Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsParasitology On Amoeba
Parasitology On Amoeba
Uploaded by
KaoriMarieSembranoThis document describes the life cycles and characteristics of various amoeba species including Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli. E. histolytica has a 5 stage life cycle within the human host involving the ingestion of cysts, excystation in the small intestine, colonization and feeding in the cecum, and eventual encystation and shedding of cysts in feces. Diagnosis involves examining wet mounts of stool samples for motile trophozoites or cysts. E. histolytica can also cause hepatic amoebiasis through the presence of intestinal infection, clinical manifestations, and examination of abscess aspirates. The document provides details on the morphology, pathogenic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- English8Q2F (PIVOT)Document40 pagesEnglish8Q2F (PIVOT)Iris Rivera-Perez89% (9)
- Intestinal Amoebiasis - CSDocument33 pagesIntestinal Amoebiasis - CSMASII100% (1)
- Para - AmoebaDocument2 pagesPara - AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Protista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Document6 pagesProtista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyWeng WengNo ratings yet
- Histology Lab Practicals - AY 2021-2022Document15 pagesHistology Lab Practicals - AY 2021-2022H TNo ratings yet
- EPITHELIUMDocument2 pagesEPITHELIUMALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- Ameba and E.histolyticaDocument18 pagesAmeba and E.histolyticapenonia.abegailashleyNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)Document4 pages1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)arvinkennethdelacruzNo ratings yet
- Amoeba: Ms. Helga SyDocument7 pagesAmoeba: Ms. Helga Syanti romantic txtNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Exam ReviewerDocument11 pages2nd Exam Reviewerdmt01081991No ratings yet
- Zoology - Animal Tissues - Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesZoology - Animal Tissues - Lecture NotesKARYLLE JUNE PONTERASNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFDocument4 pagesParasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- 2 Approaches: 1. Clinical Diagnosis 2. Laboratory Diagnosis 2 Phases: 1. MacroscopicDocument4 pages2 Approaches: 1. Clinical Diagnosis 2. Laboratory Diagnosis 2 Phases: 1. Macroscopiccayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument2 pagesAnimal TissuesMami AmihanNo ratings yet
- Epithelial-Cells 2Document5 pagesEpithelial-Cells 2Edeilaine JadraqueNo ratings yet
- Histo - Fresh Tissue Examination and Intro To Histological TechniquesDocument4 pagesHisto - Fresh Tissue Examination and Intro To Histological TechniquesBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaNo ratings yet
- Dientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesDocument4 pagesDientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- Two Main Excretory Ducts CA Cells and Intercalated Duct CellsDocument3 pagesTwo Main Excretory Ducts CA Cells and Intercalated Duct CellsNoel JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Jaw and Soft Tissues: A-Odontogenic Keratocyst. B - Dentigerous CystDocument15 pagesCysts of The Jaw and Soft Tissues: A-Odontogenic Keratocyst. B - Dentigerous CystruchikaNo ratings yet
- PROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyDocument7 pagesPROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyReyven Niña DyNo ratings yet
- Module # Epitheleal TransDocument5 pagesModule # Epitheleal TransLara VanessNo ratings yet
- Free Living AmoebaDocument5 pagesFree Living AmoebaEiveren Mae SutillezaNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane Types of Cell Division - Mitosis - MeiosisDocument4 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane Types of Cell Division - Mitosis - MeiosisAlex SerdeñaNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument8 pagesParasitologyNonki VargasNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman CacingDocument111 pagesRangkuman CacingNyomantrianaNo ratings yet
- Parasites by Apple TanDocument16 pagesParasites by Apple TanOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- AMOEBADocument11 pagesAMOEBAMicaella RemilloNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson 1Document4 pagesBiology Lesson 1Charles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument4 pages4 TissuesCarea CruzNo ratings yet
- Tabular Parasitology MICROPARADocument19 pagesTabular Parasitology MICROPARAJerlyn FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708Document3 pagesTumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708CitrusNo ratings yet
- Fit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesDocument3 pagesFit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesCaithlyn KirthleyNo ratings yet
- OkieDocument3 pagesOkieFebeval CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesLesson 7 Cell MembraneThea MillanesNo ratings yet
- Porifera 1 STETH3.ODocument25 pagesPorifera 1 STETH3.OAshwinee KadelNo ratings yet
