Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.1 One Pager The Ear - Memo
3.1 One Pager The Ear - Memo
Uploaded by
Rudzi Udzi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views1 page1. The document describes the anatomy and functions of the major parts of the human ear, including how sound is transmitted from the outer ear to the inner ear.
2. It explains that damage to structures like the ossicles or auditory nerve would disrupt the transmission of vibrations and prevent hearing.
3. Blockage of the Eustachian tube could cause a buildup of pressure in the middle ear and potentially rupture the eardrum, leading to hearing loss.
Original Description:
the ear system
Original Title
3.1 one pager The Ear_Memo
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document describes the anatomy and functions of the major parts of the human ear, including how sound is transmitted from the outer ear to the inner ear.
2. It explains that damage to structures like the ossicles or auditory nerve would disrupt the transmission of vibrations and prevent hearing.
3. Blockage of the Eustachian tube could cause a buildup of pressure in the middle ear and potentially rupture the eardrum, leading to hearing loss.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views1 page3.1 One Pager The Ear - Memo
3.1 One Pager The Ear - Memo
Uploaded by
Rudzi Udzi1. The document describes the anatomy and functions of the major parts of the human ear, including how sound is transmitted from the outer ear to the inner ear.
2. It explains that damage to structures like the ossicles or auditory nerve would disrupt the transmission of vibrations and prevent hearing.
3. Blockage of the Eustachian tube could cause a buildup of pressure in the middle ear and potentially rupture the eardrum, leading to hearing loss.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
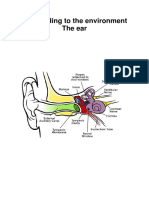
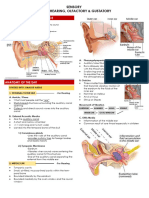
THE EAR Explain the consequences for hearing if the structures labelled D are fused
• The ossicles/structures will not be able to vibrate
Functions • and hence no vibrations will be passed to the inner ear
Transmits vibrations
• • Cochlea will not be stimulated
to the oval window
•Amplifies sounds • No amplification will occur
Tympanic membrane/Tympanum (Eardrum) C Adaptation: Made from
Function: Vibrates and converts sound waves bone… carry vibrations E Semi-circular Explain how part E and part F helps to maintain balance
into vibrations; Pass vibrations to ossicles D Ossicles (Cristae - balance) 1. The cristae in the semi-circular (E) canals are stimulated by changes in the
Adaptations direction and speed of movement
•Thin membrane which can vibrate F Sacculus and Utriculus 2. The maculae in the sacculus and utriculus (F) are stimulated by changes in
and assists in amplification of sound (Maculae - balance) the position of the head.
• When stimulated, the cristae and maculae convert the stimuli received into
Ear canal B nerve impulses. The nerve impulses are transported along the auditory nerve
Function:Directs sound waves to the to the cerebellum to be interpreted. The cerebellum then sends impulses to
tympanic membrane/tympanum the muscles to restore balance
(eardrum) Explain the consequences for hearing if part G is
G Auditory Nerve
Pinna A damaged
(Sensory neuron)
Function:Directs sound waves Oval window K Transmit impulses from the cochlea to •Auditory nerve (G) won’t be able to transmit
to the tympanic membrane Function:Coverts sound the cerebrum (hearing) and semi-circular impulses to the cerebrum
Adaptations: vibrations into pressure canals to the cerebellum (balance) •Cerebrum won’t be able to interpret the
• Grooved-directs sound waves waves. Helps amplification H Cochlea impulses
Round windowJ Contains the hearing receptors •The person won’t be able to hear
• Situated on the outside called Organ of Corti .
to capture maximum sound Function:Release/absorb
waves pressure waves to I Eustachian tube
prevent internal ear (Connects the Mouth to the middle ear ) Explain the consequences of a blockage in part I
echo. Functions • Blockage of the Eustachian tube which will not
Equalise pressure on either side of the be able to equalise the pressure in the middle ear
• tympanic membrane/eardrum
• resulting in pressure on the tympanic
• Drains moisture from the middle ear membrane
• that may cause the tympanic membrane to
HEARING DEFECTS: burst - leading to hearing loss
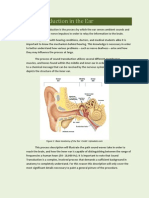
Hearing defect Causes Treatment Describe how hearing occurs.
