Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsAT Formulas
AT Formulas
Uploaded by
Charsi 1080The document provides definitions and formulas for key concepts in thermodynamics including:
1) Formulas for work, potential energy, kinetic energy, and flow energy in terms of mass, gravity, height, velocity, pressure, and volume.
2) The general gas law relating pressure, volume, temperature, and moles of gas using a proportionality constant.
3) Formulas for specific heat capacities at constant volume and constant pressure in terms of mass and temperature change.
4) Relationships between enthalpy, internal energy, and heat for both constant volume and constant pressure processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 5 Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory - 2Document43 pagesChapter 5 Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory - 2Rahim RahimunNo ratings yet
- Properties of Mixtures Mixture of Perfect GasesDocument7 pagesProperties of Mixtures Mixture of Perfect GasesAudu SanusiNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law With ExamplesDocument10 pagesIdeal Gas Law With Examplesayan hazarikaNo ratings yet
- 1617 Level L Chemistry Revision Sheet T1 Wk11Document8 pages1617 Level L Chemistry Revision Sheet T1 Wk11Hisham El KanayatiNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1157 QC KP B ANS NbsyeDocument1 pageChemsheets A2 1157 QC KP B ANS NbsyeMarinaNo ratings yet
- 9 PsychrometryDocument71 pages9 PsychrometryPratyush NagareNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Part2Document28 pagesUnit 5-Part2Nobukhosi NdlovuNo ratings yet
- Avogadro's Law: Examples1Document11 pagesAvogadro's Law: Examples1liennev02No ratings yet
- Gas Laws (Chem)Document27 pagesGas Laws (Chem)EncounteriGH100% (3)
- GasesDocument129 pagesGasesEnitiNo ratings yet
- C10 F13 3Document0 pagesC10 F13 3Rohit BandaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 1 04Document64 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 1 04Ng Swee Loong Steven100% (6)
- Order 1771128Document4 pagesOrder 1771128Nahshon M. ObiriNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws:: P V K VDocument18 pagesGas Laws:: P V K VFarah Zu'biNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 The Gaseous State Edupdf 1Document64 pagesChapter 9 The Gaseous State Edupdf 1api-386303659No ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument51 pagesGaseous StateSal Sabeela RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document14 pagesLec 3Not EmeraruduNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry: V RH T T SHDocument13 pagesPsychrometry: V RH T T SHKAL ELNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 1Document24 pagesChemistry Module 1Teofilo Matthew AriñoNo ratings yet
- States of Matter - ThermodynamicsDocument146 pagesStates of Matter - ThermodynamicsbavisyaaaaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law (Part 4)Document5 pagesIdeal Gas Law (Part 4)asapamore100% (1)
- For 2nd Year CK&EC Chapter 4 Final PDFDocument51 pagesFor 2nd Year CK&EC Chapter 4 Final PDFbahru demekeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Lecture NotesAhmad KamalNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument26 pagesGASESMaricar SantaceraNo ratings yet
- 5 Temp Ideal Gas-Fall 2022Document22 pages5 Temp Ideal Gas-Fall 2022asakr8481No ratings yet
- SH 5107 Gases, Vapour & Aerosols 2021 Version 1Document131 pagesSH 5107 Gases, Vapour & Aerosols 2021 Version 1Shuyuan LuNo ratings yet
- Gas PropertiesDocument54 pagesGas PropertiesAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Kimia Fisika 1Document7 pagesKimia Fisika 1Agung Pribadi WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 ReviewDocument45 pagesPertemuan 7 ReviewAna Sholikhatus Sa'diyah100% (1)
- Part 2Document21 pagesPart 2abdullahghaya124No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document12 pagesLecture 3Samaseen PrabhatNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountDocument9 pagesGas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountArun KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 GasesDocument23 pages4.1 GasesVasanth Kumar BatumalaiNo ratings yet