- Amoeba PrefinalsDocument5 pagesAmoeba PrefinalsKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Ex 6 - HistologyDocument9 pagesEx 6 - HistologyCarl Johnave Manigbas MonzonNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document9 pagesTopic 2Ria AccadNo ratings yet
- T I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueDocument6 pagesT I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueMarla TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Micro ParasitesDocument4 pagesMicro ParasitesKrisha Marie BadilloNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesDocument7 pages4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesJudith Dianne Ignacio100% (1)
- Amoeba Part 2 NotesDocument8 pagesAmoeba Part 2 Notesjefftuazon01No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 - Drosophila: Cleavage and BlastulaDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 11 - Drosophila: Cleavage and BlastulaAngela BalmesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 ReviewerUriel Andrei MaribbayNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2bDocument2 pagesMODULE 2bFeliza Mae BoquecosaNo ratings yet
- Biology MidSem SPOTDocument10 pagesBiology MidSem SPOTNaqiuddin MukhdirNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology First Grading NotesDocument24 pagesOral Histology First Grading NotesAli,morwan HydarNo ratings yet
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023Document5 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023VERONICA ROSE MAGPOCNo ratings yet
- Traditional Serrated Adenoma - Libre PathologyDocument3 pagesTraditional Serrated Adenoma - Libre PathologyfadoNo ratings yet
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 pagesBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangNo ratings yet
- Patho Ospe 1Document16 pagesPatho Ospe 1PomNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba Histolytica: Intestinal Amebae Ameba Nucleus Troph Cyst Pathogenicity OtherDocument7 pagesEntamoeba Histolytica: Intestinal Amebae Ameba Nucleus Troph Cyst Pathogenicity OtherDarla YsavelNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesChad Laurence Vinson CandelonNo ratings yet
- Porifera, Cnidaria and Ctenophora 1Document6 pagesPorifera, Cnidaria and Ctenophora 1null dillNo ratings yet
- (PARA) 1.5 - Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDocument6 pages(PARA) 1.5 - Blood and Tissue FlagellatesGuia De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Readings On ProtozoansDocument18 pagesSupplemental Readings On Protozoansferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- Free-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesFree-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsIrvin SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Cestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanDocument4 pagesCestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanMicael Andrei MendozaNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument2 pagesTrematodesIan Josef R. VibarNo ratings yet
- DRUGS2Document1 pageDRUGS2KaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Para - AmoebaDocument2 pagesPara - AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Para - Amoeba TabulatedDocument1 pagePara - Amoeba TabulatedKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests in MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesBiochemical Tests in MicrobiologyKaoriMarieSembrano100% (1)
- Tabulated Review On AmoebaDocument1 pageTabulated Review On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Intro ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntro ParasitologyKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Table Review of ParasitesDocument6 pagesTable Review of ParasitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- TrophozoitesDocument4 pagesTrophozoitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti-Epileptic DrugsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Micro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeDocument5 pagesMicro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Psychoactive and AntibioticsDocument2 pagesPsychoactive and AntibioticsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Anti Protozoal AgentsDocument37 pagesAnti Protozoal AgentsGunjan YadavNo ratings yet
- Amoebic Liver Abscess: Clinical MedicineDocument5 pagesAmoebic Liver Abscess: Clinical MedicineAizat KamalNo ratings yet
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument15 pagesAscaris LumbricoidesJyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Parasitology:: Classification of ParasitesDocument17 pagesParasitology:: Classification of ParasitesIrfan Pathan KakarNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle and Infection Mode From Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument30 pagesLife Cycle and Infection Mode From Entamoeba HistolyticaSynthesis is What MattersNo ratings yet
- FECALYSISDocument4 pagesFECALYSISMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Lifecycle of EntamoebaDocument86 pagesLifecycle of EntamoebaAman ShaikNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Parasitism: ProtozoansDocument10 pagesIntestinal Parasitism: ProtozoansdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- AmoebiasisDocument33 pagesAmoebiasisMike Serge Razafi0% (1)
