Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Para - Amoeba Tabulated
Para - Amoeba Tabulated
Uploaded by
KaoriMarieSembrano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
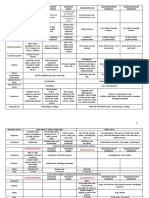
14 views1 pageThis document provides information about different species of Entamoeba and their characteristics:
1. It lists several Entamoeba species including E. histolytica, E. coli, E. nana, E. buetschlii, and provides their other common names.
2. For each species, it describes their geographical distribution, trophozoite morphology including size, nucleus, pseudopodia, cytoplasm, and trophic characteristics.
3. It also notes characteristics of cysts for some species such as number of nuclei, presence of glycogen vacuoles and chromatoidal bodies.
Original Description:
Tables Amoeba
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about different species of Entamoeba and their characteristics:
1. It lists several Entamoeba species including E. histolytica, E. coli, E. nana, E. buetschlii, and provides their other common names.
2. For each species, it describes their geographical distribution, trophozoite morphology including size, nucleus, pseudopodia, cytoplasm, and trophic characteristics.
3. It also notes characteristics of cysts for some species such as number of nuclei, presence of glycogen vacuoles and chromatoidal bodies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pagePara - Amoeba Tabulated
Para - Amoeba Tabulated
Uploaded by
KaoriMarieSembranoThis document provides information about different species of Entamoeba and their characteristics:
1. It lists several Entamoeba species including E. histolytica, E. coli, E. nana, E. buetschlii, and provides their other common names.
2. For each species, it describes their geographical distribution, trophozoite morphology including size, nucleus, pseudopodia, cytoplasm, and trophic characteristics.
3. It also notes characteristics of cysts for some species such as number of nuclei, presence of glycogen vacuoles and chromatoidal bodies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
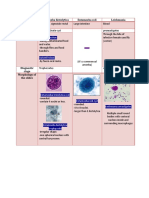
E. gingivalis E. coli E. nana I.
buetschlii E histolytica
Entamoeba nana, E.Iodine Cyst of Wenyon, A. coli / dysenteriae,
A. coli, Endamoeba homini,
Entamoeba dysenteriae /
Other names A. gingivalis, A. / E. buccalis Loschia coli, Councilmania intestinalis Entamoeba williamsi/ buetshclii,
dispar / tetragena, Endamoeba
lafleuri Endolimax williamsi
histolytica / dysenteriae
worldwide, pop. w/ warm - cosmo, prevalent infection
Worldwide
Geographical climates; if in cold à unsanitary as E.coli Worldwide, high in tropics &
cosmopolitan Less common infection than
Distribution disposal of human waste - warm, moist climates subtropics
nana & coli
(primitive hygiene) - low hygiene standard
Troph -5-35µ (ave. 10-20) (NSS) - 16-15µ -6-25µ (small-medium) - invasive, growing, feeding
Diameter -nearly spherical 20-30µ -in living & stained - 10-60µ (living)
Nucleus -well-defined, small, near - not easily visualized -unstained: surrounded by - NSS: center of endop
Karyosome center periendosomal granule (fine
fibrils connect it to NM)
-Multiple pseudopodia (Long &
Pseudopod/ lobose OR Short & blunt) - Sluggish movement, rarely -short, blunt, hyaline - active troph - progressive
Movement progressive w/ broad, short (sluggish) -Blunt, hyaline pseudo; fairly directional movement (long,
pseudopodia active, progressive in fresh fingerlike pseudopodia) à
stools, older à sluggish direction changes in response
to conditions of microclimate
-Demarcation bet. clear
ectoplasm & granular endo -clear ectop (not well diff. from - NSS: ground glass
Cytoplasm Endop - food vacuole, - colorless, viscous (no - granular, vacuolated w/ endop) à clear demarcation
phagocytosed demarcation) narrow rim of ectoplasm -endop - has food vacuoles w/ à food vacuoles w/ ingested
-Nuclear fragments of WBC in bacteria, yeast cell, debri RBC (green refractile bodies in
stained à ID of amoeba wet mt) - doesn't have
essential food for amoeba
Troph (IH) - nuc: spherical, spoke of wheel
- condensed, thick, round - food vacuole, crystals, small
or bulls-eye
- Spherical nucleus w. thick NM veggie cells
- kary: small, dot-like; anchored
lined w/ coarse chromatin - spherical/oval nucleus
- Kary: large mass (center or to inner NM by radiating
- eccentric karyosome - conspicuous, irregular
eccentric), large, surrounded by achromatic fibrils
- Nongranular ectoplasmic rim, karyosome (central or
periendosomal granules - NM: lined by fine, regularly
densely gran. Endoplasm eccentric)
arranged chrom. granules w/c
- Endoplasm - vacuolated - achromatic strands
can be aggregated into large
(honeycomb or dirty-looking) -thin marginal chroma
plaquelike masses
-1-2 nuclei
Cyst -1-4 nuclei - 5-14µ
- 6-15µ - glycogen mass w/ hazy
Young - Glycogen mass w/in vacuole w/ - oval/round
- irregularly pyriform or ovoidal margins
diffuse borders - 1-2 nuclei
