Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti-Epileptic Drugs
Anti-Epileptic Drugs
Uploaded by
KaoriMarieSembranoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anti-Epileptic Drugs
Anti-Epileptic Drugs
Uploaded by
KaoriMarieSembranoCopyright:
Available Formats
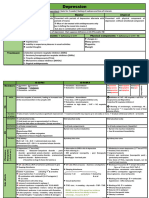
Anti-epileptic drugs
- used as prophylactics
-most are analysed by Immunoassay or Chromatographic methods
- Measurement of the free or bound drug in a serum or plasma sample
-Total Drug concentration is usually measured for those with normal physiological state
- Free Drug Measurement may only be necessary when there is cause for alteration in patient plasma protein
*Pregnancy
*Liver or Kidney Dss
*Malnutrition
*Drug-drug interaction
-TDM indicated in initially establishing individual baseline concentrations at which the patient is responding well
-consistent sampling time
-preferred specimen: Trough serum concentration collected at the end of the dosing interval
Prevelant Neurological disorders: Epilepsy, convulsions, and seizures
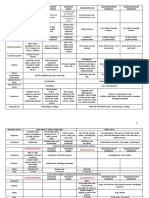
FIRST GENERATION ANTI-EPILEPTIC DRUGS (AED)
Phenobarbital Phenytoin Valproic acid Carbamazepine Ethosuximide Felbamate
Importance slow acting barbiturate “ Dilantin” monotherapy to treat “Tegretol” “Zarotin” Indicated in severe
petit mal and absence epilepsies such as
Effective in treating Commonly used for seizures Effective treatment for Controlling petit mal Lennox-Gastaut
seizures seizures and as short seizures seizures Syndrome and
term prophylactic refractory epilepsy
agent Highly toxic, less used
Route of Oral adm.,., slow but Oral adm.,., Oral adm.,., rapid and Oral adm., Oral adm., Oral adm.,,
administration complete absorption incomplete absorption complete absorption complete
absorption
therapeutic 1-2 ug/ml (free) 50-120 ug/ml 4-12 ug/ml 40-100 ug/ml 30-60 ug/ml
range
10-20 g/ml (total)
major toxicities depression, fatigue, initiation of seizures hepatic dysfxn (in leukopenia, febrile rxn, aplastic anemia
reduced mental therapeutic conc.) rashes and hepatic failure
capacity Vitamin D def.,
hirsutism, hyperplasia Pancreatitis, Mild transient liver
hyperammonemia (high dysfxn
serum level)
hematologic dyscrasia
Nausea, lethargy, weight and aplastic anemia
gain (common ) ( conc . >15)
half life 70-100 hrs 14-22 hrs
(In renal failure =
27-34 hr)
peak/trough peak serum is reached dose dependent
serum in 10hrs
concentration
% serum 50% 87-97% 93% 70-80% 30%
protein binding
Tests Total potential amount Peak levels are Determination of free
of phenobarbital; evaluated after the fraction
trough levels are conversion of
usually evaluated Fosphenytoin
route of hepatic mixed hepatic metabolism hepatic metabolism hepatic metabolism renal and hepatic
elimination function oxidase (zero order kinetics) metabolism
system
OTHERS primidone- inactive fosphenytoin- inactive inhibited by Felbamate enhanced by:
form form (75 minutes to primidone,
Induction period- 10- convert into active phenytoin,
15 days form) carbamazepine
Kaori Sembrano ‘17||1
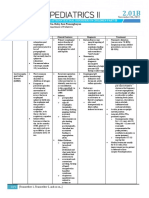
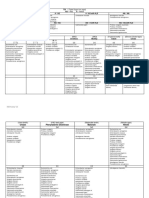
Gabapentin Lamotrigine Levetiracetam Oxcarbazepine Tiagabine Zonisamide Topiramate
Importance monotherapy for indicated with indicated in partial A Prodrug treating partial therapy for partial for partial and
complex partial partial and and generalized seizures and generalized generalized
seizures with/or generalized seizures Metabolized, active seizures seizures
generalized seizures form =
seizures Licarbazepine Accumulates in the
erythrocytes
most likely Monotherapy of
treatment partial seizures and
consideration in 2* tonic-clonic
patients with seizures
Liver dss and
partial-onset
seuizures with
acute
intermittent
porphyria
route of Oral adm., Oral adm.,., rapid Oral adm.,., entirely Oral adm.,., Oral adm.,., Oral adm.,., Oral adm.,.,
administratio and complete bioavailable rapid and
n absorption complete
absorption
therapeutic 12-20 ug/ml 2.5-15 ug/ml 8-26 ug/ml licabazepine= 12-35 20-100 ug/ml 10-38 ug/ml
range ug/ml
major Kidney CNS: CNS, parasthesia
toxicities impairment paraesthesia,
mild sedation,
confusion
half life 5-9 hrs (linear 15-30 hrs 6-8 hrs 8-10 hrs 4-13 hrs 50-70 hrs 20-30 hrs
increase) (30% decrease in the (prolonged in (in monotherapy)
(With valproic elderly) Hepatic
