Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity 1 Speech Sounds
Activity 1 Speech Sounds
Uploaded by
Maryjoice Camo LiwanaganCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- (Cambridge Studies in Linguistics) John Laver - The Phonetic Description of Voice Quality (2009, Cambridge University Press) PDFDocument208 pages(Cambridge Studies in Linguistics) John Laver - The Phonetic Description of Voice Quality (2009, Cambridge University Press) PDFNathalia Martins100% (1)
- GHL #02Document8 pagesGHL #02esha khanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Organs of SpeechDocument22 pagesPresentation On Organs of Speechseptiani zakariaNo ratings yet
- Articulatory Phonetics: 1) VoiceDocument3 pagesArticulatory Phonetics: 1) VoiceDorepeNo ratings yet
- Articulatory PhoneticsDocument3 pagesArticulatory PhoneticszelindaaNo ratings yet
- Place and Manner of Articulation PresentationDocument14 pagesPlace and Manner of Articulation PresentationBettina GomezNo ratings yet
- Report On Articulatory PhoneticsDocument4 pagesReport On Articulatory PhoneticsJobed EspantoNo ratings yet
- A Paper PhoneticsDocument17 pagesA Paper PhoneticsDevinaa hsNo ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation: Speech OrganDocument7 pagesManner of Articulation: Speech OrganLipak gmailNo ratings yet
- Speech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageDocument7 pagesSpeech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageSherwin Ryan AvilaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Muhammad Irwan Phonology NIM: 17111024210002Document5 pagesNama: Muhammad Irwan Phonology NIM: 17111024210002Roby Pandu PradanaNo ratings yet
- U9 Cavity FeaturesDocument3 pagesU9 Cavity Featureslornanyaga4No ratings yet
- Consonants and Allophonic VariationDocument33 pagesConsonants and Allophonic VariationAgustina AcostaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Report 1-10-15Document47 pagesPhonetics Report 1-10-15Maria Victoria PadroNo ratings yet
- DescriptiveDocument75 pagesDescriptiveAmani SalmanNo ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation DefinitionDocument9 pagesManner of Articulation DefinitionAdmin LinguizNo ratings yet
- The Sounds of EnglishDocument58 pagesThe Sounds of EnglishSara Albina0% (1)
- Phonetics and Phonology PDFDocument62 pagesPhonetics and Phonology PDFCarlos Rojas CamachoNo ratings yet
- Phonetics & Spoken EnglishDocument12 pagesPhonetics & Spoken EnglishCharanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 8: Phonological System of The English Language Ii: Consonants. Phonetic SymbolsDocument8 pagesTopic 8: Phonological System of The English Language Ii: Consonants. Phonetic SymbolsLaura Irina Lara SánchezNo ratings yet
- First Session of Phonetics and PhonologyDocument13 pagesFirst Session of Phonetics and PhonologyKhlifibrahimNo ratings yet
- Organ of SpeechDocument10 pagesOrgan of SpeechWinda Rizki Listia DamanikNo ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument5 pagesOrgans of SpeechMohd Shahrin BasniNo ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument5 pagesOrgans of Speechlittle large2100% (1)
- Articulators/ Speech Organs: 1. The Larynx & The Vocal FoldsDocument6 pagesArticulators/ Speech Organs: 1. The Larynx & The Vocal FoldsGulfam RiazNo ratings yet
- Macro Factors in Financial ThinkingDocument24 pagesMacro Factors in Financial ThinkingMarlon M. LucesNo ratings yet
- Módulo IVDocument10 pagesMódulo IVAlejandraFloresPérezNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument3 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyCarlos Antonio Mancebo HerediaNo ratings yet
- Phonology Is, Broadly Speaking, The Subdiscipline of Linguistics ConcernedDocument16 pagesPhonology Is, Broadly Speaking, The Subdiscipline of Linguistics ConcernedNur Haidah100% (3)
- Speech MechanismDocument3 pagesSpeech Mechanismহুমায়রা জাহানNo ratings yet
- Linguistics 2Document45 pagesLinguistics 2Bani AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Paper Group 5 - GA 1Document3 pagesPaper Group 5 - GA 1idayanti830No ratings yet