Middle ear • Excess fluid in the middle ear • Antibiotics • Sound waves are directed into the auditory canal by the pinna.
infection caused by pathogen infection • Inserting grommets in the • The sound waves make the tympanic membrane vibrate and the vibrations are passed
tympanic membranes on to the ossicles in the middle ear.
Deafness • Injury to parts of the ear, • Hearing aids • The ossicles make the oval window vibrate and this causes pressure waves to be set up
nerves or parts of brain • Cochlear implants in the inner ear.
responsible for hearing • These vibrations also cause the organ of Corti to be stimulated and it generates
• Hardened wax • Hardening of impulses which are sent to the cerebrum along the auditory nerve.
ear tissues such as ossicles • The cerebrum interprets the impulses as sound.
You might also like
- Krisis - Elisabeth Eybers1Document2 pagesKrisis - Elisabeth Eybers1Thato Moratuwa Moloantoa100% (1)
- Physiology of Hearing OtolaryngologyDocument26 pagesPhysiology of Hearing OtolaryngologyDr.Sherif Bugnah88% (8)
- Microteaching EARDocument8 pagesMicroteaching EARRebizz BizzNo ratings yet
- The Ear. The Helix. The External Auditory Canal and Tympanic Membrane. Air and Bone JoiningDocument40 pagesThe Ear. The Helix. The External Auditory Canal and Tympanic Membrane. Air and Bone JoiningHarshit BhardwajNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECT PHILIPPINES Outline Spec For ArkiDocument39 pagesARCHITECT PHILIPPINES Outline Spec For ArkiBenjie LatrizNo ratings yet
- Haier in India Building Presence in A Mass Market Beyond ChinaDocument14 pagesHaier in India Building Presence in A Mass Market Beyond ChinaArun Kumar80% (5)
- Electricians GuideDocument296 pagesElectricians Guidemaeid75% (4)
- 5.1 One Pager Reflex Action - MEMODocument1 page5.1 One Pager Reflex Action - MEMORudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDFDocument1 page4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDFRudzi Udzi100% (1)
- 6.1 One Pager Nervous System - MEMODocument1 page6.1 One Pager Nervous System - MEMORudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing: Note-Taking Guide 2021)Document28 pagesObstetric Nursing: Note-Taking Guide 2021)Benedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Practical Examination Marking Guideline Grade 12 Physical Science 2019 PDFDocument5 pagesPractical Examination Marking Guideline Grade 12 Physical Science 2019 PDFWonder Bee Nzama100% (1)
- 7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Document1 page7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Rudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Fiela Se Kind Chapter SummariesDocument19 pagesFiela Se Kind Chapter Summariesst10437025100% (1)
- Updated All New Poetry Guide 2023Document139 pagesUpdated All New Poetry Guide 2023Michelle0% (1)
- Support System in Animals and PlantsDocument37 pagesSupport System in Animals and PlantsRusya YahayaNo ratings yet
- GR 12 - Tourism - Term 1 - Global Events of International Significance - Revision Question Answers - EcdoeDocument21 pagesGR 12 - Tourism - Term 1 - Global Events of International Significance - Revision Question Answers - Ecdoebongiweshibe55No ratings yet
- Euclidean Geometry Grade 12. (2) DocxDocument27 pagesEuclidean Geometry Grade 12. (2) Docxnomthandazoyende38No ratings yet
- Module 4 PPT The Ear 2022 EditDocument43 pagesModule 4 PPT The Ear 2022 Editaesthete541No ratings yet
- Core CH 15 Detecting The Environment Part 2Document3 pagesCore CH 15 Detecting The Environment Part 2TH TNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Human Ear Structure and Function LessonDocument7 pagesLesson 1 The Human Ear Structure and Function LessonCarvia CusNo ratings yet
- KC - Longitudinal and Transverse - KnowDocument50 pagesKC - Longitudinal and Transverse - KnowT WNo ratings yet
- HEARINGDocument7 pagesHEARINGrrkn9njjhzNo ratings yet
- The EarDocument17 pagesThe Earmzwakhemagagula649No ratings yet
- SAS - Session 7 - PSY079 - Intro To PsychologyDocument8 pagesSAS - Session 7 - PSY079 - Intro To PsychologyLordelee Mae N PamaylaonNo ratings yet
- Hearing Outline: - AnatomyDocument82 pagesHearing Outline: - AnatomyFadil BachmidNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Physiology of Hearing and Balance: Dr. CalaquianDocument6 pagesSpecial Senses Physiology of Hearing and Balance: Dr. CalaquianHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Life Science The Ear PDFDocument5 pagesGrade 12 Life Science The Ear PDFLethabo Mngomezulu100% (2)
- Ossicles: The Malleus, The Incus, and The StapesDocument6 pagesOssicles: The Malleus, The Incus, and The StapesLili M.No ratings yet
- Special Senses Part II - PearsonsDocument5 pagesSpecial Senses Part II - Pearsonsblando.shaneNo ratings yet
- WS - Ear Structure and Function WORDDocument4 pagesWS - Ear Structure and Function WORDAlvand HormoziNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Auditory SystemDocument26 pagesPhysiology of Auditory SystemVictor EnachiNo ratings yet
- Auditory ScriptDocument8 pagesAuditory ScriptKC White Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Week 16. INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT Review of Ear Ana PhysioDocument2 pagesWeek 16. INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT Review of Ear Ana PhysioSOPHIA PILLENANo ratings yet
- Anatomy + Objective PhenomenaDocument31 pagesAnatomy + Objective PhenomenaHoussemNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 - Week 16 CTDocument2 pagesNCMB 316 - Week 16 CTangelica bordadorNo ratings yet
- Research Task - Ear Anatomy FunctionDocument2 pagesResearch Task - Ear Anatomy Functionapi-350036419No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Human Ear Structure and Function LessonDocument5 pagesLesson 1 The Human Ear Structure and Function Lessonعمر الفاروق عبيديةNo ratings yet
- 3 EarDocument2 pages3 EarCarlo BarriosNo ratings yet
- Mosby's Medical Dictionary (E)Document90 pagesMosby's Medical Dictionary (E)Anonymous 6TsBkXVZUI0% (1)
- 05 Auditory ProcessingDocument111 pages05 Auditory ProcessingsethNo ratings yet
- LO SSS Week 5Document8 pagesLO SSS Week 5Tony StarkNo ratings yet
- Sound Transduction EarDocument7 pagesSound Transduction Earhsc5013100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanSharathNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EarDocument80 pagesPhysiology of EarPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer50% (2)
- Assessment of The Ear MEDSURGDocument18 pagesAssessment of The Ear MEDSURGzildjian joyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of HearingDocument9 pagesPhysiology of HearingDel LinenbergerNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Hearing PDFDocument6 pagesMechanism of Hearing PDFShruthi DanielNo ratings yet
- Xibraho: AuditoryDocument6 pagesXibraho: AuditoryYousuf skNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - BSN 2BDocument16 pagesGroup 3 - BSN 2BJan Clarisse RamosNo ratings yet
- Biopsych Audition Mechanical ChemicalDocument6 pagesBiopsych Audition Mechanical ChemicalnaomiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear: Perry C. Hanavan, Au.D. AudiologistDocument92 pagesAnatomy of The Ear: Perry C. Hanavan, Au.D. AudiologistRahma AssayeghNo ratings yet
- The World Through Our Senses The World Through Our SensesDocument11 pagesThe World Through Our Senses The World Through Our SensesduanyushaNo ratings yet
- Auditory System of Human BodyDocument149 pagesAuditory System of Human Bodysayan27.sikdarNo ratings yet
- Hearing 2nd YearDocument20 pagesHearing 2nd YearAliaa MahamadNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing For Auditory SystemsDocument108 pagesSignal Processing For Auditory SystemsKarthikeya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Anatomy of The Ear (Edited)Document26 pages10 - Anatomy of The Ear (Edited)Enlighten usNo ratings yet
- CNS 4 GoodDocument16 pagesCNS 4 GoodJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- The Auditory System: B. The Intensity of Amplitude of The Sound Measured inDocument10 pagesThe Auditory System: B. The Intensity of Amplitude of The Sound Measured inFikri RamaNo ratings yet
- The EarDocument103 pagesThe Eardharmendra kirarNo ratings yet
- SSIP PPT Life Sciences Module 4the EarDocument32 pagesSSIP PPT Life Sciences Module 4the EarchynarrsitholeNo ratings yet