(Children needs acid= 60 hrs) dysfunction) (Reduced to 25-35
30% more dose hrs if added with
to attain the half- other AEDs)
life)
peak/trough -low level trough peak conc.: 8 hrs peak conc.: peak conc. at 4-7 peak conc at 1-4
serum conc. concentrations 0.5-2 hrs hrs hrs
lead to
breakthrough
seizures
% serum Does not bind 55% Does not bind with 40% 96% 60% 15%
protein with serum serum CHON
binding CHON
route of renal clearance hepatic metabolism glomerular filtration Hepatic metabolism.: hepatic mixed hepatic met: renal filtration
elimination (unchanged (dependent on Age, rate/ renal clearance Keto reduction and function Glucuronide (remainder is
drug) Physiologic Glucuronide oxidase Conjugation, eliminated in
Condition, conjugation system/pathwa Acetylation, hepatic
Pregnancy At 32 y (MFO) Oxidation and metabolism)
Weeks And Renal excretion
Recognized
Enzyme-Inducing
AEDs)
OTHERS bioavailability of enzyme-inducing Rate of clearance licarbazepine is ratio of free to Absorbed by GIT/ use of Dose
60% (reduced if AEDs: correlates well with sensitive to Phenytoin bound drug is bioavailable 65% titration to
administered phenobarbital, glomerular filtration and. Phenobarbital affected by: or higher balance
with Antacids) phenytoin, Rate= use in valproic acid, therapeutic effect
carbamazepine monitoring patients TDM is indicated: naproxen, TDM is indicated
multiple daily with -steady state is salicylates and to establish a TDM is indicated
doses- preferred Inhibited by: renal impairment established pregnancy baseline level, to if:
regimen: Valproic acid -therapeutic failure detect drug-drug -steady state is
- Excessively Lacks -drug – drug Dose Titration interactions and established
high blood TDM is needed Pharmacokinetic interactions is used in therapeutic failure -there is
concentrations because of the variability, hence -pregnancy balancing therapeutic
lead to toxic drug-drug cannot est. TDM therapeutic failure
effects interactions effects with -drug – drug
adverse CNS interactions
side-effects
Kaori Sembrano ‘17||2
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Injection Pump, Setting On EngineDocument2 pagesInjection Pump, Setting On EngineSherzad Chem86% (7)
- CKE6150 Spare Parts ManualDocument74 pagesCKE6150 Spare Parts ManualVanessa RiveraNo ratings yet
- FlecainideDocument3 pagesFlecainideAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticDocument3 pagesAnti EpilepticVeran, Arzel S.No ratings yet
- Fluphenazine Drug Study - DoxDocument3 pagesFluphenazine Drug Study - Doxan naNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- "Antiepileptic Drugs": Clinical Chemistry 3Document2 pages"Antiepileptic Drugs": Clinical Chemistry 3Maam ShaNo ratings yet
- Antiseizure DrugsDocument10 pagesAntiseizure DrugsJoyce SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Classification of InfectiousDocument3 pagesClassification of InfectiousabubakarNo ratings yet
- Ings Pre MedsDocument1 pageIngs Pre MedsIngrid LarobisNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs (Aed) : R. Anita. IndriyantiDocument36 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs (Aed) : R. Anita. Indriyantiandisti2323No ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument43 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsdrpraneethpremkumarNo ratings yet
- DRUGS2Document1 pageDRUGS2KaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name (Generic & Brand) : Ondansetron HCLDocument6 pagesDrug Name (Generic & Brand) : Ondansetron HCLnetanya DoanNo ratings yet
- Age Drug StudyDocument13 pagesAge Drug StudyLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- DilantinDocument2 pagesDilantinMarinel AgultoNo ratings yet
- Metaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyDocument8 pagesMetaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyFrauline GagaracruzNo ratings yet
- Min Lect PK - 1Document3 pagesMin Lect PK - 1fandi_cah_ganteng3367No ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- TOP DRUGS - Doc Version 1Document12 pagesTOP DRUGS - Doc Version 1Charme Jean RaygonNo ratings yet
- Noradrenergic Drugs/alpha BlockersDocument27 pagesNoradrenergic Drugs/alpha BlockersDana PrabagaranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument2 pagesDrug Study ICUErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Omeprazol - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOmeprazol - Drug StudyMae Visperas100% (1)
