesCARDIAC FAILURE NewJake MillerNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease in PregnancyDocument15 pagesHeart Disease in PregnancyAnkur YadavNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diseases Management Amp Nursing CareDocument76 pagesCardiovascular Diseases Management Amp Nursing CareAlberto MeroNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Heart FailureDocument31 pagesPediatric Heart Failureanwar jabariNo ratings yet
- CHF Left SidedDocument21 pagesCHF Left SidedSandie Daniel GabalunosNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Diseases During PregnancyDocument10 pagesCardiac Diseases During PregnancySandyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument38 pagesCardiovascular Disordersmark100% (4)
- PP CardiacDocument62 pagesPP CardiacMarie Queenly Pagaran100% (1)
- Heart FailureDocument40 pagesHeart FailureRebira WorkinehNo ratings yet
- Patho 1Document153 pagesPatho 1ademabdellaaleNo ratings yet
- The Heart-1Document30 pagesThe Heart-1Ebuka AniNo ratings yet
- By: Darryl Jamison Nremt-P Macon County EMS Training CoordinatorDocument52 pagesBy: Darryl Jamison Nremt-P Macon County EMS Training CoordinatordafaferNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument11 pagesCardiovascular SystemMihraban OmerNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure & Circulatory ShockDocument34 pagesHeart Failure & Circulatory ShockMuskaan ZaharaNo ratings yet
- (311 - Rakshita) (312 - Aashish Bharti) - There Are Six Principal Mechanisms of Cardiovascular DysfunctionDocument15 pages(311 - Rakshita) (312 - Aashish Bharti) - There Are Six Principal Mechanisms of Cardiovascular DysfunctionAyshwarya LalNo ratings yet
- Cardio and Hema - DR PueyoDocument161 pagesCardio and Hema - DR Pueyoapi-3735995100% (2)
- CHFDocument3 pagesCHFROSE COLLINSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermDocument11 pagesChapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermJœnríčk AzueloNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument10 pagesCongestive Heart FailureGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Pulmo HPNDocument36 pagesPulmo HPNAlexander Santiago ParelNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument6 pagesCongenital Heart Diseasestheglobalnursing100% (2)
- HY CardioDocument73 pagesHY Cardio190004No ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument55 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasesRajaNo ratings yet
- Heart Valve Problems and Homeopathy - (50 PP)Document50 pagesHeart Valve Problems and Homeopathy - (50 PP)Marcelo Guerra100% (1)
- OXY-Cardio Care ManagementDocument114 pagesOXY-Cardio Care Managementlalaine22daleNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Heart FailureDocument25 pagesLec 3 Heart FailureDelete AccountNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Slides 2024Document43 pagesHeart Failure Slides 2024b9p6vmfnc4No ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease - SeminarDocument35 pagesCongenital Heart Disease - SeminarAsha jilu100% (2)
- HHFFDocument56 pagesHHFFNesru Ahmed AkkichuNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Failure 1Document83 pagesCardiac Failure 1Unathi MbamboNo ratings yet
- 42 Kelainanpatologi Cardiovasc Dr. DianDocument126 pages42 Kelainanpatologi Cardiovasc Dr. DianSurya ArhNo ratings yet
- Cardiac II Study GuideDocument6 pagesCardiac II Study GuiderunnermnNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure and ShockDocument34 pagesHeart Failure and Shockfrenee aradanasNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy With Internal Medical Diseases: Department of Gynaecology and ObstetricsDocument84 pagesPregnancy With Internal Medical Diseases: Department of Gynaecology and ObstetricssanjivdasNo ratings yet
- 18 Heartpart1 Basiccongestiveheartfailure 110919083613 Phpapp01Document43 pages18 Heartpart1 Basiccongestiveheartfailure 110919083613 Phpapp01Atikah PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- 1cardiovascular System DisordersDocument13 pages1cardiovascular System DisordersArvin MalondrasNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument35 pagesCHFMarione GimenezNo ratings yet
- 8 CardiovascularDocument18 pages8 Cardiovascularfiji drNo ratings yet
- Cardiac (Heart) FailureDocument27 pagesCardiac (Heart) FailureSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary HypertensionDocument9 pagesPulmonary HypertensionPricob ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument7 pagesHeart FailureBea Marie A. ValdezNo ratings yet
- Decompensatio Cordis: Disusun Oleh: Andi Rizky Fatir 2010730122 Pembimbing: Dr. Toton Suryotono Sp. PDDocument17 pagesDecompensatio Cordis: Disusun Oleh: Andi Rizky Fatir 2010730122 Pembimbing: Dr. Toton Suryotono Sp. PDHuda KamalNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesDisorders of The Circulatory Systemistep100% (1)
- Mengapa VSR Lebih Sering Terjadi Pada PerempuanDocument2 pagesMengapa VSR Lebih Sering Terjadi Pada PerempuanIde Yudis TiyoNo ratings yet
- الباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فوراDocument163 pagesالباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فورانادين مطر0% (1)
- Reviewer For LM, NBS and FPDocument2 pagesReviewer For LM, NBS and FPJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology in NursingDocument1 pagePharmacology in NursingJessa Mae Barquilla100% (1)
- Reviewer in Oxy and Fluids MidtermsDocument3 pagesReviewer in Oxy and Fluids MidtermsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Skills LabDocument2 pagesSkills LabJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in TheoryDocument1 pageReviewer in TheoryJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesReviewer in Fluids and ElectrolytesJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Care of Older AdultsDocument2 pagesCare of Older AdultsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- CHN - Nursing ConceptsDocument5 pagesCHN - Nursing ConceptsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CHN ReviewerDocument2 pagesChapter 8 CHN ReviewerJessa Mae Barquilla100% (1)
- CHN - School Nursing and OccupationalDocument4 pagesCHN - School Nursing and OccupationalJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- CARE 0F OLDERS ADULTS MidtermsDocument2 pagesCARE 0F OLDERS ADULTS MidtermsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet