Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)
Reviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)
Uploaded by
HelloCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Unit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthDocument218 pagesUnit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthBlop100% (1)
- Iso 668 1995 (E)Document10 pagesIso 668 1995 (E)alinpreliNo ratings yet
- Psma PrelimsDocument42 pagesPsma PrelimsPrincess Rose GamboaNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec ReviewerDocument42 pagesChem Lec ReviewerMaryashlyn NableaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science MidtermsDocument4 pagesPhysical Science MidtermsKimberly MedranoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Atoms and Atomic Theory)Document47 pagesChapter 4 (Atoms and Atomic Theory)Raynan TabaldoNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC AND INORGANIC CHEMISTRY REVIEWER - COPYRIGHT@villanuevarDocument5 pagesORGANIC AND INORGANIC CHEMISTRY REVIEWER - COPYRIGHT@villanuevarreyellahvillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv-VDocument18 pagesUnit Iv-VIvy Marie ToyonganNo ratings yet
- Concept+1+Notes+ +Structure+of+the+AtomDocument9 pagesConcept+1+Notes+ +Structure+of+the+AtomsanchezsolsalmaNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument46 pagesAtomic ModelShannelle Anne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Junction Diodes: Module-2Document46 pagesJunction Diodes: Module-2NILESH TIWARINo ratings yet
- Science-Q2-Notes BanzonDocument3 pagesScience-Q2-Notes BanzonfeytNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Atomic TheoryDocument47 pagesAtoms and The Atomic TheoryEdgar PeninsulaNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument29 pagesSci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesFlorenze GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Chem 1Document2 pagesReviewer in Chem 1MARY ZIANNE GABRIELLE QUINTONo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceGutierrez, Patricia MaeNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Chemistry 2023 2Document60 pagesYr 9 Chemistry 2023 2mkkit2105No ratings yet
- Atomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Document16 pagesAtomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Nilimoy Choudhury100% (1)
- Atomic PhysicsDocument5 pagesAtomic Physicslove meNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument2 pagesScience NotesLoladeNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Urning Back Time - The Theory of AtomsDocument14 pagesAtomic Structure: Urning Back Time - The Theory of AtomsUmer AzharNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221114 080033 0000Document2 pagesPDF 20221114 080033 0000John Marithe PutunganNo ratings yet
- Atomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Document7 pagesAtomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Venugopal RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4, Section 2Document20 pagesChapter 4, Section 2Abdullah AlthaniNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics Circuits - ReviewerDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Electronics Circuits - Revieweraguilaclaudette35No ratings yet
- AtomsDocument35 pagesAtomsAnna Carmela BERANIANo ratings yet
- The Atom For AnatomyDocument106 pagesThe Atom For AnatomyAlexandra B. FloresNo ratings yet
- Physci Prelims Reviewer L1 3 1Document4 pagesPhysci Prelims Reviewer L1 3 1Yael Duane CabaisNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument9 pagesPhysical Science ReviewerRuzuiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Chemistry Atomic Models and Structure of The Atom I. Learning CompetencyDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Chemistry Atomic Models and Structure of The Atom I. Learning CompetencyLoreen Jane AbogadoNo ratings yet
- Img20240325 01023517 PDFDocument1 pageImg20240325 01023517 PDFpagtama.136530120101No ratings yet
- 1 - The AtomDocument2 pages1 - The AtomCyrene ManansalaNo ratings yet
- 2.1. The Nuclear Atom - Atomic StructureDocument65 pages2.1. The Nuclear Atom - Atomic StructureSaniya DautovaNo ratings yet
- Atoms: NucleusDocument6 pagesAtoms: Nucleusヒルデガルダ HILDEGARDENo ratings yet
- Atoms and Nuclear Energy RevisionDocument5 pagesAtoms and Nuclear Energy RevisionLeona Valentina VračarNo ratings yet
- First Year Chemistry 20-02Document100 pagesFirst Year Chemistry 20-02Ahmed Hassan Mina HamadNo ratings yet
- Sci2Q Reviewer PDFDocument5 pagesSci2Q Reviewer PDFFire RobloxNo ratings yet
- 2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Document12 pages2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Keshia KatarinaNo ratings yet
- What Is An AtomDocument3 pagesWhat Is An Atomsithumsethika7No ratings yet
- Block 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityDocument70 pagesBlock 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityMac Justine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Atomic Structure Physical ScienceDocument18 pagesChapter 4 - Atomic Structure Physical Scienceapi-30718309No ratings yet
- Subatomic Particles of AtomsDocument8 pagesSubatomic Particles of AtomsRose Ann Marie BabiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawDocument32 pagesLecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawВалентина ЮзьковаNo ratings yet
- Leaving Cert Chemistry NotesDocument116 pagesLeaving Cert Chemistry NotesSnivySerpentNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Postulates of Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesPostulates of Dalton's Atomic TheoryVenugopal RNo ratings yet
- S1 2022 P Fisika - Inti I - Struktur Inti AtomDocument64 pagesS1 2022 P Fisika - Inti I - Struktur Inti AtomMuhammad Agustian AdhityaNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)Document22 pagesCHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)ogedengbed28No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 AtomDocument48 pagesLesson 1 Atom12 John Paolo DumaguinNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theories Quatum ModelDocument31 pagesAtomic Theories Quatum Modelerinallyson20No ratings yet
- General Chemistry Organic Chemistry Biochemistry: MatterDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry Organic Chemistry Biochemistry: MatterFRANCYM PRINCESSRICH BATENGANo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument57 pagesAtomic StructureMary Rose JasminNo ratings yet
- Quimica y Biomogia SnapseepDocument34 pagesQuimica y Biomogia SnapseepDana LopezNo ratings yet
- Atoms 1Document30 pagesAtoms 1poorv1235570No ratings yet
- Structure of An Atom and The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesStructure of An Atom and The Periodic TableErika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A-Level Edexcel ChemistryDocument22 pagesA-Level Edexcel ChemistryElyssa Mcpe100% (1)
- CIVE 205 Spring2017 Week2Document31 pagesCIVE 205 Spring2017 Week2haloNo ratings yet
- Envi Scie QuizDocument5 pagesEnvi Scie QuizJenemarNo ratings yet
- Jsy Ea Ky : Vuqla/Kku Vfhkdyi VKSJ Ekud Laxbu Y (Kuå&226 011Document67 pagesJsy Ea Ky : Vuqla/Kku Vfhkdyi VKSJ Ekud Laxbu Y (Kuå&226 011Bala RajuNo ratings yet
- Systemic Pathology QuestionDocument4 pagesSystemic Pathology QuestionAnderson Amaro100% (1)
- Quantum Voyager-Understanding Quantum Tunneling With Conway's Game of LifeDocument5 pagesQuantum Voyager-Understanding Quantum Tunneling With Conway's Game of Life張凱捷No ratings yet
- Lorentz PS1800 CS-36-1Document4 pagesLorentz PS1800 CS-36-1SINES FranceNo ratings yet
- 0 - 30 V / 10 A Power Supply: Scientech 4181Document2 pages0 - 30 V / 10 A Power Supply: Scientech 4181kalidasdoraemonNo ratings yet
- ASME Manual Edition 2019Document69 pagesASME Manual Edition 2019hgag selimNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY - Smart Stores Reinvent The Retail SpaceDocument1 pageCASE STUDY - Smart Stores Reinvent The Retail Spacetranthihien29604No ratings yet
- Final Wind LoadDocument23 pagesFinal Wind LoadjohnrendeltumaronNo ratings yet
- ITMO 2017 - Keystage III - Individual PDFDocument6 pagesITMO 2017 - Keystage III - Individual PDFzarifNo ratings yet
- Oishi GroupDocument20 pagesOishi GroupCamilleJoyceAdrianoNo ratings yet
- Reddit - PDF For Handbook On PCTDocument43 pagesReddit - PDF For Handbook On PCTGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- LandingString, 80%, 5.875 OD, 0.750 Wall, IEU, S-135.. XT57 (7.250 X 3.500)Document3 pagesLandingString, 80%, 5.875 OD, 0.750 Wall, IEU, S-135.. XT57 (7.250 X 3.500)Garcia C L AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Radial Fan Conical Vs Parallel Impeller Casing AnalysisDocument10 pagesRadial Fan Conical Vs Parallel Impeller Casing AnalysisvirgilioNo ratings yet
- Earthscienceforstem q1 Mod8 Energyresources v2Document35 pagesEarthscienceforstem q1 Mod8 Energyresources v2Angelynne DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Week1 FAQ-2Document6 pagesWeek1 FAQ-2Baldau Gupta0% (1)
- Analysis and Modelling of CFT Members Moment Curvature AnalysisDocument10 pagesAnalysis and Modelling of CFT Members Moment Curvature AnalysisMahdi ValaeeNo ratings yet
- Mucopolysaccharidoses EditedDocument6 pagesMucopolysaccharidoses EditedSamuel NjengaNo ratings yet
- Dexter 1x01 - PilotDocument67 pagesDexter 1x01 - PilotmarkayartNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Religion Institutions and Rituals of The Mamanwas of Caraga Region PhilippinesDocument19 pagesIndigenous Religion Institutions and Rituals of The Mamanwas of Caraga Region PhilippinesMomay Ü100% (1)
- Bimco Standard Bunker ContractDocument5 pagesBimco Standard Bunker Contractca vaNo ratings yet
- National Biogas Manure Management Programme (NBMMP) 12thplanDocument7 pagesNational Biogas Manure Management Programme (NBMMP) 12thplanRG SegaranNo ratings yet
- @canotes - Final Customs Question Bank May, Nov 20 by ICAI PDFDocument111 pages@canotes - Final Customs Question Bank May, Nov 20 by ICAI PDFPraneelNo ratings yet
- Botanical Garden - BuitenzorgDocument74 pagesBotanical Garden - BuitenzorgBalingkangNo ratings yet
- Understanding Reality - Nina Van GorkomDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Reality - Nina Van Gorkom5KevNo ratings yet
- 11 DeionizerDocument14 pages11 Deionizerfaiz faridNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Consumption in The Fast Fashion IndustryDocument9 pagesAn Analysis of Consumption in The Fast Fashion IndustryFulbright L.No ratings yet
- Pest Control: About This ChapterDocument21 pagesPest Control: About This ChapterRaul TejedaNo ratings yet
- BMEDocument11 pagesBMEtemesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
Reviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)
Reviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)
Uploaded by
HelloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)
Reviewers-In-Science (Atomic Theory)
Uploaded by
HelloCopyright:
Available Formats
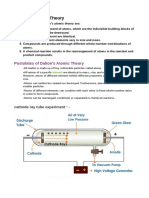
Origin and Formation of the Element • James Chadwick
Atomic Theory Timeline - proved the existence of neutrons
Democritus • Erwin Schrodinger
-first person to deal with atoms. -modern
-he called it "atomos" meaning indivisible" - electron cloud model / quantum mechanical model.
- all matter was formed of different types. of tiny discrete -the atom consists of a small but massive nucleus
particles. surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons.
-billiard ball model → we cannot know exactly where an electron. is at any
• John Dalton atomic theory given time, but the electrons are more likely to be in
specific areas
- atomic theory
-three- dimentional
- all matter is made of atom and it cannot be divided,
created or destroyed. - formulated a wave equation that accurately calculated
the energy levels of electrons.
-the atoms of a given element are identical
Atoms
- atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and
other properties - are the basic units of matter and the defining structure
- atoms of different elements combine with each other to of elements
create / form compounds -nucleus
- solid sphere model
- 3 particles (proton, neutron, electron)
• J.J. Thomson
Element
- discovered electrons through the cathode ray
- is a substance that cannot be broken down into any
-plum pudding model other substance.
→ atom consisted of a positively charged mass in which -is a specific type of atom
are embedded the negatively charged electrons
Origin and Formation of Elements
-plum- negatively charged particles.
• Light Elements
-pudding- positively charged particles.
-formed during the Big Bang
• Ernest Rutherford
-Big Bang nucleosyntheses
- discovered nucleus and protons.
-Deuterium, Hydrogen, Helium, and Lithium.
-nuclear atomic model.
-associated it with the discovery of nucleus • Heavy Element
-the electrons surround /occupy the nucleus -stellar nucleosynthesis
-composed of protons and electrons. - stellar → stars, nucleus nucleo→ nucleus;
• Niels Bohr synthesis →combination / fusion
- planetary model. - elements are created within stars by combining the
protons and neutrons together from the nuclei of lighter
-the electrons not only surround the nucleus, but it also
elements.
encircles around nucleus called orbits
-shell - Carbon plus helium produces oxygen. oxygen plus
helium produces neon, Neon plus helium producer
magnesium.
Supernova Nucleosynthesis
-the creation of elements during the explosion of a
massive star
- uranium, gold
Exploration about Elements.
•fire - Heraclitus Molecular shape and Polarity
• water- Thaler air Anaximenes • Electron Geometry
• earth- Empedocles -arrangement of electron groups and atoms
Isotopes -atom → central atom and attached atoms.
- are atoms of the rame element that have different -electron group→ lone pair
numbers of neutrons but the same number of protons → at the central atom (if compound)
and electrons
- no. of total electron groups are calculated
"Element name” - usually from a Greek or Latin word for
the element or a substance containing the element. Molecular shape
Atomic number- the number of protons in the nucleus of -the arrangement of atoms in a molecule,usually relative
the atom to a single central atom
Symbol-short hand abbreviation for the element name - excludes lone pairs from determining a molecule's shape
Atomic mars- the average mars of the atoms in an -applicable to two atoms and more.
element
- covalent bond→ compound is combination of two
Electron Configuration - where electrons are located nonmetal elements.
around the nucleus of an atom.
VSEPR Theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair: Repulsion)
model used to predict 3-D molecular geometry based on
the number of valence shell electron bond pairs among
the atoms in a molecule or ion.
Finding Out Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons - basic to remember:
Rules: • linear bent
• trigonal
1) The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom is
equal to the atomic number. • tetrahedral
• octahedral
2) The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to
the number of protons.
3) The mass number of the atom is equal to the sum of
the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
4) The number of neutrons is equal to the difference
between the mass number of the atom and the atomic
number.
Isotopes of Magnesium
You might also like
- Unit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthDocument218 pagesUnit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthBlop100% (1)
- Iso 668 1995 (E)Document10 pagesIso 668 1995 (E)alinpreliNo ratings yet
- Psma PrelimsDocument42 pagesPsma PrelimsPrincess Rose GamboaNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec ReviewerDocument42 pagesChem Lec ReviewerMaryashlyn NableaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science MidtermsDocument4 pagesPhysical Science MidtermsKimberly MedranoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Atoms and Atomic Theory)Document47 pagesChapter 4 (Atoms and Atomic Theory)Raynan TabaldoNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC AND INORGANIC CHEMISTRY REVIEWER - COPYRIGHT@villanuevarDocument5 pagesORGANIC AND INORGANIC CHEMISTRY REVIEWER - COPYRIGHT@villanuevarreyellahvillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv-VDocument18 pagesUnit Iv-VIvy Marie ToyonganNo ratings yet
- Concept+1+Notes+ +Structure+of+the+AtomDocument9 pagesConcept+1+Notes+ +Structure+of+the+AtomsanchezsolsalmaNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument46 pagesAtomic ModelShannelle Anne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Junction Diodes: Module-2Document46 pagesJunction Diodes: Module-2NILESH TIWARINo ratings yet
- Science-Q2-Notes BanzonDocument3 pagesScience-Q2-Notes BanzonfeytNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Atomic TheoryDocument47 pagesAtoms and The Atomic TheoryEdgar PeninsulaNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument29 pagesSci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesFlorenze GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Chem 1Document2 pagesReviewer in Chem 1MARY ZIANNE GABRIELLE QUINTONo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceGutierrez, Patricia MaeNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Chemistry 2023 2Document60 pagesYr 9 Chemistry 2023 2mkkit2105No ratings yet
- Atomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Document16 pagesAtomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Nilimoy Choudhury100% (1)
- Atomic PhysicsDocument5 pagesAtomic Physicslove meNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument2 pagesScience NotesLoladeNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Urning Back Time - The Theory of AtomsDocument14 pagesAtomic Structure: Urning Back Time - The Theory of AtomsUmer AzharNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221114 080033 0000Document2 pagesPDF 20221114 080033 0000John Marithe PutunganNo ratings yet
- Atomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Document7 pagesAtomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Venugopal RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4, Section 2Document20 pagesChapter 4, Section 2Abdullah AlthaniNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics Circuits - ReviewerDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Electronics Circuits - Revieweraguilaclaudette35No ratings yet
- AtomsDocument35 pagesAtomsAnna Carmela BERANIANo ratings yet
- The Atom For AnatomyDocument106 pagesThe Atom For AnatomyAlexandra B. FloresNo ratings yet
- Physci Prelims Reviewer L1 3 1Document4 pagesPhysci Prelims Reviewer L1 3 1Yael Duane CabaisNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument9 pagesPhysical Science ReviewerRuzuiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Chemistry Atomic Models and Structure of The Atom I. Learning CompetencyDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Chemistry Atomic Models and Structure of The Atom I. Learning CompetencyLoreen Jane AbogadoNo ratings yet
- Img20240325 01023517 PDFDocument1 pageImg20240325 01023517 PDFpagtama.136530120101No ratings yet
- 1 - The AtomDocument2 pages1 - The AtomCyrene ManansalaNo ratings yet
- 2.1. The Nuclear Atom - Atomic StructureDocument65 pages2.1. The Nuclear Atom - Atomic StructureSaniya DautovaNo ratings yet
- Atoms: NucleusDocument6 pagesAtoms: Nucleusヒルデガルダ HILDEGARDENo ratings yet
- Atoms and Nuclear Energy RevisionDocument5 pagesAtoms and Nuclear Energy RevisionLeona Valentina VračarNo ratings yet
- First Year Chemistry 20-02Document100 pagesFirst Year Chemistry 20-02Ahmed Hassan Mina HamadNo ratings yet
- Sci2Q Reviewer PDFDocument5 pagesSci2Q Reviewer PDFFire RobloxNo ratings yet
- 2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Document12 pages2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Keshia KatarinaNo ratings yet
- What Is An AtomDocument3 pagesWhat Is An Atomsithumsethika7No ratings yet
- Block 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityDocument70 pagesBlock 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityMac Justine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Atomic Structure Physical ScienceDocument18 pagesChapter 4 - Atomic Structure Physical Scienceapi-30718309No ratings yet
- Subatomic Particles of AtomsDocument8 pagesSubatomic Particles of AtomsRose Ann Marie BabiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawDocument32 pagesLecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawВалентина ЮзьковаNo ratings yet
- Leaving Cert Chemistry NotesDocument116 pagesLeaving Cert Chemistry NotesSnivySerpentNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Postulates of Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesPostulates of Dalton's Atomic TheoryVenugopal RNo ratings yet
- S1 2022 P Fisika - Inti I - Struktur Inti AtomDocument64 pagesS1 2022 P Fisika - Inti I - Struktur Inti AtomMuhammad Agustian AdhityaNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)Document22 pagesCHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)ogedengbed28No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 AtomDocument48 pagesLesson 1 Atom12 John Paolo DumaguinNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theories Quatum ModelDocument31 pagesAtomic Theories Quatum Modelerinallyson20No ratings yet
- General Chemistry Organic Chemistry Biochemistry: MatterDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry Organic Chemistry Biochemistry: MatterFRANCYM PRINCESSRICH BATENGANo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument57 pagesAtomic StructureMary Rose JasminNo ratings yet
- Quimica y Biomogia SnapseepDocument34 pagesQuimica y Biomogia SnapseepDana LopezNo ratings yet
- Atoms 1Document30 pagesAtoms 1poorv1235570No ratings yet
- Structure of An Atom and The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesStructure of An Atom and The Periodic TableErika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A-Level Edexcel ChemistryDocument22 pagesA-Level Edexcel ChemistryElyssa Mcpe100% (1)
- CIVE 205 Spring2017 Week2Document31 pagesCIVE 205 Spring2017 Week2haloNo ratings yet
- Envi Scie QuizDocument5 pagesEnvi Scie QuizJenemarNo ratings yet
- Jsy Ea Ky : Vuqla/Kku Vfhkdyi VKSJ Ekud Laxbu Y (Kuå&226 011Document67 pagesJsy Ea Ky : Vuqla/Kku Vfhkdyi VKSJ Ekud Laxbu Y (Kuå&226 011Bala RajuNo ratings yet
- Systemic Pathology QuestionDocument4 pagesSystemic Pathology QuestionAnderson Amaro100% (1)
- Quantum Voyager-Understanding Quantum Tunneling With Conway's Game of LifeDocument5 pagesQuantum Voyager-Understanding Quantum Tunneling With Conway's Game of Life張凱捷No ratings yet
- Lorentz PS1800 CS-36-1Document4 pagesLorentz PS1800 CS-36-1SINES FranceNo ratings yet
- 0 - 30 V / 10 A Power Supply: Scientech 4181Document2 pages0 - 30 V / 10 A Power Supply: Scientech 4181kalidasdoraemonNo ratings yet
- ASME Manual Edition 2019Document69 pagesASME Manual Edition 2019hgag selimNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY - Smart Stores Reinvent The Retail SpaceDocument1 pageCASE STUDY - Smart Stores Reinvent The Retail Spacetranthihien29604No ratings yet
- Final Wind LoadDocument23 pagesFinal Wind LoadjohnrendeltumaronNo ratings yet
- ITMO 2017 - Keystage III - Individual PDFDocument6 pagesITMO 2017 - Keystage III - Individual PDFzarifNo ratings yet
- Oishi GroupDocument20 pagesOishi GroupCamilleJoyceAdrianoNo ratings yet
- Reddit - PDF For Handbook On PCTDocument43 pagesReddit - PDF For Handbook On PCTGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- LandingString, 80%, 5.875 OD, 0.750 Wall, IEU, S-135.. XT57 (7.250 X 3.500)Document3 pagesLandingString, 80%, 5.875 OD, 0.750 Wall, IEU, S-135.. XT57 (7.250 X 3.500)Garcia C L AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Radial Fan Conical Vs Parallel Impeller Casing AnalysisDocument10 pagesRadial Fan Conical Vs Parallel Impeller Casing AnalysisvirgilioNo ratings yet
- Earthscienceforstem q1 Mod8 Energyresources v2Document35 pagesEarthscienceforstem q1 Mod8 Energyresources v2Angelynne DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Week1 FAQ-2Document6 pagesWeek1 FAQ-2Baldau Gupta0% (1)
- Analysis and Modelling of CFT Members Moment Curvature AnalysisDocument10 pagesAnalysis and Modelling of CFT Members Moment Curvature AnalysisMahdi ValaeeNo ratings yet
- Mucopolysaccharidoses EditedDocument6 pagesMucopolysaccharidoses EditedSamuel NjengaNo ratings yet
- Dexter 1x01 - PilotDocument67 pagesDexter 1x01 - PilotmarkayartNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Religion Institutions and Rituals of The Mamanwas of Caraga Region PhilippinesDocument19 pagesIndigenous Religion Institutions and Rituals of The Mamanwas of Caraga Region PhilippinesMomay Ü100% (1)
- Bimco Standard Bunker ContractDocument5 pagesBimco Standard Bunker Contractca vaNo ratings yet
- National Biogas Manure Management Programme (NBMMP) 12thplanDocument7 pagesNational Biogas Manure Management Programme (NBMMP) 12thplanRG SegaranNo ratings yet
- @canotes - Final Customs Question Bank May, Nov 20 by ICAI PDFDocument111 pages@canotes - Final Customs Question Bank May, Nov 20 by ICAI PDFPraneelNo ratings yet
- Botanical Garden - BuitenzorgDocument74 pagesBotanical Garden - BuitenzorgBalingkangNo ratings yet
- Understanding Reality - Nina Van GorkomDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Reality - Nina Van Gorkom5KevNo ratings yet
- 11 DeionizerDocument14 pages11 Deionizerfaiz faridNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Consumption in The Fast Fashion IndustryDocument9 pagesAn Analysis of Consumption in The Fast Fashion IndustryFulbright L.No ratings yet
- Pest Control: About This ChapterDocument21 pagesPest Control: About This ChapterRaul TejedaNo ratings yet
- BMEDocument11 pagesBMEtemesgen adugnaNo ratings yet