Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap003 Colalge
Chap003 Colalge
Uploaded by
GabrielSabariagaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap003 Colalge
Chap003 Colalge
Uploaded by
GabrielSabariagaCopyright:
Available Formats
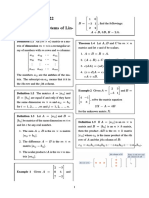
3 RATIONALS
3.1 Fundamental Principle of Fractions
a
Definition of Division: ¿ c if and only if a=bc .
b
a ak
Theorem 3.1: Given real numbers a , b ≠ 0, and k ≠ 0, =
b bk
Statements Reasons
1 Let a /b=x Given
2 a=bx Definition of division
3 ak =bkx Multiplication Property of Equality
ak
4 =x Definition of division
bk
a ak
5 =¿ , where b ≠ 0 and k ≠ 0, Transitive Property of Equality
b bk
a c
Theorem 3.2: = if and only if ad=bc
b d
Definition of division is used to prove this theorem.
3.2 Sign of Fractions
Theorem 3.3
a −a −−a −a
= = =
b −b b −b
Theorem 3.4
−a −a a −−a
= = =
b b −b −b
Properties of negative numbers are used to prove this theorem.
3.3 Operations of Fractions
a a
Definition of Reciprocal: The reciprocal of is .
b b
Axiom 3.1: Multiplication of Fractions
a c ac
∙ =
b d bd
Axiom 3.2: Division of Fractions
a c a d ad
÷ = ∙ =
b d b c bc
Axiom 3.3: Adding and Subtracting Similar Fractions
a b a±b
± =
c c c
Axiom 3.4: Adding and Subtracting Dissimilar Fractions
a b ad ± bc
± =
c d cd
You might also like
- GMAT Equation Guide - TTPDocument15 pagesGMAT Equation Guide - TTPDanielNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Economists: Linear Models and Matrix AlgebraDocument58 pagesMathematics For Economists: Linear Models and Matrix AlgebraELEFTHERIOS GIOVANISNo ratings yet
- Number Theory: ITT9131 Konkreetne MatemaatikaDocument78 pagesNumber Theory: ITT9131 Konkreetne MatemaatikaTanzeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Math 402 LECTURE Week 1partial Fraction DecompositionDocument9 pagesMath 402 LECTURE Week 1partial Fraction Decompositiondragh meh downNo ratings yet
- Math For Quantitative MethodsDocument29 pagesMath For Quantitative MethodsTram LuongNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Foundations of MathematicsDocument35 pagesLecture Notes in Foundations of MathematicsmohammedNo ratings yet
- S1 Unit 13Document8 pagesS1 Unit 13Snow WinNo ratings yet
- Supplement: The Inductive Discovery of DeterminantsDocument6 pagesSupplement: The Inductive Discovery of DeterminantsSyedaNo ratings yet
- More On Vector Products: Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford MT 2012Document10 pagesMore On Vector Products: Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford MT 2012Afzaal GhaziNo ratings yet
- 3.4.2 The Box ProductDocument1 page3.4.2 The Box ProductJaime Andrés GómezNo ratings yet
- Partial Fractions by Mahatma MurthiDocument20 pagesPartial Fractions by Mahatma MurthiMahatma MurthiNo ratings yet
- Topic 7: Matrices and Determinants ObjectivesDocument5 pagesTopic 7: Matrices and Determinants ObjectivesMD ROKNUZZAMANNo ratings yet
- RatioLog and ProportionDocument6 pagesRatioLog and ProportionshlokNo ratings yet
- Finding Angle Between Vectors Using Python and C PDFDocument18 pagesFinding Angle Between Vectors Using Python and C PDFSrijith Reddy PakalaNo ratings yet
- Ratio English-19 PDFDocument2 pagesRatio English-19 PDFrajeevNo ratings yet
- Gradeup RatioDocument2 pagesGradeup RatiorajeevNo ratings yet
- Prelim Paper 2 - 2022 - Solution (Comments)Document17 pagesPrelim Paper 2 - 2022 - Solution (Comments)Bryan TangNo ratings yet
- Module 1 SimilarityDocument29 pagesModule 1 SimilarityShahani Abdulkarim100% (1)
- Proportion Exam 1to4Document2 pagesProportion Exam 1to4saad sheikhNo ratings yet
- En 0304 Serge Lang Basic Mathematics AnswersDocument10 pagesEn 0304 Serge Lang Basic Mathematics AnswersRM_1958No ratings yet