- Voicing and Consonants: Present by Afdhol Zikri English Department University of Pasir PengaraianDocument14 pagesVoicing and Consonants: Present by Afdhol Zikri English Department University of Pasir PengaraianlucianoNo ratings yet
- Place of Articulation - Knight - Unit 3Document5 pagesPlace of Articulation - Knight - Unit 3Tomás RicardinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linguistics: Phonetics: July 27, 2017Document17 pagesIntroduction To Linguistics: Phonetics: July 27, 2017zyanmktsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsDocument15 pagesChapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsBearish PaleroNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument31 pagesEnglish Phonetics and PhonologyIzzati Azman100% (1)
- Speech OrgansDocument5 pagesSpeech OrgansprivateceeNo ratings yet
- Manner of ArticulationDocument3 pagesManner of Articulationlalila melikaNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm - Handout 1Document12 pagesOral Comm - Handout 1Teresa Borja0% (1)
- Week 2+ 3 PhoneticsDocument7 pagesWeek 2+ 3 PhoneticsNhân ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Production of Speech SoundDocument31 pagesIntroduction and Production of Speech SoundNguyệt MaiNo ratings yet
- Theory Unit 7 - 1993 Listing - April 2012Document13 pagesTheory Unit 7 - 1993 Listing - April 2012Sil RuizNo ratings yet
- Speech and Theater ExamDocument22 pagesSpeech and Theater ExamCres Jules ArdoNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology PDFDocument6 pagesPhonetics and Phonology PDFanyi porfirioNo ratings yet
- Fonetica Resumen Primer ParcialDocument11 pagesFonetica Resumen Primer Parcialemilse RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Intro To Phonetics & PhonologyDocument20 pagesIntro To Phonetics & Phonologyzainsaghir7576No ratings yet
- BEGEDocument485 pagesBEGENARENDRANo ratings yet
- Phonetic and Phonology": Miranti Widyasari Tatebale 17091102047Document12 pagesPhonetic and Phonology": Miranti Widyasari Tatebale 17091102047MIRANTI WIDYASARI TATEBALENo ratings yet
- Organ of Speech Airstream Mechanism (Kel 1)Document7 pagesOrgan of Speech Airstream Mechanism (Kel 1)Vera AsifaNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active ArticulatorsDocument3 pagesPassive and Active ArticulatorsAishwarya NagrajNo ratings yet
- The Organs of SpeechDocument6 pagesThe Organs of SpeechAnonymous ToHeyBoEbX100% (1)
- Phonetic ADocument28 pagesPhonetic ANina BandalacNo ratings yet
- Intro Ling Unit 3Document14 pagesIntro Ling Unit 3Zain ChNo ratings yet
- Session II Phonology Presentation-D SnowdenDocument10 pagesSession II Phonology Presentation-D Snowdenapi-218621193No ratings yet
- 1st - Sem - English - Unit - 2 B EdDocument27 pages1st - Sem - English - Unit - 2 B EdBrilliant Brainz MalayalamNo ratings yet
- Types of PhoneticDocument5 pagesTypes of PhoneticDwiqha Qatrunnada100% (2)
- Allo PhonesDocument5 pagesAllo PhonesElitee72No ratings yet
- Theme 8: The Phonological System of The English Language (Ii) - The Consonants. Phonetic Symbols. Comparison With The Phonological System of SpanishDocument11 pagesTheme 8: The Phonological System of The English Language (Ii) - The Consonants. Phonetic Symbols. Comparison With The Phonological System of SpanishminimunhozNo ratings yet
- Actividad 1Document2 pagesActividad 1Alberto Seisdedos BernalNo ratings yet
- Nayla PPT Report Text 9bDocument14 pagesNayla PPT Report Text 9bAlikaNo ratings yet
- Copyreading & Headline WritingDocument54 pagesCopyreading & Headline WritingLEONARDO JR ENRIQUEZ100% (1)
- Sounds and Pronunciation: Bab 1: Bunyi Dan SebutanDocument13 pagesSounds and Pronunciation: Bab 1: Bunyi Dan Sebutanbarry Elhadj AbdoulayeNo ratings yet
- First Conditional Practice 3rd Secondary SchoolDocument1 pageFirst Conditional Practice 3rd Secondary SchoolEnglish straight to the point straight to the pointNo ratings yet
- Comment Adverbs and Usage IELTSDocument2 pagesComment Adverbs and Usage IELTSJohn ClampNo ratings yet
- EnglishFile4e Pre-Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 5ADocument1 pageEnglishFile4e Pre-Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 5ASona ProudloveNo ratings yet
