Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diagram
Diagram
Uploaded by
ryanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diagram
Diagram
Uploaded by
ryanCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Baby Pearl Date of Admission: March 6, 2023
Age/Sex: 9 months old / F Attending Physician: Dr. Becina
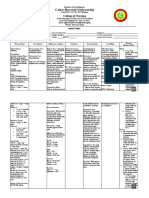
PREMATURITY
PREDISPOSING FACTORS: PRECIPITATING FACTORS:
- Maternal Diabetes -Obesity and overweight
- Maternal Asthma
-CS delivery before term
- Maternal history of
hypertension
- Male infant
Immature lung structure -Ventilation-perfusion mismatch
-Hypoxemia
Inadequate surfactant
Respiratory and Metabolic Acidosis Absent or depressed breathing
Pulmonary vasoconstriction -Fetal bradycardia
-Cyanosis
Endothelial and Epithelial cell injury Hypoxia
Diagnostic Tools:
Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
-Physical Assessment
-APGAR scoring
-Chest x-ray
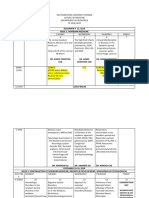
PROGNOSIS
IF NOT TREATED: IF TREATED:
Respiratory Distress Syndrome if not treated may Neonates with RDS may need extra
result to the development of a serious lung oxygen through nasal cannula or by
condition called Bronchopulmonary dysplasia ventilation.
(BPD). Administration of artificial surfactant as
a preventative measure for babies that
If left untreated can lead to medical condition such are high risk for RDS.
as cerebral palsy, lung complications, impaired Provide medication such as antibiotics
vision, sepsis, multiple organ failure, and neonatal for suspected infection.
death.
MANAGEMENT: TETRATOLOGY OF FALLOUT
Initiate oxygen therapy to maintain adequate
oxygen
Place the patient on supine position to provide
clear airway
Monitor patient’s oxygen saturation
Consider administering a surfactant
Monitor hemodynamics
Manage secretions, use suctioning if necessary
You might also like
- CASE PRESENTATION ON. Respiratory DistresssDocument13 pagesCASE PRESENTATION ON. Respiratory DistresssArchana Sahu78% (9)
- Essential Revision For DOHNS PDFDocument128 pagesEssential Revision For DOHNS PDFasiyazaidia100% (2)
- Dressing and Bandaging With ProcedureDocument4 pagesDressing and Bandaging With ProcedureRose DumayacNo ratings yet
- SOP For Administration IV InjectionDocument22 pagesSOP For Administration IV InjectionLimYiNo ratings yet
- Esmé Weijun Wang, The Collected Schizophrenias (2019)Document4 pagesEsmé Weijun Wang, The Collected Schizophrenias (2019)gghyo88No ratings yet
- Children: Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension in The NewbornDocument14 pagesChildren: Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension in The Newbornanon_93717866No ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- case studyDocument10 pagescase studygourimsc1No ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYmarwasindatocmamongcalNo ratings yet
- The Preterm InfantDocument26 pagesThe Preterm Infantnursereview100% (7)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing FactorsDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing FactorsRosemary Joy SiarotNo ratings yet
- Summary - Hyaline Membrane DiseaseDocument1 pageSummary - Hyaline Membrane DiseaseJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- The Preterm InfantDocument26 pagesThe Preterm Infantmardsz100% (10)
- Pitfalls, Problems, and Progress in Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaDocument14 pagesPitfalls, Problems, and Progress in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasiatrixie2k7No ratings yet
- Treatment Options For Apnoea of Prematurity. 2016Document6 pagesTreatment Options For Apnoea of Prematurity. 2016memoaranedaNo ratings yet
- E20153757 FullDocument9 pagesE20153757 FullClara Sima PongtuluranNo ratings yet
- Apnea de La Prematuridad-439Document7 pagesApnea de La Prematuridad-439Patricia AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Fetal DIstress - A Review Based On Modern Concept and Ancient Ayurvedic GranthasDocument3 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Fetal DIstress - A Review Based On Modern Concept and Ancient Ayurvedic GranthasaginaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Newborn Medicine Clinical Practice GuidelinesDocument15 pagesPediatric Newborn Medicine Clinical Practice GuidelinesJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- The Need For Testing-The Exercise Challenge Test To Disentangle Causes of Childhood Exertional DyspneaDocument7 pagesThe Need For Testing-The Exercise Challenge Test To Disentangle Causes of Childhood Exertional DyspneaClaudia Evelyn Calcina MuchicaNo ratings yet
- 1 PEDIAII 2 - Neonatology 2Document20 pages1 PEDIAII 2 - Neonatology 2Andrassy Twinkle AlineaNo ratings yet
