Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Immunity
Types of Immunity
Uploaded by
· a n n i e ·Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Immunity
Types of Immunity
Uploaded by
· a n n i e ·Copyright:
Available Formats
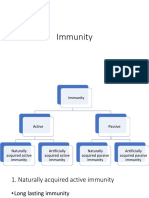
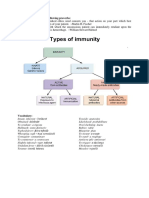
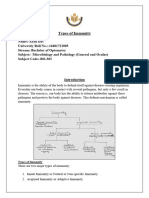
Types of immunity -> active -> produce naturally,
->remains for long period of time
-> passive -> does not produce antibodies,
-> obtained from external source
-> give immediate short term, temporary protection
Active immunity
1. Natural active immunity – immune system (acquired after an individual recover from an infection)
-pathogen attacks, lymphocyte produces antibodies
-recover from an infection, individual gain a permanent immunity against the disease
-if attacked again, the memory cells will produce antibodies rapidly to react immediately with the same
antigen
2. Artificial active immunity -immunisation , vaccines
-immunisation – process tht stimulates immunity against specific disease thru vaccination
-vaccine – suspension of weakened, dead or non-virulent pathogens
Process of vaccination
- When vaccine is injected, lymphocyte is stimulated to produce antibodies to fight the pathogen
- First injection – results in low level of antibody production which is insufficient to protect the
individual from disease
- Vaccine stimulates the lymphocyte to produce antibodies slowly
- A booster dose – increase the antibody production that exceeds the immunity level
Passive immunity
1. Natural passive immunity -acquired thru breastfeeding & mother to foetus during pregnancy
-mother’s antibodies diffuses thru the placenta into the blood flow of the foetus
- antibodies are also found in the mother’s milk / colostrum when breastfeeding (the first few
months after birth)
2. Artificial passive immunity – antiserum injection
-antiserum contains specific antibodies to fight with specific antigen
- gives immediate protection but only for a short period of time
- it is only given when antibody level in the blood drops below the immunity level and the
patient is still infected by the disease.
Health Issues Related to Human Immunity
- HIV ( human immunodeficiency virus ) -> disease is called AIDS ( acquired immunodeficiency
syndrome)
Individual affected by AIDS
- The first few years, the symptoms will not show although the HIV has been actively attacking the
immune system (?)
- Progressive destruction of the individual’s immune system
➢ Spreads in lymphocyte and destroys the lymphocyte
- Immune system of the patient is weakened, body can be easily infected by other diseases
- Immune system will be paralysed and the patient will die due to other infections
HIV transmission
- Enters the body thru the transfer of body fluids such as semen and blood or across the placenta
- Women infected with HIV can transfer the virus to the foetus thru pregnancy, birth or
breastfeeding
- However, baby from a HIV positive mother can be prevented from getting HIV with proper
medical treatment
Ways of getting infected
- Having unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected individuals
- Sharing contaminated needles used to inject drugs/ tattoo ink
- HIV infected blood transfusion
You might also like
- Immunization (Immunisasi)Document27 pagesImmunization (Immunisasi)DindaalifiahNo ratings yet
- Immunization (Immunisasi)Document27 pagesImmunization (Immunisasi)Dinda FirdasariNo ratings yet
- Immunization (Immunisasi)Document27 pagesImmunization (Immunisasi)Andhy Andha Dhyan HardhyantiNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument1 pageImmunityandressookdeo29No ratings yet
- Active ImmunityDocument1 pageActive ImmunityshaliniNo ratings yet
- Immunization: (Document Subtitle)Document5 pagesImmunization: (Document Subtitle)Abigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Disease-ImmunityDocument10 pagesDisease-ImmunityAshantiwa EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Vaccination: DR Hodan Ahmed, MBBS, Mmed, Depr of Pediatrics, Amoud Medical School, AuDocument13 pagesVaccination: DR Hodan Ahmed, MBBS, Mmed, Depr of Pediatrics, Amoud Medical School, Auabdisalaan hassanNo ratings yet
- Immunisation: Lorem Ipsum DolorDocument60 pagesImmunisation: Lorem Ipsum DolorDr. Ajeta GuptaNo ratings yet
- Immunity and Immunization, Vaccines and Their Role in Prevention of DiseaseDocument14 pagesImmunity and Immunization, Vaccines and Their Role in Prevention of Diseaseshivani.priyaNo ratings yet
- Aids To HealthDocument7 pagesAids To HealthAbhi LiteNo ratings yet