- Noun Clause ExerciseDocument5 pagesNoun Clause ExerciseEylül AltunayNo ratings yet
- אוריינות אנגלית ג'קליןDocument1 pageאוריינות אנגלית ג'קליןShiran MasarwaNo ratings yet
- (1978) Drum Languages and Their MessagesDocument99 pages(1978) Drum Languages and Their MessagesFrancesco RofiNo ratings yet
- Parables: Embodiment of Moral Points: ObjectivesDocument2 pagesParables: Embodiment of Moral Points: ObjectivesHanna CarpioNo ratings yet
- Grammar 2 Modals Lesson & Exercises Version BDocument9 pagesGrammar 2 Modals Lesson & Exercises Version Bmr.mohamed.rakidNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verb and Regular Verb-1-1Document24 pagesIrregular Verb and Regular Verb-1-1SilvanaNo ratings yet
- Test 6 JunaidDocument11 pagesTest 6 JunaidJunaid MalikNo ratings yet
- Ma 2ND YyDocument1 pageMa 2ND YycanigetyournmbrrNo ratings yet
- Edtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPGDocument5 pagesEdtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPGapi-714785994No ratings yet
- Fl2 ReviewerDocument13 pagesFl2 ReviewerKissie SarnoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Spanish - Present TenseDocument6 pagesForm 2 Spanish - Present TenseskylarNo ratings yet
- Grammar Hacks!Document19 pagesGrammar Hacks!AestheticNo ratings yet
- Function of Conversational Implicatures in Saturday Night Live Talk ShowDocument6 pagesFunction of Conversational Implicatures in Saturday Night Live Talk ShowInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Word Perfect Spelling Book 1 9780602209858 Ronald - 5b4e3ca8097c47617d8b45b4Document1 pageWord Perfect Spelling Book 1 9780602209858 Ronald - 5b4e3ca8097c47617d8b45b4John Olekaifenma100% (1)
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocument2 pagesAdverbs of FrequencyJOSE LUIS ARISTIZABAL DUARTENo ratings yet
- Reflexive Verbs FullDocument4 pagesReflexive Verbs Full19 - Dishan Das - VI - F100% (1)
- Tiếng AnhDocument25 pagesTiếng AnhQuyên Nguyễn Huỳnh PhươngNo ratings yet
- TET 1A SGT UM Session 1 16 08 22Document60 pagesTET 1A SGT UM Session 1 16 08 22Farheen FathimaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 9 Matrix-for-the-Learning-Continuity-PlanDocument8 pagesGRADE 9 Matrix-for-the-Learning-Continuity-PlanMarliel P. CastillejosNo ratings yet
- Key Principles of Effective CommunicationDocument3 pagesKey Principles of Effective CommunicationShaihanNo ratings yet
- Bright Ideas 5 Reinforcement WorksheetsDocument2 pagesBright Ideas 5 Reinforcement WorksheetsThànhh LongNo ratings yet
- Politeness Strategy1Document5 pagesPoliteness Strategy1Fariz ArdiansyachNo ratings yet
- Demonstrative Pronouns: This, That, These, ThoseDocument2 pagesDemonstrative Pronouns: This, That, These, ThoseBondfriendsNo ratings yet
Activity 1 Speech Sounds
Activity 1 Speech Sounds
Uploaded by
Maryjoice Camo LiwanaganOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity 1 Speech Sounds
Activity 1 Speech Sounds
Uploaded by
Maryjoice Camo LiwanaganCopyright:
Available Formats
1
SCIENCES
ACTIVITY/ EXERCISE/ ASSIGNMENT
Name: Liwanagan, Maryjoice C. Date: March 12, 2023
Year/Course: III-BSED
1. Differentiate voiceless and voiced sound. Give examples
English produces some sounds that are not generated in other languages, and
vice versa. For English language learners, this is yet another source of
phonological difficulties. Communication may be affected by distorted sounds
(phonemes). Let's examine the voiced and voiceless groups of sound. Either
spoken or voiceless, all noises exist. When spoken sounds are created, our vocal
cords begin to vibrate. Air enters the mouth at various locations and produces
voiceless sounds.
There are voiced and voiceless consonant sounds. A wordless sound is one that
is produced solely by air, without the use of a voice.
Placing your thumb softly on your throat will allow you to determine whether or not
a sound is heard. If you can vibrate when you pronounce a sound, it is voiced.
Voicing is crucial because often it's the only variation in the pronunciation of two
very distinct words, such as 'bet' and 'pet'.
Bet /bet/ - the /b/ sound is voiced.
Pet makes a voiceless /p/ sound.
2. What are the different place of articulation? Give examples
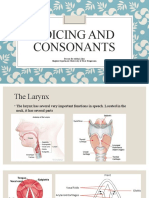
The place of articulation (also known as the point of articulation) of a consonant is
the place along the vocal tract where it is produced in articulatory phonetics: 10 It
is the location where a constriction is made between an active and a passive
articulator. So, although passive articulators are so named because they are often
immobile and are the portions with which an active articulator makes contact,
active articulators are organs capable of voluntary movement that induce the
contraction.
Three points of articulation are present. The hard palate on the roof of the mouth,
the alveolar ridge, the gum line immediately behind the teeth (alveolar), and the
back of the alveolar ridge (post-alveolar) (palatal)
1
SCIENCES
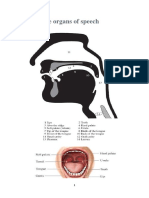
3. What are the different Manner of Articulation? Give examples
The arrangement and interaction of the articulator’s speech organs such the
tongue, lips, and palate during the production of a spoken sound is referred to as
the mode of articulation. Stricture, or how closely the speech organs are spaced
from one another, is one aspect of style.
Plosive, also known as stop, is a type of oral occlusive in which the oral vocal tract
is blocked and there is no nasal airflow, resulting in a total cessation of airflow.
Examples include the voiceless English consonants /p t k/ and /b d /. (voiced)
When the nasal passages are blocked yet air still enters the body through the
nose, this condition is called a nasal occlusive. The resonant cavity that gives
different nasals their distinctive sounds is determined by the shape and
positioning of the tongue.
When there is continuous frication (noisy, turbulent airflow) near the site of
articulation, the sound is referred to as spirant, or fricative. English /f, s/
(voiceless), /v, z/ (voiced), etc. are examples.
You might also like
- (Cambridge Studies in Linguistics) John Laver - The Phonetic Description of Voice Quality (2009, Cambridge University Press) PDFDocument208 pages(Cambridge Studies in Linguistics) John Laver - The Phonetic Description of Voice Quality (2009, Cambridge University Press) PDFNathalia Martins100% (1)
- GHL #02Document8 pagesGHL #02esha khanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Organs of SpeechDocument22 pagesPresentation On Organs of Speechseptiani zakariaNo ratings yet
- Articulatory Phonetics: 1) VoiceDocument3 pagesArticulatory Phonetics: 1) VoiceDorepeNo ratings yet
- Articulatory PhoneticsDocument3 pagesArticulatory PhoneticszelindaaNo ratings yet
- Place and Manner of Articulation PresentationDocument14 pagesPlace and Manner of Articulation PresentationBettina GomezNo ratings yet
- Report On Articulatory PhoneticsDocument4 pagesReport On Articulatory PhoneticsJobed EspantoNo ratings yet
- A Paper PhoneticsDocument17 pagesA Paper PhoneticsDevinaa hsNo ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation: Speech OrganDocument7 pagesManner of Articulation: Speech OrganLipak gmailNo ratings yet
- Speech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageDocument7 pagesSpeech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageSherwin Ryan AvilaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Muhammad Irwan Phonology NIM: 17111024210002Document5 pagesNama: Muhammad Irwan Phonology NIM: 17111024210002Roby Pandu PradanaNo ratings yet
- U9 Cavity FeaturesDocument3 pagesU9 Cavity Featureslornanyaga4No ratings yet
- Consonants and Allophonic VariationDocument33 pagesConsonants and Allophonic VariationAgustina AcostaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Report 1-10-15Document47 pagesPhonetics Report 1-10-15Maria Victoria PadroNo ratings yet
- DescriptiveDocument75 pagesDescriptiveAmani SalmanNo ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation DefinitionDocument9 pagesManner of Articulation DefinitionAdmin LinguizNo ratings yet
- The Sounds of EnglishDocument58 pagesThe Sounds of EnglishSara Albina0% (1)
- Phonetics and Phonology PDFDocument62 pagesPhonetics and Phonology PDFCarlos Rojas CamachoNo ratings yet
- Phonetics & Spoken EnglishDocument12 pagesPhonetics & Spoken EnglishCharanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 8: Phonological System of The English Language Ii: Consonants. Phonetic SymbolsDocument8 pagesTopic 8: Phonological System of The English Language Ii: Consonants. Phonetic SymbolsLaura Irina Lara SánchezNo ratings yet
- First Session of Phonetics and PhonologyDocument13 pagesFirst Session of Phonetics and PhonologyKhlifibrahimNo ratings yet
- Organ of SpeechDocument10 pagesOrgan of SpeechWinda Rizki Listia DamanikNo ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument5 pagesOrgans of SpeechMohd Shahrin BasniNo ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument5 pagesOrgans of Speechlittle large2100% (1)
- Articulators/ Speech Organs: 1. The Larynx & The Vocal FoldsDocument6 pagesArticulators/ Speech Organs: 1. The Larynx & The Vocal FoldsGulfam RiazNo ratings yet
- Macro Factors in Financial ThinkingDocument24 pagesMacro Factors in Financial ThinkingMarlon M. LucesNo ratings yet
- Módulo IVDocument10 pagesMódulo IVAlejandraFloresPérezNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument3 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyCarlos Antonio Mancebo HerediaNo ratings yet
- Phonology Is, Broadly Speaking, The Subdiscipline of Linguistics ConcernedDocument16 pagesPhonology Is, Broadly Speaking, The Subdiscipline of Linguistics ConcernedNur Haidah100% (3)
- Speech MechanismDocument3 pagesSpeech Mechanismহুমায়রা জাহানNo ratings yet
- Linguistics 2Document45 pagesLinguistics 2Bani AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Paper Group 5 - GA 1Document3 pagesPaper Group 5 - GA 1idayanti830No ratings yet
- Voicing and Consonants: Present by Afdhol Zikri English Department University of Pasir PengaraianDocument14 pagesVoicing and Consonants: Present by Afdhol Zikri English Department University of Pasir PengaraianlucianoNo ratings yet
- Place of Articulation - Knight - Unit 3Document5 pagesPlace of Articulation - Knight - Unit 3Tomás RicardinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linguistics: Phonetics: July 27, 2017Document17 pagesIntroduction To Linguistics: Phonetics: July 27, 2017zyanmktsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsDocument15 pagesChapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsBearish PaleroNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument31 pagesEnglish Phonetics and PhonologyIzzati Azman100% (1)
- Speech OrgansDocument5 pagesSpeech OrgansprivateceeNo ratings yet
- Manner of ArticulationDocument3 pagesManner of Articulationlalila melikaNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm - Handout 1Document12 pagesOral Comm - Handout 1Teresa Borja0% (1)
- Week 2+ 3 PhoneticsDocument7 pagesWeek 2+ 3 PhoneticsNhân ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Production of Speech SoundDocument31 pagesIntroduction and Production of Speech SoundNguyệt MaiNo ratings yet
- Theory Unit 7 - 1993 Listing - April 2012Document13 pagesTheory Unit 7 - 1993 Listing - April 2012Sil RuizNo ratings yet
- Speech and Theater ExamDocument22 pagesSpeech and Theater ExamCres Jules ArdoNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology PDFDocument6 pagesPhonetics and Phonology PDFanyi porfirioNo ratings yet
- Fonetica Resumen Primer ParcialDocument11 pagesFonetica Resumen Primer Parcialemilse RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Intro To Phonetics & PhonologyDocument20 pagesIntro To Phonetics & Phonologyzainsaghir7576No ratings yet
- BEGEDocument485 pagesBEGENARENDRANo ratings yet
- Phonetic and Phonology": Miranti Widyasari Tatebale 17091102047Document12 pagesPhonetic and Phonology": Miranti Widyasari Tatebale 17091102047MIRANTI WIDYASARI TATEBALENo ratings yet
- Organ of Speech Airstream Mechanism (Kel 1)Document7 pagesOrgan of Speech Airstream Mechanism (Kel 1)Vera AsifaNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active ArticulatorsDocument3 pagesPassive and Active ArticulatorsAishwarya NagrajNo ratings yet
- The Organs of SpeechDocument6 pagesThe Organs of SpeechAnonymous ToHeyBoEbX100% (1)
- Phonetic ADocument28 pagesPhonetic ANina BandalacNo ratings yet
- Intro Ling Unit 3Document14 pagesIntro Ling Unit 3Zain ChNo ratings yet
- Session II Phonology Presentation-D SnowdenDocument10 pagesSession II Phonology Presentation-D Snowdenapi-218621193No ratings yet
- 1st - Sem - English - Unit - 2 B EdDocument27 pages1st - Sem - English - Unit - 2 B EdBrilliant Brainz MalayalamNo ratings yet
- Types of PhoneticDocument5 pagesTypes of PhoneticDwiqha Qatrunnada100% (2)
- Allo PhonesDocument5 pagesAllo PhonesElitee72No ratings yet
- Theme 8: The Phonological System of The English Language (Ii) - The Consonants. Phonetic Symbols. Comparison With The Phonological System of SpanishDocument11 pagesTheme 8: The Phonological System of The English Language (Ii) - The Consonants. Phonetic Symbols. Comparison With The Phonological System of SpanishminimunhozNo ratings yet
- Actividad 1Document2 pagesActividad 1Alberto Seisdedos BernalNo ratings yet
- Nayla PPT Report Text 9bDocument14 pagesNayla PPT Report Text 9bAlikaNo ratings yet
- Copyreading & Headline WritingDocument54 pagesCopyreading & Headline WritingLEONARDO JR ENRIQUEZ100% (1)
- Sounds and Pronunciation: Bab 1: Bunyi Dan SebutanDocument13 pagesSounds and Pronunciation: Bab 1: Bunyi Dan Sebutanbarry Elhadj AbdoulayeNo ratings yet
- First Conditional Practice 3rd Secondary SchoolDocument1 pageFirst Conditional Practice 3rd Secondary SchoolEnglish straight to the point straight to the pointNo ratings yet
- Comment Adverbs and Usage IELTSDocument2 pagesComment Adverbs and Usage IELTSJohn ClampNo ratings yet
- EnglishFile4e Pre-Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 5ADocument1 pageEnglishFile4e Pre-Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 5ASona ProudloveNo ratings yet
- Noun Clause ExerciseDocument5 pagesNoun Clause ExerciseEylül AltunayNo ratings yet
- אוריינות אנגלית ג'קליןDocument1 pageאוריינות אנגלית ג'קליןShiran MasarwaNo ratings yet
- (1978) Drum Languages and Their MessagesDocument99 pages(1978) Drum Languages and Their MessagesFrancesco RofiNo ratings yet
- Parables: Embodiment of Moral Points: ObjectivesDocument2 pagesParables: Embodiment of Moral Points: ObjectivesHanna CarpioNo ratings yet
- Grammar 2 Modals Lesson & Exercises Version BDocument9 pagesGrammar 2 Modals Lesson & Exercises Version Bmr.mohamed.rakidNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verb and Regular Verb-1-1Document24 pagesIrregular Verb and Regular Verb-1-1SilvanaNo ratings yet
- Test 6 JunaidDocument11 pagesTest 6 JunaidJunaid MalikNo ratings yet
- Ma 2ND YyDocument1 pageMa 2ND YycanigetyournmbrrNo ratings yet
- Edtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPGDocument5 pagesEdtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPGapi-714785994No ratings yet
- Fl2 ReviewerDocument13 pagesFl2 ReviewerKissie SarnoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Spanish - Present TenseDocument6 pagesForm 2 Spanish - Present TenseskylarNo ratings yet
- Grammar Hacks!Document19 pagesGrammar Hacks!AestheticNo ratings yet
- Function of Conversational Implicatures in Saturday Night Live Talk ShowDocument6 pagesFunction of Conversational Implicatures in Saturday Night Live Talk ShowInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Word Perfect Spelling Book 1 9780602209858 Ronald - 5b4e3ca8097c47617d8b45b4Document1 pageWord Perfect Spelling Book 1 9780602209858 Ronald - 5b4e3ca8097c47617d8b45b4John Olekaifenma100% (1)
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocument2 pagesAdverbs of FrequencyJOSE LUIS ARISTIZABAL DUARTENo ratings yet
- Reflexive Verbs FullDocument4 pagesReflexive Verbs Full19 - Dishan Das - VI - F100% (1)
- Tiếng AnhDocument25 pagesTiếng AnhQuyên Nguyễn Huỳnh PhươngNo ratings yet
- TET 1A SGT UM Session 1 16 08 22Document60 pagesTET 1A SGT UM Session 1 16 08 22Farheen FathimaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 9 Matrix-for-the-Learning-Continuity-PlanDocument8 pagesGRADE 9 Matrix-for-the-Learning-Continuity-PlanMarliel P. CastillejosNo ratings yet
- Key Principles of Effective CommunicationDocument3 pagesKey Principles of Effective CommunicationShaihanNo ratings yet
- Bright Ideas 5 Reinforcement WorksheetsDocument2 pagesBright Ideas 5 Reinforcement WorksheetsThànhh LongNo ratings yet
- Politeness Strategy1Document5 pagesPoliteness Strategy1Fariz ArdiansyachNo ratings yet
- Demonstrative Pronouns: This, That, These, ThoseDocument2 pagesDemonstrative Pronouns: This, That, These, ThoseBondfriendsNo ratings yet