- SensoryDocument56 pagesSensoryNatalie AwadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology of HearingDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and Physiology of HearingDana AhmadNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument9 pagesMeiosisRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Life Science Needs To KnowDocument3 pagesLife Science Needs To KnowRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 5.1 One Pager Reflex Action - MEMODocument1 page5.1 One Pager Reflex Action - MEMORudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Document1 page7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Rudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 6.1 One Pager Nervous System - MEMODocument1 page6.1 One Pager Nervous System - MEMORudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDFDocument1 page4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDFRudzi Udzi100% (1)
- P1 Diagram Book GR12Document30 pagesP1 Diagram Book GR12Rudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 2.1 One Pager Female Reproduction MEMODocument1 page2.1 One Pager Female Reproduction MEMORudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Solution Step AheadDocument127 pagesSolution Step AheadRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Revision LiveDocument71 pagesLife Sciences P1 Revision LiveRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 5Document36 pagesPractical Research 1 5Maria Cristina AldasNo ratings yet
- Basic Customer Service Principles-ImportantDocument39 pagesBasic Customer Service Principles-Importantzoltan2014100% (6)
- Company Introduction PDFDocument14 pagesCompany Introduction PDFJeff SmithNo ratings yet
- H JSC She G 10406300Document2 pagesH JSC She G 10406300Satria ThocksNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their Properties PDFDocument13 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their Properties PDFpieNo ratings yet
- Steyr S MaticDocument6 pagesSteyr S Maticclcasal0% (1)
- Unit 1,2,3,4,5 MaDocument97 pagesUnit 1,2,3,4,5 MaPRADYUMN KUMAR DUBEYNo ratings yet
- PF100/PF150 Manual Postformers: Process For Postforming A Waterfall (90°) EdgeDocument1 pagePF100/PF150 Manual Postformers: Process For Postforming A Waterfall (90°) EdgeAngel CazaresNo ratings yet
- NCP IrritabilityDocument3 pagesNCP IrritabilityBruce Kelly MamarilNo ratings yet
- Vastu-Truths and UntruthsDocument5 pagesVastu-Truths and Untruthsbas daNo ratings yet
- Institute of Food Security (Food Corporation of India) Gurgaon Management Trainee Batch:V/2010 Objective Test:Commercial (Sales&Export)Document2 pagesInstitute of Food Security (Food Corporation of India) Gurgaon Management Trainee Batch:V/2010 Objective Test:Commercial (Sales&Export)Swarup MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Yawmc-0406-Us (2) Valvulas YarwayDocument8 pagesYawmc-0406-Us (2) Valvulas YarwayLuis Manuel VazquezNo ratings yet
- Final Stilt Floor Plan 16042022Document1 pageFinal Stilt Floor Plan 16042022rajesh lankaNo ratings yet
- The Environment PDFDocument6 pagesThe Environment PDFchaituNo ratings yet
- Permutation & Combination Theory - EDocument9 pagesPermutation & Combination Theory - Ethinkiit100% (1)
- LFL A Comprehensive Guide To EQUIA Forte en PDFDocument16 pagesLFL A Comprehensive Guide To EQUIA Forte en PDFAsus AsusNo ratings yet
- MGT 534 Organizational Behavior2Document3 pagesMGT 534 Organizational Behavior2Phattyin ZaharahNo ratings yet
- Characterization RO NF MembranesDocument13 pagesCharacterization RO NF MembranesEri Dwi ListiantoNo ratings yet
- AshokDocument27 pagesAshoksudheeNo ratings yet
- Vxflex Data SheetDocument5 pagesVxflex Data SheetJesus SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Lector Aspergillus LFARDR IFU - EnglishDocument2 pagesLector Aspergillus LFARDR IFU - EnglishMelissa MelendezNo ratings yet
- National Insurance Company Ltd. Policy No: 57150031216760012077 1 Year Liability Only From 00:00:01 Hours On 28-Jan-2022 To Midnight of 27/01/2023Document2 pagesNational Insurance Company Ltd. Policy No: 57150031216760012077 1 Year Liability Only From 00:00:01 Hours On 28-Jan-2022 To Midnight of 27/01/2023Benson BennyNo ratings yet
- RSTWS LTE Market View CMW500 Communication Test FunctionDocument131 pagesRSTWS LTE Market View CMW500 Communication Test FunctionHong ShanNo ratings yet
- Transportation orDocument5 pagesTransportation orAaditya shahNo ratings yet
- JEE 2024 RoadmapDocument42 pagesJEE 2024 Roadmaplilop27557No ratings yet
- Extended Abstract Comparison of Effectiveness of The Various Species of Citrus' Peels As Styrofoam DecomposerDocument3 pagesExtended Abstract Comparison of Effectiveness of The Various Species of Citrus' Peels As Styrofoam DecomposerKen EzekielNo ratings yet
- FFXV Checklist - HuntsDocument1 pageFFXV Checklist - HuntsarashibirruNo ratings yet