- Acquired Imm and Infection - BPTDocument15 pagesAcquired Imm and Infection - BPTKathal 66No ratings yet
- H.S.Z.H Govt (Autonomous) Unani Medical College Bhopal: Immunity and Immunization ScheduleDocument18 pagesH.S.Z.H Govt (Autonomous) Unani Medical College Bhopal: Immunity and Immunization ScheduleĦajra KhaŋNo ratings yet
- Che 224 Immunity and ImmunizationDocument54 pagesChe 224 Immunity and ImmunizationAbdullahi Bashir SalisuNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ImmunityDocument6 pagesAdaptive ImmunityAvinash SahuNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument46 pagesImmunityLalyn Balasbas100% (2)
- ImmunityDocument9 pagesImmunityafsheen24akramNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument9 pagesImmunologyNivedita DasNo ratings yet
- Biologics: by DR TanginaDocument41 pagesBiologics: by DR TanginaAnam AbidNo ratings yet
- Immunity and ImmunizationDocument11 pagesImmunity and Immunizationbasu mosesNo ratings yet
- Immunity NewDocument17 pagesImmunity NewWijesiri D WNo ratings yet
- Immuno AssgtDocument2 pagesImmuno Assgtapi-3727388No ratings yet
- Comment On The Following ProverbsDocument4 pagesComment On The Following ProverbsArina CucuruzaNo ratings yet
- Course 1 - Session 6 StudentDocument29 pagesCourse 1 - Session 6 StudenthelpNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument40 pagesImmunitydrkhalidfcps100% (5)
- 3rd Notes-Why Do We Fall IllDocument3 pages3rd Notes-Why Do We Fall IllLAKSH MITTALNo ratings yet
- ImmunizationDocument12 pagesImmunizationOke AdasenNo ratings yet
- Type of ImmunityDocument3 pagesType of ImmunitySRI SHIVANI SARAWANANNo ratings yet
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- (PPT) DPC 1.4.2 Immunity and Disease - Dr. Cabanos PDFDocument83 pages(PPT) DPC 1.4.2 Immunity and Disease - Dr. Cabanos PDFJennifer Pisco LiracNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument25 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologySohail AhmedNo ratings yet
- VaccinationDocument2 pagesVaccinationmonkeysaltaccNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument6 pagesThe Immune Systemapi-277065304No ratings yet
- Preventive PediatricsDocument2 pagesPreventive PediatricsJoseph D. WangNo ratings yet
- ImmunisationDocument42 pagesImmunisationDr. Ajeta GuptaNo ratings yet
- Disease N Immunity NotesDocument4 pagesDisease N Immunity NotesFrozenYtNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument15 pagesBiology Projectdevendra kasoteNo ratings yet
- Immunology For BSCNDocument39 pagesImmunology For BSCNHamas AliNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGICS LectureDocument36 pagesBIOLOGICS LectureRao Salman LatifNo ratings yet
- What Is The Immune System AboutDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Immune System Aboutchelsearamdial21No ratings yet
- l3 Immunization & Cold ChainDocument53 pagesl3 Immunization & Cold ChainNur AinaaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Human Health and DiseasesDocument18 pagesNotes On Human Health and Diseasesraushankumar05072No ratings yet
- Unza NRS 3110 - VaccinologyDocument27 pagesUnza NRS 3110 - VaccinologyTabitha Lumbwe PhiriNo ratings yet
- EPI Lesson TwoDocument10 pagesEPI Lesson Twomaryanruuney1212No ratings yet
- l2.1 Immunization Cold ChainDocument53 pagesl2.1 Immunization Cold Chainsinuaish syaNo ratings yet
- Immunity and Its TypesDocument3 pagesImmunity and Its TypesBenazir SheikhNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 Specific Host Defense MechanismsDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 16 Specific Host Defense MechanismsedemcantosumjiNo ratings yet
- MMR ImmunizationDocument43 pagesMMR ImmunizationkukuruziNo ratings yet
- Live Attenuated VaccinesDocument24 pagesLive Attenuated VaccinesBanduNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Production (L1F17PHMD0174)Document22 pagesVaccine Production (L1F17PHMD0174)Faizah Khalid100% (1)
- Different Types of VaccinesDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of VaccinesBhuvaneshNo ratings yet
- سمينار 1Document18 pagesسمينار 1NabaNo ratings yet
- Ayan Das 16401722005 BO-303Document4 pagesAyan Das 16401722005 BO-303Ayan DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Basic ImmunologyDocument39 pagesChapter 12 Basic ImmunologyTofik100% (1)
- Principle of VaccineDocument10 pagesPrinciple of VaccineRasyid WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Immune System - Scott.k12+Document26 pagesImmune System - Scott.k12+Amit BhadhanaNo ratings yet