- AntidepressantsDocument4 pagesAntidepressantsAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Top DrugsDocument12 pagesTop DrugsStephanie Villanueva AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- AntiepilepticiDocument29 pagesAntiepilepticiIskraNo ratings yet
- RanitidineDocument2 pagesRanitidineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Children Part I Continuation TABLEDocument5 pagesChildren Part I Continuation TABLEMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Vii. Drug Study: Parkinsonis M. Pheochrom Ocytoma (Risk of Hypertensiv e Crisis)Document5 pagesVii. Drug Study: Parkinsonis M. Pheochrom Ocytoma (Risk of Hypertensiv e Crisis)Darwin AndalNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Drug MonitoringJanielle Medina FajardoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyDean Angelo BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Barbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABADocument10 pagesBarbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABAAvi WerdesheimNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICSDocument25 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICSCheetahboi Shopee100% (4)
- Year 2 Drug ListDocument8 pagesYear 2 Drug ListRay100% (1)
- For MaDocument9 pagesFor MaKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid Drug StudyDocument4 pagesValproic Acid Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- Antiseizure DrugsDocument8 pagesAntiseizure DrugsCamile ParreñoNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Anticonvulsants WebDocument23 pagesAnticonvulsants WebVictor YaremkoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 3Document5 pagesDrug Study 3jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOmeprazole Drug StudyjoanneNo ratings yet
- AnP - PsychopharmacologyDocument37 pagesAnP - PsychopharmacologyNicole JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- 10-Antimalarial DrugsDocument15 pages10-Antimalarial DrugsSaman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyApril Sarol67% (3)
- Pharm Drugs ChartsDocument21 pagesPharm Drugs ChartsTris100% (1)
- Name of DrugDocument6 pagesName of DrugKathleen ColinioNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsDocument19 pagesEpilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument3 pagesDiazepamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyDocument3 pagesDrugs Used in Neuro PharmacologyNabeel Kouka, MD, DO, MBA, MPH100% (1)
- Drug Study Omeprazole CompressDocument2 pagesDrug Study Omeprazole CompressAngelica TolledoNo ratings yet
- DiphenhydramineDocument3 pagesDiphenhydramineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Metocloprramide HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesMetocloprramide HydrochlorideBeatrizz P GellaNo ratings yet
- AntiepilepticsDocument25 pagesAntiepilepticsMurali Krishna Kumar MuthyalaNo ratings yet
- Obat Antijamur Dan Antihistamin: Dr. Elly Usman, M.Si, AptDocument17 pagesObat Antijamur Dan Antihistamin: Dr. Elly Usman, M.Si, AptChindyNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration WorksheetDocument42 pagesMedication Administration WorksheetPandesal with EggNo ratings yet
- Eti Nurwening Sholikhah: Department of Pharmacology & Therapy Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaDocument43 pagesEti Nurwening Sholikhah: Department of Pharmacology & Therapy Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaadystiNo ratings yet
- PR STEPLADDER CTS AmmaliaDocument27 pagesPR STEPLADDER CTS AmmaliaAmmalia RachmiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For HepatitisDocument4 pagesDrug Study For Hepatitisunyokies100% (1)
- Drug Study OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug Study Omeprazoleelmer.platiljrNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- DRUGS2Document1 pageDRUGS2KaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Para - Amoeba TabulatedDocument1 pagePara - Amoeba TabulatedKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Para - AmoebaDocument2 pagesPara - AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Intro ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntro ParasitologyKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Tabulated Review On AmoebaDocument1 pageTabulated Review On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- TrophozoitesDocument4 pagesTrophozoitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology On AmoebaDocument2 pagesParasitology On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Table Review of ParasitesDocument6 pagesTable Review of ParasitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests in MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesBiochemical Tests in MicrobiologyKaoriMarieSembrano100% (1)