- 2.3 - Properties of Sets - Mathematics LibreTextsDocument2 pages2.3 - Properties of Sets - Mathematics LibreTextsSayeed OfficialNo ratings yet
- GMH 10 NoRestrictionDocument10 pagesGMH 10 NoRestrictionKarma Pema DorjeNo ratings yet
- Math Chapter 5Document38 pagesMath Chapter 5Carl Martin EsparraggoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document57 pagesLecture 01James luoNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 76Document3 pagesMechanics 76Adrian CabreraNo ratings yet
- CD PDFDocument9 pagesCD PDFshrish9999No ratings yet
- Partial Fractions: X B X A X X XDocument21 pagesPartial Fractions: X B X A X X XMohamed ToqeerNo ratings yet
- Ratio, Proportion, Indices & LogarithmsDocument7 pagesRatio, Proportion, Indices & LogarithmsTariq50% (2)
- On Maximisation of Prod (A-B)Document13 pagesOn Maximisation of Prod (A-B)NadiaNo ratings yet
- Algebra ReviewDocument2 pagesAlgebra Reviewsoufiane8fkaNo ratings yet
- Meb 2023 Lec 11Document14 pagesMeb 2023 Lec 11ngovietha406No ratings yet
- LN: 15.1 Algebraic Fraction: ExampleDocument2 pagesLN: 15.1 Algebraic Fraction: ExampleMiku NakanoNo ratings yet
- 145 Ch01 MATHS RatioProportionandMixturesDocument14 pages145 Ch01 MATHS RatioProportionandMixturesBijay Aryan DhakalNo ratings yet
- Ratios GateDocument2 pagesRatios GateRohul SibiNo ratings yet
- Precal2022 PDFDocument7 pagesPrecal2022 PDFThorung BOONKAEWNo ratings yet
- Module4 Dividing Radical Expressions PDFDocument5 pagesModule4 Dividing Radical Expressions PDFJohn Luis Masangkay BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Mensuration II (Important Results)Document13 pagesMensuration II (Important Results)Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Copiumhs Trial23 Solutions-1Document33 pagesCopiumhs Trial23 Solutions-1tedzone9No ratings yet
- 001 - Lecture - 3 - Annotated - Matrix MultiplicationDocument25 pages001 - Lecture - 3 - Annotated - Matrix MultiplicationSahana NayakaNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry: Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument2 pagesPlane Trigonometry: Trigonometric IdentitiesSine CosineNo ratings yet
- Section 9.3: The Dot ProductDocument7 pagesSection 9.3: The Dot ProductBakari HamisiNo ratings yet
- Plane TrigonometryDocument2 pagesPlane TrigonometryLhee Anne Zha DapdapigNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra: The Determinant of A MatrixDocument229 pagesLinear Algebra: The Determinant of A MatrixBrunéNo ratings yet
- Last 1.5 Day Revision QuestionsDocument1,657 pagesLast 1.5 Day Revision QuestionsRidhima AggarwalNo ratings yet
- A Math Common Test Practise 3Document8 pagesA Math Common Test Practise 3Fangru CaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 of 5Document31 pagesLecture 4 of 5awangpaker xxNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 1Document3 pagesQuestion Paper 1Sanjeet KotaryaNo ratings yet
- 2.4. Zero Negative and Fractional ExponentsDocument7 pages2.4. Zero Negative and Fractional ExponentsNikki LaudeNo ratings yet
- PlymouthUniversity MathsandStats Matrix MultiplicationDocument37 pagesPlymouthUniversity MathsandStats Matrix MultiplicationGood DeedsNo ratings yet
- E9ci903w5 - Q3-Learning Kit 1 & 2Document5 pagesE9ci903w5 - Q3-Learning Kit 1 & 2Rolando AloguinNo ratings yet
- 6 3partialfractionsDocument17 pages6 3partialfractionsRyo Geoffrey WidjajaNo ratings yet
- Quant Formula SheetDocument15 pagesQuant Formula Sheetdhwani shahNo ratings yet
- Ca Maths 1Document32 pagesCa Maths 1netic17284No ratings yet
- Exponent CompleteDocument8 pagesExponent CompletevkumarNo ratings yet
- 19.solutions of TrianglesDocument67 pages19.solutions of TrianglesJaysha GamingNo ratings yet
- Algebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsFrom EverandAlgebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsNo ratings yet