- Gatot Sugiharto, MD, Internist Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine, Wijaya Kusuma University SurabayaDocument78 pagesGatot Sugiharto, MD, Internist Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine, Wijaya Kusuma University SurabayaRandy HuangNo ratings yet
- Apolon paraDocument4 pagesApolon paraHanin ArakamaNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- AmebiasisDocument32 pagesAmebiasisRizty Mayang FachleviNo ratings yet
- TOPNOTCH Parasitology-Supertable-by-Yns-Pereyra-Cocoy-Calderon-Troy-Soberano-UPDATED-NOVEMBER-2017Document25 pagesTOPNOTCH Parasitology-Supertable-by-Yns-Pereyra-Cocoy-Calderon-Troy-Soberano-UPDATED-NOVEMBER-2017Waiwit KritayakiranaNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesAmoebiasis PathophysiologyApril CornejoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical Parasitology - ProtozoologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Medical Parasitology - ProtozoologyHellNo ratings yet
- GIDocument196 pagesGIswagmasterNo ratings yet
- Crew Health PrecautionsDocument59 pagesCrew Health PrecautionsshireenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Fecal Oral Transmitted DiseasesDocument60 pagesUnit 2 - Fecal Oral Transmitted DiseasesAbdulmajid AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Unit 1Document95 pagesCase Study For Unit 1family_jvcNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Compre Review 2021 - Dr. HemedezDocument65 pagesMicroPara Compre Review 2021 - Dr. HemedezStephenMontoyaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectDocument11 pages3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectThaiz P.SNo ratings yet
- Soal ParasitologiDocument14 pagesSoal ParasitologiFirman SugihartoNo ratings yet
- Etiology 1-Deficiency of Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) 2 - PathogenesisDocument139 pagesEtiology 1-Deficiency of Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) 2 - PathogenesisAlston Foods BVNo ratings yet
- The Prevalence of Parasitic Protozoan Diseases in Iraq, 2016Document5 pagesThe Prevalence of Parasitic Protozoan Diseases in Iraq, 2016Jeremia AnkesaNo ratings yet
- Ameboma: A Colon Carcinoma-Like Lesion in A Colonoscopy FindingDocument4 pagesAmeboma: A Colon Carcinoma-Like Lesion in A Colonoscopy FindingSitha WisesaNo ratings yet
- General Characteristic and Classification of ProtozoaDocument50 pagesGeneral Characteristic and Classification of ProtozoaTLM A181No ratings yet
Parasitology On Amoeba
Parasitology On Amoeba
Uploaded by
KaoriMarieSembrano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesThis document describes the life cycles and characteristics of various amoeba species including Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli. E. histolytica has a 5 stage life cycle within the human host involving the ingestion of cysts, excystation in the small intestine, colonization and feeding in the cecum, and eventual encystation and shedding of cysts in feces. Diagnosis involves examining wet mounts of stool samples for motile trophozoites or cysts. E. histolytica can also cause hepatic amoebiasis through the presence of intestinal infection, clinical manifestations, and examination of abscess aspirates. The document provides details on the morphology, pathogenic
Original Description:
REVIEW TABLE OF AMOEBA PART 2.. MLT
Original Title
Parasitology on Amoeba
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the life cycles and characteristics of various amoeba species including Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli. E. histolytica has a 5 stage life cycle within the human host involving the ingestion of cysts, excystation in the small intestine, colonization and feeding in the cecum, and eventual encystation and shedding of cysts in feces. Diagnosis involves examining wet mounts of stool samples for motile trophozoites or cysts. E. histolytica can also cause hepatic amoebiasis through the presence of intestinal infection, clinical manifestations, and examination of abscess aspirates. The document provides details on the morphology, pathogenic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesParasitology On Amoeba
Parasitology On Amoeba
Uploaded by
KaoriMarieSembranoThis document describes the life cycles and characteristics of various amoeba species including Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli. E. histolytica has a 5 stage life cycle within the human host involving the ingestion of cysts, excystation in the small intestine, colonization and feeding in the cecum, and eventual encystation and shedding of cysts in feces. Diagnosis involves examining wet mounts of stool samples for motile trophozoites or cysts. E. histolytica can also cause hepatic amoebiasis through the presence of intestinal infection, clinical manifestations, and examination of abscess aspirates. The document provides details on the morphology, pathogenic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
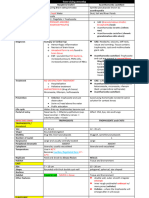
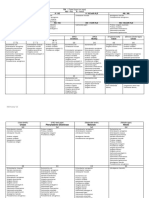
AMOEBA a. E.