- REVIEW FINALDocument36 pagesREVIEW FINALnguyenbaotran241104No ratings yet
- ME REVIEW ThermodynamicsDocument65 pagesME REVIEW ThermodynamicsKhate ÜüNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument9 pagesGas LawsGineNo ratings yet
- PV NRT: PM RT DRT PDocument19 pagesPV NRT: PM RT DRT PRyle ArbonNo ratings yet
- Gas Density CalculationDocument10 pagesGas Density CalculationKhurshid AhmadNo ratings yet
- SCES3163 Lap Report 2: Institut Pendidikan GuruDocument12 pagesSCES3163 Lap Report 2: Institut Pendidikan GuruSN2-0618 Muhamad Syahmi Rifqi Bin SharimanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument49 pagesChapter 5 GasesdeemahhwNo ratings yet
- Pure SubstanceDocument42 pagesPure SubstanceNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- 01-1a Psychrometry & ProcessesDocument24 pages01-1a Psychrometry & ProcessesEarl EsparesNo ratings yet
- 1112 Grade 12 Chemistry Revision Sheet Final Term 2Document32 pages1112 Grade 12 Chemistry Revision Sheet Final Term 2aalharthy_1No ratings yet
- Concentrations and Other Units of Measure: (Nazaroff & Alvarez-Cohen, Section 1.C.1)Document7 pagesConcentrations and Other Units of Measure: (Nazaroff & Alvarez-Cohen, Section 1.C.1)Vivian SolangonNo ratings yet
- Gases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsDocument106 pagesGases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsMia YukimuraNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 Lecture Note-Gas LawsDocument11 pagesCHM 101 Lecture Note-Gas LawsMichael DanielsNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Teknik KimiaDocument6 pagesPengantar Teknik KimiabihaqibibiNo ratings yet
- Hein Chem12 Ch2 AnsDocument9 pagesHein Chem12 Ch2 AnsPyNo ratings yet
- The Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThe Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- ChapterII - GasesDocument40 pagesChapterII - Gasesjumanahelmy12No ratings yet
- IChO-2013 Teoretical Problem With SolutionsDocument38 pagesIChO-2013 Teoretical Problem With SolutionsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two (1)Document26 pagesChapter Two (1)abdomoshref9No ratings yet
- Lecture-1b - Aqueos SolutionDocument28 pagesLecture-1b - Aqueos SolutionHaziq Alias NanoMalaysiaNo ratings yet
- Chem 181 Chemistry of GasesDocument15 pagesChem 181 Chemistry of GasesJoey PooleNo ratings yet
- ''Chapter 2 PhysicsDocument14 pages''Chapter 2 PhysicsAung LayNo ratings yet
- Taimoor Inayat Assi 3Document10 pagesTaimoor Inayat Assi 3Charsi 1080No ratings yet
- Luqman Bio Ass#1Document11 pagesLuqman Bio Ass#1Charsi 1080No ratings yet
- Asad Bio #1Document10 pagesAsad Bio #1Charsi 1080No ratings yet
- Ali Raza Bio #01Document11 pagesAli Raza Bio #01Charsi 1080No ratings yet
- AyazDocument3 pagesAyazCharsi 1080No ratings yet
- Gazanfar Abbas 024Document14 pagesGazanfar Abbas 024Charsi 1080No ratings yet
AT Formulas
AT Formulas
Uploaded by
Charsi 10800 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe document provides definitions and formulas for key concepts in thermodynamics including:
1) Formulas for work, potential energy, kinetic energy, and flow energy in terms of mass, gravity, height, velocity, pressure, and volume.
2) The general gas law relating pressure, volume, temperature, and moles of gas using a proportionality constant.
3) Formulas for specific heat capacities at constant volume and constant pressure in terms of mass and temperature change.
4) Relationships between enthalpy, internal energy, and heat for both constant volume and constant pressure processes.
Original Description:
kjjn
Original Title
AT formulas (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides definitions and formulas for key concepts in thermodynamics including:
1) Formulas for work, potential energy, kinetic energy, and flow energy in terms of mass, gravity, height, velocity, pressure, and volume.
2) The general gas law relating pressure, volume, temperature, and moles of gas using a proportionality constant.
3) Formulas for specific heat capacities at constant volume and constant pressure in terms of mass and temperature change.
4) Relationships between enthalpy, internal energy, and heat for both constant volume and constant pressure processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesAT Formulas
AT Formulas
Uploaded by
Charsi 1080The document provides definitions and formulas for key concepts in thermodynamics including:
1) Formulas for work, potential energy, kinetic energy, and flow energy in terms of mass, gravity, height, velocity, pressure, and volume.
2) The general gas law relating pressure, volume, temperature, and moles of gas using a proportionality constant.
3) Formulas for specific heat capacities at constant volume and constant pressure in terms of mass and temperature change.
4) Relationships between enthalpy, internal energy, and heat for both constant volume and constant pressure processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Formulas
M =mass G=gravity Z= hight = 𝒘𝒐𝒓𝒌 = 𝒎𝒈z
P.E =Potential energy M =mass G=gravity Z= hight = 𝑷.𝑬 = 𝒎𝒈𝒛
K.E=kinetic energy M= mass V=velocity= 𝑲. 𝑬 = 𝒎𝒗^2/2
F.E=flow energy P=pressure V=volume Internal energy= 𝑭. 𝑭 = 𝑷𝑽
∆U=internal energy M=mass C=constant ∆T=change in temperature =∆𝑼 = 𝒎𝒄∆𝑻
H=enthalpy F.E=flow energy U=internal energy = Enthalpy 𝑯 = 𝑭. 𝑬. + 𝑼
Pressure = Force/area 𝒑 = 𝑭 /𝑨 @ 𝒖𝒏𝒊𝒕𝒔 𝑵 /𝒎𝟐 𝒐𝒓 𝑷𝒂𝒔𝒄𝒂𝒍𝒔 10^3𝑃𝑎 = 1 𝑘𝑃𝑎 ,10 ^6𝑃𝑎 = 1 𝑀𝑝𝑎 ,10 ^5 𝑃𝑎 = 1 𝑏𝑎𝑟
P=pressure
V=volume
T=temperature
C=content
CONSTANT VOLUME LAW 𝒑 = 𝒄 𝑻 𝒘𝒉𝒆𝒏 𝑽 𝒊𝒔 𝒄𝒐𝒏𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒕
CHARLE’S LAW 𝑽 = 𝒄 𝑻 𝒘𝒉𝒆𝒏 𝒑 𝒊𝒔 𝒄𝒐𝒏𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒕
BOYLE'S LAW 𝒑 = 𝒄/ 𝑽 𝒘𝒉𝒆𝒏 𝑻 𝒊𝒔 𝒄𝒐𝒏𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒕
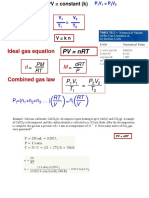
GENERAL GAS LAW 𝒑𝟏𝑽𝟏/ 𝑻𝟏 = 𝒑𝟐𝑽𝟐 /𝑻𝟐 = 𝒄
CHARACTERISTIC GAS LAW 𝑷𝑽 = 𝒎𝑹𝑻 𝒖𝒏𝒊𝒕𝒔 = 𝑱/ 𝒌𝒈 𝑲
Since m/V is the density , it follows that 𝒅𝒆𝒏𝒊𝒔𝒕𝒚 𝒑 = 𝑷 /𝑹𝑻
Since V/m is the specific volume 𝒗 = 𝑹𝑻 /𝑷
Gas Symbol Mm
Hydrogen H2 2
Oxygen o2 32
Carbon dioxide co2 44
Methane ch4 16
Nitrogen n2 28
Dry air 28.96
THE UNIVERSAL GAS LAW :
𝒑𝑽 = 𝒎𝑹𝒐𝑻 /𝑴𝒎
𝑹 = 𝑹𝒐 /𝑴𝒎
𝑹𝒐 = 𝟖𝟑𝟏𝟒.3
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITIES :
Constant Volume ∆𝑼 = 𝒎𝒄𝒗∆𝑻
Constant pressure ∆𝑯 = 𝒎𝒄𝒑∆𝑻
CONSTANT VOLUME HEATING 𝑸 = ∆𝑼 = 𝒎𝒄𝒗∆𝑻
CONSTANT PRESSURE HEATING ∆𝑯 = 𝑸 = 𝒎𝒄𝒑∆𝑻
LINK BETWEEN cv, cp AND R 𝒄𝒑 = 𝒄𝒗 + 𝑹
For Liquid 𝑸 = 𝒎𝒄 ∆𝑻
Latent enthalpy and latent internal energy
𝒉𝒈 = 𝒉𝒇 + 𝒉𝒇𝒈
𝑼𝒈 = 𝒖𝒇 + 𝒖𝒇g
𝒉 = 𝒉𝒇 + 𝒙𝒉𝒇𝒈
𝒖 = 𝒖𝒇 + 𝒙𝒖𝒇𝒈
X = 0. If all the liquid is Evaporated then x = 1. X cannot be larger than 1 as this would mean the vapour is Superheated.
𝒗 = 𝒗𝒇 + 𝒙𝒗𝒇𝒈
𝑽 = 𝒎𝒙𝒗g
You might also like
- Chapter 5 Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory - 2Document43 pagesChapter 5 Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory - 2Rahim RahimunNo ratings yet
- Properties of Mixtures Mixture of Perfect GasesDocument7 pagesProperties of Mixtures Mixture of Perfect GasesAudu SanusiNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law With ExamplesDocument10 pagesIdeal Gas Law With Examplesayan hazarikaNo ratings yet
- 1617 Level L Chemistry Revision Sheet T1 Wk11Document8 pages1617 Level L Chemistry Revision Sheet T1 Wk11Hisham El KanayatiNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1157 QC KP B ANS NbsyeDocument1 pageChemsheets A2 1157 QC KP B ANS NbsyeMarinaNo ratings yet
- 9 PsychrometryDocument71 pages9 PsychrometryPratyush NagareNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Part2Document28 pagesUnit 5-Part2Nobukhosi NdlovuNo ratings yet
- Avogadro's Law: Examples1Document11 pagesAvogadro's Law: Examples1liennev02No ratings yet
- Gas Laws (Chem)Document27 pagesGas Laws (Chem)EncounteriGH100% (3)
- GasesDocument129 pagesGasesEnitiNo ratings yet
- C10 F13 3Document0 pagesC10 F13 3Rohit BandaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 1 04Document64 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 1 04Ng Swee Loong Steven100% (6)
- Order 1771128Document4 pagesOrder 1771128Nahshon M. ObiriNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws:: P V K VDocument18 pagesGas Laws:: P V K VFarah Zu'biNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 The Gaseous State Edupdf 1Document64 pagesChapter 9 The Gaseous State Edupdf 1api-386303659No ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument51 pagesGaseous StateSal Sabeela RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document14 pagesLec 3Not EmeraruduNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry: V RH T T SHDocument13 pagesPsychrometry: V RH T T SHKAL ELNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 1Document24 pagesChemistry Module 1Teofilo Matthew AriñoNo ratings yet
- States of Matter - ThermodynamicsDocument146 pagesStates of Matter - ThermodynamicsbavisyaaaaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law (Part 4)Document5 pagesIdeal Gas Law (Part 4)asapamore100% (1)
- For 2nd Year CK&EC Chapter 4 Final PDFDocument51 pagesFor 2nd Year CK&EC Chapter 4 Final PDFbahru demekeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Lecture NotesAhmad KamalNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument26 pagesGASESMaricar SantaceraNo ratings yet
- 5 Temp Ideal Gas-Fall 2022Document22 pages5 Temp Ideal Gas-Fall 2022asakr8481No ratings yet
- SH 5107 Gases, Vapour & Aerosols 2021 Version 1Document131 pagesSH 5107 Gases, Vapour & Aerosols 2021 Version 1Shuyuan LuNo ratings yet
- Gas PropertiesDocument54 pagesGas PropertiesAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Kimia Fisika 1Document7 pagesKimia Fisika 1Agung Pribadi WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 ReviewDocument45 pagesPertemuan 7 ReviewAna Sholikhatus Sa'diyah100% (1)
- Part 2Document21 pagesPart 2abdullahghaya124No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document12 pagesLecture 3Samaseen PrabhatNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountDocument9 pagesGas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountArun KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 GasesDocument23 pages4.1 GasesVasanth Kumar BatumalaiNo ratings yet
- REVIEW FINALDocument36 pagesREVIEW FINALnguyenbaotran241104No ratings yet
- ME REVIEW ThermodynamicsDocument65 pagesME REVIEW ThermodynamicsKhate ÜüNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument9 pagesGas LawsGineNo ratings yet
- PV NRT: PM RT DRT PDocument19 pagesPV NRT: PM RT DRT PRyle ArbonNo ratings yet
- Gas Density CalculationDocument10 pagesGas Density CalculationKhurshid AhmadNo ratings yet
- SCES3163 Lap Report 2: Institut Pendidikan GuruDocument12 pagesSCES3163 Lap Report 2: Institut Pendidikan GuruSN2-0618 Muhamad Syahmi Rifqi Bin SharimanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument49 pagesChapter 5 GasesdeemahhwNo ratings yet
- Pure SubstanceDocument42 pagesPure SubstanceNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- 01-1a Psychrometry & ProcessesDocument24 pages01-1a Psychrometry & ProcessesEarl EsparesNo ratings yet
- 1112 Grade 12 Chemistry Revision Sheet Final Term 2Document32 pages1112 Grade 12 Chemistry Revision Sheet Final Term 2aalharthy_1No ratings yet
- Concentrations and Other Units of Measure: (Nazaroff & Alvarez-Cohen, Section 1.C.1)Document7 pagesConcentrations and Other Units of Measure: (Nazaroff & Alvarez-Cohen, Section 1.C.1)Vivian SolangonNo ratings yet
- Gases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsDocument106 pagesGases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsMia YukimuraNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 Lecture Note-Gas LawsDocument11 pagesCHM 101 Lecture Note-Gas LawsMichael DanielsNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Teknik KimiaDocument6 pagesPengantar Teknik KimiabihaqibibiNo ratings yet
- Hein Chem12 Ch2 AnsDocument9 pagesHein Chem12 Ch2 AnsPyNo ratings yet
- The Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThe Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- ChapterII - GasesDocument40 pagesChapterII - Gasesjumanahelmy12No ratings yet
- IChO-2013 Teoretical Problem With SolutionsDocument38 pagesIChO-2013 Teoretical Problem With SolutionsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two (1)Document26 pagesChapter Two (1)abdomoshref9No ratings yet
- Lecture-1b - Aqueos SolutionDocument28 pagesLecture-1b - Aqueos SolutionHaziq Alias NanoMalaysiaNo ratings yet
- Chem 181 Chemistry of GasesDocument15 pagesChem 181 Chemistry of GasesJoey PooleNo ratings yet
- ''Chapter 2 PhysicsDocument14 pages''Chapter 2 PhysicsAung LayNo ratings yet
- Taimoor Inayat Assi 3Document10 pagesTaimoor Inayat Assi 3Charsi 1080No ratings yet
- Luqman Bio Ass#1Document11 pagesLuqman Bio Ass#1Charsi 1080No ratings yet
- Asad Bio #1Document10 pagesAsad Bio #1Charsi 1080No ratings yet
- Ali Raza Bio #01Document11 pagesAli Raza Bio #01Charsi 1080No ratings yet
- AyazDocument3 pagesAyazCharsi 1080No ratings yet
- Gazanfar Abbas 024Document14 pagesGazanfar Abbas 024Charsi 1080No ratings yet