- Apnea of PrematurityDocument7 pagesApnea of PrematurityCrisu AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Newborn: ObjectivesDocument17 pagesDiseases of The Newborn: ObjectivesIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (AutoRecovered)Document4 pagesRespiratory System (AutoRecovered)Evans KorirNo ratings yet
- M Soir M ProtectorDocument67 pagesM Soir M ProtectorADNo ratings yet
- RDSDocument18 pagesRDSElvis JinjikaNo ratings yet
- WRIGHT 2016 - Continuous Positive Airway Pressure To Prevent Neonatal Lung InjuryDocument10 pagesWRIGHT 2016 - Continuous Positive Airway Pressure To Prevent Neonatal Lung InjuryRafael JustinoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Pedia (Sanaani)Document4 pagesWorksheet Pedia (Sanaani)Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Adjunctive Therapies in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia, NeoReview 2017Document9 pagesAdjunctive Therapies in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia, NeoReview 2017Edrei Lopez CNo ratings yet
- Gibbs2020 2Document14 pagesGibbs2020 2Dan ZhouNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument10 pagesFetal DistressLady Jane CaguladaNo ratings yet
- Lung Parenchymal DiseaseDocument21 pagesLung Parenchymal DiseaseCamille KayeNo ratings yet
- Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: By: Hazel R. BelmonteDocument31 pagesBronchopulmonary Dysplasia: By: Hazel R. BelmonteShaira Mae RamosNo ratings yet
- Apnea Del Prematuro, Practicas Actuales y Tendencias FuturasDocument14 pagesApnea Del Prematuro, Practicas Actuales y Tendencias FuturasHUMBERTO MARTiNEZ GARCiANo ratings yet
- Newborn Respiratory DisorderDocument13 pagesNewborn Respiratory DisorderDini Fajriah Omari100% (1)
- Study of Different Treatment Modalities and Outcome in Preterm Babies With Respiratory Distress Syndrome 2017Document4 pagesStudy of Different Treatment Modalities and Outcome in Preterm Babies With Respiratory Distress Syndrome 2017Vita DesriantiNo ratings yet
- Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension: Novel Mechanisms and Approaches For Disease Prevention and TreatmentDocument6 pagesBronchopulmonary Dysplasia-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension: Novel Mechanisms and Approaches For Disease Prevention and Treatmentyesi adistiNo ratings yet
- Sleep Disordered Breathing in Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaDocument9 pagesSleep Disordered Breathing in Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaJHONATAN MATA ARANDANo ratings yet
- Enfermedad Neuromuscular y Sintomas Respiratorios PCNA 2009Document13 pagesEnfermedad Neuromuscular y Sintomas Respiratorios PCNA 2009Christian Andrés CasasNo ratings yet
- Reproductive PaedDocument150 pagesReproductive PaedThimira WaidyasekaraNo ratings yet
- Apnea of Prematurity. 2016. AAPDocument7 pagesApnea of Prematurity. 2016. AAPmemoaranedaNo ratings yet
- SDR Segun EdadDocument9 pagesSDR Segun EdadLuzbenia ChaparroNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Iniego Carlo Jay)Document9 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome (Iniego Carlo Jay)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- 9 Delacruz PerfDocument4 pages9 Delacruz PerfJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeeDocument42 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeeRoman MamunNo ratings yet
- 1 Persiapan Penanganan Bayi Baru LahirDocument54 pages1 Persiapan Penanganan Bayi Baru LahirRosa NinmusuNo ratings yet
- Retrospective Analysis of Inpatient Polysomnogram Characteristics in Infants With Broncopulmonary DisplasiaDocument30 pagesRetrospective Analysis of Inpatient Polysomnogram Characteristics in Infants With Broncopulmonary DisplasiaJHONATAN MATA ARANDANo ratings yet
- Ajol File Journals - 356 - Articles - 150133 - Submission - Proof - 150133 4249 394744 1 10 20170118Document5 pagesAjol File Journals - 356 - Articles - 150133 - Submission - Proof - 150133 4249 394744 1 10 20170118Mich KingsNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration SyndromeDocument10 pagesMeconium Aspiration SyndromeSampat KumawatNo ratings yet
- BRONCHIOLITISDocument19 pagesBRONCHIOLITISKamilla AbdullahNo ratings yet
- SWU 2018-19pdfDocument10 pagesSWU 2018-19pdfI.k sidneyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress of The New BornDocument15 pagesRespiratory Distress of The New BornJicko Street HooligansNo ratings yet
- 2 Persiapan Penanganan Bayi Baru LahirDocument51 pages2 Persiapan Penanganan Bayi Baru LahirFITRINo ratings yet
- SturbDocument13 pagesSturbAtzi FNo ratings yet
- Daftary 2019 Polysomnography Reference Values in PDFDocument7 pagesDaftary 2019 Polysomnography Reference Values in PDFGustavo MartinezNo ratings yet