coli - Wet mounts – NSS (I2 inhibits movement)
• Pseudopodial locomotion: • LC: (5 stages) - Preservative:
- Rootlike, finger-like or tongue like 1. Mature cyst Ingested – infective stage 1) MIF (Merthiolate iodine formaldehyde)
- Locomotor organelle (ameboid) 2. Stomach (gastric juices on cystic wall) 2) PVA (Polyvinyl alcohol)
- Procurement of food (pseudopodial encirclement) → Holozoic (ingest 3. Small intestine (Excystation) 3) Schaudinn’s fixative
organic matter) 4. Enclosed Metacyst (w/o wall, 8-nuclei) escapes Cyst W #2) & 3) – for permanent staining
Subkingdom: Protozoa 5. Metacyst – cytop. division - Permanent mounts – IH or Trichome stain
Phylum: Sarcomastigophora 6. Metacystic trophozoites 2. Solid or formed feces – CYST (carriers/chronic patient)
Subphylum: Sarcodina 7. Large intestine (cecum) – maturation to troph (feeding st) - Should include a portion of any fleck of mucus
Family: Endamoebidae 8. Mature troph multiply by binary fission adherent to feces or blood
• Strictly parasitic in GIT (alimentary canal) 9. Encystation start – unfavorable condition in cecum - Wet mounts – NSS or I2
• Small; binary fission 10. Undigested food extruded - If only few cysts → conc. → by ZnSO4 centrifugal
• Lack contractile vacuoles 11. Precyst – spherical flotation method → cyst on surface → troph killed
• Most undergo encystation 12. Precyst secrete tough wall → Encystation complete b. Saline-purged specimens (for TROPH)
Genus: 13. Uninucleate cyst - Provide mat for (+) diagnosis if routine fecal exam has
Achromatic 14. Nuclear division been rewarding
Karyosome Chromatin thread 15. Binucleate cyst (Young cyst) - Na2SO4 (Glauber salts) or phosphosoda preferred
(connect K-NM) 16. Quadrinucleate cyst - After purgation → discard earlier fecal evacuations →
17. Octanucleate cyst (Mature cyst) pipette sedimented el. of mucus & tissue cells from 2 nd &
Entamoeba
Numerous 18. Passed out w/ feces 3rd bowel movement onto slide → coverslip → examine
Small, center of N Present b. E. histolytica c. Sigmoidoscopy material
granules line NM
• LC: (5 stages) - Scrapings from suspected sites of amoebic ulceration by
1. Mature cyst ingested gentle pressure from long handled curette or loop
Endolimax
2. Stomach - 1/3 of scrapings are from sigmoidorectal area
Thin layer, periph,
Large, blot-like Present 3. Excystation – duodenum - Look for typical lesions
inconspicuous
4. Enclosed metacyst (4 nuclei) escapes its cystic wall - NSS suspension immediately – for motile TROPH
5. Metacyst – cytoplasmic division → 4 metacystic troph - Punch biopsy – fix, section & stain 1st before examining
Iodamoeba Large (1/2 Nuc. 1 layer of
Radiating (Amoebulae) d. Culture – last resort
Diameter) Periendosomal
Rich in chroma granules, no
achromatic 6. Cecum (colonize & feed) → maturation to troph - Study metabolism, pathogenicity & production of
(endosome) periph. chroma
fibrils 7. Mature troph – binary fission antigens for serodiagnosis
8. Start of encystation – unfavorable envi - Inoculum – troph / cyst from feces or mat from c
• Parasitic amoeba (accdg to pathogenicity & habitat):
9. Undigested food extruded out - Medium: dibasic medium of Boeck & Drbohlav (egg slant
A. Nonpathogenic
10. Troph rounds up → Precyst base w/ isotonic overlay = Locke egg serum)
a. Mouth (gingivalis → easy to transfer)
11. Precyst secretes cystic wall - Diamond’s medium TYI-S-33 → reveal E. histo if
b. Intestinal (coli, nana, buetschlii, dispar, hartmanni)
12. Uninucleate cyst (has glycogen mass & chroma. bodies) microscopic exam has failed
B. Pathogenic
13. 2 nuclear divisions → binucleate → quadrinucleate (mature) B. Hepatic Amoebiasis
a. Intestinal (histolytica)
14. Mature cyst a. Presence of Intestinal amoebiasis
• 2 main stages:
- 2 significant sizes for strains: b. Clinical manifestations, inc. WBC, liver function tests
Trophozoite Cyst
a) Large race – ave. diameter: > 10µ, generally virulent (BSP, ALP)
- Chromatoidal bars – crystallized b) Small race - < 10µ (cyst: 5-9µ; troph: 12-15µ) c. Aspiration of abscess – punch/needle biopsy
- Bacteria & food particles,
ribonucleoproteins in cytop. ➢ Commensal, non-pathogenic, “E. hartmanni” - Troph recovered in 1/3 of cases
ingestion (feeding stage)
Only protein source 15. Passed out w/ feces - Content of abscess (choco colored, “anchovy sauce”)
- RBC
- Glycogen vacuole– carb source → mix of sloughed liver tissue & blood or degenerated
- Motility (living state) • Divided into 2:
- Both are lost in mature cyst liver cells, RBC, leukocytes (sometimes)
1. Non-invasive – E. dispar
- Irregular – cytop. extension - Nonpathogenic in man d. X-ray: exhibit damage extent
- Smooth & rounded walls
Most → undergo fixation - In experimental animals: produce intestinal lesions e. Seroimmunologic test:
- Multinuclear (old); young = 1
- Uninuclear - Difficult to distinguish from E. histo (done by culture & 1. Complement fixation
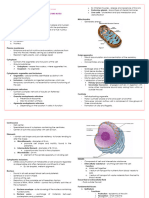
A. Entamoeba biochemical methods) 2. FAT of Goldman
• 3 grps accdg to no. of nuclei in mature cyst: 2. Invasive (?) 3. Indirect hemagglutination (IHA) – more sensitive
1. 1 – E. polecki (pigs, monkey, man) • Strains of E.histo – differing in pathogenicity – distinguished • Contamination thru:
2. 4 – E. histo from nonpathogenic by isozyme analysis 1. Polluted H2O supply – cyst viable in damp soil (8 days), cool
3. 8 – E. coli • Diagnosis: (12 days), H2O (9-30 days), H2O at -4°C (3 months)
• Gingivalis – no encysted form A. Intestinal Amoebiasis 2. Unclean handling of infected indivs (formites, hands, clothes)
• Natural parasites of GIT of vertebrates & invertebrate hosts except a. Stool exam by direct smears & stained mounts 3. Droppings of flies & other insects
E. moshkovskii (sewage H2O & plants) 1. Diarrheic/dysenteric/liquid feces - TROPH - Cysts unchanged in intestine of flies & cockroach
• Inhibit large intestine of vertebrate hosts except gingivalis (man’s - Non-fecal mat: blood & mucus (pick out) - Viable in their feces & vomitus for 48 hrs.
