Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kimmulato Resource Manual Fragile X Syndrome
Kimmulato Resource Manual Fragile X Syndrome
Uploaded by
KimLawrence MulatoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kimmulato Resource Manual Fragile X Syndrome
Kimmulato Resource Manual Fragile X Syndrome
Uploaded by
KimLawrence MulatoCopyright:
Available Formats
FATHER SATURNINO URIOS UNIVERSITY
San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII
Caraga, Philippines Nursing
Program
FRAGILE X SYNDROME
DEFINITION
Fragile X Syndrome is the most common inherited form of mental
retardation. It results from a change, or mutation, in a single
gene, which can be passed from one generation to the next.
Fragile X appears in families of every ethnic group and income
level.
RISK FACTOR
You are at greater risk if you have: A family history of fragile
X syndrome. A family history of mental retardation,
developmental delay or autism of unknown cause. Infertility
problems associated with elevated follicle stimulating hormone
(FSH) levels or premature ovarian failure (POF).
CAUSES
Fragile X syndrome is caused by a change in the fragile X mental
retardation (FMR1) gene. The FMR1 gene is located on the X
chromosome. This abnormal gene, which can be passed from
generation to generation, is usually inherited through the gene
that is carried by women.
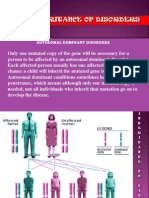
A fragile X carrier is someone who has an altered FMR1 gene, but
does not show any obvious signs or symptoms of fragile X
syndrome. Women who are fragile X carriers have up to a 50
percent chance of having a child with fragile X syndrome. Men
who are fragile X carriers will pass the altered gene to all of
their daughters but none of their sons. Daughters of carrier
men are expected to be intellectually normal but are at risk of
having children affected with fragile X syndrome.
The genetics of fragile X syndrome are complicated. Genetic
counseling is recommended when someone has a family history of
fragile X syndrome or is shown to be a carrier of fragile X
SIGNS AND SYMPTOOMS
Behavioral problems associated with fragile X Syndrome include:
Delay in crawling, walking, or twisting
Hand clapping or hand biting
Impulsive behavior
Mental retardation
Speech and language delay
Tendency to avoid eye contact
Physical signs may include:
Flat feet
Flexible joints and low muscle tone
Large body size
Long face
Soft skin
TREATMENT
There is no specific treatment for Fragile X syndrome. Instead,
training and education have been developed to help affected
children function at as high a level as possible.
Early intervention services help children from birth to 3 years
old (36 months) learn important skills. These services may
improve a child’s development. Even if the child has not been
diagnosed with FXS, they may be eligible for services. These
services are provided through an early intervention system in
each state. Through this system, you can ask for an evaluation.
In addition, treatment for particular symptoms, such as speech
therapy for language delays, often does not need to wait for a
formal diagnosis. While early intervention is extremely
important, treatment services at any age can be helpful
REFERENCES
Carrier Testing for Fragile X Syndrome. Retrieved from
https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/faq-carrier-testing-for-
fragile-x-syndrome
Presentation on Fragile X Syndrome (2019). Retrieved from
https://slideplayer.com/slide/13460922/
How to Recognize the Symptoms of Fragile X Syndrome (2022).
Retrieved from https://www.wikihow.com/Recognize-the-Symptoms-
of-Fragile-X-Syndrome
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Fragile X Syndrome.
Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/fxs/facts.html
You might also like
- Chapter 15-Basics of Electrical Systems: True/FalseDocument190 pagesChapter 15-Basics of Electrical Systems: True/FalsewesamNo ratings yet
- Food Hub Operator Letter of Intent - ApplicationDocument2 pagesFood Hub Operator Letter of Intent - ApplicationKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Kenya DocumentsDocument43 pagesKenya Documentsmike_hills6221No ratings yet
- Fragile X Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandFragile X Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fragile X SyndromeDocument8 pagesFragile X SyndromeMay Pearl NuñalNo ratings yet
- Flagile X SyndromeDocument2 pagesFlagile X Syndromeapi-314093325No ratings yet
- Other Names Used For Fragile X Syndrome Other Names Used For Fragile X SyndromeDocument26 pagesOther Names Used For Fragile X Syndrome Other Names Used For Fragile X SyndromeTintin TagupaNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet 47Document2 pagesFact Sheet 47Anonymous LAWfm7No ratings yet
- Most of The Symptoms For Fragile X Are For BoysDocument9 pagesMost of The Symptoms For Fragile X Are For BoysAnonymous mPPBzSNo ratings yet
- Fragile X Syndrome Research PaperDocument6 pagesFragile X Syndrome Research Paperaflbqtfvh100% (3)
- Meeting The Need of Children and Families AssignmentDocument47 pagesMeeting The Need of Children and Families AssignmentYaoRippleNo ratings yet
- Educ 223 M1Document5 pagesEduc 223 M1Celon Jr. GultimoNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 - 014300Document3 pagesBiology 12 - 014300Perry MorillaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Fragile X SyndromeDocument4 pages2 - Fragile X Syndromechenelyn_15No ratings yet
- Cognitive DisabilitiesDocument38 pagesCognitive DisabilitiesbardajereginaNo ratings yet
- Pisharody Genetic CounselingDocument15 pagesPisharody Genetic Counselingapi-228136529No ratings yet
- Fragile X Syndrome: Group 3Document11 pagesFragile X Syndrome: Group 3mballestaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders in Humans PresentationDocument16 pagesGenetic Disorders in Humans PresentationKaty W. IvesNo ratings yet
- XYY SyndromeDocument4 pagesXYY SyndromesakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Fragile X Mental RetardationDocument8 pagesFragile X Mental RetardationFianirazhaPrimesaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Cri Du ChatDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Cri Du Chatcapz4pp5100% (1)
- Fragile X SyndromeDocument10 pagesFragile X SyndromeOmaNo ratings yet
- Human GeneticsDocument15 pagesHuman GeneticsKLENNY ADRIA BATISANNo ratings yet
- Triple X Syndrome Group 7Document16 pagesTriple X Syndrome Group 7Laura HernandezNo ratings yet
- Document Ni IndayDocument7 pagesDocument Ni IndayAj Myco EstorNo ratings yet
- Kelainan GenetikDocument36 pagesKelainan GenetikNicko Erdy Kusuma100% (1)
- Uk Fragile XDocument4 pagesUk Fragile XChristin Natalia KalembangNo ratings yet
- Thesis About DwarfismDocument8 pagesThesis About Dwarfismcdayxnzcf100% (1)
- Efectos de La Variación GenéticaDocument1 pageEfectos de La Variación GenéticaMARIA DE JESUS SANCHEZ MURGUIANo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument45 pagesUntitledMary Grace SunioNo ratings yet
- Fragile X Syndrome - Clinical Features A... in Children and Adolescents - UpToDateDocument23 pagesFragile X Syndrome - Clinical Features A... in Children and Adolescents - UpToDatecapt_zoeNo ratings yet
- Global Develpmental DelayDocument3 pagesGlobal Develpmental DelayDanielle OnaNo ratings yet
- Patterns: OF InheritanceDocument45 pagesPatterns: OF InheritanceMary Grace SunioNo ratings yet
- Kelainan GenetikDocument36 pagesKelainan GenetikImas Siti MNo ratings yet
- Fragile X Syndrome PabhungkornDocument7 pagesFragile X Syndrome Pabhungkorn07251No ratings yet
- N512 Assignment 1 Wanda MossDocument7 pagesN512 Assignment 1 Wanda MossWanda MossNo ratings yet
- Fragile XDocument7 pagesFragile Xapi-360330020No ratings yet
- Fragile X Syndrome (Martin-Bell Syndrome)Document6 pagesFragile X Syndrome (Martin-Bell Syndrome)yudhi kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Assignment OneDocument6 pagesAssignment Onebrandy.franklinNo ratings yet
- NCMDocument56 pagesNCMPatrick Perreras Dela CuadraNo ratings yet
- Biology 1610 E-Portfolio Assignment PDFDocument4 pagesBiology 1610 E-Portfolio Assignment PDFapi-437601454No ratings yet
- Trisomy XDocument10 pagesTrisomy Xmarianne.gugulan07No ratings yet
- Fragile X SyndromeDocument16 pagesFragile X SyndromeManisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Genetics Case Study - MicrocephalyDocument4 pagesGenetics Case Study - MicrocephalyHeru WNo ratings yet
- Genetic CounsellingDocument3 pagesGenetic Counsellingavinash dhameriyaNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Project Report (1) 38408300Document15 pagesTinywow Project Report (1) 38408300advaith0717No ratings yet
- Human GeneticsDocument9 pagesHuman Geneticseli pascualNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: Structure of A ChromosomeDocument27 pagesChromosomes: Structure of A ChromosomeLaika LaiNo ratings yet
- Genetice Disorders: Genetic Disorder Is A Disease or Disorder Caused by Damage or Change and Mutation On Individual's DNADocument46 pagesGenetice Disorders: Genetic Disorder Is A Disease or Disorder Caused by Damage or Change and Mutation On Individual's DNAAna Subol AñonuevoNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Definition: Down Syndrome, Down's Syndrome, or Trisomy 21 Is A Chromosomal Disorder Caused by TheDocument3 pagesDefinition: Down Syndrome, Down's Syndrome, or Trisomy 21 Is A Chromosomal Disorder Caused by TheLove Shery SabrosoNo ratings yet
- Notes - Genetic DisordersDocument6 pagesNotes - Genetic Disordersanirudhramesh289No ratings yet
- MENTAL RETARDATION GROUP 1 TruelalaaaaaaaaaaaaaDocument65 pagesMENTAL RETARDATION GROUP 1 TruelalaaaaaaaaaaaaaMaiden PogoyNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Down Syndrome PDFDocument6 pagesThesis On Down Syndrome PDFHelpWithWritingPaperUK100% (1)
- Clinical Vignette 1Document9 pagesClinical Vignette 1Joanne Alyssa Hernandez LascanoNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectAnmol Dhungel100% (9)
- FINALLLDocument58 pagesFINALLLImie AldoyesaNo ratings yet
- Medical Genetics LectureDocument81 pagesMedical Genetics LectureIMUSIC Corp.No ratings yet
- Genetic Diseases in The Philippines: Genetic Diseases Are Related To Genetic Mutations and InheritanceDocument4 pagesGenetic Diseases in The Philippines: Genetic Diseases Are Related To Genetic Mutations and InheritanceGracy JavierNo ratings yet
- Framework For Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument147 pagesFramework For Maternal and Child Health NursingRouie Björn ABrianNo ratings yet
- Articulo InglesDocument4 pagesArticulo InglesAlejandra PalacioNo ratings yet
- Klinefelter SyndromeDocument28 pagesKlinefelter SyndromeKimberly Anne Marica0% (1)
- Trisomy/ Down SyndromeDocument2 pagesTrisomy/ Down SyndromeDanah Grace SanchezNo ratings yet
- Philippine-American Political CartoonDocument1 pagePhilippine-American Political CartoonKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Kim Mulato PosterDocument2 pagesKim Mulato PosterKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Kimmulato Practice Exercise#2Document1 pageKimmulato Practice Exercise#2KimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Reflection ABIVADocument1 pageReflection ABIVAKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Kimmulato ReflectionDocument1 pageKimmulato ReflectionKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Kimmulato InsightsDocument1 pageKimmulato InsightsKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Describe The Schematic and Narrative Pathophysiology of The DiseaseDocument1 pageDescribe The Schematic and Narrative Pathophysiology of The DiseaseKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Citizen's Charter 2023 (1st Edition) - Website - Consolidated - C PDFDocument1,007 pagesCitizen's Charter 2023 (1st Edition) - Website - Consolidated - C PDFKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- SUMMARYDocument4 pagesSUMMARYKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- ResourceManual MateoDocument3 pagesResourceManual MateoKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Resource ManualDocument1 pageResource ManualKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Article9 13 - Sec17 36Document5 pagesArticle9 13 - Sec17 36KimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Blessings in DisguisedDocument1 pageBlessings in DisguisedKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- 2ND Part Assignment - TopicDocument8 pages2ND Part Assignment - TopicKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Reading in Philippine HistoryDocument3 pagesReading in Philippine HistoryKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- PPT9 WeatheringDocument24 pagesPPT9 WeatheringKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Kimmulato EbrDocument2 pagesKimmulato EbrKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- PPT9.3 Mass WastingDocument45 pagesPPT9.3 Mass WastingKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- The HelenDocument19 pagesThe HelenKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Kimmulato 750words NSTPDocument2 pagesKimmulato 750words NSTPKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Kim Lawrence S. Mulato BSN - N24Document3 pagesKim Lawrence S. Mulato BSN - N24KimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Pericare With Heat Lamp TreatmentDocument6 pagesPericare With Heat Lamp TreatmentKimLawrence MulatoNo ratings yet
- Geography Mock Test PopulationDocument8 pagesGeography Mock Test PopulationMain AccountNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual 1T-4T (LPG) - EN 英语Document128 pagesMaintenance Manual 1T-4T (LPG) - EN 英语Jose Luis LavinNo ratings yet
- Rice Pests (Sucking Group)Document10 pagesRice Pests (Sucking Group)Biresh KoleyNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence ReflectionDocument5 pagesEmotional Intelligence Reflectionapi-336005635No ratings yet
- Cooling System OperationDocument4 pagesCooling System OperationSRL MECHNo ratings yet
- Climate Action Incentive Payment Notice 2022 06 25 09 46 45 07823 PDFDocument3 pagesClimate Action Incentive Payment Notice 2022 06 25 09 46 45 07823 PDFalex mac dougallNo ratings yet
- (5).pptDocument15 pages(5).pptAKINYEMI ADISA KAMORUNo ratings yet
- This Set of Building Construction Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesThis Set of Building Construction Multiple Choice QuestionspransuNo ratings yet
- John The Baptists DietDocument2 pagesJohn The Baptists DietAnida Maria Moraes GomesNo ratings yet
- Terapi Keluarga StrategikDocument18 pagesTerapi Keluarga StrategikNurulArifahNo ratings yet
- 11 Plus Comprehension Summary Test Paper 4 IjhDocument12 pages11 Plus Comprehension Summary Test Paper 4 IjhKrishnapriya GovindNo ratings yet
- Safety Inspection Report Template: Submitted By: Jheremae D. DeypalubosDocument4 pagesSafety Inspection Report Template: Submitted By: Jheremae D. DeypalubosMikaNo ratings yet
- Best, 2019 - Selection and Management of Commonly Used Enteral Feeding TubesDocument5 pagesBest, 2019 - Selection and Management of Commonly Used Enteral Feeding TubesThuane SalesNo ratings yet
- PrE6 Acctg Cycle and JournalizingDocument28 pagesPrE6 Acctg Cycle and JournalizingAlexa Mae SanchezNo ratings yet
- SOALDocument4 pagesSOALFitri ShanumNo ratings yet
- Anterior Teeth Selection and Its ArrangementDocument48 pagesAnterior Teeth Selection and Its ArrangementAnonymous NFiQTb1No ratings yet
- The Corporation and External StakeholdersDocument19 pagesThe Corporation and External StakeholdersNur AtierahNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Pidicryl 120V - 2021-EuDocument17 pagesMSDS - Pidicryl 120V - 2021-Euhai nguyenNo ratings yet
- Aluminium GMAW GuideDocument32 pagesAluminium GMAW GuideDaniel Salinas100% (2)
- (Ebook PDF) Introduction To Food Science and Food Systems 2nd Edition Rick Parker - Ebook PDF All ChapterDocument69 pages(Ebook PDF) Introduction To Food Science and Food Systems 2nd Edition Rick Parker - Ebook PDF All Chapterfaishdarron100% (7)
- What Is Your TypeDocument2 pagesWhat Is Your TypeΛευτέρης ΚαπετανάκηςNo ratings yet
- Attachment 15 The Silent Genocide of The Boer Nation in South Africa IndexDocument3 pagesAttachment 15 The Silent Genocide of The Boer Nation in South Africa Indexapi-232649836No ratings yet
- Soap Notes 101Document45 pagesSoap Notes 101CELINE MARTJOHNSNo ratings yet
- Original ICIAHP-23 Brochure - 20230826 - 103321 - 0000Document15 pagesOriginal ICIAHP-23 Brochure - 20230826 - 103321 - 0000Neeri BatraNo ratings yet
- File 274804260391Document22 pagesFile 274804260391Nemanja NikolicNo ratings yet
- Josef Mengele, Dr. Green, and The American Mind Control Network - Www-Angelfire-comDocument2 pagesJosef Mengele, Dr. Green, and The American Mind Control Network - Www-Angelfire-comTortured-Targeted-IndividualsNo ratings yet
- ESCVS ProgramDocument122 pagesESCVS ProgramNaser Hamdi ZalloumNo ratings yet
- 29102015000000B - Boehler DCMS-IG - SWDocument1 page29102015000000B - Boehler DCMS-IG - SWErdinc BayatNo ratings yet