- Concept Communicable DiseasesDocument477 pagesConcept Communicable DiseasesrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument10 pagesImmune Systemailyn regaladoNo ratings yet
- AQA Vaccinations - AS Level BiologyDocument3 pagesAQA Vaccinations - AS Level BiologymonkeysaltaccNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument5 pagesEnglish Project· a n n i e ·No ratings yet
- How Social Media Lowers Self EsteemDocument13 pagesHow Social Media Lowers Self Esteem· a n n i e ·No ratings yet
- Yoji FuyohiakiDocument3 pagesYoji Fuyohiaki· a n n i e ·No ratings yet
- HomeschoolingDocument1 pageHomeschooling· a n n i e ·No ratings yet
- Listeria MonocytogenesDocument28 pagesListeria Monocytogenestummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- GASTRODocument47 pagesGASTROMada mada DaneNo ratings yet
- ImpetigoDocument34 pagesImpetigoSarang LeeNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin InfectionsDocument9 pagesBacterial Skin InfectionskateverdadNo ratings yet
- Audit Program PpiDocument37 pagesAudit Program PpiIkrar DinataNo ratings yet
- What Are The Symptoms Measles (Focus On Measles More, Then Talk About Mumps and Rubella)Document2 pagesWhat Are The Symptoms Measles (Focus On Measles More, Then Talk About Mumps and Rubella)RexDavidGidoNo ratings yet
- Detection of Fusobacterium Species in Human FecesDocument5 pagesDetection of Fusobacterium Species in Human FecesHà Phương MaiNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Nasional Pengendalian TuberkulosisDocument111 pagesPedoman Nasional Pengendalian TuberkulosisYusriNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Short Quiz 1.2Document2 pagesParasitology Short Quiz 1.2JAIRISH YZABELLE SALVADORNo ratings yet
- Efisiensi Pakan, Pertumbuhan, Kelangsungan Hidup Dan Respon Imun Ikan Patin (Pangasius SP.) Yang Diberi Pakan BersinbiotikDocument15 pagesEfisiensi Pakan, Pertumbuhan, Kelangsungan Hidup Dan Respon Imun Ikan Patin (Pangasius SP.) Yang Diberi Pakan Bersinbiotikrifaldi ichsanNo ratings yet
- Aust Clinical Parasitology CLS 450: Dr. Renée Zakhia Rzakhia@aust - Edu.lbDocument33 pagesAust Clinical Parasitology CLS 450: Dr. Renée Zakhia Rzakhia@aust - Edu.lbChristine KamaleddineNo ratings yet
- Traditional Starter Cultures in CheesethDocument88 pagesTraditional Starter Cultures in CheesethCAPRINOS BAJA CALIFORNIA SUR, MEXICO100% (1)
- Situational Analysis EPI 2015 Final 1Document9 pagesSituational Analysis EPI 2015 Final 1At Day's Ward0% (1)
- Chicken PoxDocument26 pagesChicken PoxKrishna GandhiNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Gram-Negative BacilliDocument7 pagesAerobic Gram-Negative BacilliNhoz DoHoNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis C Treatment in CorrectionsDocument25 pagesHepatitis C Treatment in CorrectionsTopan BagaskaraNo ratings yet
- PinwormsDocument2 pagesPinwormsPieck FingerNo ratings yet
- Membrane Filter TechniqueDocument14 pagesMembrane Filter TechniqueQusay Al MaghayerhNo ratings yet
- EUROArray DermatomycosisDocument16 pagesEUROArray Dermatomycosisbeatriz.maia.alvesNo ratings yet
- Return To Work Guidelines For The COVID-19Document6 pagesReturn To Work Guidelines For The COVID-19Gabriela Cifuentes ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex SymptomsDocument3 pagesHerpes Simplex SymptomsInes JianaNo ratings yet
- Golden Hour CCM Arthur Van Zanten IC1Document3 pagesGolden Hour CCM Arthur Van Zanten IC1Sara NicholsNo ratings yet
- Rundown SeminarDocument5 pagesRundown SeminarMuhamad AriefNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument30 pagesTyphoid FeversakuarNo ratings yet
- CBSE CBSE Class 9 NCERT Solution Science Why Do We Fall IllDocument9 pagesCBSE CBSE Class 9 NCERT Solution Science Why Do We Fall IlldashNo ratings yet
- A SepsisDocument5 pagesA SepsisAi KogaNo ratings yet
- Micro Notes 1Document49 pagesMicro Notes 1Apryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- Parinaud Oculoglandular Syndrome 2015 Review of The Literature and Update On Diagnosis and Management 2155 9570 1000443Document5 pagesParinaud Oculoglandular Syndrome 2015 Review of The Literature and Update On Diagnosis and Management 2155 9570 1000443Nia AprilitaNo ratings yet
- TAREA 13 Safety Data Sheet For Quality SpecimensDocument5 pagesTAREA 13 Safety Data Sheet For Quality SpecimensRosa CanahuiNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Doh Related Programs: Epi - Types of VaccinesDocument32 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Doh Related Programs: Epi - Types of VaccinesAngelaNo ratings yet