mouth) & bovis (cow mouth) - w/in 30 mins. after voiding (if not, troph disintegrates) - Filth flies (Musca domestica) & cockroaches – mechanical
• Exclusive lumen dwellers exc. E. histo (invade tissue) & E. - do at 3-4 day intervals, not daily vectors of cysts (sticky, bristly appendages carry cyst from
invadens (invade tissue – reptiles) fresh stool; their habit of vomiting & defecating when
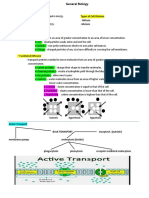
feeding → MoT) FREE-LIVING AMOEBA
4. Human excreta in veggie gardens • Order: Schizopyrenida
5. Carelessness in personal hygiene in children’s asylums, • Fam: Valkamphidae
mental hospitals, prisons & other congested areas • Genus:
• Transmission – sexually transmitted disease (oral – anal route) A. Naegleria
- Human carrier (cyst passers) – sources; show no symptoms a. N. fowleri = N. aerobia
• Pathogenicity - Cause of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
1. Intestinal amoebiasis – localized in colon (colonize & feed) - From lakes, swimming pools (dive - troph → nasal passages
- multiply in crypts → olfactory nerves → cribriform plate → cranium)
- attachment mediated by amoebal galactose or N-acetyl-d- - Uninucleate cyst
galactosamine adherence lectins - 2 forms:
- when ingesting starch granules (rice) 1. Flagellate
- utilize mucous secretions as food ✓ 2 long flagella at one end
- Metabolize anaerobically w/ enteric bacteria ✓ Elongated
- Once they invade tissue – cause lysis ✓ Form pseudopods
- Don’t depend on bacteria – obtain their nourishment thru 2. Ameboid
absorption of dissolved tissue juices ✓ Single blunt lobopodium
- Encystation – not in tissue or outside intestinal lumen → B. Acanthamoeba
specimen taken outside lumen will contain troph only a. Several species (i.e. culbertsoni)
- Affect other organs (liver, brain, lungs, spleen - Can’t tolerate hot H2O as A
- Cause chronic infection of skin or CNS in:
E. coli E. histo 1. Immunocompromised hosts
Nuclear divisions 3 2 2. Agents of keratits (corneal inflammation) w/ contact lenses
Infective stage Mature cyst Young cyst & meningoencephalitis
Metacystic troph 8 4
c. E. hartmanni – LC, morpho & appearance identical to E. histo
except size (like E. nana)
Troph: - don’t ingest RBC
- motility less vigorous than histo
- Nuc: like coli in char. of its chromatin & karyosome
Cyst: - glycogen mass
- chromatoidal bodies (short w/ tapered ends; rice-grain
shaped or thin, bar-like)
d. E. dispar
B. Endolimax
a. E. nana - Same stage & LC as E.coli
C. Iodamoeba
a. I. buetschlii
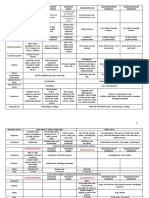
Amoebic Dysentery Bacillary Dysentery
Gross Appearance Gelatinous mixture of Mucopurulent mass
blood, mucus & feces streaked w/ blood
Amt Copious Small
Odor Offensive (fishy) Inoffensive
Color Dark red Bright red
Reaction Acidic Alkaline
Microscopic
Ghost cells
None 95% degenerated
(WBC remnants)
Macrophages Rare Present
Never clumped,
RBC Clumped
discrete
Charcot-Leyden
crystals (in stools Present Absent
w/ parasitic infxn)
Bacteria Numerous Nil to none
Pus cells Scanty numerous
You might also like
- English8Q2F (PIVOT)Document40 pagesEnglish8Q2F (PIVOT)Iris Rivera-Perez89% (9)
- Intestinal Amoebiasis - CSDocument33 pagesIntestinal Amoebiasis - CSMASII100% (1)
- Para - AmoebaDocument2 pagesPara - AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Protista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Document6 pagesProtista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyWeng WengNo ratings yet
- Histology Lab Practicals - AY 2021-2022Document15 pagesHistology Lab Practicals - AY 2021-2022H TNo ratings yet
- EPITHELIUMDocument2 pagesEPITHELIUMALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- Ameba and E.histolyticaDocument18 pagesAmeba and E.histolyticapenonia.abegailashleyNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)Document4 pages1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)arvinkennethdelacruzNo ratings yet
- Amoeba: Ms. Helga SyDocument7 pagesAmoeba: Ms. Helga Syanti romantic txtNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Exam ReviewerDocument11 pages2nd Exam Reviewerdmt01081991No ratings yet
- Zoology - Animal Tissues - Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesZoology - Animal Tissues - Lecture NotesKARYLLE JUNE PONTERASNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFDocument4 pagesParasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- 2 Approaches: 1. Clinical Diagnosis 2. Laboratory Diagnosis 2 Phases: 1. MacroscopicDocument4 pages2 Approaches: 1. Clinical Diagnosis 2. Laboratory Diagnosis 2 Phases: 1. Macroscopiccayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument2 pagesAnimal TissuesMami AmihanNo ratings yet
- Epithelial-Cells 2Document5 pagesEpithelial-Cells 2Edeilaine JadraqueNo ratings yet
- Histo - Fresh Tissue Examination and Intro To Histological TechniquesDocument4 pagesHisto - Fresh Tissue Examination and Intro To Histological TechniquesBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaNo ratings yet
- Dientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesDocument4 pagesDientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- Two Main Excretory Ducts CA Cells and Intercalated Duct CellsDocument3 pagesTwo Main Excretory Ducts CA Cells and Intercalated Duct CellsNoel JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Jaw and Soft Tissues: A-Odontogenic Keratocyst. B - Dentigerous CystDocument15 pagesCysts of The Jaw and Soft Tissues: A-Odontogenic Keratocyst. B - Dentigerous CystruchikaNo ratings yet
- PROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyDocument7 pagesPROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyReyven Niña DyNo ratings yet
- Module # Epitheleal TransDocument5 pagesModule # Epitheleal TransLara VanessNo ratings yet
- Free Living AmoebaDocument5 pagesFree Living AmoebaEiveren Mae SutillezaNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane Types of Cell Division - Mitosis - MeiosisDocument4 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane Types of Cell Division - Mitosis - MeiosisAlex SerdeñaNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument8 pagesParasitologyNonki VargasNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman CacingDocument111 pagesRangkuman CacingNyomantrianaNo ratings yet
- Parasites by Apple TanDocument16 pagesParasites by Apple TanOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- AMOEBADocument11 pagesAMOEBAMicaella RemilloNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson 1Document4 pagesBiology Lesson 1Charles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument4 pages4 TissuesCarea CruzNo ratings yet
- Tabular Parasitology MICROPARADocument19 pagesTabular Parasitology MICROPARAJerlyn FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708Document3 pagesTumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708CitrusNo ratings yet
- Fit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesDocument3 pagesFit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesCaithlyn KirthleyNo ratings yet
- OkieDocument3 pagesOkieFebeval CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesLesson 7 Cell MembraneThea MillanesNo ratings yet
- Porifera 1 STETH3.ODocument25 pagesPorifera 1 STETH3.OAshwinee KadelNo ratings yet
- Amoeba PrefinalsDocument5 pagesAmoeba PrefinalsKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Ex 6 - HistologyDocument9 pagesEx 6 - HistologyCarl Johnave Manigbas MonzonNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document9 pagesTopic 2Ria AccadNo ratings yet
- T I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueDocument6 pagesT I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueMarla TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Micro ParasitesDocument4 pagesMicro ParasitesKrisha Marie BadilloNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesDocument7 pages4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesJudith Dianne Ignacio100% (1)
- Amoeba Part 2 NotesDocument8 pagesAmoeba Part 2 Notesjefftuazon01No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 - Drosophila: Cleavage and BlastulaDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 11 - Drosophila: Cleavage and BlastulaAngela BalmesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 ReviewerUriel Andrei MaribbayNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2bDocument2 pagesMODULE 2bFeliza Mae BoquecosaNo ratings yet
- Biology MidSem SPOTDocument10 pagesBiology MidSem SPOTNaqiuddin MukhdirNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology First Grading NotesDocument24 pagesOral Histology First Grading NotesAli,morwan HydarNo ratings yet
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023Document5 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023VERONICA ROSE MAGPOCNo ratings yet
- Traditional Serrated Adenoma - Libre PathologyDocument3 pagesTraditional Serrated Adenoma - Libre PathologyfadoNo ratings yet
- Bot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesDocument4 pagesBot 3 2 Lec Exam Reviewer: I. Euglenophyta Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Charophyceae Iii. BryophytesXearis SangalangNo ratings yet
- Patho Ospe 1Document16 pagesPatho Ospe 1PomNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba Histolytica: Intestinal Amebae Ameba Nucleus Troph Cyst Pathogenicity OtherDocument7 pagesEntamoeba Histolytica: Intestinal Amebae Ameba Nucleus Troph Cyst Pathogenicity OtherDarla YsavelNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesChad Laurence Vinson CandelonNo ratings yet
- Porifera, Cnidaria and Ctenophora 1Document6 pagesPorifera, Cnidaria and Ctenophora 1null dillNo ratings yet
- (PARA) 1.5 - Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDocument6 pages(PARA) 1.5 - Blood and Tissue FlagellatesGuia De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Readings On ProtozoansDocument18 pagesSupplemental Readings On Protozoansferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- Free-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesFree-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsIrvin SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Cestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanDocument4 pagesCestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanMicael Andrei MendozaNo ratings yet
- TrematodesDocument2 pagesTrematodesIan Josef R. VibarNo ratings yet
- DRUGS2Document1 pageDRUGS2KaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Para - AmoebaDocument2 pagesPara - AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Para - Amoeba TabulatedDocument1 pagePara - Amoeba TabulatedKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests in MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesBiochemical Tests in MicrobiologyKaoriMarieSembrano100% (1)
- Tabulated Review On AmoebaDocument1 pageTabulated Review On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Intro ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntro ParasitologyKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Table Review of ParasitesDocument6 pagesTable Review of ParasitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- TrophozoitesDocument4 pagesTrophozoitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti-Epileptic DrugsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Micro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeDocument5 pagesMicro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Psychoactive and AntibioticsDocument2 pagesPsychoactive and AntibioticsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Anti Protozoal AgentsDocument37 pagesAnti Protozoal AgentsGunjan YadavNo ratings yet
- Amoebic Liver Abscess: Clinical MedicineDocument5 pagesAmoebic Liver Abscess: Clinical MedicineAizat KamalNo ratings yet
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument15 pagesAscaris LumbricoidesJyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Parasitology:: Classification of ParasitesDocument17 pagesParasitology:: Classification of ParasitesIrfan Pathan KakarNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle and Infection Mode From Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument30 pagesLife Cycle and Infection Mode From Entamoeba HistolyticaSynthesis is What MattersNo ratings yet
- FECALYSISDocument4 pagesFECALYSISMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Lifecycle of EntamoebaDocument86 pagesLifecycle of EntamoebaAman ShaikNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Parasitism: ProtozoansDocument10 pagesIntestinal Parasitism: ProtozoansdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- AmoebiasisDocument33 pagesAmoebiasisMike Serge Razafi0% (1)
- Gatot Sugiharto, MD, Internist Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine, Wijaya Kusuma University SurabayaDocument78 pagesGatot Sugiharto, MD, Internist Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine, Wijaya Kusuma University SurabayaRandy HuangNo ratings yet
- Apolon paraDocument4 pagesApolon paraHanin ArakamaNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- AmebiasisDocument32 pagesAmebiasisRizty Mayang FachleviNo ratings yet
- TOPNOTCH Parasitology-Supertable-by-Yns-Pereyra-Cocoy-Calderon-Troy-Soberano-UPDATED-NOVEMBER-2017Document25 pagesTOPNOTCH Parasitology-Supertable-by-Yns-Pereyra-Cocoy-Calderon-Troy-Soberano-UPDATED-NOVEMBER-2017Waiwit KritayakiranaNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesAmoebiasis PathophysiologyApril CornejoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical Parasitology - ProtozoologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Medical Parasitology - ProtozoologyHellNo ratings yet
- GIDocument196 pagesGIswagmasterNo ratings yet
- Crew Health PrecautionsDocument59 pagesCrew Health PrecautionsshireenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Fecal Oral Transmitted DiseasesDocument60 pagesUnit 2 - Fecal Oral Transmitted DiseasesAbdulmajid AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Unit 1Document95 pagesCase Study For Unit 1family_jvcNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Compre Review 2021 - Dr. HemedezDocument65 pagesMicroPara Compre Review 2021 - Dr. HemedezStephenMontoyaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectDocument11 pages3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectThaiz P.SNo ratings yet
- Soal ParasitologiDocument14 pagesSoal ParasitologiFirman SugihartoNo ratings yet
- Etiology 1-Deficiency of Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) 2 - PathogenesisDocument139 pagesEtiology 1-Deficiency of Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) 2 - PathogenesisAlston Foods BVNo ratings yet
- The Prevalence of Parasitic Protozoan Diseases in Iraq, 2016Document5 pagesThe Prevalence of Parasitic Protozoan Diseases in Iraq, 2016Jeremia AnkesaNo ratings yet
- Ameboma: A Colon Carcinoma-Like Lesion in A Colonoscopy FindingDocument4 pagesAmeboma: A Colon Carcinoma-Like Lesion in A Colonoscopy FindingSitha WisesaNo ratings yet
- General Characteristic and Classification of ProtozoaDocument50 pagesGeneral Characteristic and Classification of ProtozoaTLM A181No ratings yet