- Prematures With Respiratory Distress Syndrome Do Not Have Increased The Chance of Patent Ductus Arteriosus Requiring Indomethacin Therapy ThereafterDocument58 pagesPrematures With Respiratory Distress Syndrome Do Not Have Increased The Chance of Patent Ductus Arteriosus Requiring Indomethacin Therapy ThereafterAndy SungNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Haemorrhage: Section: 2 Respiratory Problems and ManagementDocument2 pagesPulmonary Haemorrhage: Section: 2 Respiratory Problems and ManagementЛена ДуминикNo ratings yet
- Present Newborn AnatomyDocument42 pagesPresent Newborn AnatomyBilly Untu0% (1)
- Medication: Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument3 pagesMedication: Respiratory Distress Syndromenoeh_olofernesNo ratings yet
- Adrenarca Prematura, Una Condición Común Con Presentación Variable, Horm Res Paediatr. 2015 83 (4) 221-31Document11 pagesAdrenarca Prematura, Una Condición Común Con Presentación Variable, Horm Res Paediatr. 2015 83 (4) 221-31RUBY JOJOANo ratings yet
- North Carolina Children’s Global Health Handbook: A Pediatrician’s Guide to Integrating IMCI Guidelines in Sub-Saharan AfricaFrom EverandNorth Carolina Children’s Global Health Handbook: A Pediatrician’s Guide to Integrating IMCI Guidelines in Sub-Saharan AfricaErica C. BjornstadNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hyperinsulinism: A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and ManagementFrom EverandCongenital Hyperinsulinism: A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and ManagementDiva D. De León-CrutchlowNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia and the FetusFrom EverandAnesthesia and the FetusYehuda GinosarNo ratings yet
- Cop-5-Policy On Uniform Use of CPRDocument23 pagesCop-5-Policy On Uniform Use of CPRanithaNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument2 pagesParacetamolsleep whatNo ratings yet
- Furuncle and Carbuncle FootDocument0 pagesFuruncle and Carbuncle Footrasputin22100% (1)
- Stephen Munjanja ZMPMS Short Report FVDocument42 pagesStephen Munjanja ZMPMS Short Report FVClamore Solar - ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Daftar Singkatan RSUP PDocument32 pagesDaftar Singkatan RSUP Pmaria ulfaNo ratings yet
- Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2018 Lindblad Wollmann Risk of Repeat Cesarean Delivery in Women Undergoing Trial of LaborDocument6 pagesActa Obstet Gynecol Scand 2018 Lindblad Wollmann Risk of Repeat Cesarean Delivery in Women Undergoing Trial of LaborMillennials ShopifyNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Needle Stick Injuries and Their Underreporting Among Healthcare Workers in The Department of Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument16 pagesPrevalence of Needle Stick Injuries and Their Underreporting Among Healthcare Workers in The Department of Obstetrics and GynaecologymochkurniawanNo ratings yet
- SpinalinjuryDocument29 pagesSpinalinjurymustikaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy in NewbornsDocument10 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Therapy in NewbornsJaner BanosNo ratings yet
- Point MarmaDocument2 pagesPoint MarmaAnonymous yzbnd8No ratings yet
- Baclofen 2007Document3 pagesBaclofen 2007panda louis100% (1)
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsDocument59 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Course QuestionsVan halenNo ratings yet
- OBS HC PROTOCOL 2021 - FinalDocument152 pagesOBS HC PROTOCOL 2021 - FinalWorkineh GizawNo ratings yet
- Tissues Surrounding Teeth: PeriodontiumDocument33 pagesTissues Surrounding Teeth: PeriodontiumSweet SumanNo ratings yet
- Host Defense Against Viral Infection-AnimalsDocument25 pagesHost Defense Against Viral Infection-AnimalsAshleyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsDocument23 pagesThyroid and Parathyroid Glandsmoimoi819No ratings yet
- Body System ChecklistDocument4 pagesBody System Checklistapi-421863843No ratings yet
- Chemotherapy PolicyDocument4 pagesChemotherapy PolicyNicholas HammondNo ratings yet
- LDS PeriodontalDocument38 pagesLDS PeriodontalSorin BotezzNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument10 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesJenna Abuan100% (1)
- The Tongue - Facts, Function & Diseases - Live SciencerDocument12 pagesThe Tongue - Facts, Function & Diseases - Live SciencerImtiax LaghariNo ratings yet
- Soal AAODocument33 pagesSoal AAOwidyawirapNo ratings yet
- Peds Drug Mixing PDFDocument18 pagesPeds Drug Mixing PDFeialcaheNo ratings yet
- Lippincott - Lippincott Nursing Procedures-LWW Wolters Kluwer Health (2018)Document3,609 pagesLippincott - Lippincott Nursing Procedures-LWW Wolters Kluwer Health (2018)Youssef MokdadNo ratings yet
- D11.44 - Kel10 - Gagal Ginjal KronisDocument16 pagesD11.44 - Kel10 - Gagal Ginjal KronisNAZILLA PUTRINo ratings yet
- Opciones Reconstructivas en Tibia JAAOS 2021Document9 pagesOpciones Reconstructivas en Tibia JAAOS 2021Sebastian CardonaNo ratings yet