- uninucleate (rarely binuc.) - chromatoidal bodies à
- Chromatoidal bars (spicules / - ill-defined glycogen mass
- large ovoid, polygonal or long/short rods w/ rounded
irregular masses of hema-toxylin, - slightly curved chromatoidal
broadly reniform (kidney ends (cigar/sausage shape)
broomlike / rods w/ splintered bodies
NO CYST shaped) glycogen vacuole à ------------------------------------
ends)
pushes nuclei aside - 10-20µ
--------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
à I2 - golden brown - 4 nuclei, rarely 8
Mature -Spherical, 10-33µ diameter - 4 nuclei, rarely 8
à IH - devoid of content - central karyosome
- 8 nuclei (rarely 16-32) - no cytoplasmic inclusions
(dissolved) - spherical, subspherical or
-No cytoplasmic inclusions
ovoidal
- eccentric karyosome
- no cytoplasmic inclusions
mouth (clean / unhygienic) à
- Lumen of large intestine Cecum (contact w/ mucosa or
gum disease
Habitat lumen of large intes (cecum) Lumen dweller of cecum (cecum) become lodged in glandular
-Pyorrheal pockets bet teeth &
- troph feeds on enteric bac. crypts)
gums in tonsillar crypts
Stool exam:
Stool examination:
Stool examination: - Direct - w/ I2, specific Dx can
in scrapings from: - Direct (fresh-NSS or I2)
-Diarrheic / dysenteric / liquid à be made on type of glycogen
1.Gingival margins of gums - stained (IH) - ovoidal cyst in
Diagnosis (Dx) troph vacuole Look at other paper
2.Bet teeth or dentures fecal films; round cyst & living
-Semi-formed à troph & cyst - Stained IH permanent mounts
3.Soft tartar of teeth troph can't be diff. from E.
-Well-formed à cyst - nuclear structure & glycol are
histo
species Dx
better hygiene & sanitary Personal hygiene & proper
Prevention proper care of teeth & gums same Same
disposal of human excreta disposal
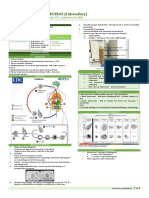
- ingest food w/ mature cyst
Same as coli (cysts more
droplet spray from mouth of - feces
MoT susceptible to dessication & same as coli Same
infected (close contact - soiled fingers or on objects w/
putrefaction than coli)
mature cyst
- tissue invading
- only pathogenic bacteria of
- Atrial [in a cavity] man
-1st parasitic of man to be - not as organized as histo Formites - bacteria has - cause amoebiasis, amoebic
Others
described (Leeuwenhoek) - I2 inhibits troph infectious agent dysentery & hepatitis
- Only species that ingest cells (perforation of intestinal lining)
& liver abscess (Am. goes to
liver)
Drawing
You might also like
- Atlas of Pyrenulaceae and Trypetheliaceae - Volume 1: Lichenized AscomycotaFrom EverandAtlas of Pyrenulaceae and Trypetheliaceae - Volume 1: Lichenized AscomycotaNo ratings yet
- Nematodes Lab Reviewer PDFDocument7 pagesNematodes Lab Reviewer PDFRobi Alegre MedinaNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument18 pagesParasitologyLudwig359100% (2)
- Tabulated Review On AmoebaDocument1 pageTabulated Review On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- AMOEBADocument11 pagesAMOEBAMicaella RemilloNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Part 2 NotesDocument8 pagesAmoeba Part 2 Notesjefftuazon01No ratings yet
- 6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsDocument35 pages6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsHeyzel joy FabianNo ratings yet
- Free Living AmoebaDocument5 pagesFree Living AmoebaEiveren Mae SutillezaNo ratings yet
- E. Histolytica: Associated DiseasesDocument11 pagesE. Histolytica: Associated DiseasesCorinne MandrezaNo ratings yet
- Amoeba paraDocument9 pagesAmoeba paraHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Tables - WormsDocument3 pagesTables - WormsOmphile DansonNo ratings yet
- Amoeba PrefinalsDocument5 pagesAmoeba PrefinalsKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Week 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument4 pagesWeek 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Protista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Document6 pagesProtista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Amoeba: Cytoplasm (Both in Cyst and Peripheral Chromatin (Both Trophozoite Cyst AmoebaDocument1 pageAmoeba: Cytoplasm (Both in Cyst and Peripheral Chromatin (Both Trophozoite Cyst AmoebapasambalyrradjohndarNo ratings yet
- Parasites High YoieldDocument4 pagesParasites High Yoieldnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Free-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesFree-Living Amoeba: General CharacteristicsIrvin SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- 2 - ProtozoaDocument10 pages2 - ProtozoaSherwin BumanglagNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument6 pagesCestodesKathryn JeuelNo ratings yet
- Nonpathogenic Amoebae - FlagellatesDocument20 pagesNonpathogenic Amoebae - FlagellatesHend AtijaniNo ratings yet
- Protozoa 1Document21 pagesProtozoa 1CDNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Readings On ProtozoansDocument18 pagesSupplemental Readings On Protozoansferrerjericho300No ratings yet