- Micro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeDocument5 pagesMicro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Psychoactive and AntibioticsDocument2 pagesPsychoactive and AntibioticsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- AAM EnglishDocument7 pagesAAM EnglishYannick ÜzümNo ratings yet
- SkyEdge II Pro Brochure 2011-10-03Document2 pagesSkyEdge II Pro Brochure 2011-10-03FreddySaltosNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Manual Part IIDocument21 pagesHeat Treatment Manual Part IIAnonymous lmCR3SkPrK100% (3)
- Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Polymers With A Vinyl Acetate Content of 10-15 MoleDocument1 pageEthylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Polymers With A Vinyl Acetate Content of 10-15 MoleGłfghh GhklNo ratings yet
- History of WirelessDocument7 pagesHistory of WirelessHarshaNo ratings yet
- PESNARKADocument37 pagesPESNARKAAnia SvetozarovNo ratings yet
- Catalog: Kawai Music IndonesiaDocument20 pagesCatalog: Kawai Music IndonesiaKhairul UmamNo ratings yet
- Video Processing SyllabusDocument4 pagesVideo Processing SyllabusChandan PurohitNo ratings yet
- Innovation ReadingsDocument9 pagesInnovation Readingsafca32No ratings yet
- Patent Agent Exam Preparation Training CourseDocument3 pagesPatent Agent Exam Preparation Training CourseGlobal Institute of Intellectual PropertyNo ratings yet
- CNS - Module 2.1-AESDocument17 pagesCNS - Module 2.1-AESNIKSHITH SHETTYNo ratings yet
- Institute of Cost and Management Accountants of Pakistan Spring (August) 2012 ExaminationsDocument2 pagesInstitute of Cost and Management Accountants of Pakistan Spring (August) 2012 ExaminationsAmmar KashanNo ratings yet
- VM651, Pi-2555Document8 pagesVM651, Pi-2555Carlos Rubén Oliveras RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Montes Etal 2019 Palispastic Recon Northern Andes Southern Caribbean PDFDocument25 pagesMontes Etal 2019 Palispastic Recon Northern Andes Southern Caribbean PDFAlvaro Ishaam Rafael Bermejo FontalvoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Design Simulation and OptimizationDocument354 pagesChemical Process Design Simulation and OptimizationJose Heli Vallejos CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Essay On Ratan Tata ...Document3 pagesEssay On Ratan Tata ...GAURAV JAINNo ratings yet
- Food Composition TableDocument3 pagesFood Composition Tablehafeesadetunji01No ratings yet
- D1780 - EN - 02 (Signets) GL314F3 - AlstomDocument224 pagesD1780 - EN - 02 (Signets) GL314F3 - Alstomtuantz206No ratings yet
- Yearly PlanDocument36 pagesYearly Planapi-542955727No ratings yet
- QRC Nfpa 7 08Document2 pagesQRC Nfpa 7 08TUZERONo ratings yet
- Yom Ha'atzmaut Missing Letters: Fill in The Missing Letters To Complete The WordsDocument34 pagesYom Ha'atzmaut Missing Letters: Fill in The Missing Letters To Complete The WordsRachel MalagaNo ratings yet
- BUS Chap 1 PDF 1Document17 pagesBUS Chap 1 PDF 1Tamanna Sharmin ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - AnswerDocument16 pagesChapter 16 - AnswerAgentSkySkyNo ratings yet
- 5G TransportDocument42 pages5G TransportDaniel Cafu100% (1)
- CHOLELITHIASISDocument12 pagesCHOLELITHIASISShenbagam MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 7 Human Nutrition - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument153 pagesFlashcards - Topic 7 Human Nutrition - CAIE Biology IGCSESamiullah TahirNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Engineering Transformers and Induction Machines Starting and Speed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor NotesDocument26 pagesElectrical Engineering Engineering Transformers and Induction Machines Starting and Speed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor NotesPraiseNo ratings yet
- System Manuals: EBTS and Integrated Site ControllerDocument3 pagesSystem Manuals: EBTS and Integrated Site ControllerIsac LimaNo ratings yet