- Amoeba: Ms. Helga SyDocument7 pagesAmoeba: Ms. Helga Syanti romantic txtNo ratings yet
- Parasites by Apple TanDocument16 pagesParasites by Apple TanOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases TableKavya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- ProtozoansDocument3 pagesProtozoansJansen SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Cestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanDocument4 pagesCestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanMicael Andrei MendozaNo ratings yet
- Tissue FlagellatesDocument2 pagesTissue FlagellatesRed Bernaldez NiniNo ratings yet
- Amoeba ChartDocument4 pagesAmoeba ChartRafael CastilloNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Nematodes (Unholy Trinity)Document6 pagesIntestinal Nematodes (Unholy Trinity)DAN JR. M. BAUSANo ratings yet
- Significance of Commensal Amebae in StoolDocument12 pagesSignificance of Commensal Amebae in StoolNicolle PanchoNo ratings yet
- Lab Act 5Document5 pagesLab Act 5mikeeNo ratings yet
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases Tableanushkasingh300806No ratings yet
- Micro ParasitesDocument4 pagesMicro ParasitesKrisha Marie BadilloNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Document9 pagesPARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Allyssa AniNo ratings yet
- (MT 57) PARA - Pathogenic ProtozoaDocument5 pages(MT 57) PARA - Pathogenic ProtozoaLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)Document4 pages1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)arvinkennethdelacruzNo ratings yet
- Module 6.4 ParasitesDocument6 pagesModule 6.4 ParasitesPNo ratings yet
- Macabanding m5 Mt2h Subphylumsarcodina FlashcardsDocument56 pagesMacabanding m5 Mt2h Subphylumsarcodina FlashcardsNailah MacabandingNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument2 pagesNematodesRheila DuyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasDocument8 pages2 Parasitology Parasitic AmoebasknkjnNo ratings yet
- Nematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Document4 pagesNematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFDocument4 pagesParasitic Amoebas by Dr. C. J. Castro PDFMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Endoparasites: (Edit) Protozoan OrganismsDocument5 pagesEndoparasites: (Edit) Protozoan OrganismsimarzenNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Amoeba - SarcodinaDocument14 pagesWeek 3 - Amoeba - SarcodinaShine CalarananNo ratings yet
- Gram Pos, Spore Former BacilliDocument5 pagesGram Pos, Spore Former BacilliRach ReyesNo ratings yet
- PROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyDocument7 pagesPROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyReyven Niña DyNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument390 pagesParasitologyVench DemicaisNo ratings yet
- Mycology 1 PrelimDocument4 pagesMycology 1 PrelimKaye Angel VillonNo ratings yet
- Enperiment For Spotting-3Document18 pagesEnperiment For Spotting-3Debayan Bhattacharyya class:- 11-ANo ratings yet
- Parasit Ology 3Document4 pagesParasit Ology 3Adel AlomarNo ratings yet
- 8 - Intro To Cestodes & D. LatumDocument2 pages8 - Intro To Cestodes & D. LatumRich NyleNo ratings yet
- Common Medical PrefixesDocument5 pagesCommon Medical PrefixesRoshua DaclanNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Notes 2015Document6 pagesAmoeba Notes 2015Ivy FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- PARASITIC AMOEBAS (Lab)Document5 pagesPARASITIC AMOEBAS (Lab)Xie LianNo ratings yet
- Cestodes/ Tapeworms CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesCestodes/ Tapeworms CharacteristicsChinissa Ann LanonNo ratings yet
- RMTnotes PARASITOLOGYDocument68 pagesRMTnotes PARASITOLOGYArvin O-CaféNo ratings yet
- DRUGS2Document1 pageDRUGS2KaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Tabulated Review On AmoebaDocument1 pageTabulated Review On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Para - AmoebaDocument2 pagesPara - AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Intro ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntro ParasitologyKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- TrophozoitesDocument4 pagesTrophozoitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology On AmoebaDocument2 pagesParasitology On AmoebaKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Table Review of ParasitesDocument6 pagesTable Review of ParasitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests in MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesBiochemical Tests in MicrobiologyKaoriMarieSembrano100% (1)
- Micro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeDocument5 pagesMicro Lab EnterobacteriaceaeKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti-Epileptic DrugsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Psychoactive and AntibioticsDocument2 pagesPsychoactive and AntibioticsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet